Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Rec CME
Încărcat de
Patrick KelvianTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Rec CME
Încărcat de
Patrick KelvianDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Recommendations on Continuing Medical
Education
3rd, revised edition
Publisher:
German Medical Association
Texts and Materials of the German Medical Association
on Continuing Medical Education and Specialist Training
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
Copyright
German Medical Association
Federation of the German Chambers of Physicians
Berlin, 30.05.2007
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
Contents
Page
Continuing medical education as an inherent element
of physicians' activities ........................................................................................................4
Legal framework conditions.................................................................................................4
Content of continuing education..........................................................................................4
Types of continuing education.............................................................................................5
Personal study ...................................................................................................5
Continuing education events .............................................................................5
Quality requirements for (attendance-based)
continuing education offerings.............................................................................................7
Organisation ......................................................................................................7
Speakers/Course managers ..............................................................................8
Financial interests..............................................................................................8
Additional quality requirements for media-based
continuing education offerings.............................................................................................8
Organisation ......................................................................................................8
Authorship..........................................................................................................9
Financial interests..............................................................................................9
Appendix
(Model) Regulations on Continuing Education
Continuing Medical Education and Sponsoring
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
Continuing medical education as an inherent element of physicians' activities
The in-service updating of knowledge and continuous expansion of professional skills is part
of the self-image of physicians.
The aim of continuing education is to safeguard and continuously improve the quality of
treatment, and thus to guarantee optimum provision of medical care for patients. Regular
continuing education is consequently of major importance for quality assurance in medicine.
Continuing education can only be successful if, on the one hand, it closes objective gaps in
knowledge and action and, on the other hand, satisfies the subjective, individually perceived
need for continuing education.
The Chambers of Physicians support the quality assurance efforts of their members by issuing recommendations regarding the form and content of continuing education, and by offering suitable events of their own.
Like quality assurance and quality improvement efforts, constant continuing education follows a cycle:
- Recognition of the need for continuing education
- Definition of the learning target
- Selection of the continuing education content
- Review of the teaching offers
- Selection of the learning method
- Check of learning success
- Application of the new knowledge in daily work
- Continuous review of knowledge
Legal framework conditions
In addition to the obligation to engage in continuing medical education pursuant to Art. 4 of
the (Model) Professional Code, an obligation to furnish proof of continuing medical education
has been rooted in the law since 1 January 2004 (SHI Modernisation Act (GMG)), both for
SHI-accredited physicians (Section 95 d Book V Social Security Code (SGB V)) and for specialists in hospitals (Section 137 Para. 1 No. 2 SGB V). Reference is made to the version of
SGB V valid at any one time.
Formulation of the content of criteria for the recognition of suitable continuing education
events and the crediting of continuing education certificates of individual physicians are subject to the regulatory competence of the medical community. The basis for this are the
(Model) Regulations on Continuing Education of the German Medical Association, which
were adopted at the 104th German Medical Assembly in 2004 (see Appendix). Regarding
the rating of continuing education measures, Art. 6 Para. 3 stipulates: "The State Medical
Chamber issues supplementary guidelines on the rating of the continuing education measures, these being based on the nationally applicable, standard criteria." The "Recommendations of the German Medical Association on Continuing Medical Education" formulate these
criteria in detail.
In the framework of the statutory obligation, physicians can in principle only be given credits
for continuing education events that have previously been recognised by a State Chamber of
Physicians, or a chamber of another healthcare profession, and rated with continuing education points. Further details are governed by the respective Continuing Education Regulations
of the State Chambers of Physicians.
Content of continuing education
Continuing medical education gives consideration to scientific and procedure-related knowledge necessary for maintaining and further developing skills. This means the communication
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
of subject-specific, interdisciplinary and interprofessional knowledge and information, as well
as the acquisition of practical skills.
Learning content serving to improve social skills, communication and leadership skills, as
well as methods of medical teaching, are just as much integral elements of continuing medical education as methods of quality management and evidence-based medicine. Health system-related, business-related and legal content serving the practice of the medical profession
can be given consideration.
Regardless of the individual need for continuing education, the content of continuing medical
education must meet the following criteria:
- Benefit for patients
- Comprehensibility
- Relevance and up-to-dateness
- Scientific evidence / corresponding to the general state of the science
- Applicability of the knowledge acquired in professional practice
- Benefit for the workflow
- Transparency (cost/benefit ratio / quality assurance / error management)
- Critical appraisal in the context of the subject area
- Independence from ideological and commercial interests
- Conformity with the specifications of the medical community (Continuing Education
Regulations, Professional Codes)
- Conformity with ethical principles (WHO Declaration)
Types of continuing education
According to the (Model) Regulations on Continuing Education, recognition and the award of
points presupposes a continuing education unit lasting at least 45 minutes and classification
in one of the following categories of continuing education:
Personal study (professional literature, audiovisual teaching and learning media)
- Reading of scientific articles in journals and technical books (Cat. E)
- Use of audiovisual media and corresponding online offerings without checking of
the learning success (Cat. E)
- Media-based continuing education with checking of the learning success in written
form (Cat. D)
Continuing education events
- Presentation and discussion, conferences (Cats. A and B)
- Courses and seminars, work in small groups (Cat. C)
Continuing education in interactive small groups of approx. 20 participants for the
thematically circumscribed communication of in-depth knowledge under professional supervision.
For all types of event classified in Category C, the Regulations on Continuing Education require that the "concept envisages the involvement of every individual participant". This can usually not be ensured in larger groups. Therefore, Category C
generally applies only to groups with up to 25 participants and leads to the award
of an additional point. Exceptions are possible following examination of a differentiated continuing education concept.
Workshop (Cat. C)
Joint working meeting involving a moderator, with the aim of confronting
complex problems relating to a previously defined topic in cooperative,
and often also practical, form. Workshops occasionally go beyond the
5
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
communication of knowledge and exchange of experience by creating
new approaches and/or giving the participants new ideas for further developments. The number of participants and the duration are limited.
Working group (Cat. C)
Meeting of a group for a concrete reason to deal with a task, examine a
subject or factual situation, or solve a problem. All participants are equal.
The number of participants and the duration are limited.
Work in small groups (Cat. C)
Elaboration of the factual situation or a proposed solution in connection
with a specific problem over a defined period of time in a group comprising 3 to a maximum of 6 participants.
Case-based conference (Cat. C)
Joint deliberations on concrete cases that take place outside the daily
routine meetings of everyday hospital work and involve external participants.
Interdisciplinary case-based conference (Cat. C)
Joint deliberations on concrete cases with representatives of several disciplines that take place outside the daily routine meetings of everyday
hospital or practice work and involve external participants.
Quality circle (Cat. C)
Group of physicians / psychological psychotherapists from the same or
different disciplines, who deal with the constant further development of
quality in the "practical provision of medical services". In an exchange of
experience between colleagues, the participants' own work is analysed,
evaluated and, if necessary, specifically altered in the spirit of improving
quality. The quality circle is headed by a moderator, who must furnish
proof of training as quality circle moderator.
Balint group (Cat. C)
The Balint group comprises 8 to 12 physicians, who meet to regularly
discuss problem patients from private and hospital practice. The group is
headed by a psychotherapist with corresponding experience with Balint
group work. The aim of Balint group work is to detect and correct problems in the relationship between physician and patient (definition of the
German Balint Society).
Supervision (Cat. C)
Special form of discussion that serves professional qualification. The
group is headed by a supervisor. Supervision is based on concrete experiences in the working environment and focuses on the interplay of
person, professional role, institution and addressee. Supervision provides
a sheltered environment in which to examine conflicts, stressful occurrences and current difficulties in everyday professional work, from a distance and without immediate pressure to act.
Intervision (Cat. C)
Intervision is supervision among colleagues: a discussion is held in a
team without a moderator. An intervision group consists of 3 to 7 participants. It is a periodic event designed on a relatively long-term basis. The
participants report on their own experience in dealing with patients in order to review their own conduct and the therapeutic decisions.
Literature conference (Cat. C)
Meeting for the purpose of presenting, evaluating and critically appraising
current medical literature following presentations by individual speakers,
outside the daily routine meeting and involving external participants.
Scientific publications and activities as a speaker (Cat. F)
6
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
-
Time as a visiting doctor (Cat. G)
Time as a visiting doctor is spent in other hospitals, private practices, institutes or
departments. It serves the acquisition of new specialist knowledge or the expansion and perfection of knowledge and skills, the improvement of, and reflection on,
own work, and the promotion of mutual understanding and respect through becoming acquainted with other organisational forms and working methods. Visiting doctors participate fully or partially in the everyday professional work of their host facility without remuneration. It must be ensured in this context that the visiting doctor
has a permanent contact, who supports him/her during the familiarisation period,
promotes his/her integration and is available to provide information and background information. Some State Chambers of Physicians only recognise times as a
visiting doctor if the Chamber of Physicians was informed thereof beforehand.
Specialist training courses, curricular continuing education measures, postgraduate
study courses (Cat. H)
Department-internal discussions of patient cases and/or decision-making processes in everyday hospital work cannot be recognised as separate continuing medical education, even if
learning effects are achieved in this context.
Events restricted to a specific group of participants, e.g. members' meetings, for the purpose
of political opinion-forming or representation of professional political interests, can likewise
not be credited. Partial recognition of scientific items on the agenda of such events is possible.
Quality requirements for (attendance-based) continuing education offerings:
Organisation
- Definition of the participant target group
- Selection of suitable experts / speakers
- Preparation and communication of the continuing education content in accordance
with the above criteria
- Timely, comprehensive and formally appropriate information on learning targets,
content, methods, venue and time of a continuing education measure
- Selection of the venue, time, room and media to suit the form and objective of the
continuing education event, as well as the size of the continuing education group
- Obstacle-free access for people with disabilities
- Adherence to the planned time schedule of a continuing education event, or adaptation of the course of the event to the receptive capacity of the participants, allowing sufficient time for breaks and discussions
- Offer of suitable learning success checks to complete the learning process (interactive voting system, multiple-choice questions, verbal or written attestations, etc.)
- Appropriate personal support of the continuing education participant by the organiser and correspondingly trained personnel
- Timely application for corresponding recognitions (continuing education points /
relevance for specialist training, where appropriate) from the respectively competent State Chambers of Physicians
- Evaluation of every event, preferably with feedback to the speakers
- Use of the Electronic Information Distributor (EIV) of the German Medical Association (www.eiv-fobi.de)
- Issue of attendance certificates, indicating the following: name of the organiser, title
and date of the event, name of the participant; in the framework of continuing education modules eligible for points, also: the nationally uniform event number (VNR)
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
and information on the recognising State Chamber of Physicians, as well as the
number of continuing education points acquired and the category
At the request of the recognising State Chamber of Physicians, granting of an insight into all above-mentioned organisational and content-related procedures
Speakers/Course managers
- Multi-year medical professional experience and, preferably, current activity in the
corresponding field/sector
- Where appropriate, authorisation to provide specialist training in the field/sector
(specialist training courses)
- Medical teaching skills, teaching experience, enthusiasm and willingness to encourage discussion
- Practice and participant-oriented presentation of the teaching content, using appropriate, modern media
- Provision of an informative summary in the form of a handout
Financial interests
- Continuing medical education must be free of commercial interests
- Sponsoring must be made transparent
- The sponsor may not influence the form and content of the continuing education
measure
- Speakers must disclose their connections with industry
- The scientific managers of continuing education events ensure product-neutrality
- Product advertising on the invitations and programmes of single-subject continuing
education events is fundamentally not permissible; there are no objections to the
advertising of several products by several manufacturers in the programmes of
multi-subject events (conferences). The names of sponsors must be indicated
- Objective product information based on scientific criteria is permissible if the active
ingredient (generic) is indicated instead of the product name, e.g. by the pharmaceutical industry
- All continuing education measures must communicate a balanced overview of the
respective status of knowledge relating to corresponding diagnostic and therapeutic alternatives
- Commercial exhibitions with a temporal or spatial link to continuing education
measures may influence neither the concept nor the implementation of the actual
continuing education measure
- A commercially backed accompanying programme may neither take place at the
same time as the content of the programme proper, nor may it last longer than the
continuing education itself
- The admissibility of accepting benefits in kind for attendance at scientific continuing
education events is governed by the Professional Code of the State Chambers of
Physicians
Additional quality requirements for media-based continuing education offerings:
In addition to the quality requirements for attendance-based continuing education events,
media-based continuing education offerings must also satisfy the following criteria:
Organisation
- Disclosure of, and compliance with, a quality assurance procedure for appraisal of
the continuing education offering (review procedure by experts)
8
RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
-
Clear distinction between learning programmes and other parts of the online publication
Clear references to the possibility of acquiring (the respective number of) continuing education points, with a description of the procedure
Indication of the duration of the media-based continuing education offering and,
where appropriate, the validity period of the recognition granted and the name of
the recognising State Chamber of Physicians
Granting of free access to password-protected continuing education offerings on
the Internet to the recognising State Chamber of Physicians
Minimum time requirement of 45 minutes for processing continuing education
modules eligible for points
Check of learning success (obligatory in the context of continuing education modules eligible for points) with obstacles to obtaining a pass
Printable online participation certificates must contain the following information: organiser, title and date of the continuing education programme, name of the participant and, in the framework of continuing education modules eligible for points, the
nationally uniform event number (VNR) and information on the recognising State
Chamber of Physicians
Compliance with the provisions of data protection law when handling personal
data. Users should be able to reject any use exceeding the necessary purpose
Authorship
- Clear naming of specialist authors, publisher, publication date and/or version numbers, as well as legal accountabilities
- Guarantee of the high scientific topicality of the content
- Citation method and references to external sources similar to those used in scientific publications in print media
Financial interests
- Media-based continuing education modules involving product advertising cannot be
recognised; the sponsors of the publication and/or the operator of the website may
be named
- Processing of online continuing education modules by the participants may not be
disturbed by banners, pop-ups or similar electronic applications
- The linking of continuing education modules to commercial websites is not permissible
As with all other types of continuing medical education, crediting to the continuing education
certificate is only possible if the media-based continuing education offering has previously
been recognised by a State Chamber of Physicians and rated with continuing education
points.
German Medical Association
Status: 20 May 2004
(Model) Regulations
Continuing Education and
Continuing Education Certificate
Art. 1
Objective of Continuing Education
The continuing education of physicians is intended to maintain and constantly update
their professional competence.
Art. 2
Content of Continuing Education
Taking into account scientific findings and new medical procedures, continuing education is intended to communicate the knowledge of medicine and medical technology
necessary to maintain and update professional competence. Continuing education
should comprise both specialised and interdisciplinary knowledge and the learning of
practical clinical skills. In this context, continuing education should cover all medical disciplines in a balanced manner. Continuing medical education also encompasses the
improvement of communication and social skills. Continuing medical education also includes methods of quality assurance, quality management and evidence-based medicine. Nationally applicable, standard specifications regarding the reasonable scope of
continuing education are to be observed.
German Medical Association
Art. 3
Continuing Education Methods
(1)
The physician is free to choose the nature of his/her continuing education. The
manner in which knowledge is acquired is to be geared to the individually different forms of learning behaviour.
(2)
Insofar as continuing education particularly takes place through participation in
continuing education events according to Para. 3 No. 2, the physician should
comply with the obligation to undergo continuing education by attending continuing education measures recognised by the State Medical Chamber.
(3)
Suitable methods of continuing education include, in particular:
1. Media-based personal study (e.g. professional literature, audiovisual teaching
and learning materials, structured interactive continuing education);
2. Attendance at continuing education events (e.g. conferences, seminars,
group exercises, courses, colloquia, quality circles);
3. Continuing clinical education (e.g. time as visiting doctor, case presentations);
4. Curriculum-based content, e.g. in the form of curricular continuing education,
specialist training courses prescribed for a specialist qualification under the
Regulations on Specialist Training, supplementary courses of study.
Art. 4
Organisation of Proof of Continuing Education
(1)
The State Medical Chamber promotes the continuing education of Chamber
members by offering its own continuing education measures and by recognising
suitable continuing education measures as a basis for proof of compliance with
the obligation to undergo continuing professional education.
(2)
The purpose of promoting the obligation to undergo continuing education, and of
proving compliance with it, is particularly served by the Continuing Education
Certificate of the State Medical Chamber (Art. 5), which is awarded, on the basis
German Medical Association
of the regulations below, to every physician upon application, subject to the proviso that the regulated requirements are fulfilled.
Art. 5
Continuing Education Certificates of the State Medical Chamber
A Continuing Education Certificate is issued if, within a period of [three] [five] years prior
to application, the physician has completed continuing education measures, the sum total of which reaches the minimum rating of [150] [250] points, determined according to
the rules in Art. 6.
Only the continuing education measures regulated in Art. 6 Para. 2 can be considered
for acquisition of the Continuing Education Certificate; a further prerequisite is prior recognition of the continuing education measures to be credited pursuant to Art. 7. This
does not affect Art. 12. The recognition procedure is governed by Arts. 7 to 11.
Art. 6
Rating of Continuing Education Measures
(1)
The continuing education measures are rated using a points system. The basic
unit is a 45-minute continuing education unit. The categories and the details of
the rating scale are defined in Para. 2.
(2)
The following categories of continuing education measures are suitable for the
Continuing Education Certificate and are rated as follows:
Category A:
Presentation and discussion
1 point per continuing education unit; max. 8 points per day
Category B:
Multi-day conferences at home and abroad
If no proof according to Category A or C is furnished:
3 points per half-day or 6 points per day
Category C:
Continuing education whose concept envisages the involvement of every individual participant (e.g. workshops,
3
German Medical Association
working groups, quality circles, Balint groups, work in small
groups, supervision, case-based conferences, literature conferences, practical exercises)
1. 1 point per continuing education unit
1 bonus point per event up to 4 hours
2. Max. 2 bonus points per day
Category D:
Structured interactive continuing education via print media,
online media and audiovisual media with proven qualification
and evaluation of the learning success in written form
1 point per exercise unit
Category E:
Personal study by means of professional literature/books
and teaching materials
A maximum of [30] [50] points for [three] [five] years will be
recognised in Category E
Category F:
Scientific publications and presentations
1. Authors are awarded 1 point per contribution
2. Speakers/quality-circle moderators are awarded 1 point
per contribution/poster/presentation in addition to the
points for participants
Category G:
Time as a visiting doctor
1. 1 point per hour; max. 8 points per day
Category H:
Curriculum-based content, e.g. in the form of curricular continuing education measures, specialist training courses prescribed for a specialist qualification under the Regulations on
Specialist Training, supplementary courses of study.
1. 1 point per continuing education unit
Success check:
1 bonus point for Categories A and C
German Medical Association
(3)
The State Medical Chamber issues supplementary guidelines on the rating of the
continuing education measures, these being based on the nationally applicable,
standard criteria ["..."]. The guidelines also define the exceptions in which the
maximum crediting of rating points may be exceeded in justified exceptional
cases in the individual Categories in the event of otherwise equivalent continuing
education.
Art. 7
Recognition of Continuing Education Measures
(1)
In principle, continuing education measures in Categories A to D, G and H of
Art. 6 Para. 2 can only serve as a basis for award of the Continuing Education
Certificate if they were recognised by a State Medical Chamber prior to their implementation. For measures in Category F of Art. 6 Para. 2, the physician must
furnish suitable proof when submitting the application for award of the Continuing
Education Certificate.
(2)
Continuing education measures offered by other organisers are recognised in
accordance with Arts. 8 and 9.
Art. 8
Prerequisites for Recognition of Continuing Education Measures
(1)
Recognition of a continuing education measure presupposes that the continuing
education content to be communicated
1. Is in keeping with the objectives of the code of professional conduct and
these Continuing Education Regulations,
2. Gives consideration to the nationally applicable, standard recommendations
of the State Medical Chambers on quality assurance in continuing medical
education (in: "Recommendations of the German Medical Association on
Continuing Medical Education") [alternatively: the criteria of the German
Medical Association, dated ...],
3. Is free of business interests.
German Medical Association
Continuing education should generally be open to all physicians. Organisers and
speakers must disclose economic ties with industry to the State Medical Chamber.
(2)
A physician must always be appointed to bear scientific responsibility for continuing education measures in Categories A to D, G and H of Art. 6 Para. 2.
Art. 9
Recognition Procedure for Continuing Education Measures
(1)
Recognition is granted upon application by the organiser. The application must
state the name of the responsible person according to Art. 8 Para. 2.
(2)
The Board of the State Medical Chamber adopts guidelines relating to the recognition procedure. In uniform manner for all measures in Categories A to D, G and
H of Art. 6 Para. 2 open to consideration, the guidelines define the prerequisites
for recognition, based on the criteria of the German Medical Association, in respect of the following details:
1. Application deadlines
2. Content of applications
3. Methods of checking the learning success
4. Lists of participants
5. Participant certificates
6. Special regulations for the recognition of individual categories of continuing
education.
(3)
The organiser must provide a written declaration of compliance with the recommendations of the German Medical Association pursuant to Art. 8 (1) 2.
(4)
The organiser can be commissioned by the State Medical Chamber to send, with
the consent of the participating physicians, the proof of their participation in the
recognised continuing education event directly to the State Medical Chamber.
German Medical Association
Art. 10
Recognition of Continuing Education Organisers
On application, a suitable organiser can be given the promise by the State Medical
Chamber, for all the events staged by it or for specific events, that the continuing education events will be recognised without being reviewed individually. Conditions are attached to this promise. It must be ensured in this context that the organiser demonstrably observes the provisions of these Regulations when selecting and rating the events.
Art. 11
Mutual Recognition of Continuing Education Measures
The State Medical Chamber recognises continuing education measures recognised by
the chamber of another healthcare profession as a basis for award of a Continuing Education Certificate.
Art. 12
Continuing Education Abroad
(1)
Continuing education measures implemented abroad are recognised if they essentially correspond to the requirements of these Continuing Education Regulations. The need for prior recognition can be dispensed with.
(2)
The physician must furnish proof of the nature of the continuing education that
permits the verification of compliance with the criteria according to Art. 8.
Continuing Medical Education and Sponsoring
(Version of 18 April 2007)
Continuing education as a life-long learning process is a professional duty of physicians. Owing to the prevailing structures, fulfilment of this duty makes cooperation between the medical
community and third parties necessary and desirable in many areas.
However, this cooperation must be structured in such a way that neither the good of the patient nor the preservation of physicians' independence is jeopardised at any time.
In particular, this means that the content of continuing medical training must be kept independent of financial interests of third parties and free of commercial influences on diagnosis
and therapy in hospitals and private practice.
This results in the following demands:
Sponsoring must be made transparent
The sponsor may not influence the form and content of the continuing education measure
Speakers must disclose their connections with industry
The scientific managers of continuing education events ensure product-neutrality
Product advertising on the invitations and programmes of single-subject continuing education events is fundamentally not permissible; there are no objections to the advertising
of several products by several manufacturers in the programmes of multi-subject events
(conferences). The naming of sponsors is permissible
Objective product information based on scientific criteria is permissible if the active ingredient (generic) is indicated instead of the product name, e.g. by the pharmaceutical industry
All continuing education measures must communicate a balanced overview of the respective status of knowledge relating to corresponding diagnostic and therapeutic alternatives
Commercial exhibitions with a temporal or spatial link to continuing education measures
may influence neither the concept nor the implementation of the actual continuing education measure
A commercially backed accompanying programme may neither take place at the same
time as the content of the programme proper, nor may it last longer than the continuing
education itself
The admissibility of accepting benefits in kind for attendance at scientific continuing education events is governed by the Professional Codes of the Federal States.
Supplementary recommendations for written or audiovisual media
Product advertising is not permissible in recognised media-based continuing education
modules; the sponsors of the publication and/or the operator of the website may be
named
Processing of online continuing education modules by the participants may not be disturbed by banners, pop-ups or similar electronic applications
The linking of continuing education modules to commercial websites is not permissible
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Reduction of Cortisol Levels and Participants Responses Following Art MakingDocument8 paginiReduction of Cortisol Levels and Participants Responses Following Art MakingPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Case Study FIXDocument66 paginiCase Study FIXPatrick Kelvian100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- OS X El Capitan Power User Keyboard ShortcutsDocument1 paginăOS X El Capitan Power User Keyboard ShortcutsPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Mac Most Keyboard Shortcuts MavericksDocument1 paginăMac Most Keyboard Shortcuts MavericksAzobeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Photoshop CS6 Mac ShortcutsDocument2 paginiPhotoshop CS6 Mac ShortcutsPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Mac Most Keyboard Shortcuts Mountain LionDocument1 paginăMac Most Keyboard Shortcuts Mountain LionPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- OS X El Capitan Power User Keyboard ShortcutsDocument1 paginăOS X El Capitan Power User Keyboard ShortcutsPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- IC CDC CatheterizationRecommendationsDocument2 paginiIC CDC CatheterizationRecommendationsPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Create A Hyperlink To A Slide in The Same PresentationDocument5 paginiCreate A Hyperlink To A Slide in The Same PresentationPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduction of Cortisol Levels and Participants Responses Following Art MakingDocument8 paginiReduction of Cortisol Levels and Participants Responses Following Art MakingPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- DX TX ApendikDocument5 paginiDX TX ApendikAhmed MawardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- CHF Drug TheraphyDocument3 paginiCHF Drug TheraphyPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- FP2015 Applicants HandbookDocument37 paginiFP2015 Applicants HandbookVirginia C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
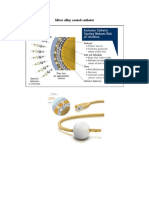
- Silver Alloy Coated CatheterDocument1 paginăSilver Alloy Coated CatheterPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Absen CoassDocument6 paginiAbsen CoassPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHF Drug TheraphyDocument3 paginiCHF Drug TheraphyPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- FP2015 Applicants HandbookDocument37 paginiFP2015 Applicants HandbookVirginia C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Kamus Indonesia SundaDocument15 paginiKamus Indonesia SundaBelajar HatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Absen ReferatDocument4 paginiAbsen ReferatPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photoshop CS6 Mac ShortcutsDocument2 paginiPhotoshop CS6 Mac ShortcutsPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photoshop CS6 Mac ShortcutsDocument2 paginiPhotoshop CS6 Mac ShortcutsPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
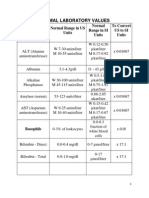
- Normal Laboratory Values: Laboratory Test Normal Range in Us Units Normal Range in Si Units To Convert Ustosi UnitsDocument6 paginiNormal Laboratory Values: Laboratory Test Normal Range in Us Units Normal Range in Si Units To Convert Ustosi UnitsPatrick Kelvian100% (1)
- Writing A SummaryDocument5 paginiWriting A SummaryPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypo ThyroidDocument36 paginiHypo ThyroidPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison Between Vacuum and Forceps Extraction To Neonatal Outcome On Prolonged Second Stage of LaborDocument4 paginiComparison Between Vacuum and Forceps Extraction To Neonatal Outcome On Prolonged Second Stage of LaborPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- B3 - Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - A Cautionary Tale, Rosemarie ThomasDocument2 paginiB3 - Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - A Cautionary Tale, Rosemarie ThomasPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypo ThyroidDocument36 paginiHypo ThyroidPatrick KelvianÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1Document12 paginiQuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1subhrajitm47Încă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- MS Word Lecture NotesDocument11 paginiMS Word Lecture NotesMoguriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 111a - Activity No. 2Document5 paginiChem 111a - Activity No. 2MARY KATE FATIMA BAUTISTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12-24VDC Powered Ignition System: N N N N N N NDocument2 pagini12-24VDC Powered Ignition System: N N N N N N NLeinner RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERP Final PPT 22-4Document10 paginiERP Final PPT 22-4ramesh pokhriyaalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research and Practice in HRM - Sept 8Document9 paginiResearch and Practice in HRM - Sept 8drankitamayekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathfinder House RulesDocument2 paginiPathfinder House RulesilililiilililliliI100% (1)
- Introduction To Parallel Programming 1st Edition Pacheco Solutions ManualDocument5 paginiIntroduction To Parallel Programming 1st Edition Pacheco Solutions Manualyvonnewelchdoafexwzcs100% (11)
- COO Direct Response Marketing in Miami FL Resume Mark TaylorDocument2 paginiCOO Direct Response Marketing in Miami FL Resume Mark TaylorMarkTaylor1Încă nu există evaluări
- Needs Assessment Form Company Name: HRMO Address: Sta. Barbara Agoo, La UnionDocument2 paginiNeeds Assessment Form Company Name: HRMO Address: Sta. Barbara Agoo, La UnionAlvin LaroyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company Grasim ProfileDocument48 paginiCompany Grasim ProfileNitu Saini100% (1)
- EE/CS-320 - Computer Organization & Assembly Language (Fall Semester 2013-14) Assignment 2Document11 paginiEE/CS-320 - Computer Organization & Assembly Language (Fall Semester 2013-14) Assignment 2Haris AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Arts Q1W3Document44 paginiArts Q1W3LEILANI PELISIGASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual: Department of Computer EngineeringDocument65 paginiLab Manual: Department of Computer EngineeringRohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Calculation of Braking System (Landcruiser) : AbstractDocument4 paginiDesign Calculation of Braking System (Landcruiser) : AbstractDr. Aung Ko LattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alabama GOP ResolutionDocument2 paginiAlabama GOP ResolutionFox News67% (6)
- Heist Story ScriptDocument3 paginiHeist Story Scriptapi-525637110Încă nu există evaluări
- OOAD Documentation (Superstore)Document15 paginiOOAD Documentation (Superstore)Umâir KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overhead Line SolutionsDocument8 paginiOverhead Line SolutionsDomingo O Chavez PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALLOY 7150-T7751 PLATE AND 7150-T77511 EXTRUSIONS: Alcoa Mill ProductsDocument4 paginiALLOY 7150-T7751 PLATE AND 7150-T77511 EXTRUSIONS: Alcoa Mill Productshitesh_tilalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Journal On Cryptography and Information Security (IJCIS)Document2 paginiInternational Journal On Cryptography and Information Security (IJCIS)ijcisjournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 110Q Pump Catalog SheetDocument2 pagini110Q Pump Catalog SheetJohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Glossary Reuters PDFDocument241 paginiFinancial Glossary Reuters PDFPablo Bouvier100% (1)
- Activity 3 Data SheetDocument9 paginiActivity 3 Data SheetEli GabuatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bagheri Gavkosh2021Document17 paginiBagheri Gavkosh2021Dan Alfred SebualaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 010 Informed Search 2 - A StarDocument20 pagini010 Informed Search 2 - A StarRashdeep SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labour and Human Resource Issues in Industry 4.0: A Case Study Report OnDocument20 paginiLabour and Human Resource Issues in Industry 4.0: A Case Study Report OnNPMYS23100% (1)
- Andrew Beale - Essential Constitutional and Administrative LawDocument123 paginiAndrew Beale - Essential Constitutional and Administrative LawPop Rem100% (4)
- Crisostomo Vs Courts of Appeal G.R. No. 138334 August 25, 2003Document5 paginiCrisostomo Vs Courts of Appeal G.R. No. 138334 August 25, 2003RGIQÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Diet Guide PDFDocument43 pagini1 Diet Guide PDFYG1Încă nu există evaluări
- $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoDe la Everand$100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (23)
- The Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeDe la EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (90)
- Summary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendDe la EverandSummary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffDe la Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (19)
- Portfolio management strategies for technical analystsDe la EverandPortfolio management strategies for technical analystsÎncă nu există evaluări