Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chemical Change Answers PDF
Încărcat de
Sara JonesTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chemical Change Answers PDF
Încărcat de
Sara JonesDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chemical change - worksheet answers
Glossary:
Anion: atom carrying a negative charge.
Cation: atom carrying a positive charge.
Compound: pure substance with a fixed ratio of atoms.
Ductile: can be drawn into a wire.
Electrical conductor: a substance which has charged particles which are capable of
moving.
Element: a substance containing only one type of atom.
Lattice: an ordered arrangement of particles
Malleable: able to have its shape modified - i.e. bent
Molecule: one or more atoms chemically bonded together
Valence electron: an electron situated in the outer shell (energy level)
Questions:
1.
2.
Element
Number of
electrons
lost
Number of
electrons
gained
Number of
electrons in
the ion
Number of
protons in
the ion
Ion
potassium
18
19
fluorine
10
oxygen
10
sodium
10
11
Na
magnesium
10
12
Mg
chlorine
18
17
Cl
calcium
18
20
Ca
bromine
36
35
Br
2+
2+
-
2+
Atoms sometimes gain or lose electrons to attain a stable electron arrangement like that of a
noble gas. Atoms that gain electrons have more electrons than protons and form ions with a
negative charge. Atoms that lose electrons have more protons than electrons and form ions
with a positive charge. Positive and negative ions are attracted to each other and form ionic
bonds. Ionic bonds tend to form between atoms of metallic and non-metallic elements.
Molecular substances form between atoms of non-metallic elements. They share valence
electrons in covalent bonds. By sharing electrons, each atom has the same number of
electrons as a noble gas. The atoms share electrons but they do not gain or lose electrons
like ions do.
Metallic substances consist of positive ions in fixed positions called a lattice with valence
electrons that are free to move throughout the lattice. The electrons are not held by particular
ions or shared between particular atoms.
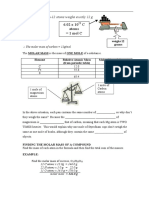
3.
a) Ionic. Magnesium is a metal and oxygen (in air) is a non-metal. Metals and non-metals
combine to form ionic compounds.
b) It would be solid at room temperature and have a very high melting point. It would be
brittle. It will not conduct electricity in solid form, but will when molten or dissolved in
water.
c)
d) No. Though it has charged particles (anions and cations), they are in fixed positions in a
lattice. For a substance to be able to conduct electricity, there must be free moving
charged particles.
e) Magnesium oxide would conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in solution
(aqueous).
4.
5.
a) calcium fluoride
c) ammonium nitrate
e) calcium hydrogen
carbonate
g) tin (IV) chloride
i) aluminium nitrate
k) potassium phosphate
m) ammonium sulphate
o) chromium (III) oxide
a)
c)
e)
(NH4)SO4
Mg(NO3)2
NaHCO3
g)
i)
k)
m)
o)
SnS2
Ba(HSO4)2
HgO
Al2O3
ZnS
CaF2
NH4NO3
Ca(HCO3)2
b) silver nitrate
d) iron (II) chlorate
f) sodium carbonate
AgNO3
Fe(ClO3)2
Na2CO3
SnCl4
Al(NO3)3
K3PO4
(NH4)2SO4
Cr2O3
h)
j)
l)
n)
p)
Sn(SO4)2
Al2(SO4)3
Ba3(PO4)2
ZnSO3
Al2(CO3)3
ammonium sulfate
magnesium nitrate
sodium hydrogen
carbonate
tin(IV) sulfide
barium hydrogen sulfate
mercury (II) oxide
aluminium oxide
zinc sulfide
tin (IV) sulphate
aluminium sulphate
barium phosphate
zinc sulphite
aluminium carbonate
b) K2SO4
d) CrF3
f) PbCl2
potassium sulfate
chromium (III) fluoride
lead (II) chloride
h)
j)
l)
n)
p)
copper (II) phosphate
nickel iodide
calcium carbonate
iron (III) phosphate
zinc oxide
Cu3(PO4)2
NiI2
CaCO3
FePO4
ZnO
6.
carbon dioxide (CO2)
water (H2O)
methane (CH4)
ammonia (NH3)
7.
a) For a material to conduct electricity, there must either free electrons or ions able to move
and carry charge.
b) In a salt solution, there + and ions that are able to move.
c)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Molar MassDocument3 paginiMolar MassSara Jones100% (1)
- Module 3 Further ReadingDocument3 paginiModule 3 Further ReadingSara JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 Further ReadingDocument13 paginiModule 4 Further ReadingSara JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDFDocument1 paginăResultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDFSara JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distance and Velocity Time GraphsDocument1 paginăDistance and Velocity Time GraphsSara JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed Velocity and AccelerationDocument1 paginăSpeed Velocity and AccelerationSara JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychology Units 1 & 2Document408 paginiPsychology Units 1 & 2Sara Jones100% (4)
- Evolution: Glossary: Define The Following TermsDocument2 paginiEvolution: Glossary: Define The Following TermsSara JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taking Notes in Class: Key TipsDocument2 paginiTaking Notes in Class: Key TipsSara JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Super EssayDocument5 paginiSuper EssaySyed Arif AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing A Literature Review AssignmentDocument2 paginiWriting A Literature Review AssignmentSara Jones100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Rubifloor 2021Document43 paginiRubifloor 2021Sandro CaeiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resin AmberliteDocument2 paginiResin Amberlitegreat_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Verification of Debye-Hückel-Onsager EquationDocument3 paginiVerification of Debye-Hückel-Onsager EquationJOSEPH HERBERT MABEL50% (6)
- Railways: Mechanical Stabilisation of Track Ballast and Sub-BallastDocument12 paginiRailways: Mechanical Stabilisation of Track Ballast and Sub-BallastJohn Archie Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEM - Threaded Inserts For Plastics PDFDocument20 paginiPEM - Threaded Inserts For Plastics PDFHenrique MarquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 - Boat Building MaterialsDocument8 pagini05 - Boat Building MaterialsPhong TuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- N2XSEBY cable specificationsDocument5 paginiN2XSEBY cable specificationsKiki WidyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Die Casting DieDocument156 paginiDie Casting DieHeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Momentum, Heat and Mass TransferDocument87 paginiFundamentals of Momentum, Heat and Mass TransferSlim KanounÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilovepdf Merged RemovedDocument19 paginiIlovepdf Merged RemovedNeet AspirantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Test Methods For Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture, and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic MaterialsDocument14 paginiStandard Test Methods For Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture, and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic MaterialsviverefeliceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Calculation MemoriesDocument43 paginiStructural Calculation MemoriesScott Wade100% (1)
- Evaporation and CondensationDocument3 paginiEvaporation and CondensationHadi AskabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601Document32 paginiRobinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601MarcWorld100% (1)
- Design For Production of PropyleneDocument168 paginiDesign For Production of PropyleneEmiliano Rohwein100% (1)
- Preliminary Technical Program HMnS2016Document33 paginiPreliminary Technical Program HMnS2016manjumv27Încă nu există evaluări
- TubesheetDocument8 paginiTubesheetVaibhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purification of Wastewater by Metal Oxide NanoparticlesDocument12 paginiPurification of Wastewater by Metal Oxide NanoparticlesEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masterseal 622 TdsDocument3 paginiMasterseal 622 TdsMahmoud SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- D375 PDFDocument4 paginiD375 PDFArnold RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2720 (Part-20) PDFDocument5 pagini2720 (Part-20) PDFSoundar PachiappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Che1015 Petrochemical-Technology TH 1.0 37 Che1015 55 AcpDocument2 paginiChe1015 Petrochemical-Technology TH 1.0 37 Che1015 55 AcpAGSI FAFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Llautó M38 CuZn37Document2 paginiLlautó M38 CuZn37Josep TanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabric in ArchitectureDocument28 paginiFabric in ArchitecturesubalakshmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arkema - Polymer Selection Guide For Liquid ResinsDocument28 paginiArkema - Polymer Selection Guide For Liquid ResinsYoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tle 6 (Industrial Arts) Week 8 Day 2Document3 paginiTle 6 (Industrial Arts) Week 8 Day 2Krisna HundosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panamax Cargo Hold Cleaning Manual Rev00Document36 paginiPanamax Cargo Hold Cleaning Manual Rev00Cenk ÇobanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSSB 20190812aDocument4 paginiPSSB 20190812asrinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sans 1200 LeDocument9 paginiSans 1200 Lefilipe100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Lubrication ManagementDocument41 paginiChapter 5 - Lubrication ManagementAdinz DinÎncă nu există evaluări