Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Left Circumflex Artery-Right Atrium Fistula Demonstrated by Transthoracic Echocardiography
Încărcat de
Peertechz Publications Inc.Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Left Circumflex Artery-Right Atrium Fistula Demonstrated by Transthoracic Echocardiography
Încărcat de
Peertechz Publications Inc.Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Imaging Journal of Clinical and Medical Sciences
Clinical Image
Left Circumflex ArteryRight Atrium Fistula
Demonstrated By Transthoracic Echocardiography
Rahul Choudhary*, Vijay Pathak, Vimla Kumari and Dinesh Gautam
Department of Cardiology, Sawai Man Singh Medical college, Jaipur and 2 Dr SN Medical College, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India
*Corresponding author: Rahul Choudhary, Department of Cardiology, Sawai Man Singh Medical college, Jaipur and 2 Dr SN Medical College, Jodhpur,
Rajasthan, India. E-mail:
Received: 09 December, 2015; Accepted: 11 January, 2016; Published: 25 January, 2016
Clinical Image
Eight year-old child presented with two year history of dyspnoea
on exertion. Clinical examination revealed a continuous murmur
peaking in diastole. Two dimensional transthoracic echocardiography
revealed a dilated left circumflex artery (LCX) in parasternal short
axis view with enlarged right atrium (RA) and right ventricle (Figures
1A,B). Apical four chamber view demonstrated fistulous flow from
LCX to RA (Figures 1C,D, arrows); flow travelled initially in left
atrioventricular groove and then along inter-atrial septum before
opening into RA near its superior wall (Movie 1).
Coronary cameral fistulae are rare congenital vascular anomalies
that present largely as asymptomatic, incidental findings on
imaging studies [1,2]. Coronary angiography has traditionally been
used to diagnose coronary artery fistula. With the advent of highresolution two-dimensional and colour Doppler echocardiography,
the accurate detection of coronary artery fistula has increased
[3]. Echocardiographic evidence of coronary-cameral fistula is
continuous flow from the epicardial surface into the RA cavity on
colour Doppler imaging.
References
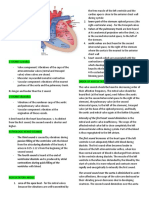
Figure 1: A and B. Parasternal short axis view showing dilated left circumflex
artery (LCX) and enlarged right atrium (RA). C and D. Apical four chamber
view showing fistulous flow from LCX to RA (arrow).
(Ao,Aorta; LA,left atria; LCx.left circumflex artery; LV,left ventricle; RA.right
atria; RV, right ventricle; RVOT,right ventricular outflow tract).
1. Friedman W, Silverman N (2001) Congenital heart disease in infancy
and childhood. In : Braunwald E, Editor, Heart disease, A textbook of
cardiovascular medicine. Ed 6, Philadelphia, WB saunders 1505-1591.
2. Vavuranakis M, Bush CA, Boudoulas H (1995) Coronary artery fistulas in
adults: incidence, angiographic characteristics, natural history. Cathet
Cardiovasc Diagn 35: 116120.
3. Barbosa MM, Katina T, Oliveira HG, Neuenschwander FE, Oliveira EC (1999)
Doppler echocardiographic features of coronary artery fistula: Report of 8
cases. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 12: 149-154.
Movie 1
Copyright: 2016 Choudhary R, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits
unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: Choudhary R, Pathak V, Kumari V, Gautam D (2016) Left Circumflex ArteryRight Atrium Fistula Demonstrated By Transthoracic Echocardiography.
Imaging J Clin Med Sciences 3(1): 001.
01
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Study On Improvement of Manpower Performance & Safety in Construction FirmsDocument5 paginiStudy On Improvement of Manpower Performance & Safety in Construction FirmsPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- COMAMMOX - A New Pathway in The Nitrogen Cycle in Wastewater Treatment PlantsDocument3 paginiCOMAMMOX - A New Pathway in The Nitrogen Cycle in Wastewater Treatment PlantsPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Should National Environmental Policy Focus On Developing More Oil Resources or Developing Renewable Energy Sources?Document3 paginiShould National Environmental Policy Focus On Developing More Oil Resources or Developing Renewable Energy Sources?Peertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- A Survey of Solid Waste Management in Chennai (A Case Study of Around Koyambedu Market and Madhavaram Poultry Farms)Document4 paginiA Survey of Solid Waste Management in Chennai (A Case Study of Around Koyambedu Market and Madhavaram Poultry Farms)Peertechz Publications Inc.100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- User Response - Based Sustainable Solutions To Traffic Congestion Problem Using Public Transport: The Case of Uttara, DhakaDocument7 paginiUser Response - Based Sustainable Solutions To Traffic Congestion Problem Using Public Transport: The Case of Uttara, DhakaPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Modulation of Immune Response in Edible Fish Against Aeromonas HydrophilaDocument5 paginiModulation of Immune Response in Edible Fish Against Aeromonas HydrophilaPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Comparative Analysis of Collapse Loads of Slabs Supported On Orthogonal Sided Frames With Beam/column Joint FixedDocument7 paginiComparative Analysis of Collapse Loads of Slabs Supported On Orthogonal Sided Frames With Beam/column Joint FixedPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Perceptive Journey Through PostmodernismDocument4 paginiA Perceptive Journey Through PostmodernismPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Role of Decavanadate in Anti - Tumour ActivityDocument3 paginiThe Role of Decavanadate in Anti - Tumour ActivityPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Diagnosing HPV-Related Oropharyngeal Cancers: The Need To Speak A Common LanguageDocument4 paginiDiagnosing HPV-Related Oropharyngeal Cancers: The Need To Speak A Common LanguagePeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Is It Time For The Introduction of Colostomy Free Survival in Rectal Cancer PatientsDocument4 paginiIs It Time For The Introduction of Colostomy Free Survival in Rectal Cancer PatientsPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Primary Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma of Prostate: A Case Report With Review of LiteratureDocument3 paginiPrimary Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma of Prostate: A Case Report With Review of LiteraturePeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Promise of Disease Management in GreeceDocument8 paginiThe Promise of Disease Management in GreecePeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Abrikossoff's Tumour Mimicking A Neoplastic Tumour of The Breast: A Case ReportDocument3 paginiAbrikossoff's Tumour Mimicking A Neoplastic Tumour of The Breast: A Case ReportPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Body Mass Index Impact and Predictability On Preeclamptic ToxemiaDocument6 paginiBody Mass Index Impact and Predictability On Preeclamptic ToxemiaPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Bacterial Vaginosis: Risk of Adverse Pregnancy OutcomeDocument3 paginiBacterial Vaginosis: Risk of Adverse Pregnancy OutcomePeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Role of Tumor Heterogeneity in Drug ResistanceDocument2 paginiRole of Tumor Heterogeneity in Drug ResistancePeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Angiosarcoma of The Scalp and Face: A Hard To Treat TumorDocument4 paginiAngiosarcoma of The Scalp and Face: A Hard To Treat TumorPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- MEK Inhibitors in Combination With Immune Checkpoint Inhibition: Should We Be Chasing Colorectal Cancer or The KRAS Mutant CancerDocument2 paginiMEK Inhibitors in Combination With Immune Checkpoint Inhibition: Should We Be Chasing Colorectal Cancer or The KRAS Mutant CancerPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Video Endoscopic Inguinal Lymphadenectomy: Refi Ning Surgical Technique After Ten Years ExperienceDocument4 paginiVideo Endoscopic Inguinal Lymphadenectomy: Refi Ning Surgical Technique After Ten Years ExperiencePeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Outcomes of Postoperative Total Hip Arthroplasty Following Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) : A Prospective StudyDocument6 paginiThe Outcomes of Postoperative Total Hip Arthroplasty Following Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) : A Prospective StudyPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- PLGF, sFlt-1 and sFlt-1/PlGF Ratio: Promising Markers For Predicting Pre-EclampsiaDocument6 paginiPLGF, sFlt-1 and sFlt-1/PlGF Ratio: Promising Markers For Predicting Pre-EclampsiaPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating Mechanical Ventilation in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument5 paginiEvaluating Mechanical Ventilation in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromePeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Steroid Withdrawal Protocols in Renal TransplantationDocument8 paginiSteroid Withdrawal Protocols in Renal TransplantationPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- An Overview: Laboratory Safety and Work Practices in Infectious Disease ResearchDocument6 paginiAn Overview: Laboratory Safety and Work Practices in Infectious Disease ResearchPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Outcomes of Postoperative Total Hip Arthroplasty Following Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) : A Prospective StudyDocument6 paginiThe Outcomes of Postoperative Total Hip Arthroplasty Following Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) : A Prospective StudyPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- An Overview: Laboratory Safety and Work Practices in Infectious Disease ResearchDocument6 paginiAn Overview: Laboratory Safety and Work Practices in Infectious Disease ResearchPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Echinocandins and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapies: The Role of AdsorptionDocument3 paginiEchinocandins and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapies: The Role of AdsorptionPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Exercise-Induced Time-Dependent Changes in Plasma BDNF Levels in People With SchizophreniaDocument6 paginiExercise-Induced Time-Dependent Changes in Plasma BDNF Levels in People With SchizophreniaPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Exercise-Induced Time-Dependent Changes in Plasma BDNF Levels in People With SchizophreniaDocument6 paginiExercise-Induced Time-Dependent Changes in Plasma BDNF Levels in People With SchizophreniaPeertechz Publications Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- PacemakersDocument13 paginiPacemakersNader Smadi100% (2)
- Auscultation - Cardiac - Learning Cardiac Auscultation From Essentials To Expert Clinical Interpretation 1st Ed2015Document428 paginiAuscultation - Cardiac - Learning Cardiac Auscultation From Essentials To Expert Clinical Interpretation 1st Ed2015programgrabberÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Dog Encyclopedia (VetBooks - Ir)Document362 paginiThe Dog Encyclopedia (VetBooks - Ir)miki122295% (22)
- MRI in NSTEMI N STEMIDocument11 paginiMRI in NSTEMI N STEMIBenjamin GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Vertebrate Is Any Chordate That Has ADocument7 paginiA Vertebrate Is Any Chordate That Has AomariaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature Pulse + RespirationsDocument2 paginiTemperature Pulse + RespirationsMarshin Thea Celocia100% (1)
- ESC Arterial Hypertension 2018Document98 paginiESC Arterial Hypertension 2018ddantoniusgmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pijat Kaki THD HipertensiDocument8 paginiPijat Kaki THD Hipertensidedi wahyudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lutembacher SyndromeDocument12 paginiLutembacher SyndromeDiany LarasatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- A Coronary Angiogram Is A Procedure That Uses XDocument5 paginiA Coronary Angiogram Is A Procedure That Uses XSathya PatcheappinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument2 paginiValvular Heart DiseaseAnonymous TVk12eX4Încă nu există evaluări
- What Keeps The Blood Moving!Document25 paginiWhat Keeps The Blood Moving!mikeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Surgical Anatomy of The HeartDocument79 pagini4 Surgical Anatomy of The HeartKacper DaraszkiewiczÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Heart - Print - QuizizzDocument5 paginiThe Heart - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Unit 5-Heart QuestionsDocument37 paginiUnit 5-Heart Questionsareyouthere92100% (1)
- CP On Pre-EclampsiaDocument152 paginiCP On Pre-Eclampsiakathy100% (2)
- GCE Biology-Human Biology-Teachers' Guide Revised 18-02-14 PDFDocument93 paginiGCE Biology-Human Biology-Teachers' Guide Revised 18-02-14 PDFTara MillsÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Lecture Notes EuropeanDocument906 paginiAll Lecture Notes Europeanabdul100% (1)
- DudjDocument4 paginiDudjsyaiful rinantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Output Monitoring PDFDocument9 paginiCardiac Output Monitoring PDFJAIDY CARRILLO SOTOMAYORÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 paginiNursing Care Planaln00550% (2)
- Metabolism NotesDocument208 paginiMetabolism Notesbairdman89Încă nu există evaluări
- Atrioventricular Conduction AbnormalitiesDocument11 paginiAtrioventricular Conduction AbnormalitiesRaul OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Sounds:: The Third Sound Is Caused by Vibrations During Passive Filling of The Ventricles With The BloodDocument2 paginiHeart Sounds:: The Third Sound Is Caused by Vibrations During Passive Filling of The Ventricles With The BloodShmuel BarshalomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System - Multiple Choice TestDocument2 paginiCirculatory System - Multiple Choice Testkirki pÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Basic Circulatory SystemDocument44 paginiBest Basic Circulatory SystemJerilee SoCute WattsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aortic Valve Stenosis A D A7Document15 paginiAortic Valve Stenosis A D A7Ahmed DsoukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Keep Your Brain HealthyDocument3 paginiHow To Keep Your Brain HealthySyahidah IzzatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 - Diretrizes CMD (European Society of Veterinary Cardiology)Document11 pagini2017 - Diretrizes CMD (European Society of Veterinary Cardiology)Flávia PinheiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutia Sukma Dewi 2010.04.0.0142 (Jurnal) PDFDocument12 paginiMutia Sukma Dewi 2010.04.0.0142 (Jurnal) PDFmutiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (28)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDe la EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDe la EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDe la EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (404)