Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Design of Transmission Systems Part A
Încărcat de
kannanviknesh086319Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Design of Transmission Systems Part A
Încărcat de
kannanviknesh086319Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
ME2352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS
UNIT I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS
1. What are the factors co n t roll in g s e l e c t i o n o f a transmission drive?
The factors are,
a) Amount of power to be transmitted
b) Velocity ratio
c) Service conditions
d) Centre distance
e) Space availability
f) Efficiency
g) Nature of load
h) Cost, etc.
2. What are the main types of belt drives?
Flat belt drive, V belt drive, ribbed belt drive, round belt drive and timing belt drive are
the main type of belt drives.
3. What are the various types of flat belt drives?
Open belt drive, crossed belt drive, belt drive with idler pulley, quarter turn belt drive,
compound belt drive, fast and loose pulley drive and stepped pulley drive are the various
types of flat belt drives.
4. What is slip in a flat belt drive?
When the frictional grip between the pulley and belt is insufficient, the driver will
have some forward m o t i o n without belt. This phenomenon is called as slip.
5. What is creep in a flat belt?
Due to difference in tensions on tight and slack side, the belt undergoes a change in
length as it passes around the pulley. To compensate for these different strains the belt
moves relative to the surface of the pulley. This relative movement is called creep.
6. Why tight side of the belt should be at the bottom side of the pulley?
If the tight side of the belt is at bottom side of the pulley and the slack side is at the top
side, then the sag caused by the self weight of the belt, for long centre distance drive
will increase the arc of contact of belt with pulley and hence the effect of power
transmission is increased.
7. What are the different types of belt materials?
Leather, rubber, cotton and canvas, nylon, balata etc., are the different types of belt
materials.
8. What is ply in belt?
Ply in belt is one of a layer of fabrics of the belts. Belt strips called plies are cemented
together so as to increase thickness and are specified according to the number of the
constituent layers.
9. Explain crowning of pulleys.
To keep the belt running on the face pulley, it is necessary that then face to be
crowned. It is used to avoid the belt to run off sideways.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 1
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
10. What are the factors upon which the coefficient of friction between the belt and
the pulley depends?
The factors are,
a) Material of the belt
b) Slip
c) Speed
The value of varies from 0.25 to 0.3.
11. What is the condition to transmit maximum power in a flat belt drive?
Maximum power transmitted is one third of maximum tension developed as centrifugal
tension.
12. How to calculate the design HP in flat belt drive
The design HP in flat belt drive is calculated as follows.
Rated HP Service factor
Design HP = ---------------------------------------------------Arc of contact factor Diameter factor
13. What are the advantages of flat belt drive?
The advantages of flat belt drive are.
a) They are more flexible and absorb shock loads and vibration.
b) They are relatively cheap and easy to maintain.
c) They can be used in dusty or abrasive atmosphere.
d) The design of flat belt drive is simple and inexpensive.
e) They can be used for long distance, even up to 15m.
f) They are quiet and efficient.
14. What are the major drawbacks of a flat belt drive?
The major drawbacks of a flat belt drive are,
a) Change in velocity ratio (due to creep and slip) during power transmission.
b) More space requirement.
c) Limitation on speed reduction.
d) It is not suitable for other than horizontal position.
15. Write the advantages of V-belts.
The advantages of V-belts are,
a) High velocity ratio.
b) Possibility of employment with smaller centre distance.
c) Reliability of drive in any position.
d) Smoothness of operation.
16. What is the meaning of a V-belt designated as B - 2286 - IS 2494?
B - represents cross section
2286 - represents its nominal length
IS2494 - represents Indian standard code.
17. State reasons for the V-belt drive being preferred to flat belt drive.
According to the following reasons, the V-belt drive is preferred to flat belt drive.
a) Replacement of V-belt is easy, because V-belts available according to the standards.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 2
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
b) Power transmitted by the V-belts is more.
c) For smaller centre distance V-belts are suitable.
d) Efficiency is high, when compared to flat belt.
18. When do we prefer V-belt?
V-belt drive is preferred, when the distance between the shafts is too short, high
amount of power has to be transmitted, vertical and angular position power drive and
high speed applications.
19. Write the common types of chains.
Roller chains, bushed chains and silent chains are the common types of chains.
20. What is meant by chordal action in chain drives?
When chain passes over a sprocket, it moves as a series of chords instead of a
continuous arc in case of a belt drive. When the driving sprocket rotates at a constant
speed, the driven rotates at a varying speed due to continuously varying radius of the
chain line.
21. What is slack adjuster?
It is a movable bearing which is employed for regulating chain sag and tensions in
order to get alignment. The movable bearings are in the form of slides in which the
sprocket shafts are installed.
22. What are silent chains?
Silent chains consist of special profile plates corresponding to the profile of
sprocket teeth. As the name implies they are relatively quieter in operation. Silent
chains are also known as inverted toothed chains.
23. How are chains classified?
Chains are classified as follows.
a) Power transmitting chains
b) Hauling chains
c) Load or lifting chains.
24. What are the possible failures of a chain drive?
The possible failures of a chain drive are,
a) Extensive chain elongation
b) Failure of joints and plates
c) Wear of sprocket teeth
d) Fatigue failure of links
e) Chipping and breaking of rollers
f) Pitting at the surface of the rollers and bushes, etc.
25. How are timing belts made?
A timing belt is made of rubberized fabric with steel wire to take the tension load. It
has teeth that fit into grooves cut on the periphery of the pulleys. These belts are coated
with a nylon fabric.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 3
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
26. What are the advantages of chain drive?
The advantages of chain drive are,
a) No slip between chain and sprocket.
b) Efficiency of the drive is high.
c) Possibility of driving several sprockets using a single chain.
d) Drive is compact.
27. What are the advantages of the chain drives over the belt drives?
The following are the advantages of chain drives.
a) No slip between chain and sprocket.
b) Reduced load on the shafts than in belt drives.
c) Higher efficiency.
d) They can be operated at adverse temperature and atmospheric conditions.
28. How are chains designated?
According to BIS (IS:2403-1967) the roller chains are designated as per roller diameter and
number of stands in the chains. Example :
IS:2403-1967-represents single strand chain with roller diameter 5mm.
10.0 D IS:2403-1967 - represents double strand chain with roller diameter 12.17 mm.
24.0 T IS: 2403-1967 - represents triple strand chain with roller diameter 25.5 mm.
29. How the wire ropes are designated?
The wire ropes are designated by a number,
a) Specifying the number of strands and number of wires in each strand.
b) The wire diameter.
c) Type of construction.
d) Wire material grade.
30. What are the stresses induced in a wire rope?
The stresses induced in a wire rope are,
a) A wire rope is generally subjected to the following stresses.
b) Direct stress due to axial loads.
c) Bending stresses due to bending of ropes over sheaves.
d) Stresses due to acceleration or retardation of moving masses.
e) Stresses during starting.
31. Name the different types of wire ropes.
The different types of wire ropes are, regular lay and lang lay.
Regular lay ropes:
When the wires in the strand are twisted in a direction opposite to that of the strands, the
rope is said to be regular lay rope.
Lang lay ropes:
When the wires in the strand are twisted in the same direction to that of the strands, the
rope is said to be regular lay rope.
32. What is the meaning of wire designated 6 12 /6 / 1?
6 - refers number of strands.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 4
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
12 / 6 / 1 - refers the number of wires in a strand (12 + 6 + 1 = 19) (i.e.,19
wires are formed by 12 wires over 6 wires with 1 core wire).
33. What is the effect of centre distance and diameter of pulley on the life of a belt?
The life of the belt is the function of centre distance between the driver and driven
shafts as well the diameter of the pulleys because the shorted CD, the more often the belt
wil be subjected to bending stress while running around the pulleys and
is
damaged by antiques. Hence longer belt will last more than shorter one.
34. What are the various losses in the power transmission by belts? (Dec. 2005)
The various losses in the power transmission by belts are,
a) Slip and creep of the belt on the pulleys.
b) Windage or air resistance to the movement of belt and pulleys.
c) Bending of the belt over the pulleys.
d) Friction in the bearings of pulley.
35. What are flexible drives? Why they are called so?
The belt, chain and rope drives are called as flexible drives. Flexible drive means that the
centre distance between driver and driven can be changed conveniently during design.The
power transmitting members of the drives are more flexible to take shock loads.
36. Define law of belting.
The law of belting states that the centre of the belt approaching the pulley must be
in a plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
37. State the effects of slip and creep on the belt drive.
The effect of creep is small and is generally neglected. The effect of slip(power
loss) at slow speed is small. But at high speeds slip produce considerable loss of power and
cannot be neglected.
38. How does creep affect the belt design?
The creep in belt leads to slip, loss of power and velocity ratio. So, elastic nature of the
belt also taken into account in the belt design.
39. What is centrifugal tension in a belt drive?
When the belt runs over the pulley, some centrifugal force is created due to the belt
velocity, which increases the belt tension on both tight as well as the slack side.The
increase of tension due to centrifugal force is called centrifugal tension.
40. What are the factors affecting the belt life?
The belt value is very much affected by the following factors. a) Decrease in small
pulley diameter
b) Increase in belt thickness
c) Increase in tight side tension
d) Too large centre distance
e) Service and environmental conditions f) Fluctuation in load, e tc.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 5
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
41. Why is thin belt preferred instead of thick one?
Thick belts stretch more at outer layers when move pulley. This produces high
amount of cyclic stresses. To prevent excessive fatigue stress in belts, a thin wide belt is
always preferred over the thicker ones.
42. Discuss various stresses induced in belts.
The belts are subjected to tensile stress due to tension in the belt whether it is in tight
side or slack side. When the belt passes over pulley, it is subjected to bending stress. When
the belt runs at high speed, in addition it also subjected to tensile runs at high speed, in
addition it also subjected to tensile (centrifugal) stress.
43. Why is larger of the two pulleys to be placed at the bottom in a vertical drive?
In a vertical drive, the belt tension at the top of the belt on each side of the pulley is
greater than the tension at the bottom, by an amount equal to the weight of the freely
hanging belt. It is preferable to have the larger pulley at the bottom, so that an
increased arc of contact may offset the loss of tension.
44. What is the safety velocity ratio for flat belt and V-belt drive?
The safe velocity ratio for flat belt drive is less than or equal to three and for
V-belt drive, it is ten.
45. State the assumption made while deciding the cross section of pulley arm.
The cross section of each arm of the pulley is decided by assuming that a
cantiliever fixed at the boss of the pulley and loaded at the rim and each arm takes an
equal share of the BM.
46. What is chain drive?
The chain drive consists of an endless chain running over two or more sprockets to
transmit power. The chain consists of large number of links connected by pin joints and
the sprockets are toothed wheels with a special tooth profile.
47. List the applications of the chain drives.
Chain drives are widely used in machine tools, material handling equipments,
bicycles, wood working machinery, construction machinery, agricultural machinery,
rolling mills, coal cutter, etc.
48. What is limit value of angle of contact of a chain drive?
The limiting value of angle of contact of a chain drive is not less than 120.
49. What is backsliding in chain drives?
Wear in the chain joints leads to an increase in pitch length of the links. This increases
the chain length. Now the chain compensates for its greater length, by moving up and
outward on tooth flanks and eventually out of mesh. This is known as back sliding in chain
drives.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 6
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
50. Roller chains are designed to fail not in tension but by wear - Explain.
If the chain is designed to fail in tension, then the increase in length produces
backsliding which is accompanied by jerky motion and noise. This condition is
undesirable for proper functioning of the chain. The failure due to wear is not sudden.
So the roller chains are designed to fail by wear not by tension.
51. When do we prefer silent chain over roller and bush chain?
Silent chains are preferred over roller and bush chains for high speed applications,
smooth and noiseless operations and for more reliable operations.
52. How is tension in chain adjusted?
Chain tension is adjusted by,
a) Moving the axis of the sprocket and
b) Employing an adjustable idler sprockets or pulleys.
53. Why is odd number of teeth for sprocket preferred?
In order to distribute wear evenly as all the chain links, it is the usual practise to have odd
numbers of teeth on the smaller sprocket and an even number of pitches in the chain.
54. Name some applications for wire rope drive.
Wire rope drive is best suited for the applications where large amount of power is
to be transmitted over a larger distances. They are extensively used in elevators, mine
hoists, cranes, conveyors, hauling devices, suspension bridges, tram ways, etc.
55. What are the types of failure in wire ropes?
The wire ropes fail mainly due to wear and fatigue.
56. What do you mean by the static load in a wire rope?
The static load in a wire rope is the sum of the following loads.
a) The known dead weight.
b) Additional load caused by sudden stops and starts.
c) Shock loads and
d) Load required to overcome friction between ropes and sheeve.
57. How can the flexibility of wire be increased?
The flexibility of the wire can be increased by using non metal core, by increasing the
number of wires in a strand, by decreasing the wire diameter or combination of the above.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 7
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
UNIT II SPUR GEARS AND PARALLEL AXIS HELICAL GEARS
1. Specify the conditions based on which gear cutters are selected.
Gear cutters are selected based on,
a) Properties of materials for workpiece and tools b) Production rate
c) Cost of production
d) Structure of gears
e) Module of gear.
2. Why dedendum value more than addendum value?
To get clearance between the teeth of one gear and bottom surface of mating gear
so as to avoid interference.
3. What are the materials used for the gears?
The materials used for the gears are,
a) Cast iron
b) Steel
c) Non metals (Nylon, fiber reinforced plastics).
4. State fundamental law of gearing.
For maintaining constant velocity ratio, the common normal drawn at the point of
contact must always pass through the pitch point, which is at the intersection of common
tangent to the pitch circle diameters and the line joining the centres.
5. Where do we use skew gears?
Skew gears are employed in instruments, distributor drive of automobile engine etc.
where small loads are applied.
6. How the gears are classified based on the position of teeth on the wheel?
The gears are classified as follows.
a) Spur gear
b) Helical gear
c) Bevel gear (Straight and spiral)
d) Worm and worm wheel
e) Rack and pinion.
7. Explain cluster gear.
If two or more are cut on the same blank with gap between them, they are functioning
as a single unit,then they called cluster gears.
8. List the types of failure of toothed gear drive.
The types of failure of toothed gear drive are,
a) Breaking of tooth
b) Pitting of tooth
c) Surface abrasion
d) Seizure.
9. Define transmission ratio with reference to spur gear.
Transmission ratio of a spur gear is defined as the ratio between number of teeth on
driven and number of teeth on driver.
10. Backlash for spur gear depends on which of two factors.
Backlash for spur gear depends on the following factors.
a) Tooth space
b) Tooth thickness.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 8
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
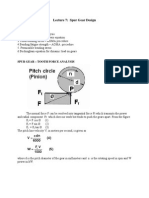
11. Define angle of obliquity or pressure angle of a gear.
It is the angle between the common normal to the two gear teeth at the point. It is
denoted by . The standard pressure angles are 14.5 involutes, 20 involute stub teeth.
12. Define module of a gear.
The module is the basic parameter, by which a gear tooth is specified and is equal to the
ratio between pitch circle diameter in mm and number of teeth.
13. What is interference in gears?
In a pair of gears in mesh, the possibility of the tip of one tooth digging into the
portion of the flank of the mating tooth gear can occur in certain conditions. This
phenomenon is termed as interference.
14. How can interference in gears be avoided?
The interference in gears can be avoided by ensuring that the point of contact
between the two teeth always remains on the involute profiles of both the teeth. This also
can be avoided by,
a) Reducing the tooth height.
b) Increasing the pressure angle.
c) The radial flank of pinion teeth be cut back.
15. What are the advantages of using non-metallic gears?
The advantages of using non-metallic gears are,
a) Noiseless operation.
b) Low weight.
c) Corrosion free.
d) Damping of shocks and vibrations.
16. What are the common profiles used for gear tooth?
The common profiles used for gear tooth are,
a) Involute
b) Cycloidal.
17. What is backlash?
Backlash is defined as the play between a mating pair of gear teeth in assembled
condition. It is the amount by which the width of the tooth space exceeds the thickness
of the meshing tooth measured on pitch circle.
18. Explain undercutting in gears.
While generating gear teeth, if there is interference of the cutter with the rotating job,
then a recess is cut at the root of the gear tooth, which is known as undercutting. This
happens when the cutter extends beyound the base circle of the pinions having small
number of teeth.
19. Give the requirements of gear materials.
The requirements of gear materials are,
a) Low cost.
c) High strength.
e) Low coefficient of friction.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
b) Easy to manufacture.
d) High wear resistance.
Page 9
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
20. Compare cycloid and involute profiles.
Pressure angle
Involute profile
Cycloid profile
Constant.
Varies from zero to
maximum.
Running
Smooth.
Less smooth.
Manufacturing
Easy.
Complicated.
Velocity ratio
Small variation in
centre distance
does not affect
Does not permit any
variation in centre
distance.
21. What is interchangeability of gears?
In a gear drive, the ability of replacing a failed gear by a similar gear without affecting
the functionality of the drive is called interchangeability of gears.
22. Define the pitch circle with reference to the spur gear.
The imaginary diameter of the circle which allows pure rolling without slipping is
known as pitch circle for the spur gear.
23. What are the advantages of toothed gears over other types of transmission system?
The advantages of toothed gears over other types of transmission system are,
a) Drive is compact.
b) High efficiency.
c) Constant velocity ratio.
d) Reliability in operation.
24. When do you use non-metallic gears?
For reducing noise, non-metalic gears are used. Manufacturing cost of non-metallic
gears is low.
25. State the advantages of the gear drives over other type of drives.
The advantages of the gear drives over other types of drives are,
a) Gear drives are positive drives.
b) Suitable for shorter center distance
c) The gear drives are better than others in case of amount of power transmission and
efficiency.
d) Change of speed is very easy in gear drives.
26. What are the commonly used gear tooth systems?
The following four systems of gear tooth are commonly used in practice.
a) 14 composite system
b) 14 full depth involute system
c) 20 full depth involve system
d) 20 stub involute system.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 10
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
27. What are the general characteristics of spur gearing?
The general characteristics of spur gearing are,
a) Transmit torque between parallel shafts.
b) Teeth are parallel to axis.
c) Line contact takes place during mating.
d) Can be used as sliding gears in gearboxes.
e) Easy to design and manufacture.
28. What are the applications of spur gears?
The spur gears are used in sliding gearboxes, machine tools, automobiles, material
handling equipments, rolling mills, marine power plants, etc.
29. What is working depth of a gear tooth?
It is radial distance between the addendum and the dedendum circle of a gear.It is equal
to the sum of addendum and dedendum.
30. What is tooth thickness of a spur gear?
It is the width of the tooth measured along the pitch circle.
31. Define seizure / scaring.
Under heavy load, the temperature of the lubricating oil rapidly rises and its viscosity
falls. As a result, the oil film breaks and the teeth engage each other. Then as the gears
rotate, softer particles are torn away from teeth, leaving scares and scratches on the
surface.
32. How will you select the materials for pinion teeth?
The teeth of pinion undergo more number of cycles than those of gear. This may cause
quicker wear.The shape of pinion tooth gives lesser beam strength than that of gear
tooth. Hence the material of the smaller wheel (pinion)should possess mechanical
properties somewhat higher than the material of the mating gear.
33. Write the design procedure for non-metalic gears.
Maximum permissible linear velocity for non-metalic gear is limited to 12 m/sec. Due to
overheating, non-metalic pinions are usually run with cast iron gear. Pinion alone is
designed in a gear pair with only beam strength checked. In general, for non-metalic
materials [b] = u/n.
where,
u - Ultimate strength of material. N - Factor of= safety 2.5 to 3.
34. How will you design a gear when the materials for gear and pinion are same?
If the materials for both pinion and gear are same, pinion alone is designed because
pinion is weaker than gear. If different materials are used pinion is designed first and
then both pinion and gear are cheeked.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 11
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
35. What are the assumptions made in driving Lewis equation?
The assumptions are,
a) Gear tooth is a cantilever with tip load.
b) Only one pair of teeth takes the entire load.
36. What is meant by stub tooth?
Stup tooth has shorter addendum and dedendum than the standard tooth. Hence
stronger gear drive will be more compact.
37. Write the types of failures caused in a gear.
The different types of failures caused in a gear are,
a) Tooth breakage
b) Surface failure
d) Seizure/scaring
e) Pitting.
c) Abrasion
38. Define transmission ratio with reference to spur gear.
Transmission of a spur gear defined as the ratio between number of teeth on driven
and number of teeth on driver.
Z2
Transmission ratio
= Z
1
where, Z2 - Number of teeth on driven wheel
Z1 - Number of teeth on driver or pinion.
39. Give the applications of cycloidal gears.
Cycloidal gears are used in gear pumps and blowers. Clocks and watches and in
certain of instruments in case where the question of interference and strength are prime
considerations.
40. What are the various materials used for the production of gears?
The materials used for the production of gears are,
a) Matallic materials
i) Plain carbon steels
ii) Alloy steels
iii) Cast iron
iv) Bronze (Worm wheel)
b) Non-metallic materials
i) Wood
ii) Synthetic resins
iii) Compressed papers.
41. State the advantages of involute profile.
The advantages of involute profile are,
a) It allows slight alternations in center distance of two gears without change in
velocity ratio.
b) Easy to manufacture by cutting or generating.
c) The pressure angle is constant along the profile.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 12
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
42. Define circular pitch.
This is the distance measured on the circumference of the pitch circle from a point
of one tooth to the corresponding point on the adjacent tooth. It is denoted by Pc.
D
Pc
N
where, D - Pitch circle dia. of gear
N - Number of teeth on the gear.
43. What are the advantages of cycloidal gearing?
The advantages of cycloidal gearing are,
a) Cycloidal tooth is stronger than involute tooth for the same pitch, as it gives more
root area.
b) Interference is inherently absent in cycloidal gearing.
44. What points must be considered, while designing a gear drive?
The following points are considered for designing a gear drive.
a) Power to be transmitted.
b) Speed of the driver.
c) Velocity ratio.
d) Centre distance.
45. What are the favourable characteristics associated with internal gears?
The favourable characteristics associated with internal gears are,
a) Stronger tooth due to greater base width. b) More teeth in contact.
c) Less sliding action and hence less wear.
d) Higher efficiency.
e) Smoother operation.
46. What is suggested by
Wear load,
Fw
Where,
Dp
b
Q
2W
Bukingham for wear load?
= Dp bQw(N)unit
- Pitch circle diameter of pinion (mm)
- Face width of pinion (mm)
- Velocity ratio factor
- Load stress factor(N/mm ).
47. What are the forces acting on helical gear?
The forces are Tangential force, Radial force and Axial force
48. Why are gears drives called as positive drives?
In gear drives, no slip occurs (like in the belt drives) and no variation in velocity ratio
takes place. So they are called as positive drives. In this driver has number of projections
(called teeth) on its periphery, which will fit into the corresponding recesses on the periphery
of the driver (called tooth space).
49. What do you mean by tooth system?
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 13
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
A tooth system is a standard which specifies the relationships involving addendum,
working depth, tooth thickness and pressure angle. The standards were planned to attain
interchangeability of gears of all tooth numbers but of same pressure angle and pitch
(Module).
50. What are the factors affecting strength of a gear tooth?
The factors affecting the strength of a gear tooth are strength of the material used
shape and size of gear tooth, circumferential velocity, errors in teeth profile, the
amount and nature of load, etc.
51. What are the types of failures normally occur in a gear tooth?
The types of failures normally occur in a gear tooth are,
a) Breakage of the tooth due to static and dynamic load.
b) Surface destruction (Wear, pitting, seizure, etc.)
52. Write short notes on stress concentration in gears.
Stress concentration occurs at the place where tooth joins the bottom load and is
influenced by the fillet radius pressure angle and positions of the load on the tooth.
53. When will you use web and arm type construction for gears?
Web type construction : Gears up to 250 mm pitch circle diameter.
Arm type construction : Gears having P C D more than 250 mm.
54. On what basis gear cutter is selected?
The cutter is selected on the basis of gear tooth system, module (or diametral pitch)
and number of teeth to be cut.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 14
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
UNIT III BEVEL, WORM AND CROSS HELICAL GEARS
1. What is the helix angle of a herringbone gear?
The helix angle of a herringbone gear ranges from 25 to 40.
2. What is virtual number of teeth in helical gears?
Virtual number of teeth is the number of teeth on equivalent spur gear in the normal
plane. The tooth profile of equivalent spur gear tooth is identical to the tooth profile of the
helical gear tooth in the normal plane.
3. What is the specific feature of meter gear?
Meter gear is the special type of crown gear in which the shaft angle is 90 and the
pitch angles of pinion and gear are equal and each angle is equal to 45.
4. What is virtual number of teeth in bevel gears?
Virtual number of teeth is the number of teeth on a spur gear having radius equal to the
back cone radius. The profile of the tooth in the equivalent spur gear is identical to the
profile of the bevel gear tooth in the transverse plane.
5. Why the efficiency of worm gear drive is comparatively low?
Meshing of wheel teeth and worm wheel occur with sliding action. Hence, friction
and heating occurs. This makes the efficiency of the power transmission low.
6. When the number of start of a worm is increased in a worm gear drive and how it affects the
other parameters and the action of the drive?
When the number of start of a worm is increased in a worm gear drive it increases the
efficiency of the drive. Number of teeth in a worm wheel = I Z (Z = Number of starts, I
= Velocity ratio).
7. What are hypoid gears?
The axes are non parallel and non- intersecting and the tooth are curved then it is called
as hypoid gears.
8. List out the different types of failures in worm gear drives.
The different types of failures in work gear drives are,
a) Seizure
b) Pitting
c) Rupture.
9. What are face gears?
Spur gear pinion meshes with a ring gear having conjugate teeth cut into the face of it.
The advantage is that spur gear cutters and gear shapers can be used to produce face gears.
10. What types of materials are used in worm wheels?
Normally worms are made integral with the shaft. Smaller worm wheels are made from
solid blanks while larger ones are made from fabricated blanks.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 15
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
11. What is corrected gear?
Correction of gear teeth is done to avoid undercutting when the number of teeth is
below a specified limit. It is done by a correction factor 'x' or addendum modification
coefficient. The gears whose teeth are corrected by a correction factor are called corrected
gear.
12. What is crown gear?
When the bevel gear connects two shafts whose axes intersect at an angle greater than a
right angle and one of the bevel gears has a pitch of 90, then it is known as a crown gear.
13. What is the main disadvantage of a helical gear drive? How it is eliminated?
The helical gears in drive will produce axial thrusts. The axial thrusts can be eliminated
by the use of double helical gears. Both hands produce axial thrusts which are equal and
opposite to each other, so they nullify each other.
14. What is herringbone gear?
A gear fabricated such that half of its width is cut with helix in one direction and other
half of the teeth are cut in opposite direction is called herringbone gear.
15. Define the following gears.
a)
Zero bevel gear.
b)
hypoid gear.
a) Zero bevel gear is a patented bevel gear, having curved teeth with a zero spiral angle.
b) Hypoid gear is similar to spiral bevel gear but with the axis of the pinion is offset from
the axis of the gear. In hypoid gears, pitch surfaces are hyperboloids of revolution.
16. Define back cone radius for a bevel gear.
It is the length of the pitch of the cone. It is also called as pitch cone radius.
17. Name the materials used for the manufacture of worm and worm wheel.
Materials for worm - Low carbon alloy steel, medium carbon alloy steel.
Materials for worm wheel - Cast iron, tint less brass and bronze.
18. How efficiency of worm drive can be increased?
Worm gear efficiency can be increased by either
a) Increasing the lead angle.
b) Using multi start worm with small diameter.
c) Improving finish, lubrication, etc. d) Using rigid, non - yielding worms with
smooth, ground or polished flanks.
19. What are the profiles used for worm?
Trapezoidal profile, Arc median, sprial profile, CAVEX, special profile designed by
Brown and Bostock - Renk.
20. In which gear drive self locking is available?
Self locking is available in worm and worm wheel. Condition for self locking is the
friction angle of the surfaces in contact is greater than the lead angle of the worm.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 16
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
21. What is single enveloping and double enveloping worm?
In worm gear drive, to increase the length of line of contact the wheel surface or
worm surface or both is made to concave shape. In single enveloping, only wheel surface
is made as concave.In double enveloping, both worm and wheel surfaces are made as
concave to increase load carrying capacity.
22. Why heat dissipation is a very important aspect in design of worm gear drive?
In most of the worm gear units, the power transmitting capacity is limited by the heat
dissipation ability of the casing. Due to sliding between worm thread and worm wheel
tooth a great amount of heat is generated. The generated heat has to be dissipated for
proper functioning of the gear drive. So the heat dissipation is a very important factor in
the design of worm gear drive.
23. Write the advantages of helical gears over spur gears.
One prime disadvantage of spur gears is that their initial contact upon meshing is a line
contact. Instantaneous line contact produces shock effect which results in reduced load
capacity and noisy operation. The problem is alleviated when helical gears are used
because the initial contact is a point which becomes a line of increasing length as contact
continues.
24. Write the different types of bevel gears.
The different types of bevel gears are,
a) Straight bevel gears
b) Zero bevel gears
c) Spiral bevel gears
d) Face gears
e) Skew bevel gears
f) Hypoid gears.
25. What is mounting height of a bevel gear?
It is the distance of the back of the boss from the cone centre.
26. Why steel is used in worm?
Low carbon alloy steels are hardened to 58 to 63 RC or medium carbon steels and
medium carbon alloy steels, fall as surface hardened to 50 to 55 RC are used.The surface
roughness should be as low as possible, for which purpose the threads are ground and
polished.
The worms of low speed drive usually receive no heat treatment.
27. Why cast iron is used in worm wheel?
Cast iron is used for low speed, high duty drives, at sliding velocities up to 2 m/s. Tint
less bronzes and brasses are used for velocities up to 8 m/s, cast iron bronzes are used for
velocities up to 25 m/s.
Materials used for worm wheel - worm combination should have high antifriction
properties to resist seizure.
28. Where do we use skew helical gears?
When the helical gears are based on the non - parallel, non - intersecting shafts, and
mesh with each other, they form a skew gearing or crossed helical gearing. These gears are
used to drive cam shafts and auxiliaries on small internal combustion, feed mechanism
on machine tools, distributor drive of automobile engines, etc.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 17
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
29. What is cone distance and face angle of a bevel gear?
Cone distance is the length of the pitch cone element. It is also called as pitch cone
radius.
Face angle is the angle suspended by the face of the tooth at the cone centre. The face
angle is equal to the pitch angle plus addendum angle.
30. What is cone distance of a bevel gear?
It is the length of the pitch cone element. It is also called as pitch cone radius.
31. Differentiate normal pitch and axial pitch in helical gears.
The axial pitch is the distance parallel to axis between similar faces of adjacent teeth,
whereas normal pitch is the distance between similar faces of adjacent teeth along a helix
on the pitch cylinders normal to the teeth.
32. What are the two types of failure in worm gear drives?
The two types of failure in worm gear drives are,
a)
Seizure
b)
Pitting
c)
Surface wear.
33. What is irreversibility in worm gears and how is it obtained ?
The worm drive is so designed that the gear cannot turn the worm although the worm
can turn the gear. If the worm wheel is unable to drive the worm, the phenomenon is called
irreversibility (ability to transmit motion in one direction only).The irreversibility is
obtained by having the friction angle or worm greater than the lead angle.
34. State true or false and justify.
Mitre gears are used for connecting non - intersecting shafts- False. Mitre gears
represent equal bevel gears (having equal teeth and equal pitch angle) connect two shaft
whose axes intersect at right angles.
35. When do we use bevel gears?
Bevel gears are used to transmit power from one shaft to other, when the two shafts
intersect each other at any angle.
36. Give the applications of bevel gears.
Bevel gears are used in rear axle drives of automobiles, vertical spindle of a drilling
machine, elevating screw of cross rail of planner, milling machine and shaping
machine, differential of a gear hobbing machine, crushing head or cone of a gravity rock
crusher, etc.
37. What are the advantages of spiral bevel gears over straight teeth bevel gears?
The advantages of the curved tooth spiral bevel gears over the straight ones are in
general the same as those of helical gears over spur gears, namely lesser noise, greater
contact ratio, gradual engagement of the mating teeth, greater load carrying capacity (15
to 25%), lesser vibrations, etc.
38. What are the advantages of hypoid gears over bevel gears?
The advantages of hypoid gears are comparatively smoother action and possibility of
extending the shafts past each other. So the bearings can be used on both sides of the gear
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 18
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
and the pinion. This makes the drive more rigid and hence higher power can be transmitted
than bevel gears.
39. Differentiate between spiral bevel gears and hypoid gears.
The spiral and hypoid gears are similar and the most important difference being that the
pinion axis of hypoid gear set is offset above or below the gear axis.
40. What is the difference between angular gears and miter gears?
The bevel gears with shaft angle of 90 are miter gears and the bevel gears with any
other shaft angles are termed as angular bevel gears.
41. Define the following terms for bevel gears. a)Pitch angle b)Face angle.
Pitch angle
: It is the angle made by the pitch line with the axis of the shaft.
Face angle
: It is the angle subtended by the face of the tooth at the cone centre.
Face angle = Pitch angle + addendum angle.
42. Why is bevel gear design based on cone distance?
In bevel gears, teeth are tapered in height and thickness and the face of the tooth
converges at an apex point. Since the teeth are cut on pitch surfaces of their conical blank,
so the design of bevel gears are based on cone distance instead of centre distance as in spur
and helical gears.
43. State the approximation suggested for finding the radius of equivalent spur gear of any bevel
gear.
The equivalent spur gear of a straight tooth bevel gear is obtained by developing the
tooth form along a back cone. The back cone is considered as the radius of equivalent spur
gear at the mean face width on the pitch cone.
44. What are the factors decide the direction of axial thrust acting on a spiral bevel gear ?
The direction of thrust in a spiral bevel gear is dependent on three factors.
a) Hand of the spiral.
b) Direction of rotation and
c) Whether the gear is a driver or a driven member.
45. When do you prefer worm and worm wheel drive?
We can prefer the worm and worm wheel drive in following circumstances.
a) In large reduction in velocity ratio is required.
b) Self locking speciality is required.
c) To connect non - intersecting perpendicular shafts.
46. What are the factors controlling the efficiency of the worm drive ?
The factors controlling the efficiency of the worm drive are lead angle, number of
starts in worm, surface finish, type and amount of lubrication and type of design of the
system. The efficiency of the worm gearing also depends on the material of the worm and
worm wheel and the rubbing velocity.
47. What are the losses of power in worm gear drive?
The losses in worm gear drive are friction loss and oil churning loss.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 19
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
48. What are the different criteria of deciding power to be transmitted by the worm gearing?
The power transmitting capacity of worm gearing is decided by the strength, the ability
to resist wear and abrasion and the heat dissipating capacity of the drive.
49. Define the term axial pitch and normal pitch in worm gearing.
Axial pitch is the distance between a point on a worm thread and corresponding point
on the adjacent thread measured parallel to the axis of the worm.
Normal pitch is the distance between a point on a worm thread and corresponding point
on the adjacent thread measured perpendicular to helix.
50. What are the types of worms?
Worms are of three types, namely,
a) Cylindrical or straight worm
b) Single enveloping worm and
c) Double enveloping worm.
51. Why is dynamic loading is rarely considered in worm gear drives ?
Because of sliding action between the worm and the worm gear teeth, the dynamic
forces are not so severe as in the regular forms of worm gearing. So the dynamic loading is
rarely considered in worm gear drives.
52. Why equivalent number of teeth has to be used in helical gear design ?
The bending stress in helical gear cannot be readily determined like spur gear because
of curvilinear position of teeth and inclined nature of line of contact. So helical gears are
considered as spur gears having module Mn (normal module) and equivalent number of
teeth Zv.
53. What is the effect of helix angle on performance of helical gears?
In helical gearing, the axial thrust load varies directly with tan b, there is an upper limit
to the magnitude of helix angle b, in order to prevent excessive thrust loads. A lower
limit is also necessary to have smooth transfer of the load.
54. Differentiate between normal pitch and axial pitch in helical gears.
The axial pitch is the distance parallel to axis between similar faces of adjacent teeth,
whereas normal pitch is the distance between similar faces of adjacent teeth along a helix
on the pitch cylinders normal to the teeth.
55. What are the types of bevel gears?
The types of bevel gears are, a) Mitre gears b) Angular bevel gears c) Crown gears.
56. Explain mitre gear.
When bevel gears of the same size are used on intersecting shafts at right angle, they
are called mitre gears. These gears are used for power transmission at right angle without
any change in speed.
57. What is angular bevel gear?
When bevel gears are mounted in intersecting shafts making an angle other than 90,
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 20
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
they are called angular bevel gears.
58. Define crown gear.
When the pitch angle of a bevel gear is 90 , then it is called as crown gear.
UNIT IV DESIGN OF GEAR BOXES
1. What are the principles to be followed to obtain optimum design in multi speed gear box ?
To avoid excessively large diameter of the wheel and also to limit the pitch line
velocity of the gear, the following principles are considered.
a) Number of gears on the last shaft (spindle) should be minimum.
b) Number of gears on the shaft should not be more than 3, though in exceptional it
may be 4.
c) It is preferable to have nmax > ninput > nmin in all stages except in the first stage.
2. What is dipping or splashing in speed reducer?
In low power and low speed reduction units, the gears are lubricated in an oil path by
dipping or splashing. For this purpose, one of the mating gears or a ring is partly immersed
in the oil contained in the reduction unit housing. In powerful and high speed reduction
units, oil is pressure fed to the meshing gears using a pump.
3. What is speed reducer?
Speed reducer is a gear mechanism with a constant speed ratio, contained in a
separate casing and intended to reduce the angular speed of the output shaft as compared
with that of input shaft.
4. Write the classification of speed reducer .
The speed reducer are classified into,
a) Type of drive : Spur helical, bevel, worm gears.
b) Number of stages : Single stage, double stage
c) Arrangement of shafts : Horizontal, vertical, parallel, co-axial, intersecting.
5. What are the spacers as applied to a gear box?
Spacers are sleeve like parts used to maintain the distance between the gears and the
bearing.
6. What does the ray diagram of gear box indicate?
The ray diagram (and) speed diagram or structural diagram indicates the speed of
driving shaft, driven shaft and intermittent shaft and the gear ratios of various gear sets.
7. What are the main components of gear box ?
The main components of gear box are,
a) Shaft for mounting gear.
b) Bearing for supporting the shafts.
c) Proper housing to support the bearing, to hold lubricants to protect the unit from dirt
and dust.
d) Spacers
e) Oil seals.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 21
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
8. What are the possible arrangements to achieve 12 speeds from a gear box ?
The possible arrangements to achieve 12 speeds from a gear box are,
1 2 2 3 , 1 2 3 2 , 1 3 2 2.
9. What is mean by tooth system?
A tooth system is a standard which specifies the relationships involving addendum,
working depth, tooth thickness and pressure angle.
10. Define backlash.
The backlash is the amount by which the width of a tooth space exceeds the thickness
of the engaging tooth measured on the pitch circles.
11. What is step ratio?
The ratio between the adjacent speeds in a multi speed gear box is called step ratio.
12. Why are the steps of speed arranged in the geometric progression in a machine tool gear
box?
The steps of speeds of a gear box of machine tools are arranged in geometric
progression because it provides,
a) Constant loss economic cutting speed in whole rpm range
b) Constant loss of productivity in the whole rpm range.
c) Better design feature.
d) Compact design, etc.
13. What is a ray diagram?
Ray diagram (speed diagram) is a graphical representation of speed ratios between
adjacent shafts from input shaft to output shaft. The ray diagram shows at a glance the
kinematics arrangement, shaft speeds at different stages and torque at various speeds. The
ray diagram also gives information about number of shafts, number of gears, speed ratio
and combination of gears in engagement.
14. What are the methods of lubrication in the speed reducer?
The methods of lubrication in the speed reducer are,
a) Splash lubrication : Low power and low speed reduction units.
b) Pressure - fed oil lubrication : Powerful and high speed reduction units.
15. What is a gear box ?
A gear box is a device employed for stepped regulation of the input speed and to give
required output speed or speeds. It consists of gears, shafts, levers, keys, bearings etc., are
assembled in a housing.
16. What is the use of gear box in a machine tool?
The gear box is used in a machine tool to get,
a) Required torque and speed.
b) Multi speed in more number of steps.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 22
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
c) Change in the direction of rotation.
17. Give the applications of the speed reducer.
The speed reducers are used in turbine generators, between motor and machine tools,
in rolling mills, between engine and road wheels in automobiles and in many
industrial processing like cement factories, paper - plants, chemical industries, etc.
18. What is geometric progression ratio in a gear transmission ?
If the speed steps in a gear box are arranged in a manner to have the ratio at adjacent
speeds in constant, then the progression ratio (step ratio) is called geometric progression ratio
(pi ).
i.e.,
N2 = N1 pi and
where, N1 - First step rpm
N2, N3 - Adjacent rpm
N3 = N2 pi
Pi - Geometric progression ratio.
19. Distinguish between structural diagram and ray (speed) diagram.
The structural diagram show the general arrangement of the gear transmission but ray
diagram gives the gear arrangement for the required output speed.
20. What are the various components required for the automobile speed reducers?
Cashing shafts, lay shaft, splined shaft, bearings, gears keys, spacers are the various
components required for the automobile speed reducers.
21. Explain the term 'progression ratio' referring to the gear box.
To provide required cutting and feed rate in machine tools, consider the speeds in
geometric series.
Let, Nmin = Minimum speed
Nmax
Maximum speed
Z = Number of speeds required
Then, [N max/Nmin] =pi(z 1)
where,
pi- Step ratio or progression ratio.
The standard progression ratios are available according to preferred series.
22. Write the structural formula for gear box design.
The structural formula for gear box design is given by,
Z
=
P1(X1) P2(X2) P3(X3) P4(X4)
where, X1 =
V4 =
1, X2 = P1, X3 = P1P2
D1 D2 D3
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 23
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
23. Give some examples for speed raisers.
Some examples for speed raisers are automobile gear box, machine tool gear box, blower
and radial compressor.
24. What is the formula for % deviation?
The formula for % deviation is given by,
nobt nc
100
% Deviation =
nc
where,
nobt Obtainable speed rpm
nc
Calculated speed rpm
25. Classify speed reducers.
Speed reducers are classified as follows.
a) Number of reductions
b) Arrangement of shafts
c) Types of gears
d) Gear train a rrangement
e) Geared motor speed reducer f) Variable (multi speed) speed reducers.
26. What are the steps of speeds arranged in geometric progression in a machine tool gear
box?
The steps of speeds arranged in geometric progression in a machine tool gear box are,
a) Constant loss of economic cutting speed in whole rpm range.
b) Constant loss of productivity in the whole rpm range.
c) Better design feature.
d) Compact design, etc.
27. Why is geometric progression suited for better design of a gear box?
When we use geometric progression for speed steps, all the rpm values are obtained by
single transmission i.e, by changing gears between two shafts. A particular step of speed is
obtained by engaging different pair of gears between shafts by shifting the levers, keys or
clutches. This gives easy, convenient and economically feasible speed changing. The above
design is possible only if the rpm values lie in a geometric progression.
28. What is type of gear box using arithmetic progression for adjacent speed ratio?
The arithmetic progression of speed ratio is used in feed box of a screw cutting lathes,
because standard thread pitches are formed with arithmetic progression.
29. What are the minimum informations required to design a stepped gear box?
The minimum informations required to design a stepped gear box are,
a) The highest output rpm (N max).
b) The lowest output rpm (Nmin).
c) The number of steps (Z) between Nmin and Nmax.
d) The number of stages in which Z speed steps to be achieved.
e) The input speed or speeds.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 24
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
30. What are the informations given by a structural diagram?
The informations given by a structural diagram are,
a) Number of shafts in a gear box.
b) Number of gears in a shaft.
c) The order of changing transmission in individual groups to get a desired speed.
d) Transmission range and characteristics of each transmission group.
31. How is the best structural diagram selected?
By considering the following factors,
a) Transmission ratio restriction ig < 8.
b) Minimum total shaft size.
c) The number of gears in the last shaft should be minimum.
d) Speed reduction should be maximum possible in the last stage.
e) Number of gears on a shaft should not more than 3, in exceptional case it may be 4.
32. What are the general requirements for a gear transmission to perform properly?
The general requirements for a gear transmission to perform properly are,
a) The number of teeth on smallest gear should be such that there is no undercutting. (i.e.,
Zmin 17 for 20 FDI).
b) If gear pairs on parallel shaft have same module, then sum of the number of teeth on
mating gear pairs must be same.
c) The spacing between adjacent gears on a shaft should be such that one gear pair gets
completely disengaged before the next begins to engage.
d) The number of teeth of adjacent gear must differ by at least four.
33. How can the size of gear box be reduced?
The radial dimensions can be reduced by making coincidence of the axes of shaft of
adjacent group. Also maintaining (imax/imin) = 1 helps to reduce radial dimensions. Axial
dimensions are generally reduced by arranging single transmissions between groups and by
using link gears.
34. What are link gears in a gear box?
The gears which act as driving members in one transmission group and driven members
in another transmission group in a gear box is called link gears. These link gears are used to
reduce the axial dimensions of the gear box.
35. What is the characteristic of a transmission group?
The characteristic of a transmission group denotes the number of steps of the spindle
rpm in a geometric progression ratio, by which the two adjacent rpm values of the particular
transmission group are separated.
36. What are the necessities to limit the transmission ratio?
The necessities to limit the transmission ratio are,
a) Space limitations
b) Number of teeth on gear and
c) Pitch line velocity.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 25
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
37. What is composite layout of a gear box?
A gear box size can be reduced by using composite gearing. A drive with only one gear
which has a dual function of being driven as well as the driver is called single composite
gearing, whereas a drive with two dual function gears is called double composite gearing.
38. What are the steps involved in a gear box design?
The steps involved in a gear box design are,
a) Design of gears for the power to be transmitted and the velocity ratio.
b) Design of shafts.
c) Selection of rolling contact bearings or design of sliding bearings.
d) Design of casing with all details.
e) Providing bearing covers and seals.
39. What are the reasons for power loss in a gear box?
The reasons for power loss in a gear box are, a) Friction in teeth engagement. b)
Friction in bearings. c) Splashing of oil lubricant.
40. What are the main components of a gear box?
The gear box consists of casing, shafts, bearings, gears, keys, spacers, levers, oil level
indicator, heat dissipating fins, etc.
41. What are purposes served by the housing in a gear box?
The housing for a gear box serves the following purposes.
a) They are act as a reservoir for lubricant give necessary cooling.
b) Surface to dissipate heat provide necessary support to the shafts.
c) Protect the gears from dust, moisture, etc.
UNIT V DESIGN OF CAM CLUTCHES AND BRAKES
1. What is meant by positive clutch?
A clutch which transmits power from driving shaft to the driven shaft by means of
jaws or teeth is called positive clutch. Jaw clutches are superior to friction clutches in
that they ensure exact contact (without slipping),produce equality in angular velocities of
the connected shafts.
2. Why cone clutches better than disc clutches?
Since cone discs are having large frictional areas and wedging action, they can
transmit a larger torque than disc clutches with the same outside diameter and
actuating force and hence cone clutches are preferred to disc clutches. But usually
cone clutches are mainly used in low peripheral speed applications.
3. Give the essential three elements in internal shoe rim clutch.
It consists essentially of three elements.
a) The mating frictional surface.
b) The means of transmitting the torque to and from the surface.
c) The actuating mechanism.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 26
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
4. How clutches are classified?
Clutches are classified into,
a) Expanding ring b) Centrifugal
d) Hydraulic
e) Pneumatic.
c)Magnetic
5. Define expanding ring clutch.
The expanding ring clutch is often used in textile machinery, escalators, and machine
tools where the clutch may be located within the driving pulley. Expanding ring clutches
benefit from centrifugal effects. Transmit high torque, even at low speed, and require both
positive engagements and sample release force.
6. Define centrifugal clutch.
The centrifugal clutch is used mostly for automatic operation. If no spring is used the
torque transmitted is proportional to the square of the speed. This is particularly useful for
electric motor drives where during starting the driven machine comes up to speed without
shock.
7. What is the function of friction clutch?
The flow of mechanical power is controlled by means of clutch. The clutch is a
mechanical device which is used to connect or disconnect the source of power from the
remaining parts of power transmission system at the will of the operator.
8. What are the different characteristics of clutch?
The different characteristics of clutch are,
a) They do not slip.
b) No heat is generated.
c) They cannot be engaged at high speeds.
d) Sometimes they cannot be engaged when both shafts are at rest.
e) Engagement at any speed is accompanied by shock.
9. Classify clutches based on the coupling methods. (Nov. 2004)
Based on the coupling methods, clutches are classified as follows.
a) Positive b) Over running c) Friction d) Magnetic e) Fluid coupling.
10. What is the difference between a coupling and a clutch?
Clutch is coupling that permits the smooth connection and disconnection of two shafts
during rotation at the operators will. Coupling is rigid connection between two shafts for
power transmission.
11. Distingush between wet and dry operation of clutches.
Dry clutch : Friction and torque capacity are high, but heat dissipation is more difficult.
Wet clutch : To dissipate
the heat, a lubricant
is provided. This reduces the torque
carrying capacity.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 27
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
12. Name four materials used for lining of friction surfaces in clutches.
The four materials used for lining of friction surfaces in clutches are,
a) Organic materials like leather, wood, cork or felt in conjunction with cast iron, steel
or brass.
b) Metals like nodular iron, stainless steel and aluminium.
c) Materials like asbestos, moulded or woven with metal chips of brass or copper.
13. Define brakes.
A brake is defined as a mechnical device which is used to absorb the energy possessed by
a moving system or mechanism by means of friction. The primary purpose of the brake is to
slow down or completely stop the motion of a moving system, such as a rotating drum,
machine or vechile.
14. List out five important characteristics of the brake lining.
The five important characteristics of the brake lining are,
a) High coefficient of friction.
b) Low wear rate.
c) High heat resistance, high heat dissipation capacity. d) Adequate mechanical strength.
15. What are the materials used for brake lining?
Cast iron on cast iron, bronze on cast iron, steel on cast iron, wood on cast iron are the
materials used for brake lining.
16. List the classification of the mechanical brake.
The mechanical brakes are classified as follows.
a) Block brake b) Internal / external shoe brake c) Disc brake d) Band brake.
17. Define braking torque.
The braking torque depends upon the amount of energy, absorbed by the brake. That
is a mechanical system of mass m moving with a velocity v1 is allowed down to velocity
v2 during the period of braking.
18. Define internal expanding brake.
It consists of a shoe which is pivoted at one end and subjected to an acting force p at the
other end. A friction lining is fixed on the shoe and the complete assembly of shoe lining
and pivot is placed inside the brake drum.
19. What is fade?
The coefficient of friction gradually rises,reaches a peak value and falls rapidly as
drum temperature is increased.This rapid fall is known as fade.
20. Explain the desirable properties of friction material used for the lining of brake shoes.
Desirable properties of friction material,
a) Should have high coefficient of friction.
b) Should retain braking capacity at temperature up to 300C.
c) Should have high heat conductivity.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 28
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
21. Why in automobiles, braking action when traveling in reverse is not as effective as when
moving forward?
If the movement due to friction force aids the application of brake, the brake is known
as self-energizing. If the direction of rotation of the drum is reversed, friction force would
oppose the application of brake. Thats why braking action when travelling in reverse is not
as effective as moving forward.
22. Why should the temperature rise be kept within the permissible range in brakes? (Apr.
2004) or Define thermal considerations of a brake.
The energy absorbed by the brake is converted into heat,which increases the
temperature at the rubbing surfaces. When the temperature increases, the coefficient of
friction decreases, adversely affecting the torque capacity of the brake. So the temperature
rise should be kept within the permissible range in brakes.
23. Define cone clutches.
A cone clutch consists of inner and outer conical working surfaces. The outer cone is
keyed to the driving shaft, while the inner cone is free to slide axially on the driven shaft
due to splines.
24. What are the desirable properties of friction material to be used for clutches?
The desirable properties of friction material to be used for clutches are,
a) A high and uniform coefficient of friction .
b) The ability to withstand high temperatures, together with good heat conductivity.
c) God resiliency.
d) High resistance to wear, scoring and galling.
e) Resistance against environmental conditions,such as moisture, salt water and fungi.
f) Adequate mechanical and thermal strengths.
25. What is meant by a self - energizing brake?
When the moment of applied force (F . l) and the moment of the frictional force (RN.C)
are in the same direction, the frictional force helps in applying the brake. This type of brakes
is known as a self-energizing brake.
26. What is a cam?
Cam is a mechanical member having miscellaneous contour surface which transmit a
desired motion to a follower by direct contact. With help of cam, it is very easy, accurate
and efficient to produce a motion with required velocity and acceleration.
27. Why are cam mechanisms preferred?
The cam mechanisms are preferred over other types because the use of cam makes it
possible to obtain an unlimited variety of motions and the cams perform satisfactorily year
after year. The mechanical movements from cams are not readily obtained by other types of
mechanisms.
28. Define the following terms of a cam :
a) Trace point : This is a reference point on the follower which is used in laying out
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 29
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
the theoretical curve or pitch curve of the cam.
b) Stroke : This is the maximum movement of the follower away from the cam shaft from
its initial position. This also known rise or lift or threw of the cam.
29. Define the following :
Pitch point: It is the point on the cam pitch curve having the highest pressure angle.
Jerk or Pulse: The instantaneous time rate of change of acceleration is called as jerk or pulse
(i.e., sudden change in follower acceleration).
30. What are the fundamental laws of a cam design?
Any cam design for operation at other than very low speed must be designed with
following considerations :
a) The cam function must continuous through the first and second derivatives of
displacement across the entire interval of 360.
b) The jerk function must be finite across the entire interval of 360 (i.e., the displacement,
velocity and acceleration functions must have no discontinuity in them).
31. What is meant by plate cam and cylindrical cam? Plate cams
Cams are in the form of plates with its edges having desired contour.
Cylindrical cams:
Cams are cylindrical in shape having a groove cut along the cylindrical surface to direct
the movement of the follower.
32. What is meant by displacement diagram?
Displacement diagram is a graphical representation of series follower displacement
during rotation of the cam through one cycle of input motion. In such diagram, the abscissa
represents one cycle of input motion (one revolution) and the ordinate represents the
follower travel.
33. Compare flat, knife and roller follower.
Knife - edge follower is subjected to excessive wear due to sliding motion. If the load
on the follower is small, this follower can be used. The roller follower has rolling contact,so
wear is less. The roller and knife - edge follower guides are subjected to side thrust. The flat faced follower has no side thrust.
34. What are the parameters influence the cam size?
The cam size depends upon,
a) Pressure angle
b) Curvature of the cam profile and
c) Diameter of the cam shaft. For same pressure angle, the cam size depends on the type of
follower motion.
35. What are the commonly used cam - follower motions?
The commonly used cam - follower motions are,
a) Constant velocity motion
b) Simple harmonic motion c)Double harmonic motion d)
Parabolic motion
e) Cycloidal motion
f) Cubic curve motion, etc.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 30
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
36. Why is the uniform velocity follower motion not suitable for high speed cams?
In a high speed cam mechanism, the uniform velocity follower motion generates
undesirable forces and vibrations. So it is not suitable for high speed cams.
37. What is the advantage of having parabolic motion for follower over harmonic motion?
Parabolic motion for follower is advantageous over simple harmonic motion because at
high speeds, the SHM has vibratory disturbances at the beginning and end of the stroke due
to sudden inertia forces.
38. Which type of follower motion is best and why?
The cycloidal motion of the follower provides the best possible follower motion for high
speed operations. Because the acceleration curve is a sine curve and it became adrupt only if
the curve is adjacent to dwell period. Even the adruptness is not so severe compared to
other types of motion.
39. What is pressure angle of a cam?
It is the angle between normal to cam profile and line of action of cam follower at the
point of contact. The pressure angle represents the steepness of the cam profile. The
pressure angle is limited to 30 for smooth cam follower action.
40. What is the importance of pressure angle in cam design?
The size of the angle is important because,
a) Increasing pressure angle increases the side thrust and this increase the forces exerted on
cam and follower.
b) If the pressure angle is too large, jamming of follower takes place.
c) Reducing the pressure angle increase the cam size.
41. What is the maximum limit of pressure angle?
In general, the maximum pressure angle should be 30 or less for a translating roller
follower and 45 or less for a oscillating roller follower.
42. What are the main factors influencing cam forces?
The main factors influencing cam factors are displacement of follower, cam speed,
dynamic forces due to backlash and flexibility, linkage dimensions, pressure angle,
frictional forces and spring forces.
43. What are the types of failures in cams?
Cam often fail due to wear or surface fatigue action. Due to rolling and sliding or
combination of both the wear and fatigue failure occur in cams.
44. How can surface stresses be reduced by redesign of cam?
The surface stresses can be reduced through redesign of cam by,
a) Increasing the cam size.
b) Changing to an offset or swinging follower.
c) Reducing the cam speed.
d) Increasing the cam rise angle.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 31
Theni Kammavar Sangam College of Technology
e) Increasing the thickness of the cam.
g) Using more suitable cam curve or modifying the curve at critical points.
45. What are the parameters required to design a plate cam?
To design a plate cam with reciprocating follower, the geometric parameters required are,
a) Prime circle radious
b) Minimum width of the follower face and
c) Offset of the follower face.
46. When does the interference occur in cams?
The interference is occured in cams when the radius of roller is too large or when the
cam profile is too sharp. Interference usually occurs in cams fitted with flat followers.
47. What is the influence of profile errors in cam operation?
During cam manufacturing several surface imperfections may occur, such as profile
errors, waviness and roughness. These surface irregularities may induce shock, noise, wear
and vibrations to the cam and follower systems.
48. Define pitch curve of a cam.
The pitch curve of a cam is the locus generated by trace points as the follower moves
relative to the cam. For a knife edge follower the pitch curve and the cam profile are same.
For a roller follower cam they are separated by the radius of roller.
49. What is a clutch and why it is necessary?
A clutch is a machine used to connect a driving member with drive member. The
clutch is required for the following.
a) To connect and disconnect at with, without stopping
b) To avoid overloading of the driving member.
50. What are the different friction linings used in the clutches?
The following friction linings are commonly used in clutches.
a) Woven
b) Asbestos lining
c) Moulded asbestos pads, sintered metal pads, etc.
51. How the power is transmitted by clutches?
In clutches, power transmission is achieved through interlocking, friction and
wedging.
52. Differentiate clutches with flange couplings.
Flange couplings are used as permanent connecting elements, whereas clutches are used
as temporary connecting elements and hence periodical engagement is possible in clutch
connection.
Flange couplings are having less number of parts such as flanges, bolts, keys etc., whereas
the clutches consists comparatively of large number of
parts such as friction discs,
springs, bolts, keys, supporting plates and so on.
53. What factors should be considered when designing friction clutches?
The factors are,
a) The friction materials for the clutch should have high coefficient of friction and they
should not be affected by moisture and oil.
b) It may be light weight.
VI Sem/Mech/ME2352 Design of Transmission Systems
Page 32
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Renk Bearings RangeDocument2 paginiRenk Bearings Rangehumayun121Încă nu există evaluări
- Renk PBLZ enDocument7 paginiRenk PBLZ enhumayun121Încă nu există evaluări
- Renk Curved Tooth Couplings Basic Construction Series enDocument52 paginiRenk Curved Tooth Couplings Basic Construction Series enhumayun121Încă nu există evaluări
- Spec Sheet MTU 16V4000 DS2250 FC PDFDocument6 paginiSpec Sheet MTU 16V4000 DS2250 FC PDFMarison SaragihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Contact Bearings - DMEDocument28 paginiRolling Contact Bearings - DMESumitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dmu 60 / 80 / 100 Monoblock Classic Series: CNC Universal Milling MachinesDocument24 paginiDmu 60 / 80 / 100 Monoblock Classic Series: CNC Universal Milling MachinesButch BorjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987De la EverandProceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987W. R. TysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- TNK60DG Taneko Gas Generator (TNK JKT)Document2 paginiTNK60DG Taneko Gas Generator (TNK JKT)hareudangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spur Gear Design 1Document16 paginiSpur Gear Design 1Nagu SriramaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renk Etax TechonologyDocument6 paginiRenk Etax Techonologyhumayun121Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of Transmission Systems Question BankDocument10 paginiDesign of Transmission Systems Question BankDesejo SozinandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransmissionDocument24 paginiTransmissionRoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vol69 Num620 Super Abrasive Grinding Process Improvements Via Power MonitoringDocument5 paginiVol69 Num620 Super Abrasive Grinding Process Improvements Via Power MonitoringSaravana kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shaft LayoutDocument21 paginiShaft LayoutAmmar SafwtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox For All-Terrain VehicleDocument10 paginiDesign and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox For All-Terrain VehicleIJRASETPublications100% (1)
- Alwasy Step Ahead in TechnologyDocument6 paginiAlwasy Step Ahead in TechnologyDxFx100% (1)
- Galaxy Midas 0Document2 paginiGalaxy Midas 0suresh0% (1)
- Curved Tooth Couplings Disengageable at StandstillDocument8 paginiCurved Tooth Couplings Disengageable at Standstillmartensita24Încă nu există evaluări
- Haacon 4202+4585 Gebruiksaanwijzing enDocument6 paginiHaacon 4202+4585 Gebruiksaanwijzing enBasvanLeeuwen100% (2)
- Technical Data: BCMU 700S-60 BCMU 650P-60Document3 paginiTechnical Data: BCMU 700S-60 BCMU 650P-60Jun AballeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design II MDE 221 Mott CH 8 and CH 9 Spur GearsDocument42 paginiDesign II MDE 221 Mott CH 8 and CH 9 Spur GearsThieroy PelendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manuscript Tesfaye.GDocument17 paginiManuscript Tesfaye.Gtesfaye gurmesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designof Power Driven Dough Mixing MachineDocument5 paginiDesignof Power Driven Dough Mixing MachineTewodros B.Încă nu există evaluări
- Helicoil Catalog - hc2000 Rev.5Document36 paginiHelicoil Catalog - hc2000 Rev.5Hugo CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drill Press Function and OperationDocument2 paginiDrill Press Function and OperationJeremiah NayosanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DE12TISDocument2 paginiDE12TISRowan CorneliusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vpower / Mtu Series 1500RPM / 50HZ / 400V Vpower / Mtu Series 1500RPM / 50HZ / 400VDocument2 paginiVpower / Mtu Series 1500RPM / 50HZ / 400V Vpower / Mtu Series 1500RPM / 50HZ / 400Vchock channel 19Încă nu există evaluări
- U 4 Surface Finishing Process PDFDocument37 paginiU 4 Surface Finishing Process PDFSubhadip MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Lead Correction For High-Speed Gears: Sinto America, IncDocument92 paginiThermal Lead Correction For High-Speed Gears: Sinto America, IncRongbaaz BongÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTU Gendrive Spec 12V16V18V2000Gx5 3D 3E W2ADocument3 paginiMTU Gendrive Spec 12V16V18V2000Gx5 3D 3E W2Atinhotrading .jinchaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTU Thesis FormatDocument23 paginiMTU Thesis FormatHla Min Htun100% (1)
- Bearing Wear Monitoring SystemDocument16 paginiBearing Wear Monitoring Systempapaki2Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Series - Gear CouplingsDocument13 paginiBasic Series - Gear CouplingsfrarainsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATENT - Axial Flux Motor AssemblyDocument13 paginiPATENT - Axial Flux Motor Assemblyrakeshee2007Încă nu există evaluări
- P158LEDocument4 paginiP158LEjackacak100% (1)
- Gear MotorDocument45 paginiGear Motorb3ltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTU 12V1600 DS660 400-230V 600 kVA Prime Power Diesel GeneratorDocument5 paginiMTU 12V1600 DS660 400-230V 600 kVA Prime Power Diesel GeneratordinukaeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fit Selection BasicDocument1 paginăFit Selection Basicapi-3848892100% (2)
- Milling and Turning OperationsDocument17 paginiMilling and Turning OperationsMuhammad ArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Tribological & Statistical Investigation of PTFE, Tin Bronze and White MetalDocument9 paginiA Study On Tribological & Statistical Investigation of PTFE, Tin Bronze and White MetalIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worms & Worm Gears: Gear DrivesDocument11 paginiWorms & Worm Gears: Gear DrivesNeil RubsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Skiving PDFDocument11 paginiPower Skiving PDFmadhavikÎncă nu există evaluări
- SKF Filament Wound BushingsDocument8 paginiSKF Filament Wound BushingsWes VendrigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduce Engine Noise with Engine Exhaust SilencersDocument28 paginiReduce Engine Noise with Engine Exhaust SilencersMaarij AnjumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Force Analysis ProblemsDocument8 paginiDynamic Force Analysis Problemsa c s KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Turbine Blade CoatingsDocument1 paginăGas Turbine Blade CoatingsshamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass Moment of Inertia Formulas PDFDocument2 paginiMass Moment of Inertia Formulas PDFAsrar AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dse8610 Data Sheet UsDocument2 paginiDse8610 Data Sheet UsAlfonso TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Junttan PMx27 DatasheetDocument4 paginiJunttan PMx27 DatasheetIkhsan SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTU Series 2000 Mining Engines 12V2000Cx6 3235061 1505796670Document2 paginiMTU Series 2000 Mining Engines 12V2000Cx6 3235061 1505796670jamal molana100% (1)
- RENK Range of CouplingsDocument2 paginiRENK Range of CouplingssurawutwijarnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ansi Asabe D497-4-2003Document9 paginiAnsi Asabe D497-4-2003Stephan100% (2)
- Roller Screw BasicsDocument3 paginiRoller Screw BasicskiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument29 paginiRolling Contact BearingBimlendra RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Structural Analysis of Spur Gear Using Various MaterialsDocument15 paginiDesign and Structural Analysis of Spur Gear Using Various MaterialsprajeeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me8651 QBDocument27 paginiMe8651 QBselvam cÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME6601-Design of Transmission Systems PDFDocument27 paginiME6601-Design of Transmission Systems PDFJeevitha RÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME6601Document28 paginiME6601Sridiwakaran ParameswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Velammal Engineering College Machine Elements Design DocumentDocument18 paginiVelammal Engineering College Machine Elements Design DocumentSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Transmission Systems (ME61) Two MarksDocument14 paginiDesign of Transmission Systems (ME61) Two Marksgpskumar22Încă nu există evaluări
- HMT UNIVERSITY QUESTIONS ME6502 R13 - Unit Wise PDFDocument9 paginiHMT UNIVERSITY QUESTIONS ME6502 R13 - Unit Wise PDFkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- MT II Part A AU Questions Part-A PDFDocument7 paginiMT II Part A AU Questions Part-A PDFkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 3.01 AcknowledgementDocument1 pagină3.01 Acknowledgementkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review Alemayehu Gashaw and Amanu Lakachew (2) (2014) The General MethodDocument2 paginiLiterature Review Alemayehu Gashaw and Amanu Lakachew (2) (2014) The General Methodkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 10.processing and TestingDocument4 pagini10.processing and Testingkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 11.performance Test & ResultsDocument1 pagină11.performance Test & Resultskannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Bonafide Certificate CI Engine Performance EmissionDocument1 paginăAnna University Bonafide Certificate CI Engine Performance Emissionkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- MT II Part A AU Questions Part-A PDFDocument7 paginiMT II Part A AU Questions Part-A PDFkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- SAIC Boiler Efficiency ProjectsDocument51 paginiSAIC Boiler Efficiency Projectsyashpal singh bhadoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 ConclusionDocument1 pagină14 Conclusionkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 16 PublicationDocument1 pagină16 Publicationkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- Performance and Emission Characteristics of Ci: A Project ReportDocument1 paginăPerformance and Emission Characteristics of Ci: A Project Reportkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 7.problem BackgroundDocument1 pagină7.problem Backgroundkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 4.table of ContentsDocument5 pagini4.table of Contentskannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 8.problem DescriptionDocument1 pagină8.problem Descriptionkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 15 ReferencesDocument2 pagini15 Referenceskannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 9 MaterialsDocument5 pagini9 Materialskannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 IntroductionDocument5 pagini5 Introductionkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 3.02 AbstractDocument1 pagină3.02 Abstractkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- Performance and Emission Characteristics of Ci: A Project ReportDocument1 paginăPerformance and Emission Characteristics of Ci: A Project Reportkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 8.problem DescriptionDocument1 pagină8.problem Descriptionkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 10.processing and TestingDocument4 pagini10.processing and Testingkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 16 PublicationDocument1 pagină16 Publicationkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 15 ReferencesDocument2 pagini15 Referenceskannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- 3.01 AcknowledgementDocument1 pagină3.01 Acknowledgementkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- ME6505-Dynamics of MachinesDocument17 paginiME6505-Dynamics of Machinesraja30gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Report FormatDocument7 paginiAnna University Report Formatdilip_66690% (10)
- 4.table of ContentsDocument5 pagini4.table of Contentskannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review Alemayehu Gashaw and Amanu Lakachew (2) (2014) The General MethodDocument2 paginiLiterature Review Alemayehu Gashaw and Amanu Lakachew (2) (2014) The General Methodkannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- Mohrs Circle For Plane Stress - Engineers EdgeDocument2 paginiMohrs Circle For Plane Stress - Engineers Edgekannanviknesh086319Încă nu există evaluări
- MSDS VR-514 SDS 20201110Document6 paginiMSDS VR-514 SDS 20201110dennisjuntakÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Concrete Producer Article PDF - Comparing The Options For Cooling ConcreteDocument4 paginiThe Concrete Producer Article PDF - Comparing The Options For Cooling Concretearangar1100% (1)
- M2P12 JacsDocument10 paginiM2P12 JacspedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSRR 6011Document14 paginiMSRR 6011pradellesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 9 Matter in Our Surroundings McqsDocument3 paginiClass 9 Matter in Our Surroundings McqsHariharan VIIA1Încă nu există evaluări
- E53-07 (Reapproved 2013) PDFDocument4 paginiE53-07 (Reapproved 2013) PDFearth metallurgical services pvt.ltd.Încă nu există evaluări
- Ssi Schaefer Container AsDocument8 paginiSsi Schaefer Container AsRebecca HartmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nhat Huy FillerDocument7 paginiNhat Huy FillerLê NhungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toksikologi PDFDocument134 paginiToksikologi PDFPurwani Ni NyomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HDA Simulation Laboratory - 054330Document18 paginiHDA Simulation Laboratory - 054330Fussy Taksn100% (1)
- Item Codes for Pokémon Items & ModifiersDocument13 paginiItem Codes for Pokémon Items & ModifiersIsaccÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narrative Report For Environmental Protection Awareness ProgramDocument3 paginiNarrative Report For Environmental Protection Awareness ProgramFam ValerianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Systems ReviewDocument2 paginiProcess Systems ReviewjokishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal DetectorDocument7 paginiMetal DetectorAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- METAL FABRICATION RAW MATERIALS GUIDEDocument8 paginiMETAL FABRICATION RAW MATERIALS GUIDEEdbert TulipasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5054 w14 QP 11 PDFDocument20 pagini5054 w14 QP 11 PDFHaroon GhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipes, Tubes, Fittings, FlangesDocument121 paginiPipes, Tubes, Fittings, FlangesCarl Jones100% (2)
- Bosch GST 75 E ProfessionalDocument167 paginiBosch GST 75 E ProfessionalAdriana AlvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BC34.1 E9 Determination of Acid Value of FatsDocument3 paginiBC34.1 E9 Determination of Acid Value of FatsGlenn Vincent Tumimbang96% (26)
- BoilerDocument48 paginiBoilerAbdallah Mansour100% (2)
- Safely Purging Air from Pipelines and VesselsDocument7 paginiSafely Purging Air from Pipelines and Vesselsgan_raoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 RevaDocument20 paginiChapter 8 RevaanildhakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compendium Templates Nutrition Facts TablesDocument86 paginiCompendium Templates Nutrition Facts TablesFerociousWolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mowilith LDM1865 PSDocument2 paginiMowilith LDM1865 PSDen KazuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peto MSDSDocument4 paginiPeto MSDSMenoddin shaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Road Construction QuotationDocument2 paginiRoad Construction QuotationVinod Kumar Verma100% (6)
- About The Dyes: Dyes For Cellulose FibersDocument4 paginiAbout The Dyes: Dyes For Cellulose FibersmanqabatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limiting Stoich 203Document2 paginiLimiting Stoich 203api-284934591Încă nu există evaluări
- 3656-3756 ML Brochure GouldsDocument44 pagini3656-3756 ML Brochure Gouldsjulio.esc7Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 4Document22 paginiChemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 4dylandonÎncă nu există evaluări