Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Compression Member PDF
Încărcat de
SanjeevJadhavDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Compression Member PDF
Încărcat de
SanjeevJadhavDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.bookspar.
com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
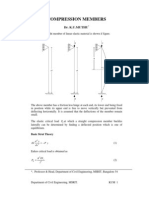
COMPRESSION MEMBERS
Dr. K.U.MUTHU*
A perfectly straight member of linear elastic material is shown if figure.
The above member has a friction less hinge at each end, its lower end being fixed
in position while its upper end is free to move vertically but prevented from
deflecting horizontally. It is assumed that the deflections of the member remain
small.
The elastic critical load PE at which a straight compression member buckles
laterally can be determined by finding a deflected position which is one of
equilibrium.
Basic Strut Theory
EI
d2y
= P y
dx 2
(1)
Eulers critical load is obtained as
PE =
2 EI y
l2
(2)
*, Professor & Head, Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT, Bangalore 54
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 1
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
In terms of the stress equation is
pE =
2E
(KL / r )2
(3)
Strut with initial curvature
In practice, columns are generally not straight and the effect out of straightness on
strength is studied. Consider a strut with an initial curvature bent in a half sine
curve as shown in Figure.
If the initial deflection, at x from A is yo and the strut deflects y further under
load, P, the equilibrium equation is
EI
d2y
= P( y + yo )
dx 2
x
Where deflection y = sin
l
(4)
(5)
If o is the deflection at the centre and the additional deflection caused by P,
then
(PE / P ) 1
(6)
The maximum stress at the centre of the strut is given by
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 2
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Pmax =
P P( 0 + )h
+
A
Iy
(7)
Where h is shown in figure
i.e.
p y = pc +
P( 0 + )h
Ary 2
i.e. p y = pc + pc
p y = pc +
( 0 + )h
ry 2
pc h
1
1 +
2 0
ry ( p E pc ) 1
(8)
(9)
(10)
Denoting the Perry factor
(p
0h
(11)
ry 2
pc
pc ) = p c 1 +
( p E pc )
(12)
On simplification it gave
( p E pc )( p y pc ) = p E pc
(13)
The value of pc, the limiting strength at which the maximum stress equal the
design strength, can be found by solving this equation and is the Perry factor.
The minimum value of pc after solving the quadratic equation is obtained as
pc = 2 p E p y
0.5
(14)
which is of the form
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 3
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
pc = 2 p E p y
and =
0.5
(15)
0h
(16)
ry2
the initial deflection 0 is taken as (1/1000)th of length of the column and hence
is given by
l h l h
2 =
1000 ry ry 1000ry
l
and hence =
ry
l
and =
r
y
(17)
(18)
(19)
a lower value of was suggested by Robertson as = 0.003 for column designs.
This approach was suggested in British code. is the slenderness ratio. The total
effect of the imperfections (initial curvature, end eccentricity and residual stresses
on strength). They are combined in to the Perry constant and is modified as
= 0.001a ( 0 )
(20)
2E
f
y
0 = 0.02
and
(21)
the value of 0 gives the limit to the plateau over which the design strength py
controls the strut load. The Robertsons constant a is assigned different values
to give the different design curves.
As per IS 800-2007;
f cd =
fy
mo
fy
(22)
mo
And = stress reduction factor for different buckling class, slenderness ratio and
yield stress.
[ + (
1
2
0.5
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
(23)
KUM 4
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
and = 0.5 1 + ( 0.2) + 2
(24)
= imperfection factor given in Table 7, in P35, IS800:207.
=non dimensional effective slenderness ratio.
fy
(25)
f cc
and f cc Eulers buckling stress =
2E
(KL / r )2
(26)
KL
and
effective slenderness ratio (or) the effective length KL to appropriate
r
radius of gyration, r, mo = partial safety factor for material strength. It is noted
that the stress reduction factor depends on buckling class, slenderness ratio and
yield stress (Table 8, P36- 39, IS800-2007).
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 5
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.1 A single angle discontinuous member ISA 130x130x10mm with single
bolted connection is 2.5m long. Calculate the safe load carrying capacity of
the section. If it is connected by one bolt at each end.
f y =250Mpa. Class 7, 5.1.2, P48, IS800:2007.
e = k1 + k 2 2vv + k 32
k1 = 1.25, k 2 = 0.5, k 3 = 0.60
l / rvv
vv =
2500 / 25.4
=
1
250
2 x 2 x105
= 1.107
250
(b1 + b2 ) / 2t = (130 + 130) / 2(10) = 0.146
2E
250
2 x 2 x10 5
250
e = 1.25 + 0.5 x1.107 2 + 60 x0.146 2 = 1.772
= 0.5[1 + ( 0.2 ) + 2 ]
= 0.5 1 + 0.49(1.772 0.2 ) + 1.772 2 = 2.455
f cd =
f cd =
Pd =
f y mo
+ [
2
2 0 .5
250 1.1
2.455 + 2.455 2 1.772 2
0.5
(250 1.1) = 54.71N / mm 2
4.154
54.7 x 2506
= 137 kN
1000
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 6
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.2 In the above problem, if the single angle discontinuous strut is connected
with 2 bolts at each end connection, determine the safe load carrying capacity
of the section.
Fixed condition, Cl 7.5.1.2, P48, IS800:2007
k1 = 0.20, k 2 = 0.35, k 3 = 20
l / rvv
vv =
= 1.107
2E
250
(b1 + b2 ) / 2t = 0.146
2E
250
e = k1 + k 2 vv 2 + k 3 2 = 0.20 + 0.35 x1.107 2 + 20 x0.1406 2 = 1.102
f cd =
f y mo
+ [
2
2 0 .5
250 1.1
1.211 + 1.2112 1.012 2
0.5
= 0.5[1 + ( 0.2 ) + 2 ]
0.5 1 + 0.49(0.012 0.2 ) + 1.012 2 = 1.211
f cd =
f y mo
+ [ 2
Pd = 137.45 x
2 0.5
227.27
= 137.45 N / mm 2
1.211 + 0.683
2506
= 344.4kN
1000
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 7
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.3 A double angle discontinuous strut ISA 150x75x10mm long leg back to
back is connected to either side by gusset plate of 10mm thick with 2 bolts.
The length of the strut between the intersection is 3.5m. Determine the safe
load carrying capacity of the section.
Ref. CL 7.5.2.1, P48, IS800:2007
Effective length factor is between 0.7 and 0.85 Assume k=0.85
Effective length of the member = 0.85x3500=2975mm
f cd = 107
2. 6
x12.4 = 103.8 N / mm 2
10
Strength of the member =
103.8 x 4312
= 447.6kN
1000
Ex.4 In the above problem if double angles discontinuous strut is connected
to one side of the gusset plate determine the safe load.
Effective length l e = 0.85 x3500 = 2975mm
rmin = 2.56cm P105
le
2975
=
= 116.2
rmin 25.6
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 8
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Table 9c; P42; IS800
f cd = 94.6
Safe load =
6.2
x10.9 = 87.87 4 N / mm 2
10
87.84 x 4312
= 378.8kN
1000
Ex.5 A rolled steel beam ISHB 300 @ 58.8 kg/m is used as a column. The
column is fixed in position but not in direction at both ends. Determine the
safe load carrying capacity in the section if the length of the column is 4.5m
t f = 10.6mm Table 10, P44, IS800:2007.
Buckling class of cross section
h 300
=
= 1. 2
b 250
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 9
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
t f 40mm
Buckling about zz axis
Buckling class a Table 7, P35, IS800:2007.
About zz axis, = 0.21
Z = 129.5mm
y = 54.1mm
4500
= 250
129.5
x 2 x10 5 = 0.391
= 0.5[1 + ( 0.2 ) + 2 ]
= 0.5[1 + 0.21(0.391 0.2 ) + 0.3912] = 0.5965
f cd = f y mo + 2 2
0.5
])
250
2
2
=
0.5965 + 0.5965 0.391
1.10
0.5
f cd = 237.9 N / mm 2
About y-y axis buckling class (b) = 0.34
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 10
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
f y (kL / r ) / 2
2
y =
4500
= 250
54.1
2 x 2 x105 = 0.9366
= 0.5[1 + ( 0.2 ) + 2 ]
= 0.5 1 + 0.34(0.9366 0.2 ) + 0.9366 2 = 1.0638
f cd =
250
1.0638 + 1.0638 2 0.9366 2
1.10
0.5
f cd = 356.42 N / mm 2
Table 9(a) P40, IS800:2007.
kL 4500
=
= 34.75
r 129.5
f cd = 220
4.75
x7 = 216.7 N / mm 2
10
kL 4500
=
= 83.2
r
54.1
Table 9(b), P41, IS 800:2007.
f cd = 150
3.2
x16 = 144.48
10
Strength = 144.88 x7485 = 1084.4kN
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 11
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.6 A built up column consists of two ISMC 400 @ 49kg/m and two plates of
500mmx10mm. The clear distance between back to back of channel is
200mm. One plate is connected to each flange. Determine the safe load
carrying capacity of the built u column if the effective length of column is 5m.
Area = 2(62.93) + 2(50 x1) = 225.86cm 2
50 x13
2
I zz = 2[15082.8] + 2
+ 50 x1(20 + 0.5)
12
4
= 72198.9cm
1x50
2
I yy = 2 504.8 + 62.93(10 + 2.42 ) + 2
12
= 41257.6cm 4
I min = 41257.6cm 4
rmin =
41257.6
= 13.5cm
225.86
kL 5000
=
= 37
r
135
f cd = 211
Safe load =
7
x13 = 201.9 N / mm 2
10
201.9 x 22586
= 4560kN
1000
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 12
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.7 Calculate the safe load of a bridge compression member of two channels
ISMC 350 @ 421.1 kg/m placed toe to toe. The effective length of member is
7m. The widths over the back of the channel is 350mm and the section is
properly connected by lacings.
A = 2(53.66 ) = 107.32cm 2
I zz = 2(10008) = 20016cm 4
I yy = 2 430.6 + 53.66(17.5 2.44 )
= 25201.7cm 4
I min
rmin =
= 13.6cm
A
kL 700
=
= 51.2
r
13.6
Table 9c
f cd = 183
1. 2
x15 = 181.2 N / mm 2
10
Strength of the member =
181.2 x10732
= 1944.6kN
1000
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 13
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.8 A column 6m high has its ends firmly built in. The column is built up
with two channels. ISMC 300 placed back to back with 180mm gap between
them. The channels are effectively laced together. Using IS800, determine the
safe load carrying capacity of the column.
Area = 9128mm2
From SP (6)
min = 11.66cm
l e = 0.65(6) = 3.9m = 390cm
kL 390
=
= 33.4
r 11.66
Table 9c class c
f cd = 211 3.4
10
x13 = 206.6 N / mm 2
Safe load carrying capacity =
206.6 x9128
= 1885.8kN
1000
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 14
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.9 A column height 5m is hinged at the ends. It is square in cross section
(plan) of side 360mm and consists of 4 angles of ISA 80x80x10mm at each
corner suitably laced. Find the minimum load on the column.
A = 4(15.05) = 60.2cm2
I x = 4 87.7 + 15.05(18 2.34 )
= 15113.98cm 4
min =
I min
= 15.85cm
A
kL 5000
=
= 31.5 Buckling class ' c'
r 158.5
f cd = 211
1.5
x13 = 209.05 N / mm 2
10
Safe load =
209.05 x6020
= 1258.5kN
1000
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 15
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Ex.10 Determine the design strength of the column section ISHB 300 @ 58.8
kg/m. The effective length of the column is 3m.
f y = 250 N / mm 2
h 300
=
= 1.2
bf
250
t f = 10.6 40mm
z z axis Buckling class ' c'
kL le
3000
=
=
= 23.17
r
rzz 129.5
kL
= 23.17
r
f cd = 224
3.17
x13 = 219.9 N / mm 2
10
y y axis Buckling class ' b'
kL 3000
=
= 55.45
r
54.1
f cd = 194
5.45
x13 = 186.9 N / mm 2
10
Design Strength =
186.9 x7485
= 1398.9kN
1000
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 16
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
DESIGN OF COMPRESSION MEMBER
Ex.11 Design a single angle section discontinuous strut to carry a load of
80kN. The length of the member between c/c intersection is 2.75m
Axial load = 80kN
Permissible stress = 0.4 f y = 100 N / mm 2
Area required = 800mm2
Gross area = 800x1.25= 1000mm2 = 10cm2
A = 13.79cm2,
Try ISA 90x90x8mm
rvv = 1.95cm
e = k1 + k 2 2vv + k32
(l
(0.85 x275 / 1.95) = 119.87
rvv )
=
0.1986
E / 250
2 x 2 x105
1
250
vv =
(b1 + b2 / 2t ) = (90 + 90) / 2 x8
2E
250
2 x 2 x10 5
250
e = k1 + k 2 2vv + k 3 2 = 1.25 + 0.5(1.35 + 60(0.1267) 2
e = 1.768
= 0.5[1 + 0.49(1.768 0.2] + 1.768 2 = 2.25
f cd =
Pd =
f y / mo
+ [
2
2 0.5
250 / 1.1
2.25 + 2.25 1.768
2 0.5
= 38.57 N / mm 2
38.57 x1379
= 53.18kN < 80kN
1000
Revise the section
Try ISA 100X100X10 Area = 1903mm2
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 17
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
e = k1 + k 2 vv2 + k32
k1 = 1.25; k 2 = 0.5, k3 = 60
l / rvv
vv =
(0.85 x 275) / 1.94 = 120.49
2 x 2 x105
1x
250
88.81
250
vv = 1.36
=
(100 + 100) / (2 x10) =
2
x 2 x10
1x
100
= 0.1126
88.81
250
e = 1.25 + 0.5(1.36) 2 + 60 x0.1126 2 = 1.713
= 0.5[1 + 0.49(1.713 0.2] + 1.7132 = 2.338
= 0.5[1 + 0.49(2.338 0.2) + 2.338 2 ]
= 3.756
f cd =
Pd =
(250 / 1.1)
3.756 + 3.756 + 1.713
2 0.5
= 32 N / mm 2
32 x1903
= 61kN < 80kN
1000
Try ISA 130 x130 x10 Area = 25.06cm 2
e = k1 + k 2 vv2 + k32
k1 = 1.25; k 2 = 0.5, k3 = 60
l / rvv
vv =
E
250
(0.85 x 275) / 1.94 = 2.63
1x
2 x 2 x10 5
250
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 18
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
(130 + 130) / (2 x10) =
2
1x
x 2 x10
13
= 0.1463
88.81
250
e = 1.25 + 0.5(2.36) 2 + 60 x 0.14632 = 2.448
= 0.5[1 + 0.49(2.448 0.2] + 2.448 2 = 4.047
f cd =
Pd =
(250 / 1.1)
4.047 + 4.047 + 2.448
2 0.5
= 31.26 N / mm 2
3126 x 2506
= 78.33kN < 80kN
1000
Try ISA 150X150X10
A=29.03cm2
rvv = 2.93cm
e = k1 + k 2 2vv + k32
k1 = 1.25; k 2 = 0.5, k3 = 60
l / rvv
vv =
(0.85 x 275) / 2.93 = 0.898
2 x 2 x105
1x
250
250
(150 + 150) / (2 x10) =
1x
2 x 2 x10 5
15
= 0.168
88.81
250
e = 1.25 + 0.5(0.898) 2 + 60 x0.1463 2 = 1.83
= 0.5[1 + 0.49(1.83 0.2] + 1.832 = 2.574
f cd =
(250 / 1.1)
2.574 + 2.574 1.83
2 0.5
= 51.84 N / mm 2
Strength = 150.5kN>80
Try ISA 130x130x10 A+25.06cm, rvv=2.54cm
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 19
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
l / rvv
vv =
(0.85 x 275) / 2.54 = 92.03 = 1.036
1x
250
250
(130 + 130) / (2 x10) =
2
1x
x 2 x10
88.81
2 x 2 x105
13
= 0.1463
88.81
250
e = 1.25 + 0.5(1.036) 2 + 60 x0.14632 = 1.752
= 0.5[1 + 0.49(1.752 0.2] + 1.752 2 = 2.415
f cd =
(250 / 1.1)
2 0.5
= 43.89 N / mm 2
2.415 + 2.415 + 1.752
Safe strength = 43.89x2506/1000=110kN>80kN
Ex.12 Design a double angle discontinuous strut to carry a load of 125kN, the
length between the intersection is 3.8m
Axial load = 125kN
Permissible stress 0.4 f y =100Nmm2
Area Required = 125000/100=1250mm2
Gross area required = 1250x1.25=1562.5mm2 = 15.63mm2
Try two ISA 75x75x6 area = 17.32cm2
min = 2.3cm
Effective length kL = 0.85 x380 = 323cm
kL
= 140.4
rmin
Table 9(c) f cd = 66.2 N / mm 2
Safe strength =
66.2 x1732
= 114.7kN < 125kN
1000
Hence revise the section, Try two angle of ISA 80x80x8
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 20
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Area = 24.42cm2
min = 2.44cm
kL
323
=
= 132.4
rmin 2.44
Table 9(c) f cd = 74.3
2.4
x8.1 = 72.4 N / mm 2
10
Safe strength = 72.4 x 2242 / 1000 = 162.3kN > 125kN
Ex.13 A column connects four equal angles arranged in the form of a square
section of side 400mm. Design the section if the column is to carry an axial
load of 800kN. The length of the column is 5m. Both the ends of the column
are restrained in position but not in direction.
Axial load = 800kN
Allowable compressive stress = 0.4x250=100N/mm2
Area of 4 angles = 800x103/100=800mm2
Area of 1 angle = 2000mm2 = 20cm2
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 21
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Increase this area by 25%, Gross area of l angle = 20x1.25=25cm2
Try 4 angle of ISA 130x130x12mm A = 29.82cm2
I x = I y = I min = 4 473.8 + 29.82(20 3.66 ) = 33742cm 4
2
33742
= 16.82cm
4 x 29.82
min =
kL
500
=
= 29.7
rmin 16.82
f cd = 211.39 N / mm 2
Strength of the member = 211.39x4x2982/1000=2521>800kN
Hence revise the section
Try 4 angles of ISA 100x100x12 A = 22.59cm2
I min = 4 207 + 22.59(20 2.92 ) = 27188.4cm 4
rmin =
27188.4
= 17.35cm
4 x 22.59
kL
500
=
= 28.8
rmin 17.35
f cd = 212.56 N / mm 2
Safe load = 212.56x4x2259/1000=212.6>80kN
Try 4 angles of ISA 90x90x10 A = 17.03cm2
I min = 4 126.7 + 17.03(20 2.59 ) = 21154.5cm 4
rmin =
21154.35
= 17.62cm
4 x17.03
kL
500
=
= 28.4
rmin 17.62
f cd = 224
8.4
x13 = 213.08 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 213x4x1703/1000=1450>800kN
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 22
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Try 4 angles of ISA 80x80x10 A = 15.05cm2
I min = 4 87.7 + 15.05(20 2.34 ) = 19125.7cm 4
2
rmin = 17.82cm
kL
500
=
= 28
rmin 17.82
8
x13 = 213.6 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 213.6x4x1505/1000=1285.2>800kN
f cd = 224
Try 4 angles of ISA 80x80x8 A = 12.21cm2
I min = 4 72.5 + 12.21(20 2.27 ) = 15642.99cm 4
2
rmin = 17.89cm
kL
500
=
= 27.95
rmin 17.89
f cd = 224
7.95
x13 = 213.67 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 213.67x4x1221/1000=1043.6kN>800kN
Try 4 angles of ISA 60x60x10 Area = 11cm2
I min = 4 34.8 + 11(20 1.85) = 14633.79cm 4
2
rmin = 18.24cm
kL
500
=
= 27.41
rmin 18.24
f cd = 224
7.41
x13 = 214.38 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 214.38x4x1100/1000=943.2kN>800kN
Try 4 angles of ISA 60x60x8mm A = 8.18cm2
I min = 4 29 + 8.96(20 1.77 ) = 12026.8cm 4
2
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 23
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
rmin = 19.17cm
kL
500
=
= 26
rmin 19.17
f cd = 224
6
x13 = 216.2 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 216.2x4x818/1000=707kN<800kN
Hence revise the section.
Adopt 4 angles of ISA 60x60x8mm
Ex.14 A rolled steel beam ISHB 300@ 58.8kg/m is used as a column. The
column is fixed in position but not in direction at both ends. Determine the
safe load carrying capacity of the section if the length of column is 4.5m
I zz = 12545.2cm 4
I yy = 2193.6cm 4
A = 74.85cm2
h 300
=
= 1.2, t f = 10.6mm < 100mm
b f 250
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 24
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
For the buckling about zz axis b
rzz =
12545.2
= 12.95cm
74.85
le
450
=
= 34.75
rzz 12.95
f cd = 216
4.75
x10 = 211.25 N / mm 2
10
For the buckling about yy axis class c
ryy =
2193.6
= 5.41cm
74.85
le
450
=
= 83.18
ryy 5.41
f cd = 136
3.2
x10 = 131.2 N / mm 2
10
Strength of the member = 131.2x7485/1000=982kN
Ex.15 Design a built up column consisting of two channel sections placed
back to back with a clear spacing of 250mm between them. The column
carries an axial load of 1000kN and is having an effective height of 6m.
Design the lacing for the column.
Axial load = 1000kN
Assume the permissible compressive stress = 0.5 f y =125N/mm2
Area required = 1000x103/125=8000mm2 = 80cm2
Area of one channel = 45cm2
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 25
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Try 2 channels of ISMC 350; area = 2x53.65=107.3cm2
rzz = 13.66cm
ryy = 15.21cm
About zz axis
le
600
=
= 43.92
rzz 13.66
f cd = 198
3.9
x15 = 192.15 N / mm 2
10
About yy axis
le
600
=
= 39.34
ryy 15.21
f cd = 211
9.4
x3 = 208.18 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 192.15x10730/1000-2061.76>1000kN hence OK
Try ISLC 300 A = 84.22cm2
rzz = 11.98cm
ryy = 15.32cm
le
600
=
= 50
rzz 11.98
f cd = 211
0.17
x13 = 210.78 N / mm 2
10
le
600
=
= 39.17
ryy 15.32
Safe load = 183x8422/1000=1541kN>1000kN
Hence adopt the section.
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 26
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Design of lacing
Cl 7.6.2 Minimum width of lacing bar = 3x16 (dia of bolt) = 48 say 50mm
Cl 7.6.4 Angle of inclination = 40 0 70 0 = = 45 0
Cl 7.6.3 Thickness of lacing bar =
1
[spacing + g + g ] = 1 [250 + 60 + 60] = 6.17mm say 10mm
60
60
Cl 7.6.5.1
Spacing of lacing
50
rmin of one component of member
l
0.7 e
rmin
whole
(250 + 60 + 60) = 12.89 50 0.7(39.17 ) = 27.42
28.7
Cl 7.6.6.3
kL
145
r flat
of the lacing bar =
0.7l
0.7 x37 2
=
= 126.86 145
t 120
1 12
Check the bars for lacing in compression
Shear force =
2.5
x1000 = 25kN
100
Force on the lacing bar =
S
25
cos ec =
cos ec45 = 8.84kN
2n
2 x2
For the flat angle, for = 127
f cd = 83.7
7
x9.4 = 77.15 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 77.12x50x10/1000=38.6kN>8.84kN
Check for the flat in Tension
= (b d )tf y / m =
(50 18)10(410 ) = 105kN
1.25
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 27
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Or f y Ag / mo = 250 x50 x10 / 1.1 = 113.4kN > for in the lacing bar
Ex.16 Design a battened column for the column shown in figure. Assume that
the channels are kept back to back.
kL
The effective slenderness ratio of battened columns shall be 1.1 times the
r
maximum actual slenderness ratio of the column.
kL
= 1.1x39.17=43
r
3
f cd = 198 x15 = 193.5 N / mm 2
10
Safe load = 193.5 x
8422
= 1629.7 kN > 1000kN
1000
l
Maximum spacing of the batten
0.7 e
rmin of one component of member
rmin
whole
Maximum spacing of batten = 143.5cm = 0.7(2.87)43= 86.4cm
Provide the battens at a spacing of 850mm
Provide 20mm bolts. For rolled, machine flameout, P74, Cl 10.2.4.2 1.5xhole
diameter = 1.5x20=33mm
Effective depth of batten
= 250+2(23.5)=297mm>2(100)=200mm
Overall depth of batten = 297+2(33)=363mm=370mm
Required thickness of batten = 1/50 (distance between inner most bolts.)
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 28
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
1/50(250+2x60)=7.4 say 8mm
Length of the batten = 250+2(100) =450mm
Provide 450x370x8mm
Size of intermediate batten
Effective depth = 3/4x297=222.75mm>2x100=200mm
Hence an effective depth of 225mm
Overall depth = 225+2x33=291say 300mm
Provide 450x300x8mm intermediate battens
Design forces
Transverse shear = V = 2.5/100x1000=25kN=25000N
Longitudinal shear Vb =
Vt C 25000 x85
=
= 28.72kN
NS
2 x370
Vt = transverse shear = 25000N
C = c/c of battens, longitudinally = 850mm
N = number of parallel planes = 2
S = minimum distance between the centroid of the bolt = 370mm
Moment M =
Vt c 25000 x850
=
= 5312500 Nmm
2N
2 x2
For end batten
Shear Stress = 28720/370x8=9.7N/mm2 <
250
= 131.2 N / mm 2
3 x1.1
250
6 M 6 x5312500
Bending stress = 2 =
= 29.10 N / mm 2 <
= 227 N / mm 2
2
td
8
x
370
1
.
1
Hence safe
For Intermediate battens
Shear stress = 28720/300x8=11.97N/mm2 < 131.2N/mm2
Bending stress = 6x53/2500/8x3002=44.27N/mm2 < 250/1.1=227N/mm2
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 29
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Connections
Strength of the bolt = 45.3kN
Required number of bolts = 28.72/45.3 < 1.0
As the bending moment is also present, provide 3 bolts
Check
Force in each bolt due to shear = 28.72/3=9.57kN
Adopt a pitch of 100mm
Force due to moment =
M r
r2
5312500 x100
= 26.56kN
100 2 x100 2
Resultant force =
9.57 2 + 26.56 2 = 28.23kN < 45.3kN
Hence safe.
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 30
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
CASED COLUMNS
Encased I sections or filled hollow sections carries more load. In cased columns,
the advantages derived from the properties of concrete and steel are used. The
concrete is strong in stronger in compression and it provides greater rigidity. The
solid concrete casing assists in carrying the load and the entire load is resisted by
concrete and steel. The design of the above columns is currently based on IS
11384-1985. As the above code is on working stress method the guide lines given
in BS5950, Part I is presented here. The role of concrete is that it acts as a fire
protection for the encased steel columns and also prevents the column from
buckling about the weak axis. As per the BS5950, Part I the column must satisfy
the following specifications.
(i)
The steel section is either a single rolled or fabricated I or H section
with equal flanges, channels and compound sections can also be used.
(ii)
The steel section should not exceed 1000mmx500mm. The dimension
100mm is in the direction of web.
(iii)
Primary structural connections should be made in the steel section.
(iv)
The steel section is unpainted and free from dirt, grease, rust, scale etc.
(v)
The steel section is encased in concrete of at least Grade 20, to BS
8110.
(vi)
The cover on the steel is to be not less than 50mm. The corners may be
chamfered.
(vii)
The concrete extends the full length of the member and is thoroughly
compacted.
(viii)
The casing is reinforced with bars not less than 5mm diameter at a
maximum spacing of 200mm to form a cage of closed links and
longitudinal bars. The reinforcement is to pass through the centre of
the cover.
(ix)
The effective length is not to exceed 40bc, 100b2c / dc or 250 r
whichever is the least, where
bc = minimum width of solid casing.
dc = minimum depth of solid casing.
r = minimum radius of gyration of steel section.
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 31
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
BS5950, Part I guidelines for estimating the compressive strength of column.
a) The radius of gyration about yy axis is shown in figure, ry should be taken
as 0.2bc but not more than 0.2 (B+150) where B = overall width of flange.
The radius of gyration for the zz axis should be taken as that of the steel
section.
b) The compression resistance Pc is
f A
Pc = Ag + 0.45 cu pc Pcs
p y
f
Pcs = Ag + 0.25 cu Ac p y
py
Where Ac = gross sectional area of concrete. Casing in excess of 75mm from the
steel section is neglected. Finish is neglected.
Ag =gross area of the steel section
f cu =characteristic strength of the concrete at 28 days. This should not exceed
40N/mm2.
p c =compressive strength of steel section determined using rx and rz in the
determination of which p y 335 N / mm 2
p y = design strength of steel
Cased Column
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 32
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
CASED COLUMN WITH AXIAL LOAD
Ex.17 An internal column in a building has an actual length of 4.5m centre to
centre of floor beams. The steel section is ISHB250 @ 51kg/m. Calculate the
compression resistance of the column if it is cased in accordance with the
codal provision. M25 concrete grade has been use. The casing has been made
325mm square.
Properties of ISHB 250
A=6496mm2
rzz =10.91cm
ryy =5.49cm
For the above cased column;
ry = 0.2(325) = 65mm
0.2(250 + 150 ) = 80mm
i) effective length = 0.7 (4500) = 3150mm of cased column
ii) 40 bc =40(325) = 13000mm
iii) 100
bc2
=100x325=32500mm
dc
iv) 250 r =250x54.9=13725mm
slenderness ratio =
kL 3150
=
= 48.46
r
65
refer Table 9(c) in P42, IS800:2007.
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 33
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
f cd = 198
8.46
x15 = 185.3 N / mm 2
10
The gross sectional area of concrete
Ac = 325 x325 = 105625mm 2
Compressive strength of concrete
25
185.3
Pc = 6496 + 0.45 x
x105625
= 2084.5kN
250
1000
Short column strength
25 x105625 250
Pcs = 6496 + 0.25 x
= 2284kN
250
1000
Compressive strength of column = 2084.5kN
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 34
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Column with axial load and moment
Ex.18 A stanchion carries an factorial axial load 500kN and a factored
bending moment of 250kNm. Design the section if the length is 6m and one
end of the column is restrained in position and direction whereas, other end is
restrained only in position but not in direction.
Try section ISWB 600@ 133.7kg/m
kL 0.8 x6000
=
= 91.43
r
52.5
Yura suggested
My
Mz
for initializing the size of the column. If the BM is
+ 7.5
d
b
predominant then the equivalent BM can be found out from
peff = P + 2
M eq = M z + Pu
d
2
In this case;
Peff = P + 2
Mz
250
= 500 + 2 x
= 1333.33kN
d
0.6
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 35
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Check the above section
h 600
=
= 2.4 > 1.2
b 250
t c = 21.3mm < 40
Buckling about yy axis, buckling class b
f cd = 134
1.43
x16 = 131.7 N / mm 2
10
Compressive strength of the trial section=131.7x17038/1000=2244kN>1333.33kN
Section properties
A = 177.38cm2
I zz = 1.06(10 ) cm 4
5
I yy = 47.7(10 ) cm 4
3
Z pz = 2bt t f (H t t ) / 2 + t w (H 2t f )/ 4
Z pz = 2(250 )21.3(600 21.3) / 2 + 11.2(600 2 x 21.3) / 4 = 3986.66cm 3
2
(P138, IS800:2007)
Z py = 2t f b 2f / 4 + (H 2t f )t w3 4 = 2(21.3)
250 3
11.2 2
+ (600 2 x 21.3)
= 683.1cm 3
4
4
Cross section classification
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 36
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
2.50
=
fy
250
= 1.0
250
Outstanding flanges
b 250 / 2
=
= 5.87 < 9.4 (Table 2, P18)
tf
21.3
Hence the flange is plastic
Web
d = H 2t f 2r1 = 600 2(21.3) 2(18) = 521.4mm
d 521.4
=
= 46.6 < 84
tw
11.2
Hence the cross section is plastic
Refer d 9.3.1.1 for plastic and compact sections
My
M
N
+
+ z 1.0
N d M dy M dz
N = factored applied axial force = 500kN
N d = design strength in compression =
mx
170.38 x10 2 x 250
= 3872.3kN
1.1x1000
M dz =
Ag f y
1x3986.66 x10 3 x 250
= 906.05kNm
1.1x10 6
500
250
+
= 0.4 < 1.0
3872.3 906.05
Member buckling resistance in compression
Effective length of member = 0.8x6000=4800mm
kLz
4800
=
= 19.22
rz
249.7
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 37
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
kLy
ry
4800
= 91.43
52.5
h 600
=
= 2.4; t f = 21.3 < 40mm
b 250
Buckling about zz axis (Buckling class a)
9.22
x1 = 226 N / mm 2
10
Buckling about minor axis (Buckling class b)
f cd = 227
f cd = 134
1.43
x16 = 131.7 N / mm 2
10
Safe compressive strength =
131.7 x17738
= 2336kN > 500kN
1000
Hence the section is conservative.
Member buckling resistance in bending
M d = b Z p f bd
b = 1.0 for plastic sec tion
LT = Imperfection parameter = 0.21 for rolled steel section P54, cl 8.2.2
f cr ,b = extreme fibre bending compressive stress
f cr ,b
1.1 2 E
1 LLT / ry
=
1+
2
(LLT ry ) 20 h f / t f
0.5
LLT
= 91.43
ry
f cr ,b
2
1.1 2 x 2 x10 5
1 91.43
=
1 +
91.43 2
20 600 / 21.3
= 259.48[1 + 0.527 ]
0.5
0.5
= 320.64 N / mm 2
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 38
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
L,T = Non dimensionless slenderness ratio
fy
f cr ,b
250
= 0.883
320.64
LT = 0.5[1 + LT ( LT 0.2) + 2LT ]
Strength reduction factor = 0.5 1 + 0.21 0.883 0.2 + 0.863 2
)]
LT = 0.96
LT = bending stress reduction factor to account for lateral Torsional buckling
=
1
2
2
LT + LT XL
LT =
1
0.96 + 0.96 2 0.853 2
f bd = LT
fy
mo
= 0.748 x
= 0.748
250
= 170 N / mm 2
1.1
Elastic lateral buckling moment
M cr = b Z p f cr ,b
M cr = Elastic lateral buckling moment
M cr =
3986.66 x10 3 x320.64
= 1278.3kNm > 250kNm
10 6
Hence it is safe
Moment amplification factors
k Z 1 = 1 + ( 0.2 )
P
Pdz
500
= 1 + 0.883 0.2
= 1.146
2336
P
500
k ZZ = 1 + 0.8
= 1 + 0.8 X
= 1.171
Pdz
2336
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 39
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
z =
M2
=0
M1
C mz = max[(0.6 + 0.4 ),0.4]
C mz = 0.6
M
P
250
+ k z C mz 1 = 0.21 + 1.146 x0.6 x
= 0.34 < 1
Pdz
M cr
1278.3
Hence the section is safe against bending moment and axial force.
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 40
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Questions on Compression members, Column Splices, Slab &
Gusset Bases and Connections between beams & columns
1. Design a single angle discontinuous strut (equal & unequal angle) to carry a
compressive force of 500kN. The c/c distance between the joints is 3m.
Design also the connections using
a) M24 bolts of property class 5.6
b) M24 HSFG bolts of property class 10.9
c) Equivalent welded connections
2. Repeat the above problem using double angles (on same side & on either side
of gusset plate) for a force of 1000kN.
3. A discontinuous double angle strut is placed back to back on the same side of
the gusset plate 8mm thick. The angles are ISA 125x95x8 with c/c distance
between the joints =3m. Calculate the safe load when:
a) connected by one bolt at each end
b) connected by two or more bolts at each end
What will the % change of load if the above angles are placed on either side of
the gusset plate?
4. A single angle discontinuous strut ISA 130x130x12 is 3m between centre to
centre of intersections. Calculate the safe load when:
i) connected by one bolt at each end
ii) connected by two or more bolts at each end
5. A truss member has a length of 3.5m between the centre of joints. The force in
the member is 150kN compression due to DL & IL; 200kN due to DL & WL.
Design the member and the connection to a 10mm thick gusset plate. Adopt
single equal angle; single unequal angle; double equal angles & double
unequal angles.
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 41
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
6. Compute the strength of the column shown in figure
7. Design a builtup column to carry an axial load of 1400kN with the length of
column being 8m. The column is effectively held in position at both ends, but
not restrained against rotation at both ends. The C/S of the column is:
a) Two channels back to back (heel to heel)
b) Two channels toe to toe separated & unseparated
c) Two I- sections - ISHB & ISMB
d) I- section with cover plates
e) Four angles equal & unequal (arranged as square or rectangular
section)
In all the cases, design also the lacings and battens, if applicable. Also, check
other end conditions as specified in the code. (Connections can be bolted or
welded)
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 42
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
8. a) Design a builtup column carrying an axial load of 1300kN. The height of
column is 7m & is effectively held in position at both ends, but restrained
against rotation
at one end only. Adopt two channels toe to toe with the
width over the back of the channels being 400mm. Also, design a suitable
lacing and battens. Connections can be bolted or welded.
b) Repeat the design in 7a) with two channels back to back with a clear
spacing of 300mm between them.
9. Design a suitable slab base and gusset base in problems (6) & (7) assuming
plain concrete pedestal of grade M15. Design the pedestal also. Adopt suitable
bolts. SBC of soil is 150kN/m2.
10. Design a column using an ISHB section with cover plates to carry a
compressive load of 3000kN. The effective length of the column is 6m. Also,
design a suitable gusset base & plain concrete pedestal of M15 grade. Adopt
suitable bolts. SBC of soil is 200kN/m2
11. An upper storey column ISHB300 @ 58.8 kg/m carries a load of 1000kN & a
BM of 40kNm. It is spliced with a lower storey column ISHB400 @ 82.2
kg/m. Ends of the columns are machined. (Milled) Design a suitable splice.
Adopt suitable bolts or welds.
12. a) A column section ISHB400 @ 82.2 kg/m carries an axial load of 1200kN &
BM of 50kNm. Design a suitable column splice. Adopt bolts or welds of
suitable size.
b) Design a suitable splice for a 5m effective length ISHB450 @ 87.2 kg/m
column carrying an axial load of 1000kN & a BM of 50kNm. Assume the
surfaces to be unmilled. Adopt bolts or welds of suitable size.
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 43
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
13. An ISMB600 @ 122.6 kg/m transfer a reaction of 300kN framing into the
flange of a column ISHB400 @ 82.2kg/m. Design a suitable
a) Stiffened seated connection;
b) Unstiffened seated connection (simple seated)
c) Framed connection.
Adopt bolts or welds of suitable size.
14. Two secondary beams ISMB300 @ 58.8kg/m are directly welded on either
side of the web of the girder ISMB600 @ 122.6 kg/m. Each secondary beam
transfer an end reaction of 250kN. Design fillet field welded connection.
15. Repeat the above problem as a framed connection adopting bolts or welds of
suitable size.
16. A secondary beam ISMB400 @ 62.6 kg/m transmit an reaction of 300kN to a
main beam ISMB550 @ 86.9 Kg/m. Design a suitable framed connection
using bolts or welds of suitable size.
17. A stanchion factorial axial load of 750kN and factored Bending moment of
300 kNm. The effective length of the column is 5 m. Design the stanchion as
per IS 800:2007
18. A column of effective length 6.5m shown in fig is subjected to the design data
as follows.
Factored axial load at the top = 1250kN
Factored axial load at the bottom = 600kN
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 44
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Moment about the major axis at the top = 100kNm
Moment about the major axis at the bottom = 55kNm
Check the adequacy of the section.
19. A column between the floor is provided with ISHB 300 @ 58.8kg/m.
Investigate its adequacy if the ultimate design loads and moments are as
follows
Axial compression = 2500kN
Ultimate Moments at Top
About Major axis = 350kNm
About Minor axis = 50kNm
Ultimate Moments at Bottom
About Major axis = 175kNm
About Minor axis = -75kNm
Effective length of the column = 6.0m
Dr. K.U. Muthu
Sri H. Narendra
Department of Civil Engineering, MSRIT.
KUM 45
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Theory 1 Degree of DeterminacyDocument12 paginiTheory 1 Degree of DeterminacyErrold Paul GagarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 BuoyancyDocument5 pagini4 BuoyancyDaniel Vasquez0% (1)
- Assignment TemplateDocument3 paginiAssignment TemplateAina Margauxe JacintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flowchart ShitDocument23 paginiFlowchart ShitSam Barotilla100% (1)
- Mastery Test MT1 and MT2 Solution: None of TheseDocument6 paginiMastery Test MT1 and MT2 Solution: None of TheseU-line Anne Roque VillafloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singly-Reinforced BeamDocument9 paginiSingly-Reinforced BeamJohn Rhey Almojallas BenedictoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 602 - Geotechnical EngineeringDocument2 paginiCE 602 - Geotechnical EngineeringJohn Michael SalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument5 paginiChapter 4 PDFtrishia arcillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4. Lesson 3 - Example For Earthquake Load Combination - Strength DesignDocument5 paginiModule 4. Lesson 3 - Example For Earthquake Load Combination - Strength DesignRich Lenard L. MagbooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemDocument1 paginăRefresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemKiki Do youÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignDocument40 paginiCe0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignjerichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction ProblemsDocument4 paginiFriction ProblemsDaniel PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Struktur C5Document41 paginiAnalisis Struktur C5Hazyema HarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 1 With AnsDocument4 paginiProblem Set 1 With AnsRaine ZaficoÎncă nu există evaluări
- File 2 Geo2 Module 1 Activity PDFDocument2 paginiFile 2 Geo2 Module 1 Activity PDFAlab IanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics EeeercDocument5 paginiPhysics EeeercJessabelle RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moren - MODULE 3 - Beams-ColumnDocument18 paginiMoren - MODULE 3 - Beams-ColumnJoshua Espanto MorenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersDocument56 paginiChapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersRami DemachkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCD Problem SetsDocument4 paginiRCD Problem SetsFlo TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 22 Integration, Area, Volume, Surface Area, Length of An Arc, CentroidDocument6 paginiProblem Set 22 Integration, Area, Volume, Surface Area, Length of An Arc, CentroidairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : PilesDocument26 paginiGeotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : PilesPascasio PascasioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo Tech FormulasDocument5 paginiGeo Tech FormulasJoy KathleenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem No: 1: Submitted ToDocument4 paginiProblem No: 1: Submitted ToLight HouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.problem Set BEAMSDocument13 pagini1.problem Set BEAMSone hundredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frames Subjected To Lateral Loads (Approximate Analysis) : Structural Theory: Lecture 02Document6 paginiFrames Subjected To Lateral Loads (Approximate Analysis) : Structural Theory: Lecture 02Michael Christ IcagoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Asst PDFDocument10 paginiModule 1 Asst PDFJay ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glanfill Module 1 - Part 2Document57 paginiGlanfill Module 1 - Part 2LeiVasAllanigueVillanueva100% (1)
- Ans. 501,438.32 MDocument2 paginiAns. 501,438.32 Maljon jamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illustrative Problems Design of Square Footing Problem 9.1Document5 paginiIllustrative Problems Design of Square Footing Problem 9.1Joshua De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis For ShearDocument20 paginiDesign and Analysis For Shearhonesto reynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Document6 paginiPEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Jc FortÎncă nu există evaluări
- Take Home ExamDocument2 paginiTake Home ExamArnab Chakraborty100% (1)
- Cagsawa, Ryan I. (Sce101-10 Problems)Document7 paginiCagsawa, Ryan I. (Sce101-10 Problems)Ryan CagsawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Steel Design: Design Philosophy of Steel Design: Universal College of ParañaqueDocument22 paginiStructural Steel Design: Design Philosophy of Steel Design: Universal College of ParañaqueFritz LuzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open ChannelsDocument21 paginiOpen ChannelsShlomo GoldbergsteinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Document1 paginăSolved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Cristian A. GarridoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCD SA4 GuideDocument15 paginiRCD SA4 GuideDionne Rhenzo MontalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agacita John PaulDocument10 paginiAgacita John PaulCarlo Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro HyrdoDocument16 paginiHydro HyrdoCherie Gold AccuhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Problem 1Document14 paginiSample Problem 1Fritz Luzon100% (1)
- Unit 2 Influence Lines Statically Determinate Trusses: StructureDocument24 paginiUnit 2 Influence Lines Statically Determinate Trusses: StructureRaj BakhtaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- WITH SOLUTIONS Open Channel and Alternate Stages of FlowDocument43 paginiWITH SOLUTIONS Open Channel and Alternate Stages of FlowMark PulongbaritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forces On Curved Surfaces 1Document13 paginiForces On Curved Surfaces 1Yours PamoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 - PlasticityDocument35 paginiModule 4 - PlasticitykaicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moren - MODULE 1 - Compression MembersDocument13 paginiMoren - MODULE 1 - Compression MembersJoshua Espanto MorenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Footing On PilesDocument12 paginiFooting On PilesRey Dominique VillarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer RCDDocument3 paginiReviewer RCDShadowiw KulitÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF Sample Problems in Pre Stressed Concretepdf DD - PDFDocument25 paginiPDF Sample Problems in Pre Stressed Concretepdf DD - PDFKeith GarridoÎncă nu există evaluări
- P5 3B Bernardo KathryneDocument5 paginiP5 3B Bernardo KathryneKATHRYNE BERNARDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 Shear and Moment Diagram Part 2Document30 paginiModule 4 Shear and Moment Diagram Part 2FLORENCE BANIAGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 7Document41 paginiDR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 7Engr.Towhidul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- TH1 CalculusDocument4 paginiTH1 CalculusEarl averzosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Design Problems With Solution Under NSCP 2015 JEDR ManuscriptDocument40 paginiReinforced Concrete Design Problems With Solution Under NSCP 2015 JEDR ManuscriptMark Bastien LizertiguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022MAY PSAD UnlockedDocument5 pagini2022MAY PSAD UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New ResumeDocument3 paginiNew Resumemqc46562Încă nu există evaluări
- M2 03 Constant and Falling Head TestDocument13 paginiM2 03 Constant and Falling Head TestPzynae FlorentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 10 SettlementDocument14 paginiLesson 10 SettlementJake CanlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compression MemberDocument45 paginiCompression MemberSatyasapath RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nonlinear GuideDocument17 paginiNonlinear Guidepiv0ter_betterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretensioned Beam Example: CE 437/537, Spring 2011 1 / 15Document15 paginiPretensioned Beam Example: CE 437/537, Spring 2011 1 / 15Haris AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOP ExcavationDocument5 paginiSOP ExcavationCharantej TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TYSONS - Food CourtDocument20 paginiTYSONS - Food CourtManivannan J100% (1)
- Six House Building DeconstructionDocument29 paginiSix House Building DeconstructionVedant PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Mix Design As Per Indian Standard CodeDocument4 paginiConcrete Mix Design As Per Indian Standard CodesemakambaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SANS1655ED1 1 - 04-10-22 - WP - TMDocument15 paginiSANS1655ED1 1 - 04-10-22 - WP - TMjohndupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceilings, Partitions & Raised FloorsDocument7 paginiCeilings, Partitions & Raised FloorsMaddala Srinivasa RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approximate BOQ For Limestone Crusher & Load CentreDocument8 paginiApproximate BOQ For Limestone Crusher & Load CentreSasanka SekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- A23b - Chalenges For Underwater Concrete Repair in Deep WaterDocument12 paginiA23b - Chalenges For Underwater Concrete Repair in Deep WaterJoão Carlos Protz ProtzÎncă nu există evaluări
- WABO Compression SealsDocument4 paginiWABO Compression SealsAndy AcousticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loa 10155030069917Document25 paginiLoa 10155030069917Abhinav KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alluminium Composite Panel-FlexibondDocument4 paginiAlluminium Composite Panel-Flexibondedars08Încă nu există evaluări
- Determining The Ambf PsoDocument32 paginiDetermining The Ambf PsoAlecsisRoeEstañolFrascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BoQ - Insulation Works (Group 1)Document5 paginiBoQ - Insulation Works (Group 1)Bhavanishankar ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conceptual Structural Design Methods of Reinforced Concrete Buildings Rev 2Document16 paginiConceptual Structural Design Methods of Reinforced Concrete Buildings Rev 2Dawit SolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot Oil Expansion TankDocument2 paginiHot Oil Expansion TankAnonymous 70lCzDJv100% (1)
- AP-T356-21 Technical Basis Guide To Pavement Technology Part 2Document54 paginiAP-T356-21 Technical Basis Guide To Pavement Technology Part 2Fernando PaivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20550e00 PDFDocument120 pagini20550e00 PDFhalim_kaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation For Civil EngineeringDocument2 paginiFoundation For Civil Engineeringmudassir2640Încă nu există evaluări
- UPVC Price List - LDocument4 paginiUPVC Price List - LPardeep Parashar100% (1)
- Abe DIY BookletDocument89 paginiAbe DIY BookletPula ConsultantsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBA Qatar Company InterviewDocument2 paginiMBA Qatar Company InterviewTradiyo ForexÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Msia) Guide To Sewer Selection and Installation (Dec2006) - VC Pipe pg17Document168 pagini(Msia) Guide To Sewer Selection and Installation (Dec2006) - VC Pipe pg17Rachael Hoo100% (7)
- SamsdataDocument296 paginiSamsdataSamuel AugustineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentry Wellhead Catalog PDFDocument129 paginiSentry Wellhead Catalog PDFMuhammad TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS 455 The Assessment of Concrete Highway Bridges and Structures-Web (3) For PubDocument104 paginiCS 455 The Assessment of Concrete Highway Bridges and Structures-Web (3) For PubAbinashÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-FOLD Houses CatalogDocument49 paginiA-FOLD Houses CatalogGiustino Lorella Di DonatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cables Catalogue 2Document6 paginiCables Catalogue 2fikih padliÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEED v4 For Interior Design and Construction ChecklistDocument3 paginiLEED v4 For Interior Design and Construction Checklisttarek.abbas8598Încă nu există evaluări
- Final - 4th - Assignment - Shallow Foundation Design1222Document47 paginiFinal - 4th - Assignment - Shallow Foundation Design1222Refisa JiruÎncă nu există evaluări
- TS6 3.5 Tubing 15.8ppfDocument1 paginăTS6 3.5 Tubing 15.8ppfKhairilsyam Abdul RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessDe la EverandThe Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (456)
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesDe la EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1636)
- Summary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosDe la EverandSummary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (294)
- Summary of The New Menopause by Mary Claire Haver MD: Navigating Your Path Through Hormonal Change with Purpose, Power, and FactsDe la EverandSummary of The New Menopause by Mary Claire Haver MD: Navigating Your Path Through Hormonal Change with Purpose, Power, and FactsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessDe la EverandSummary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (328)
- The War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesDe la EverandThe War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (274)
- Can't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsDe la EverandCan't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (386)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsDe la EverandThe One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (709)
- Essentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessDe la EverandEssentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (188)
- Book Summary of Ego Is The Enemy by Ryan HolidayDe la EverandBook Summary of Ego Is The Enemy by Ryan HolidayEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (387)
- How To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryDe la EverandHow To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (557)
- Summary of The Algebra of Wealth by Scott Galloway: A Simple Formula for Financial SecurityDe la EverandSummary of The Algebra of Wealth by Scott Galloway: A Simple Formula for Financial SecurityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Make It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningDe la EverandMake It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (55)
- Summary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsDe la EverandSummary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Whole-Brain Child by Daniel J. Siegel, M.D., and Tina Payne Bryson, PhD. - Book Summary: 12 Revolutionary Strategies to Nurture Your Child’s Developing MindDe la EverandThe Whole-Brain Child by Daniel J. Siegel, M.D., and Tina Payne Bryson, PhD. - Book Summary: 12 Revolutionary Strategies to Nurture Your Child’s Developing MindEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (57)
- Steal Like an Artist by Austin Kleon - Book Summary: 10 Things Nobody Told You About Being CreativeDe la EverandSteal Like an Artist by Austin Kleon - Book Summary: 10 Things Nobody Told You About Being CreativeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (128)
- Summary of Million Dollar Weekend by Noah Kagan and Tahl Raz: The Surprisingly Simple Way to Launch a 7-Figure Business in 48 HoursDe la EverandSummary of Million Dollar Weekend by Noah Kagan and Tahl Raz: The Surprisingly Simple Way to Launch a 7-Figure Business in 48 HoursÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Atomic Habits by James ClearDe la EverandSummary of Atomic Habits by James ClearEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (169)
- Summary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg: How to Unlock the Secret Language of ConnectionDe la EverandSummary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg: How to Unlock the Secret Language of ConnectionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of The Algebra of Wealth: A Simple Formula for Financial SecurityDe la EverandSummary of The Algebra of Wealth: A Simple Formula for Financial SecurityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Summary of Miracle Morning Millionaires: What the Wealthy Do Before 8AM That Will Make You Rich by Hal Elrod and David OsbornDe la EverandSummary of Miracle Morning Millionaires: What the Wealthy Do Before 8AM That Will Make You Rich by Hal Elrod and David OsbornEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (201)
- The 5 Second Rule by Mel Robbins - Book Summary: Transform Your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageDe la EverandThe 5 Second Rule by Mel Robbins - Book Summary: Transform Your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (329)
- Summary of Eat to Beat Disease by Dr. William LiDe la EverandSummary of Eat to Beat Disease by Dr. William LiEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (52)
- Summary of When Things Fall Apart: Heart Advice for Difficult Times by Pema ChödrönDe la EverandSummary of When Things Fall Apart: Heart Advice for Difficult Times by Pema ChödrönEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (22)
- Sell or Be Sold by Grant Cardone - Book Summary: How to Get Your Way in Business and in LifeDe la EverandSell or Be Sold by Grant Cardone - Book Summary: How to Get Your Way in Business and in LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (86)
- Blink by Malcolm Gladwell - Book Summary: The Power of Thinking Without ThinkingDe la EverandBlink by Malcolm Gladwell - Book Summary: The Power of Thinking Without ThinkingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (114)