Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
G10 LTE Heredity LC2
Încărcat de
Arman Morales0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
88 vizualizări2 paginilesson 2 grade 10
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentlesson 2 grade 10
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
88 vizualizări2 paginiG10 LTE Heredity LC2
Încărcat de
Arman Moraleslesson 2 grade 10
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
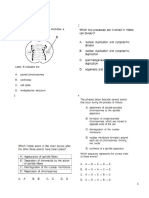
LIVING THINGS AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT
GRADE 10 LEARNING COMPETENCIES
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE AND VARIATION
LC2. Explain how mutations may cause
changes in the structure and function of a
protein. (S10LT-III e38)
1. Mutations can be transmitted to the next
generation only if they are present in
A. brain cells
B. sex cells
C. body cells
D. muscle cells
2. Which of the following is NOT a cause of
mutations of DNA?
A. chemicals
B. x-rays
C. ultraviolet light
D. polyploidy
3. The addition, removal, or substitution of
nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule may be
caused by
A. mutagenic agents
B. cloning
C. vegetative propagation
D. nondisjunction
4. Overexposure of animals to x-rays is dangerous
because x-rays are known to damage DNA. A
direct result of this damage is cells with
A. unusually thick cell walls
B. no organelles in the cytoplasm
C. abnormally large chloroplasts
D. changes in chromosome number or
structure
5. Downs syndrome is an example of which
chromosome condition?
A. inversion
B. disjunction
C. nondisjunction
D. deletion
6. A single gene mutation would most likely occur
if
A. messenger-RNA molecules temporarily
bond to DNA molecules
B. the cytoplasm lacks the amino acids
necessary to synthesize a certain
polypeptide
C. a base sequence in a DNA molecule
is changed
D. transfer-RNA molecules do not line up
properly on a messenger-RNA molecule
7. What will happen if a base sequence of a
strand of DNA is changed from ATG to
A
TC?
A. The m-RNA will be changed from
UAC to UAG.
B. The t-RNA will be changed from
UAC to TAC.
C. The m-RNA will be changed from
TUC to TUG.
D. The t-RNA will be changed from
CAU to CAC.
8. In humans, Down syndrome is often a result of
the
A. disjunction
of
homologous
chromosomes during meiotic cell
division
B. nondisjunction
of
chromosome
number 21 in one of the parents
C. combination of an egg and sperm, each
carrying a recessive allele for this
disorder
D. fusion of two 2n gametes during
fertilization
9. Identical twins were born with genes for a
genetic disorder that can be controlled by diet.
Both twins were placed on this diet, which
excludes a certain amino acid. However, one
twin chose not to follow the diet and developed
the genetic disorder. The other twin followed the
diet and did not develop the disorder. This
difference between the twins illustrates that
A. gene expression is not influenced by
biochemical factors
B. identical twins do not always have the
same genotype
C. gene expression is influenced by the
environment
D. the genetic disorder is inherited by
identical twins only
10. Sometimes a section of a chromosome is lost
during meiosis. This loss results in a change in
genetic material known as
A. a deletion
B. a replication
C. an inversion
D. a nondisjunction
11. Which disorder is characterized by fragile red
blood cells and severe pain from blocked blood
vessels?
A. Tay-Sachs
B. Phenylketonuria
C. Haemophilia
D. Sickle-cell anemia
12. A point mutation that changes a codon
specifying an amino acid into a stop codon is
called a
A. missense mutation
B. nonsense mutation
C. silent mutation
D. frameshift mutation
13. Point mutation involves
A. deletion
B. insertion
C. duplication
D. substitution
14. Gene mutation occurs at the time of
A. DNA repair
B. DNA replication
C. cell division
D. RNA transcription
15. The difference in amino acids indicated in the
circled portion of the diagram below causes a
change in the shape of red blood cells.
Portion of Normal Hemoglobin
Val
His
Leu
Thr
Pro
Glu
Glu
Thr
Val
Glu
Thr
Portion of Abnormal Hemoglobin
Val
His
Leu
Thr
Pro
Amino Acids
Glu = glutamic acid
His = histidine
Leu = leucine
Lys = lysine
Pro = proline
Thr = threonine
Val = valine
What is a probable cause of this difference in
the hemoglobin molecules?
A. a recessive allele located on the Xchromosome
B. the substitution of one kind of
nucleotide for another in a DNA
molecule
C. the failure of chromosome to separate
during cell division
D. an
abnormal
metabolism
of
phenylalanine
16. A karyotype is shown in the diagram below.
Information in this karyotype indicates that the
individual is a
A. male with sickle-cell anemia
B. female with Tay-Sachs disease
C. male with Down syndrome
D. female with phenylketonuria
17. A karyotype is shown in the diagram below.
Information in this karyotype indicates that the
individual has a condition known as
A. Turner syndrome
B. Williams syndrome
C. Klinefelter syndrome
D. Cri-du-chat syndrome
Base your answers to questions 18 through 19 on
the diagram below. The diagram shows a human
karyotype.
18. Which is correct about the person whom this
karyotype was taken?
A. The person has Downs syndrome.
B. The person has Turners syndrome.
C. The
person
has
Klinefelters
syndrome.
D. The person has a sex-linked condition.
19. Which of the following is true about this
condition?
A. One chromosome has been deleted.
B. One chromosome has been inverted.
C. This
arose
as
a
result
of
nondisjunction.
D. There has been a translocation.
20. What type of mutation describes the change of
the sequence:
Original DNA sequence: ATA CTT AGT GAA
Mutated DNA sequence: ATA CTT AGT CGT GAA
A. inversion
B. deletion
C. frameshift mutation with a deletion
D. frameshift with an insertion
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 paginiWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE ExamDocument4 paginiSCIENCE ExamLesley AntojadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meiosis I vs Meiosis II: Key Differences in Cell Division StagesDocument1 paginăMeiosis I vs Meiosis II: Key Differences in Cell Division StagesnmrasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECTION. Answer The Following Questions.: Grade 10 Science 2018-2019 Worksheet # 1Document3 paginiDIRECTION. Answer The Following Questions.: Grade 10 Science 2018-2019 Worksheet # 1Kuyang HugoteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 10 Practice TestDocument3 paginiCH 10 Practice Testrylee graceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ke & Pe PracticeDocument2 paginiKe & Pe PracticejjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 - Q3 - Summative TestDocument1 paginăScience 10 - Q3 - Summative Testzenaida a academiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Story of DNA - Script and Answer KeyDocument3 paginiThe Story of DNA - Script and Answer KeyAdam SimpsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid-Year Rpms Cover Page & TabbingDocument28 paginiMid-Year Rpms Cover Page & TabbingJEZIEL LOVE BALILIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science MELC With Online LRs Grade 9 0c0Document5 paginiScience MELC With Online LRs Grade 9 0c0REA BILANÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV BiodiversityDocument32 paginiIV BiodiversityMayden Grace Tumagan GayatgayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFDocument8 paginiStudy Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFNicolyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10Document2 paginiGrade 10letty louÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Relations SchoolDocument4 paginiHuman Relations SchoolHemant SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Waves 1Document21 paginiElectromagnetic Waves 1StephanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloze Meiosis and MitosisDocument2 paginiCloze Meiosis and MitosiscsamarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative DnaDocument11 paginiSummative DnaMarian Anion-GauranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories of EvolutionDocument12 paginiTheories of Evolutionapi-290573655Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Cycle Stages & PhasesDocument11 paginiCell Cycle Stages & PhasesJessie Katrisha TayagÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021Document4 paginiCH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021EmileMcBrokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete - Quarter 3 - Science 10 - Week 1 - 8Document42 paginiComplete - Quarter 3 - Science 10 - Week 1 - 8alyzamarie deramosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Ddl15Document3 paginiScience 10 Ddl15JOCELYN CAMACHOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science10Q3Exam TestBankDocument9 paginiScience10Q3Exam TestBankCrisante MaruquinÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewDocument12 paginiSCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewPepito Rosario Baniqued, JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plate Boundaries WorksheetDocument2 paginiPlate Boundaries WorksheetClassroomC9Încă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Incomplete, Codominance, Multiple Allele Notes and PracticeDocument7 pagini2015 Incomplete, Codominance, Multiple Allele Notes and Practiceapi-264255406100% (1)
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument26 paginiHuman Reproductive SystemAlmario DacalcapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Lesson PlanDocument7 paginiScience 10 Lesson PlanThesairah Taule100% (1)
- Science 10 Module 1 3qDocument7 paginiScience 10 Module 1 3qDionil CabilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Science 10Document3 paginiTest Science 10HajjieCortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Spectrum ApplicationsDocument2 paginiElectromagnetic Spectrum ApplicationsChristorie Ian AnchetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 BiomoleculesDocument6 paginiSCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 Biomoleculesizi iordeinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CO Digestive SystemDocument14 paginiCO Digestive SystemPrincy MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sts Quiz Reviewer 1Document11 paginiSts Quiz Reviewer 1理论Încă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Science Class Evolution WorksheetDocument9 paginiPhilippine Science Class Evolution WorksheetAngelica FulgencioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mentruation and It's CycleDocument35 paginiMentruation and It's CycleAshley SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding by Design: Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiUnderstanding by Design: Lesson Planapi-420907551Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Modifications Cell CycleDocument76 paginiCell Modifications Cell CycleGuen GanubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test in ScienceDocument6 paginiSummative Test in ScienceRalph Rexor Macarayan BantuganÎncă nu există evaluări
- G10 Weeks 4-5 (6-8)Document11 paginiG10 Weeks 4-5 (6-8)Mary-Rose CasuyonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resources Teaching Methods SOLO Taxonomy PDFDocument2 paginiResources Teaching Methods SOLO Taxonomy PDFAnant SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fun Intro To EMS WorksheetDocument6 paginiFun Intro To EMS WorksheetgraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles' LawDocument4 paginiCharles' LawGarren Jude Aquino100% (1)
- DLP Q1W4D3Document3 paginiDLP Q1W4D3LA Lloyd Arvin MontesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 AnswersDocument4 paginiActivate 1 Biology Chapter1 AnswersJohn LebizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Code: Learning Competency/iesDocument6 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Code: Learning Competency/iesMerce Tojino ManigosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10: Prepared By: Jergen A. Romulo Sst-IiiDocument8 paginiScience 10: Prepared By: Jergen A. Romulo Sst-IiiRona May EsperanzateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument11 paginiNon-Mendelian GeneticsalexandriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Template Your Name: Jailyn Jenkins Title of Lesson: SUPERCALIFRAGILISTIC Exponential Growth & Decay Grade: 8 StandardsDocument3 paginiLesson Plan Template Your Name: Jailyn Jenkins Title of Lesson: SUPERCALIFRAGILISTIC Exponential Growth & Decay Grade: 8 StandardsJailynJ7Încă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis and Meiosis Practice TestDocument13 paginiMitosis and Meiosis Practice TestCearra Mae EbronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDocument5 paginiProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Followingapi-39708077950% (2)
- 3rd Biotechnology 8 Summative TestDocument2 pagini3rd Biotechnology 8 Summative TestKristine A. LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument27 paginiCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsMARY ANN PANGANÎncă nu există evaluări
- HeredityDocument19 paginiHeredityichan0001Încă nu există evaluări
- Science 8 Q2 Exam (22-23)Document3 paginiScience 8 Q2 Exam (22-23)Sarah Jane CasipongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 3rd Quarter Exam: Share This DocumentDocument1 paginăScience 10 3rd Quarter Exam: Share This DocumentJAYM DELOS SANTOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics: Sex Determination in HumansDocument4 paginiGenetics: Sex Determination in HumansAlyn Mondrano AlonzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQs in Pathology: Key ConceptsDocument69 paginiMCQs in Pathology: Key Conceptsfadiawwad100% (4)
- Itinerary SVYFKSDocument2 paginiItinerary SVYFKSArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools For MOOE InspectionDocument2 paginiTools For MOOE InspectionArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feeding RecordDocument1 paginăFeeding RecordArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DO s2019 002-DepEdDocument7 paginiDO s2019 002-DepEdTheSummitExpress100% (1)
- Program of Works: Upgrading of School Building Distribution Lines Beff 2018Document4 paginiProgram of Works: Upgrading of School Building Distribution Lines Beff 2018Arman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bill of Quantity SampolDocument4 paginiBill of Quantity SampolArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boq Sampol Scol Estimate MNTLDocument52 paginiBoq Sampol Scol Estimate MNTLArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specs Gabaldon K. TomasDocument17 paginiSpecs Gabaldon K. TomasArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annamay List of NamesDocument4 paginiAnnamay List of NamesArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA 6713 - Code of Conduct and Ethical Standard For Public Officials and EmployeesDocument12 paginiRA 6713 - Code of Conduct and Ethical Standard For Public Officials and EmployeesCrislene Cruz83% (12)
- AISC Shapes TablesDocument64 paginiAISC Shapes TablesJose ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appointment BackDocument1 paginăAppointment BackArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bmi AnamayDocument16 paginiBmi AnamayArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 WMED 1-Blessed To Be A Blessing-PACKETDocument26 pagini2018 WMED 1-Blessed To Be A Blessing-PACKETArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parents Consent FormDocument1 paginăParents Consent FormArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Withholding Tax TablesDocument1 paginăRevised Withholding Tax TablesJonasAblangÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRC RatingDocument1 paginăPRC RatingArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spiral Progression Approach in K-To-12Document41 paginiSpiral Progression Approach in K-To-12Maria Cassandra Nirvana Guia100% (8)
- En Colon HealthDocument83 paginiEn Colon HealthArman Morales100% (2)
- Clarinet Fingering ChartDocument3 paginiClarinet Fingering ChartJorge HoyosÎncă nu există evaluări
- DepEd Order No40 S 2014Document105 paginiDepEd Order No40 S 2014Cebu Image93% (14)
- 3 Grammar RulesDocument31 pagini3 Grammar RulesArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- InstallationDocument1 paginăInstallationtrifulcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Building Code PDFDocument30 paginiGreen Building Code PDFArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stem Equipment FOR SHSDocument4 paginiStem Equipment FOR SHSArman Morales100% (1)
- Teacher Lesson Plans and Assessments GuideDocument45 paginiTeacher Lesson Plans and Assessments GuideArman Morales83% (6)
- CSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets FormDocument4 paginiCSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets Formwyclef_chin100% (6)
- 3.1 - Rule of GrammarDocument8 pagini3.1 - Rule of GrammarArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- En BW Colon HealthDocument86 paginiEn BW Colon HealthArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Technical Writing Deped Region SeminarDocument11 pagini1 Technical Writing Deped Region SeminarArman MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studies On in Vitro Culture Characteristics of Adherent Baby Hamster Kidney-21 (BHK-21) Cell LineDocument7 paginiStudies On in Vitro Culture Characteristics of Adherent Baby Hamster Kidney-21 (BHK-21) Cell LineNovena DpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On Control and CoordinationDocument27 paginiPresentation On Control and CoordinationKunal TolaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concepts of Biological ControlDocument8 paginiConcepts of Biological Controlखुशेन्द्र दाहालÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irinotecan - Topoisomerase PoisonDocument26 paginiIrinotecan - Topoisomerase PoisonAdam CoreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Section 2 OutlineDocument5 paginiChapter 7 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455051100% (1)
- 2-Substitution Matrices and Python - 2017Document65 pagini2-Substitution Matrices and Python - 2017Areej ZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology PAKMCQsDocument290 paginiBiology PAKMCQsMashooque AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Observing MitosisDocument3 paginiObserving MitosisAnonymous tlSLEPRReÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Microfluidic ConceptsDocument3 paginiBasic Microfluidic ConceptsKanika SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- March 2016 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CIE Biology A-LevelDocument16 paginiMarch 2016 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CIE Biology A-LevelSalman Farsi TaharatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-SDocument5 pagini6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-Sapi-502781581Încă nu există evaluări
- As Biology Coursework HelpDocument8 paginiAs Biology Coursework Helpafayeejka100% (2)
- Selective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsDocument7 paginiSelective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsRafael HelenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedure For Environmental Monitoring by Settle Plate MethodDocument2 paginiProcedure For Environmental Monitoring by Settle Plate Methodejazmaqsood100% (1)
- Deaf Mute PaperDocument11 paginiDeaf Mute PaperneviÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Klebsiella PneumoniaeDocument11 pagini2 Klebsiella PneumoniaeGhadah AlyousifÎncă nu există evaluări
- OHAP 11 Lab Guide Introduction To Human BodyDocument2 paginiOHAP 11 Lab Guide Introduction To Human BodyMad FromlifeuooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Organic Compounds Required in Small Quantities in DietDocument14 paginiEssential Organic Compounds Required in Small Quantities in DietSajia Abedin 1821432649Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetics - Student SampleDocument13 paginiGenetics - Student SampleMaria Isabel MorandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biofilms Review Questions - Fall 2019Document1 paginăBiofilms Review Questions - Fall 2019Abby KelleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics LabDocument5 paginiGenetics Labsyahidah nadiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolutionary Limits and Constraints: Ary HoffmannDocument6 paginiEvolutionary Limits and Constraints: Ary HoffmannIsaac BismonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patric Paul Msc-Biotechnology: ExperienceDocument4 paginiPatric Paul Msc-Biotechnology: ExperiencePatrick PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battling Beetles - STUDENTDocument11 paginiBattling Beetles - STUDENTHayden LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Exp 6Document6 paginiGenetics Exp 6Ck WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bioplastic A Bettter Alternative For Sustanable FutureDocument72 paginiBioplastic A Bettter Alternative For Sustanable FutureShanaiah Charice GanasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviews: Combating Osteoporosis and Obesity With Exercise: Leveraging Cell MechanosensitivityDocument17 paginiReviews: Combating Osteoporosis and Obesity With Exercise: Leveraging Cell MechanosensitivityThales ViníciusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine Physiology Lecture 2 Metabolic Clearance RatesDocument64 paginiEndocrine Physiology Lecture 2 Metabolic Clearance RatesHello SunshineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of EpidemiologyDocument40 paginiPrinciples of Epidemiologykhalid alatwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Answers: Chapter 12 Coordination and Response in HumansDocument5 paginiModel Answers: Chapter 12 Coordination and Response in HumansLaff IzzatulÎncă nu există evaluări