Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lab Experiment 08 BLEACHING
Încărcat de
Engr Mujahid MehdiDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lab Experiment 08 BLEACHING
Încărcat de
Engr Mujahid MehdiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lab Experiment 08
BLEACHING
Name:
Student Idi:
Score:
Signature of Lab tutor:
Dare:
BLEACHING OF 100%COTTON FABRIC BY CONTINUOUS METHOD
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
Upon the successful completion of this experiment students will be able to:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Understand the bleaching process
Understand role of auxiliaries used in this process
Understand the continuous bleaching process
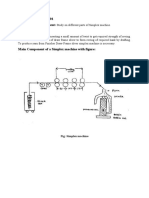
MACHINES/MATERIAL REQUIRED
Scoured fabric
Pad-steam machine
CHEMICAL REQUIRED
Hydrogen per Oxide
Caustic Soda
Stabilizer
Wetting Agent
Sequestering Agent
DISCUSSION
During the scouring of cotton impurities like fats, wax, proteins, pectins and ash is
removed. However, scouring does not remove natural color of cotton. It also does
not completely remove seed and husk. To remove natural color of the cotton and
seed fragment bleaching process follows the scouring. Sometimes both scouring
and bleaching are simultaneously carried out; the process is called solamatic
bleaching.
Cotton contain natural pigments called chlorophylls and xanthophylls, which
cause its color to be yellowish. In the process of bleaching these pigments are
removed from the cotton fiber. Along with these pigments seed fragments are
also removed. Thus bleaching accomplishes purification of the fiber.
1.
Hydrogen per Oxide (H202):
2.
Hydrogen per Oxide is comparatively expensive bleaching agent. But ,
beacause of ease of application, least threat for the substrate and
environment friendly nature, it is widely used for the removal of natural
pigments.
Sodium hypo-chlorite (NaOCl):
If the pH is not controlled during NaOCl bleaching, it will degrade
cellulose; because of the formation of the hypo-chlorous acid at neutral
pH (7) and liberation of chlorine gas at pH lower than 7. However, under
controlled condition, it may be suitable option.
3.
Sodium chlorite (NaClO2):
Sodium chlorite when used as bleaching agent produces chlorine dioxide
(event at controlled process), which is extremely toxic. At the same time,
it is extremely corrosive to the machinery because of this it is least
preferred bleaching agent.
Depending on the extent of bleaching, fabric may be said to be half bleached or
full bleached. In the half bleached fabric, some of the natural pigments are
removed and fabric yet contains chlorophyll and xanthophlls. However in case of
full bleached fabric, almost all natural pigments are removed. The removal of the
natural color of the cotton, its whiteness is increased. A normal bleached fabric
may achieve whiteness index of about 60 to 75 or sometimes 80.
Typical Recipe
Chemical
Liquor Ratio
Hydrogen per Oxide (35%)
Caustic soda (solid)
Sandoclean PC-LF (paste)
Quantity
Stabilizer SIFA (liquid)
MgCl2
PROCEDURE
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Prepare the bath according to recipe.
Pad the fabric at 80% pick up.
Steam ( saturated) the fabric for 20-30 min: at 102C.
Hot rinse at 80C-90C for 10 min:
Warm rinse at 60C for 10 min: and finally cold rinse for 5 minutes.
Calculations
S.N
O
Material
Fabric Weight
Total Liquor
Hydrogen per Oxide
Caustic Soda
Stabilizer
MgCl2
Sandoclean PC-LF
(paste)
Quantity
TEST REULTS
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. What is role of MgCl2 in H2O2 bleaching?
2. What are the advantages of continuous bleaching over exhaust bleaching
process?
3. What are reasons of foaming and how it can be avoided?
FINAL CHECK LEST
1. Clean your machinery equipment/ material and workbench before you
leave.
2. Ensure the replacement of all equipments to their specified storage area.
3. Submit your answer to questions together with your data, calculation and
results before the next laboratory/ equipment.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Bobtex Spinning ProcessDocument8 paginiBobtex Spinning Processvermadeen0% (1)
- Yarn Manufacturing Technology Lab-1 (TXE 206) Final Exam SolutionDocument16 paginiYarn Manufacturing Technology Lab-1 (TXE 206) Final Exam SolutionAlif SheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Desizing Cotton Fabric by Using Acid-1Document2 paginiStudy On Desizing Cotton Fabric by Using Acid-1Mr RiyadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textile Science - Session 3Document35 paginiTextile Science - Session 3ALOK KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textiles - DiplomaDocument9 paginiTextiles - DiplomamansiagrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SelvedgeDocument16 paginiSelvedgejony_nsu022Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Properties of Textile Fiber Introduction of Thermal PropertyDocument6 paginiThermal Properties of Textile Fiber Introduction of Thermal PropertyRashedul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Crease Recovery Test by Crease Recovery Angle Tester.Document5 paginiStudy On Crease Recovery Test by Crease Recovery Angle Tester.Naimul Hasan100% (1)
- Assignment Base On: Study On Some Fabric Faults During Processing.Document5 paginiAssignment Base On: Study On Some Fabric Faults During Processing.MD Nazrul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is AutolevellerDocument3 paginiWhat Is AutolevellersafiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yarn AssignmentDocument10 paginiYarn AssignmentHIMASHA SAMARANAYAKAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title of The Project ThesisDocument87 paginiTitle of The Project ThesisIrfan IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raymond UCO DenimDocument25 paginiRaymond UCO DenimChaitanya Gajbhiye100% (1)
- Wool FinishingDocument32 paginiWool Finishingkv100% (1)
- Mechanical FinishingDocument23 paginiMechanical Finishingmahes_texÎncă nu există evaluări
- RefrigerationDocument19 paginiRefrigerationDDCMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shed Geometry ElementsDocument21 paginiShed Geometry ElementsMuhammad Ahsan Mir100% (3)
- Patterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafDocument33 paginiPatterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafHifza khalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering of Textile StructureDocument3 paginiEngineering of Textile Structurerohit sinha100% (1)
- 2nd Lab ReportDocument13 pagini2nd Lab Reportali hasan100% (1)
- Weft Knitting PrincipleDocument11 paginiWeft Knitting PrincipleTamanna AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - IiDocument27 paginiUnit - IiJoseph KuruvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Jersey FabricDocument4 paginiSingle Jersey FabricMrcr Kapzap0% (1)
- Practical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningDocument5 paginiPractical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningTalha saeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fully FashionDocument30 paginiFully FashiondewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weft Knitting PDFDocument64 paginiWeft Knitting PDFBala SaravananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yarn Lab ReportDocument6 paginiYarn Lab ReportYeasin ArafatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3D Woven FabricDocument9 pagini3D Woven FabricCrystal NewmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Weft Knitted Jersey FabricDocument6 paginiAnalysis of Weft Knitted Jersey FabricNaimul HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bobtex Spinning TechnologyDocument13 paginiBobtex Spinning Technologychinmay566679950% (1)
- Mercerizing Cellulosic Fibres & Its EffectsDocument5 paginiMercerizing Cellulosic Fibres & Its EffectsMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- FalseDocument8 paginiFalseShailendra MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textile Engineering FYPDocument61 paginiTextile Engineering FYPUsama100% (1)
- Study On Multiphase Weaving Machine.Document11 paginiStudy On Multiphase Weaving Machine.Naimul Hasan100% (1)
- Pattern and Selection DevicesDocument18 paginiPattern and Selection DevicesAtaur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabric Formation ProcessesDocument14 paginiFabric Formation ProcessesYOghi PRatamadseecxerzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Operations in The BlowroomDocument7 paginiBasic Operations in The BlowroomVikrant KanugondaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect On Tensile Strength After WashingDocument130 paginiEffect On Tensile Strength After WashingHarmendar S Kothari100% (1)
- Wet Processing 1Document47 paginiWet Processing 1Rahul ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stitch and Roll Ubd 2016Document10 paginiStitch and Roll Ubd 2016api-246063232Încă nu există evaluări
- 1ci3pqr1q 814635Document5 pagini1ci3pqr1q 814635Santosh50% (2)
- MercerisationDocument18 paginiMercerisationVarun Mehrotra0% (1)
- What Is Sectional Warping?: Creel Drum BeamDocument6 paginiWhat Is Sectional Warping?: Creel Drum Beamamar9247Încă nu există evaluări
- To Calculate The Count of Given Samples of Lap, Sliver, Roving and Yarn.Document2 paginiTo Calculate The Count of Given Samples of Lap, Sliver, Roving and Yarn.Ammar Naeem BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ornamantation in SelvagesDocument18 paginiOrnamantation in SelvagesSatish Kulkarni100% (1)
- Textile Chemical Processing 1stDocument171 paginiTextile Chemical Processing 1stAhmad ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Jute / Cotton Blended Garment For Winter Wear By: B. Sathish BabuDocument31 paginiDevelopment of Jute / Cotton Blended Garment For Winter Wear By: B. Sathish BabuAjaz Banna100% (1)
- Crimp in Textile TestingDocument8 paginiCrimp in Textile TestingAhasn HabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Introduction of Sizing / Warping / WeavingDocument14 paginiShort Introduction of Sizing / Warping / WeavingAmir YasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02+yarn InspectionDocument24 pagini02+yarn InspectionAnand DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dying of Cotton Fabric With Azoic Dye.Document6 paginiDying of Cotton Fabric With Azoic Dye.Redwan Ibn MahbubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cut & Sew Knit WearDocument4 paginiCut & Sew Knit WearshponÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved QP of Knit Tech April 2023Document4 paginiSolved QP of Knit Tech April 2023RajendrakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary MotionsDocument59 paginiPrimary Motionsafroja hossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- SpinningDocument8 paginiSpinningAishee BhowmickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDe la EverandCarr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDavid J. TylerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Indus University: Department: Bs TextileDocument1 paginăIndus University: Department: Bs TextileEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre TreatmentDocument2 paginiPre TreatmentEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Colloid and Interface Science: Xiaodong Zhang, Fu-Gen Wu, Peidang Liu, Hong-Yin Wang, Ning Gu, Zhan ChenDocument10 paginiJournal of Colloid and Interface Science: Xiaodong Zhang, Fu-Gen Wu, Peidang Liu, Hong-Yin Wang, Ning Gu, Zhan ChenEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment 13 PH of FABRICDocument3 paginiLab Experiment 13 PH of FABRICEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter Head For Khalil 1Document3 paginiLetter Head For Khalil 1Engr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Result of Mill Engineering (Lab) BS-3 Semester EveningDocument2 paginiResult of Mill Engineering (Lab) BS-3 Semester EveningEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment 11 Whitness IndexDocument3 paginiLab Experiment 11 Whitness IndexEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment 06: To Determine The Co-Efficient of Static Friction of A Fabric On An Inclined Stainless Steel PlaneDocument4 paginiLab Experiment 06: To Determine The Co-Efficient of Static Friction of A Fabric On An Inclined Stainless Steel PlaneEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment of Textile Mechanics (Lab) BS-4 Semester EveningDocument1 paginăAssignment of Textile Mechanics (Lab) BS-4 Semester EveningEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment 14: To Study The Power Transfer in The Picking System of Rapier Weaving LoomDocument3 paginiLab Experiment 14: To Study The Power Transfer in The Picking System of Rapier Weaving LoomEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 08Document3 paginiLab 08Engr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 10Document3 paginiLab 10Engr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment 14: To Study The Power Transfer in The Picking System of Rapier Weaving LoomDocument3 paginiLab Experiment 14: To Study The Power Transfer in The Picking System of Rapier Weaving LoomEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 13Document3 paginiLab 13Engr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Determine The Linear Velocity of Fabric Running Through The PadderDocument3 paginiTo Determine The Linear Velocity of Fabric Running Through The PadderEngr Mujahid MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring AlkesDocument41 paginiMonitoring AlkesEndangMiryaningAstutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Assignment Nuclear ChemistryDocument2 paginiReading Assignment Nuclear Chemistryapi-249441006Încă nu există evaluări
- Subquery ProblemDocument9 paginiSubquery ProblemAbhi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indiana Administrative CodeDocument176 paginiIndiana Administrative CodeMd Mamunur RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- SET 2022 Gstr1Document1 paginăSET 2022 Gstr1birpal singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- C 1 WorkbookDocument101 paginiC 1 WorkbookGeraldineÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Benefits of RunningDocument1 paginăThe Benefits of Runningefendi odidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini Project 2Document9 paginiMini Project 2gunjan_pattnayak2007Încă nu există evaluări
- High School Students' Attributions About Success and Failure in Physics.Document6 paginiHigh School Students' Attributions About Success and Failure in Physics.Zeynep Tuğba KahyaoğluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised List of Maharashtra HospitalsDocument16 paginiRevised List of Maharashtra Hospitalsdummy data100% (1)
- ICSE Class 10 HRJUDSK/Question Paper 2020: (Two Hours)Document9 paginiICSE Class 10 HRJUDSK/Question Paper 2020: (Two Hours)Harshu KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gloria Pfoltzer Theresa Morris, an Infant, by Mother and Next Friend Christopher Morris, an Infant, by Mother and Next Friend Randy Morris, an Infant, by Mother and Next Friend v. Fairfax County Department of Human Development Susan Manzo Paulette Byrd Florence Hannigan, and Louis Villafane, 966 F.2d 1443, 4th Cir. (1992)Document10 paginiGloria Pfoltzer Theresa Morris, an Infant, by Mother and Next Friend Christopher Morris, an Infant, by Mother and Next Friend Randy Morris, an Infant, by Mother and Next Friend v. Fairfax County Department of Human Development Susan Manzo Paulette Byrd Florence Hannigan, and Louis Villafane, 966 F.2d 1443, 4th Cir. (1992)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- S:/admin/mpi/MP1169 - Amaia Skies Samat/000 - ACTIVE DOCUMENTS/09 - SPECS/2013-07-23 - Design Development/04-Plumbing/15050Document19 paginiS:/admin/mpi/MP1169 - Amaia Skies Samat/000 - ACTIVE DOCUMENTS/09 - SPECS/2013-07-23 - Design Development/04-Plumbing/15050Lui TCC BariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2: Loan Submission For Equipment FinanceDocument6 paginiAssignment 2: Loan Submission For Equipment FinanceIT'S SIMPLEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drill Site Audit ChecklistDocument5 paginiDrill Site Audit ChecklistKristian BohorqzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arann Magazine, Issue 1-2-Online VersionDocument36 paginiArann Magazine, Issue 1-2-Online VersionmujismileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ransport and Installation Instructions CTX 510 EcoDocument32 paginiRansport and Installation Instructions CTX 510 EcoMiliano FilhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mapeh 9 Aho Q2W1Document8 paginiMapeh 9 Aho Q2W1Trisha Joy Paine TabucolÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSB 3441 CH 1 HallucinogensDocument2 paginiPSB 3441 CH 1 HallucinogensAnonymous lm3GIU45Încă nu există evaluări
- AppendicitisDocument7 paginiAppendicitisTim LuoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studovaný Okruh: Physical Therapist Sample Test Questions (G5+)Document8 paginiStudovaný Okruh: Physical Therapist Sample Test Questions (G5+)AndreeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AQ-101 Arc Flash ProtectionDocument4 paginiAQ-101 Arc Flash ProtectionYvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 9 Organic Law On Provincial and Local-Level Government (OLPLLG) - SlidesDocument29 paginiUnit 9 Organic Law On Provincial and Local-Level Government (OLPLLG) - SlidesMark DemÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.0 Ms For Scaffolding WorksDocument7 pagini10.0 Ms For Scaffolding WorksilliasuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation - Factors Affecting ClimateDocument16 paginiPresentation - Factors Affecting ClimateAltoverosDihsarlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Lombe Mumba Ramson 2017 Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Breast Self Examination For Early Detectoin of Breast Cancer Among Women in Roan Constituency in Luanshya Copperbelt Province ZambiaDocument9 pagini13 Lombe Mumba Ramson 2017 Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Breast Self Examination For Early Detectoin of Breast Cancer Among Women in Roan Constituency in Luanshya Copperbelt Province ZambiaArick Frendi AndriyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PaintballDocument44 paginiPaintballGmsnm Usp MpÎncă nu există evaluări
- People vs. MediosDocument10 paginiPeople vs. MediostheresagriggsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sedation and Analgesia in Critically Ill Neurologic PatientsDocument24 paginiSedation and Analgesia in Critically Ill Neurologic PatientsrazaksoedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recipe: Patisserie Method: Eclair Cake RecipeDocument3 paginiRecipe: Patisserie Method: Eclair Cake RecipeEisha BibiÎncă nu există evaluări