Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
I So Enzymes
Încărcat de
Mohammed EhabTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
I So Enzymes
Încărcat de
Mohammed EhabDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ISOENZYMES
Enzymes are organic biological catalysts that accelerate the chemical reactions inside the
biological systems (living cells). Although they are involved in the reaction, they are not
consumed.
Isoenzymes:
Isoenzymes (isozymes) are multiple forms of the enzyme that have the same catalytic activity.
Although they have the same catalytic activity, they are physically distinct & differ in:
Electrophoretic mobility,
Liability to inhibitors
Biochemical properties as amino acid composition & immunological reactivities.
Many enzymes are present in isoenzyme forms e.g:
Lactate dehydrogenase
Creatine kinase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH):
Its level in plasma increases in:
1- Myocardial infarction (heart diseases).
2- Viral hepatitis (liver disease).
3- Leukaemia (blood disease).
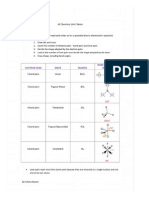
LDH enzyme is a tetramer formed of 4 protein subunits; each subunit is called protomer.
The protomers of LDH are of 2 types: H (heart) and M (muscle)
So, LDH has 5 isoenzymes:
LDH1 is formed of HHHH. It increases in myocardial infarction
LDH2 is formed of HHHM. It increases in myocardial infarction.
LDH3 is formed of HHMM. It increases in leukaemia.
LDH4 is formed of HMMM. It increases in viral hepatitis.
LDH5 is formed of MMMM. It increases in viral hepatitis.
So, LDH isoenzymes are clinically important to differentiate between heart, liver and blood
diseases.
Creatine kinase (CK)
It is an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorylation of creatine. Its level in plasma increases in:
1. Brain tumors.
2. Myocardial infarction (heart disease).
3. Skeletal muscle diseases.
CK enzyme is a dimmer formed of 2 protein subunits (protomers), B (brain) and M (muscle).
So, CK has 3 isoenzymes:
CK BB which increases in brain tumors.
CK MB which increases in heart diseases.
CK MM which increases in skeletal muscle diseases.
So, CK isoenzymes are clinically important to differentiate between brain, heart and skeletal
muscle diseases.
Source of isoenzymes:
1. Isoenzymes may be produced by more than one gene, each gene produces one subunit.
2. Isoenzymes may be produced by the same gene but the subunits undergo different posttranslation modifications in different organs.
Medical importance of isoenzymes:
-Isoenzymes are not only important for diagnosis of diseases but also indicate the diseased organ.
For example, lactate dehydrogenase enzyme (LDH) increases in:
Myocardial Infarction (Heart Disease)
Viral Hepatitis (Liver Disease)
Leukaemia (Blood Disease)
-LDH isoenzymes indicate the diseased organ as:
LDH1 and LDH2 isoenzymes increase only in myocardial infarction.
LDH3 increases in leukaemia
LDH4 and LDH5 increase in viral hepatitis.
Cardiac marker:
Cardiac markers are biomarkers measured to evaluate heart function. They are often discussed
in the context of myocardial infarction. Most of the early markers identified were enzymes, so
the term "cardiac enzymes" is sometimes used. However, not all of the markers currently used
are enzymes.
A) Creatine Kinase (CK-MB):
-It is relatively specific when skeletal muscle damage is not present.
-It rises to high peak within 1024 hours.
-Since it has a short duration, it cannot be used for late diagnosis of acute MI but can be used to
suggest infarct extension if levels rise again.
-This is usually returned back to normal within 23 days.
B) Lactate dehydrogenase:
-LDH is not as specific as troponin.
-It rises to high peak within 72 hours.
-LDH1 and LDH2 are called heart-type or heartspecific isoenzymes
-LDH-1 isozyme is normally found in the heart muscle and LDH-2 is found more in blood
serum.
-Normally, LDH-1/LDH-2 ratio is less than 1.
-A reversal of this ratio is called "flipped LDH".
-Following an acute myocardial infarct the flipped LDH ratio will appear in 12-24 hours and is
definitely present by 48 hours in over 80% of patients.
-A rise in LDH1 is the most significant in diagnosis of MI
-Also important is the fact that persons suffering chest pain due to angina only will not likely
have altered LDH levels.
-It is usually returns back to normal within 1014 days.
C) Transminases:
-Transaminases are intracellular enzymes.
-Their levels in plasma are low under normal conditions.
-There are two types of transaminases:
Alanine transaminases (ALT or GPT) is present mainly in the cytoplasm of liver .
Aspartate transaminases (AST or GOT) is present in both cytoplasm and mitochondria in
liver, heart, and skeletal muscles.
-In myocardial infarction, there is an increase in AST or GOT.
-It reaches its peak within 1-2 days and returns to normal level after 4- 6 days.
D) Glycogen phosphorylase isoenzyme BB:
-It has a high sensitivity and specificity early after chest pain and reaches to high peak within 7
hours.
-Glycogen phosphorylase exists in 3 isoforms.
-One of these Isoforms is GP-BB.
-This isoform exists in heart and brain tissue.
-Because of the blood-brain barrier, GP-BB can be seen as heart specific.
-During the process of ischemia, GP-BB is converted into a soluble form and is released into the
blood.
-GP-BB is one of the "new cardiac markers" which are discussed to improve early diagnosis in
acute coronary syndrome.
-A rapid rise in blood levels can be seen in myocardial infarction and unstable angina.
-GP-BB elevated 13 hours after process of ischemia.
Cardiac Enzymes for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction:
BE AWARE OF: Appropriate times to measure cardiac enzymes after an episode of chest pain.
The time course of release of (CK), (AST) and (LDH). CK and LDH isoenzymes in monitoring
cardiac damage.
Other important tests help in diagnosis:
a) Myoglobin:
-The earliest thing that goes up (LMW)
-Very sensitive
-Useful in early detection- Typical rise 2-4 hours after onset of AMI
-Not very specific can come from skeletal muscle
-Returns to normal very quickly
b) Troponins (T and I):
-Specific for myocardial cells even though it is found in skeletal muscle (theyre structurally
different)
-Extremely sensitive
-Elevated in blood when there is myocardial cell death
-Difficulty to make diagnosis early might take up to 9 hours.
-Troponin T can remain elevated for up to 2 weeks following myocardial cell death..useful in
late presentation of chest pain.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- OxidationDocument8 paginiOxidationMohammed EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Cycle - TableDocument1 paginăCardiac Cycle - TableMohammed EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac CycleDocument9 paginiCardiac CycleMohammed EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 2B June 2011 MsDocument12 paginiBiology 2B June 2011 MsMeeraf AlemayehuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Biology Unit 5 NotesDocument37 paginiEdexcel Biology Unit 5 NotesMohammed Ehab83% (12)
- Unit 1 NotesDocument49 paginiUnit 1 NotesTyRaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Paper 2H May 2005Document28 paginiEdexcel Paper 2H May 2005m_jabbal2223100% (1)
- ECG: A Graphic Recording of Cardiac Electrical ActivityDocument7 paginiECG: A Graphic Recording of Cardiac Electrical ActivityMohammed EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesDocument67 paginiEdexcel Biology Unit 1 Notesbookdoudah100% (5)
- Edexcel Biology JUNE 2015 Scientific Article QuestionsDocument36 paginiEdexcel Biology JUNE 2015 Scientific Article QuestionsMohammed EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Chemistry: Shapes of Molecules, Ions, and Carbon AllotropesDocument77 paginiA Level Chemistry: Shapes of Molecules, Ions, and Carbon AllotropesSan Siddz100% (1)
- Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDocument26 paginiEdexcel Chemistry Unit 1 NotesMohammed EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Chemistry: Shapes of Molecules, Ions, and Carbon AllotropesDocument77 paginiA Level Chemistry: Shapes of Molecules, Ions, and Carbon AllotropesSan Siddz100% (1)
- 6BI01 01 MSC 20140814Document24 pagini6BI01 01 MSC 20140814Mr-Mohamed AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- EffectsDocument1 paginăEffectsMohammed EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Biology Lesson Plan (Weekly) 9Document2 paginiBiology Lesson Plan (Weekly) 9Peter George100% (1)
- Biology Class Xii Cbse Investigatory Project On AntibioticsDocument37 paginiBiology Class Xii Cbse Investigatory Project On AntibioticsSaveen Kadian75% (4)
- Energy GenerationDocument4 paginiEnergy GenerationDeena ChadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type 1 Diabetes: Basis of Causes and Away of PreventionDocument11 paginiType 1 Diabetes: Basis of Causes and Away of PreventionOpenaccess Research paperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood and Cell Physiology MCQs With KeyDocument9 paginiBlood and Cell Physiology MCQs With KeyMudassar Roomi87% (63)
- BIOL 243 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument8 paginiBIOL 243 Exam 1 Study GuideMaddie BleaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To BiologyDocument4 paginiIntroduction To BiologyEury Marc Suhi-anÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Genetic Form of Autism: Antitumor Duality of ApoeDocument1 paginăA New Genetic Form of Autism: Antitumor Duality of ApoeMariana CotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester 3: Year Title Chapter 14 Taxonomy & BiodiversityDocument4 paginiSemester 3: Year Title Chapter 14 Taxonomy & Biodiversityayunna ayunniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schneider Review of Moore's The Dependent Gene PDFDocument15 paginiSchneider Review of Moore's The Dependent Gene PDFfuck offÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical DictionaryDocument2 paginiMedical DictionaryMeghanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12042020165710principals and Practices of SilvicultureDocument84 pagini12042020165710principals and Practices of SilvicultureSatsshhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Elementary Lesson PlanDocument8 paginiScience Elementary Lesson PlanMonaliza RondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worster 2 1 PDFDocument13 paginiWorster 2 1 PDFFrank Molano CamargoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0smoregulation in Fresh Water FishesDocument4 pagini0smoregulation in Fresh Water FishesKazi AfrozÎncă nu există evaluări
- MLE-01 QP 14-7-19 @onlinelibraryindia Neet 2020Document20 paginiMLE-01 QP 14-7-19 @onlinelibraryindia Neet 2020anji shÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Lecture On Skeletal Muscle Physiology by DR - RoomiDocument21 pagini3rd Lecture On Skeletal Muscle Physiology by DR - RoomiMudassar Roomi67% (3)
- GOLOBOFF - Refining Phylogenetic AnalysesDocument312 paginiGOLOBOFF - Refining Phylogenetic Analyseskatarine n. norbertinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fat: An Emerging Player in The Field of Atrial FibrillationDocument4 paginiFat: An Emerging Player in The Field of Atrial FibrillationKevinJuliusTanadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-MergedDocument14 pagini02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-Mergedsurya narayanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument8 paginiMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 08 LipidDocument10 paginiChapter 08 Lipid楊畯凱Încă nu există evaluări
- Biomolecules MCQs - 01Document24 paginiBiomolecules MCQs - 01Types100% (1)
- Diseases & Immunity 1 QPDocument7 paginiDiseases & Immunity 1 QPbdb6wxhyxfÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Ekstrakromosomal, Sifat, Dan Kegunaannya: Soraya RahmanisaDocument33 paginiDNA Ekstrakromosomal, Sifat, Dan Kegunaannya: Soraya RahmanisaRiska PriyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Vitae of Neurophysician Dr. G. M. TaoriDocument12 paginiCurriculum Vitae of Neurophysician Dr. G. M. Taorisrajan sahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Contribution of Chemical Engineering To BiotechnologyDocument18 paginiThe Contribution of Chemical Engineering To BiotechnologyMelisa KumlaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Isolation and Phenotypic Characterization of BacteriophageDocument42 pagini1 Isolation and Phenotypic Characterization of BacteriophageJanine Kate DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plants Part 1Document28 paginiPlants Part 1Puneet TatranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleotides NsDocument118 paginiNucleotides NsRishi ButolaÎncă nu există evaluări