Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Problems On Curves
Încărcat de
Tefera TemesgenTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Problems On Curves
Încărcat de
Tefera TemesgenDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
4.15. A vertical curve joins a 2.0% grade to a +0.5% grade. The Pl.
of the vertical curve
is at station 100 + 00 and elevation 69.50 m above sea level. The centerline of the
roadway must clear an overhead structure located at station 99 + 20 by 5.67 m, The
elevation of the bottom of the structure is 77 45 m above sea level. What is the maximum
length of vertical curve that can be used/
82 C H A P T E R 4: Geometric Design
4.16. Compute the minimum radius of a circular curve for a highway designed for 110 km/h.
The maximum superelevation rate is 12%
4.26. (a) A roadway goes from tangent alignment to a 275-m circular curve by means of a
100-m-long spiral transition curve. The deflection angle between the tangents is 60.
Use formulas to compute X,, Y , p, and k. Assume that the station of the P.1.,
measured.along the back tangent, is 200 + 00, and compute the stations of the TS,
SC, CS, and ST.
,
4.17. Compute the minimum radius of a circular curve for a highway designed for 80 km/h.
Because snow and ice are present. the maximum superelevation rate is 8%.
4.18. Compute the minimum radius of a circular curve for a highway designed for 100 km/h.
The maximum superelevation rate is 12%.
4.19. (a) A two-lane highway (one 3.6-m lane in each direction) goes from normal crown with
2% cross-slopes to 10% superelevation by means of a spiral transition curve. Determine the minimum length of the transition if the difference in grade between the
centerline and edge of traveled way is limited to 1/200. Round up to the next largest
20-m interval.
(b) Draw the superelevation diagram for the transition described in part a. The station
of the TS is 160 + 00
4.20. (a) A two-lane highway (one 3.6- m lane in each direction) goes from normal crown with
2% cross-slopes to 8% superelevation by means of a spiral transition curve. Determine the minimum length of the transition if the difference in grade between the
centerline and edge of traveled way is limited to 1/200. Round up to the next largest
20-m interval.
(b) Draw the superelevation diagram for the transition described in part
Use formulas to compute X Y, p, and k Assume that the station of the P.I.,
measured along the back tangent, is 250 + 00, and compute the stations of the TS,
SC, CS, and ST.
(b) Prepare a table giving coordinates, spiral angles, deflection angles and chords (from
the TS) for full stations and +20 points.
a. The station
of the TS is 120 + 00.
4.21. (a) A two-lane highway (one 3.6- m lane in each direction) goes from normal crown with
2% cross-slopes to 6% superelevation by means of a spiral transition curve. Determine the minimum length of the transition if the difference in grade between the
centerline and edge of traveled way is limited to 1/200. Round up to the next largest
20-m interval
(b) Draw the superelevation diagram for the transition described in part a The station
of the TS is 75 + 00
4.22. Prepare a table giving chords and deflection angles for staking our a 450-m-radius
circular curve with a total deflection angle of 17. The TC point is at station 22 + 40.
Give deflection angles and chords for full stations and +20 points.
4.23. Prepare a table giving chords and deflection angles for staking out a 650-m-radius
circular curve with a total deflection angle of 13. The IC point is at station 13 + 25.
Give deflection angles and chords for full stations and +20 points.
4.24. Prepare a table giving chords and deflection angles for staking out a 480-m-radius
circular curve with a total deflection angle of 22 The IC point is at station 10 + 32.
Give deflection angles and chords for full stations and +20 points.
4.25. (a) A roadway goes from tangent alignment to a 250-m circular curve by means of a
80- rn-long spiral transition curve The deflection angle between the tangents is 45 .
(b) Prepare a table giving coordinates, spiral angles, deflection angles
and chords (from
the TS) for full stations and +20 points.
4.27. (a) A roadway goes from tangent alignment to a 380-m circular curve by means of a
60-m-long spiral transition curve. The deflection angle between the tangents is 40.
Use formulas to compute X,, I's, p, and k. Assume that the station of the P.1,,
measured along the back tangent, is 100 4- 00, and compute the stations of the TS,
SC, CS, and ST.
(b) Prepare a table giving coordinates, spiral angles, deflection angles and chords (from
the TS) for full stations and +20 points.
4.28. A circular curve with a radius of 350 m is connected by 60-m spiral transition curves
to tangents with a deflection angle of 0.349 rad. If the station of the TS is 105 + 40,
determine the station of the ST.
4.29. A horizontal curve is connected by two spiral transition curves to tangents with a
deflection angle of 0.26 rad. Stations of critical points are as follows: TS, 105 + 00; SC,
105 + 80; CS, 107 + 50; ST, 108 + 30. The roadway is a two-lane highway with one
3.6-rn lane in each direction. If the difference in grade between the centerline and edge
of traveled way in the superelevation transition is exactly 1/200, at what speed can the
curve be taken with no side friction?
4.30. A horizontal curve is connected by two spiral transition curves to tangents with a
deflection angle of 0.30 rad. Stations of critical points are as follows: TS, 308 + 00, SC,
308 + 40; CS, 310 + 40, ST, 310 + 80. The roadway is a two-lane highway with one
3.6-en lane in each direction. If the difference in grade between the centerline and edge
of traveled way in the superelevation transition is exactly 1/200, what is the maximum
speed that can be maintained on the curve if the side friction is limited to 0.10?
4.31. The allowable side friction factor for horizontal curves with a design speed of 100 km/h
is 0.12.
(a) What superelevation rate would you use for a curve with a design speed of 100 km/h
and a radius of 420 m? Round to the nearest whole percent.
(a) A spiral transition curve is used to go from a normal crow n slope with 2%
cross-slopes to full superelevation for the curve described above. If the maximum
difference in grade between the centerline and the edge is 1/200 and the roadway
consists of two 3.6-m lanes, what is the minimum length of spiral? Round up to the
next integral multiple of 20 m.
(a) The station of the IS is 501 + 00. Draw the superelevatton diagram.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- JointDocument8 paginiJointTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantity Survey & Estimation: Engr. Shad MuhammadDocument28 paginiQuantity Survey & Estimation: Engr. Shad MuhammadOsama AnjumÎncă nu există evaluări
- CURVES Survey PDFDocument27 paginiCURVES Survey PDFnewton mbogori67% (3)
- Data Exploration in Python PDFDocument1 paginăData Exploration in Python PDFTuncay SakaogluÎncă nu există evaluări
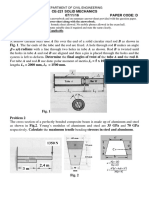
- Ce-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DDocument7 paginiCe-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DAshutosh AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2B - Fundamentals of Traffic FlowDocument16 pagini2B - Fundamentals of Traffic FlowKwasi Agyeman-BoakyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rebar Unit RateDocument10 paginiRebar Unit RateTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volumetric analysis of asphalt mixtureDocument6 paginiVolumetric analysis of asphalt mixturevarun persadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Road Design BasicsDocument13 paginiRoad Design BasicsLJD211100% (1)
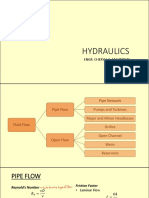
- Fluids PPT Day2Document20 paginiFluids PPT Day2Yedda M IlaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 12 Compound Reverse and Spiral CurvesDocument37 paginiLesson 12 Compound Reverse and Spiral CurvesHunter BravoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ND MechatronicsDocument260 paginiND MechatronicsaniaffiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determining Minimum Radius of Horizontal Curve for Safe OperationDocument4 paginiDetermining Minimum Radius of Horizontal Curve for Safe OperationDeep Debnath100% (1)
- General FormulaDocument53 paginiGeneral FormulaTsegawbezto97% (32)
- Ometric Design of Highway PDFDocument48 paginiOmetric Design of Highway PDFTadi Fresco Royce75% (4)
- Thermal Stresses and Temperature Control of Mass ConcreteDe la EverandThermal Stresses and Temperature Control of Mass ConcreteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical AlignmentDocument56 paginiVertical AlignmentThomas Ditto ErlanggaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Flexible Roads Reinforced with Tenax Geogrids using TNXROAD SoftwareDocument32 paginiDesign Flexible Roads Reinforced with Tenax Geogrids using TNXROAD SoftwareJose LizarragaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stair Case DesignDocument4 paginiStair Case DesignTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Yield Line Analysis For SlabsDocument52 paginiChapter 1 - Yield Line Analysis For SlabsTefera Temesgen100% (1)
- Ecv 401 Highway Engineering 1 - 2014Document32 paginiEcv 401 Highway Engineering 1 - 2014Daniel Kariuki100% (1)
- Geometric Design Note Plus ProblemsDocument48 paginiGeometric Design Note Plus ProblemsAndenet Ashagrie50% (2)
- UNIVERSITY OF GONDAR CH-2 ExamplesDocument11 paginiUNIVERSITY OF GONDAR CH-2 Examplescherinet bisetegnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arrow Head: (Engineering Dimension)Document6 paginiArrow Head: (Engineering Dimension)Mihir SevakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce 404-Sec11Document20 paginiCe 404-Sec11Yasser AlghrafyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature StressesDocument38 paginiTemperature StressesMohamed MuayidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Route TD For All Student Learner's Highway EngineeringDocument25 paginiRoute TD For All Student Learner's Highway Engineeringkrishy19sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6Document26 paginiChapter 6Hailemichael ShibabawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Situation 1. Oil at Specific Gravity 0.761 Flows From Tank A To Tank E, As ShownDocument2 paginiSituation 1. Oil at Specific Gravity 0.761 Flows From Tank A To Tank E, As ShownAgerico FunelasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3: Geometric Design of Highways: D Ep Artm Ent of Civil Engineering, Ambo UniversityDocument27 paginiChapter 3: Geometric Design of Highways: D Ep Artm Ent of Civil Engineering, Ambo UniversityTarmok Hirpo100% (1)
- Re Aastu PP 2Document46 paginiRe Aastu PP 2ellocster21Încă nu există evaluări
- Measure Distance and Elevation Using EDMDocument24 paginiMeasure Distance and Elevation Using EDMAmir Alisty0% (1)
- EARTHWORK CALCULATION FORMULASDocument14 paginiEARTHWORK CALCULATION FORMULASpaul macharia100% (1)
- Open Channel FlowDocument47 paginiOpen Channel FlowLulzim BeqirajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highway Exam 15-16 AnswersDocument8 paginiHighway Exam 15-16 AnswersHL KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Geometric Design DocumentDocument87 paginiCivil Engineering Geometric Design DocumentAbel BerhanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthworks: Volume CalculationDocument29 paginiEarthworks: Volume Calculationxia_498251729100% (1)
- Stopping Sight DistanceDocument28 paginiStopping Sight DistanceEman MousaÎncă nu există evaluări
- D - Horizontal Alignment and Super ElevationDocument22 paginiD - Horizontal Alignment and Super ElevationAva CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Design of Special BeamsDocument15 paginiChapter 1 - Design of Special BeamsSine EntertaimentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework No. 2Document3 paginiHomework No. 2Belal AL QaisiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RankineDocument4 paginiRankineVidya SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Surveying Field Scheme ReportDocument6 paginiEngineering Surveying Field Scheme ReportMohafisto SofistoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation - II: by Engr. Muhammad Waseem Lecturer Department of Civil Engineering UET, JalozaiDocument38 paginiTransportation - II: by Engr. Muhammad Waseem Lecturer Department of Civil Engineering UET, JalozaiShahid AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce123-Trip Generation and Attraction (Final)Document48 paginiCe123-Trip Generation and Attraction (Final)Vicces P. EstradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdmixturesDocument7 paginiAdmixturesCass Ysabel Guanco AtencioÎncă nu există evaluări
- TSLC Civil Post SLC Final, 2014Document98 paginiTSLC Civil Post SLC Final, 2014Rabi Krishna Budha ChhetriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Te-I - Question Bank Under Unit-I (Highway Planning & Alignment)Document4 paginiTe-I - Question Bank Under Unit-I (Highway Planning & Alignment)Charan Reddy100% (2)
- Weirs - Basic Civil Engineering Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFDocument4 paginiWeirs - Basic Civil Engineering Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFSangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highway Engineering: Subject Code - CE 2255Document43 paginiHighway Engineering: Subject Code - CE 2255HanafiahHamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- FLUID MECHANICS NOTESDocument31 paginiFLUID MECHANICS NOTESsrajubasavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1Document2 paginiTutorial 1KenBoonWong100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Design Problems SolvedDocument11 paginiReinforced Concrete Design Problems Solvedacurvz2005Încă nu există evaluări
- Isro Admit CardDocument2 paginiIsro Admit CardAnchal GoheÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECV 401 CAT Two 2013Document1 paginăECV 401 CAT Two 2013Daniel KariukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 12 Compound - CurveDocument19 paginiCH 12 Compound - CurveAbdirahman Waasuge100% (1)
- Internal Flow: Hasan HacişevkiDocument103 paginiInternal Flow: Hasan HacişevkiMukaram AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Project Management KTU Notes Module 1Document13 paginiCivil Engineering Project Management KTU Notes Module 1shalu R FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometric Design of Highways - Part 1Document14 paginiGeometric Design of Highways - Part 1Ronnel BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: A. Path Lines, Streamlines and Stream TubesDocument3 paginiFundamentals of Fluid Flow: A. Path Lines, Streamlines and Stream TubesMegan MontibonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airport Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 paginăAirport Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsengineeringmcqsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Course Content and Mechanics ProblemsDocument17 paginiCivil Engineering Course Content and Mechanics ProblemsKhalid YousafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Measurements in Surveying Objective QuestionsDocument6 paginiLinear Measurements in Surveying Objective QuestionsSujit Kumar100% (1)
- Student Number: 2015-01127 - Name: Robles, Mariecor Elsie, B. - Adviser: Engr. Maricel DC. AquinoDocument8 paginiStudent Number: 2015-01127 - Name: Robles, Mariecor Elsie, B. - Adviser: Engr. Maricel DC. AquinoMariecor Elsie RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Advance MachanisamDocument8 paginiTime Advance MachanisamVinayKumarSingh100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document51 paginiChapter 2seyoum GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Module 2 and Module 3 CE122-2Document4 paginiProject Module 2 and Module 3 CE122-2Joaquin Moulic0% (1)
- Ecohydrology: Vegetation Function, Water and Resource ManagementDe la EverandEcohydrology: Vegetation Function, Water and Resource ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985De la EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Ground ADDITIONAL PANEL Layout-ModelDocument1 paginăGround ADDITIONAL PANEL Layout-ModelTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Become An Effective Speaker and WriterDocument41 paginiHow To Become An Effective Speaker and WriterPhan SonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforcement details for columns 1 and 2Document9 paginiReinforcement details for columns 1 and 2Tefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Story Beam V2 KN M3 (KN-M) DDocument2 paginiStory Beam V2 KN M3 (KN-M) DTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Density Sand 1840kg/m3 Gravel 2250kg/m3 Cement 1400kg/m3 Cement Water Ratio 0.4-0.65Document1 paginăDensity Sand 1840kg/m3 Gravel 2250kg/m3 Cement 1400kg/m3 Cement Water Ratio 0.4-0.65Tefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Col 1 ( 2.00 0.00m) Col 1 (0.00 3.06m) : SD Take SD SD Take SD SDX SDX Sdy SdyDocument9 paginiCol 1 ( 2.00 0.00m) Col 1 (0.00 3.06m) : SD Take SD SD Take SD SDX SDX Sdy SdyTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: Grade 11 SyllabusDocument16 paginiBiology: Grade 11 SyllabusTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Shear CalculationDocument5 paginiBase Shear CalculationTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torsion in Beams - Limit State of CollapseDocument23 paginiTorsion in Beams - Limit State of Collapsesubhajit284Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16 - Structural Design PDFDocument28 paginiChapter 16 - Structural Design PDFTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beamttt DesignDocument1 paginăBeamttt DesignTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document4 pagini1Tefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Mezanee Floor Panel PDocument3 paginiFor Mezanee Floor Panel PTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProjctDocument3 paginiProjctTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On Urban Waste Management: Instructor: - FeyyiraDocument3 paginiAssignment On Urban Waste Management: Instructor: - FeyyiraTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ground ADDITIONAL PANEL Layout-Model PDFDocument1 paginăGround ADDITIONAL PANEL Layout-Model PDFTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2008-02-12 Attachment2 HCB TestDocument5 pagini2008-02-12 Attachment2 HCB TestTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On Urban Waste Management: Instructor: - FeyyiraDocument3 paginiAssignment On Urban Waste Management: Instructor: - FeyyiraTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantity and SpescificationDocument28 paginiQuantity and SpescificationTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- XXXXXXXDocument1 paginăXXXXXXXTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Building Height Regulation ManualDocument70 paginiNew Building Height Regulation ManualTefera Temesgen58% (12)
- Bar ScheduleDocument8 paginiBar ScheduleTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Steel Tension MembersDocument76 paginiDesign of Steel Tension Membersomar45Încă nu există evaluări
- CE 470 Midterm Exam: Channel Section Design StrengthDocument12 paginiCE 470 Midterm Exam: Channel Section Design StrengthTefera TemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mangaldan Distric Ii Pogo-Palua Elementary School: ND RDDocument3 paginiMangaldan Distric Ii Pogo-Palua Elementary School: ND RDFlordeliza Manaois RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
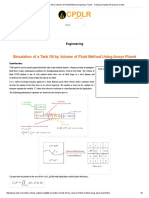
- Simulation of A Tank Fill by Volume of Fluid Method Using Ansys Fluent - Training, Projects & Research CenterDocument9 paginiSimulation of A Tank Fill by Volume of Fluid Method Using Ansys Fluent - Training, Projects & Research CenterHayderAlSamawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH08 Wooldridge 7e PPT 2pp 20231128Document3 paginiCH08 Wooldridge 7e PPT 2pp 20231128turtlefar1Încă nu există evaluări
- Evolutionary Computation:: Genetic AlgorithmsDocument49 paginiEvolutionary Computation:: Genetic AlgorithmsShobanraj LetchumananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout Diode EquationDocument1 paginăHandout Diode Equationmanpreetsingh3458417Încă nu există evaluări
- Gpelab A Matlab Toolbox For Computing Stationary Solutions and Dynamics of Gross-Pitaevskii Equations (Gpe)Document122 paginiGpelab A Matlab Toolbox For Computing Stationary Solutions and Dynamics of Gross-Pitaevskii Equations (Gpe)Pol MestresÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE380 LabmanualDocument95 paginiEE380 LabmanualsekinÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Tutorial On Cross-Layer Optimization in Wireless NetworksDocument12 paginiA Tutorial On Cross-Layer Optimization in Wireless Networkshendra lamÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cricket Winner Prediction With Applications of ML and Data AnalyticsDocument18 paginiThe Cricket Winner Prediction With Applications of ML and Data AnalyticsMuhammad SwalihÎncă nu există evaluări
- FE DP1 Math AASL P1 SolDocument10 paginiFE DP1 Math AASL P1 SolJustin Clement TjiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contingency Analisys in Power System - Amit Kumar RoyDocument84 paginiContingency Analisys in Power System - Amit Kumar RoyijkmvvÎncă nu există evaluări
- G (X) F (X, Y) : Marginal Distributions Definition 5Document13 paginiG (X) F (X, Y) : Marginal Distributions Definition 5Kimondo KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro to Algorithms & Data Structures LectureDocument30 paginiIntro to Algorithms & Data Structures LectureSaqib SherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minimum Cost Flow: A Minimum Cost Flow Problem Is A Optimization and Decision Problem To Find TheDocument3 paginiMinimum Cost Flow: A Minimum Cost Flow Problem Is A Optimization and Decision Problem To Find Thebishal maharjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9789533073248UWBTechnologiesDocument454 pagini9789533073248UWBTechnologiesConstantin PişteaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sajc 2010 Prelim Math p2Document6 paginiSajc 2010 Prelim Math p2lauyongyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Truncation Errors and The Taylor Series: Engr. Aure Flo A. Oraya, MSCEDocument29 paginiTruncation Errors and The Taylor Series: Engr. Aure Flo A. Oraya, MSCEHatsuieeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divergence and CurlDocument8 paginiDivergence and CurlaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECON 233-Introduction To Game Theory - Husnain Fateh AhmadDocument7 paginiECON 233-Introduction To Game Theory - Husnain Fateh AhmadAdeel ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Parent Workshop Jan 2020Document16 paginiMaths Parent Workshop Jan 2020Marjorie MalvedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mastering Sequences & SeriesDocument2 paginiMastering Sequences & SeriesCristina CotraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementDocument7 paginiAssignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementKetz NKÎncă nu există evaluări
- UCC Computer Science student explores greedy algorithmsDocument3 paginiUCC Computer Science student explores greedy algorithmsEmmanuel EshunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid State PhysicsDocument281 paginiSolid State PhysicsChang Jae LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparison of Subspace Methods For Sylvester Equations: Mathematics InstituteDocument9 paginiA Comparison of Subspace Methods For Sylvester Equations: Mathematics InstituteDurga SivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări