Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MNP Concept
Încărcat de
mtawritDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MNP Concept
Încărcat de
mtawritDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Mobile Number Portability Concept
HIGH LEVEL NETWORK ARCHITECTURE FOR MNP SOLUTION
Fig 1 shows high level network architecture and network components for MNP solution. On high level, complete network can be visualized
into two parts:
Central Side- MNPO ( Mobile Number Portability Operator)
The central side is a MNPO, supposed to provide MNP Service in a particular zone. It is also called MNP Clearing House (MCH). MCH
shall receive mobile number portability requests from the recipient operator; forward it to the donor operator for verification. On getting
clearance from donor operator MNP service provider shall control and coordinate the mobile number portability process. At a
predetermined date and time the MNP service provider will instruct the donor operator to disconnect the mobile number of the subscriber
and upon receiving confirmation of such effect shall instruct the recipient operator to activate the mobile number of the subscriber. Once the
mobile number is activated at the recipient operators end, the MCH will send the details of the porting to the centralised Number Portability
Database (NPDB) which in turn will update its own database by an appropriate routing number called Location Routing Number (LRN), a
unique routing number assigned to each operator in a service area by the DoT. This updation will be communicated by the NPDB to all the
service
providers
for
updating
their
respective
local
Number
Portability
database.
MNP Service provider has to deploy its system (network) in redundant way as shown in figure in two different geographical areas, one as a
production site and another as a disaster recovery site to avoid interruption in service due to failure of one site. Both side must be in sync
and work in active redundant mode.
Types of Number Portability :The various types of number portability are:
Service Provider Number Portability: Subscribers can change the service provider while retaining the same phone number It is also called
operator portability.
Location Number Portability: Subscribers can change their service location while keeping the same mobile telephone number.
Service Portability: Subscribers can change the subscribed services while retaining the same telephone number. It allows the subscribers
to enjoy the subscribed services in the same way when they roam outside their home networks.
Concept
:-
MNP functionality is used only in MT (Mobile Terminating) transactions of voice and messaging. For MO (Mobile Originating) transactions, the
current
flow
scenario
remains
unchanged.
Only for the MT functionality, the mobile number has to be identified and the corresponding service provider has to be interrogated for optimal
routing of the service.
Basic Terms :
Ported out If a subscriber moves to new service provider, for the old service provider, he is a ported out subscriber.
Ported in If a subscriber moves to new service provider, for the new service provider, he is a ported in subscriber.
Donor The service provider left by the subscriber. OR It is the network that first assigns a telephone number to a
subscriber
Recipient The service provider joined by the subscriber. OR It is the network that currently serves the ported number.
A recipient network is a network that a subscribers number is ported to when the subscriber switches the service
provider.
Old Serving Network The old serving network is the network that previously served the ported number before the
number was ported to the new serving network. Since a subscriber can switch
service provider any number of times, the old service provider is not necessarily the same as the donor network.
Participant A Participant is a service provider who is not related to the porting process in any way and still needs the
routing information for call routing and various other activities.
CDB / NPDB Central Database or Number Portability Database.
ACQ All Call Query
There are two basic implementation of MNP.
Indirect Routing or decentralized or bilateral
architecture:
This model works bilaterally between the donor and
recipient service providers who are responsible for
informing all others of the change. It would suit to markets
with less number of service providers. Each provider
will have a dedicated setup and comprehensive database of
ported out and ported in subscribers. As the number of
service providers increases, the bilateral approach becomes
a great burden to all service providers involved in terms of
time, cost and resources. FNR (Flexible Number Register)
will help the service providers have the ported database in
addition to the original HLR database.
Direct Routing or centralized architecture:
In direct routing, the concept of CDB comes into picture. This central
database or Central clearing house will handle all activities related to
porting of subscribers between service providers. This model is suited
for markets with several service providers and this model is currently
used almost in all MNP implementations. Two options are available
with this model with all the service providers updating the ported
number database in synchronization with the CDB and the other is to
query the CDB for all call interrogation to get proper routing
procedure. After obtaining the rules, rest of the call is handled
normally.
Call Routing Schemes :There are 4 schemes of call routing that support number portability.
All Call Query (ACQ) Most Efficient (No dependency on other network for routing the call, Easy Billing, Minimum Call
Set-Up Time, Minimal Impact on Signaling, Impact on network complexity is very less, etc.)
Query on Release (QoR).
Call Dropback.
Onward Routing (OR) Least Efficient.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyDe la EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile Number Portability - Theory, Introduction and Types of Solutions AvailableDocument5 paginiMobile Number Portability - Theory, Introduction and Types of Solutions AvailableKalaarangan100% (1)
- Technical, Commercial and Regulatory Challenges of QoS: An Internet Service Model PerspectiveDe la EverandTechnical, Commercial and Regulatory Challenges of QoS: An Internet Service Model PerspectiveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile-Number-Portability FinalDocument24 paginiMobile-Number-Portability Finalpradeep_sharma_1867% (3)
- Call Flow at MNP ScenarioDocument22 paginiCall Flow at MNP Scenariosayan_choudhury8193Încă nu există evaluări
- Amdocs BillingDocument7 paginiAmdocs BillingArvind ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyDe la EverandMobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Application Visibility Library (NAVL)Document2 paginiNetwork Application Visibility Library (NAVL)IsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GPRSDocument14 paginiGPRSRuhisha AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3: GSM Roaming Scenarios and HandoverDocument53 paginiUnit 3: GSM Roaming Scenarios and HandoverLanku J GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkDe la EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- Learn SoRDocument8 paginiLearn SoRRasheedKhouliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Error Information UDTS v0.2Document23 paginiDetailed Error Information UDTS v0.2Anonymous Ie0oEXP2eÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEs and Their KPIs (HSS)Document19 paginiNEs and Their KPIs (HSS)m.alnabhani9097Încă nu există evaluări
- Network Slicing and Performance Analysis of 5g Networks Based On PriorityDocument5 paginiNetwork Slicing and Performance Analysis of 5g Networks Based On Priorityzayyanu yunusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wight Paper DpiDocument17 paginiWight Paper DpiradislamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2g 3g WLL Cellular ConceptDocument39 pagini2g 3g WLL Cellular ConceptVinod KumbharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To QoSConceptsDocument48 paginiIntroduction To QoSConceptsIvica PutrićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Call FlowDocument30 paginiCall Flownaveedraza4213Încă nu există evaluări
- Mobile Number PortabilityDocument44 paginiMobile Number PortabilityJatinChadhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCAPDocument70 paginiTCAPSanghamitra Roy ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nokia Solutions and Networks Information Browser Installation and Setup ...Document16 paginiNokia Solutions and Networks Information Browser Installation and Setup ...jrashev50% (2)
- Vietnam Telecommunications ReportDocument41 paginiVietnam Telecommunications ReportQuoc Tuan TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handover Interfaces For Lawful InterceptionDocument271 paginiHandover Interfaces For Lawful InterceptionMarco LushangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5G Wireless Technology: SeminarDocument22 pagini5G Wireless Technology: SeminarBhagavan ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Missed Call SolutionDocument2 paginiMissed Call Solutionsuman_123Încă nu există evaluări
- HW Sandvine Ds Packetlogic 15000Document4 paginiHW Sandvine Ds Packetlogic 15000Asif Majeed MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- In-Building Wireless Infrastructure Solutions: D-RAN Rate Card and eRAN Concept StudyDocument30 paginiIn-Building Wireless Infrastructure Solutions: D-RAN Rate Card and eRAN Concept StudyDaniel RoureÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTE eNB L1 API DefinitionDocument106 paginiLTE eNB L1 API Definitioneng_alshimaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMART Communications, Inc.: SystraDocument50 paginiSMART Communications, Inc.: SystraKausik RaychaudhuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Camel PPSDocument82 paginiCamel PPSmugeshpv90Încă nu există evaluări
- 06) GSM Radio ParametersDocument56 pagini06) GSM Radio ParametersalfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers:: Ans: (B) (B) It Point To The Next InstructionDocument13 paginiAnswers:: Ans: (B) (B) It Point To The Next InstructionronyiutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample DiameterDocument42 paginiSample DiameterAnonymous gJHAwzEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco - Interview Docs QuestionsDocument3 paginiCisco - Interview Docs QuestionsmandeepmailsÎncă nu există evaluări
- TN - SA001 - E1 - 0 Digital Number Analysis-76Document70 paginiTN - SA001 - E1 - 0 Digital Number Analysis-76CoachArun MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM MO Call FlowDocument16 paginiGSM MO Call FlowVenkanna Annam100% (1)
- Lte Network ArchitectureDocument28 paginiLte Network ArchitectureJagannath ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAN 3G Interfaces+ProtocolsDocument15 paginiRAN 3G Interfaces+ProtocolsTushar SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Theme 3 CamelDocument47 paginiStudy Theme 3 CamelMohammed AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobileum - Brochure ROAMING CEMDocument4 paginiMobileum - Brochure ROAMING CEMMarko100% (1)
- GSM Key Performance Indicator KPI Guidebook: Security Category: Secret Serviceable Range: Radio Planning SectionDocument13 paginiGSM Key Performance Indicator KPI Guidebook: Security Category: Secret Serviceable Range: Radio Planning SectionjohnsonsemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Network SymbolDocument4 paginiComputer Network SymbolaziraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3g 4g Call FlowDocument16 pagini3g 4g Call Flowpoiuytreza26Încă nu există evaluări
- Application SMSCDocument22 paginiApplication SMSComjaijagdish.raiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AccessControlBarring in LTEDocument12 paginiAccessControlBarring in LTEAngela BarrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nokia Solutions and Networks Flexi Zone: LiquidnetDocument4 paginiNokia Solutions and Networks Flexi Zone: Liquidnetcp_gautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Call Flow PSDocument20 paginiCall Flow PSBhaskar KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Network BandwidthDocument6 paginiManaging Network Bandwidthamos_eva100% (1)
- GSM Network SignallingDocument59 paginiGSM Network SignallingAbdullah AbidÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Word FileDocument11 paginiGSM Word FileevilanubhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD 13100Document16 paginiTD 13100Lilantha Lakmal GallabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAPDocument20 paginiCAPDeepak JammyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08-GSM Radio Network Optimization Guide ManualDocument124 pagini08-GSM Radio Network Optimization Guide ManualCatherine RyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Saturation: Effects, Caveats, and Issues Encountered in Testing SIP ServersDocument9 paginiTesting Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Saturation: Effects, Caveats, and Issues Encountered in Testing SIP ServersChalla VaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetHawk M5 Analyser Vs Wireshark OverviewDocument23 paginiNetHawk M5 Analyser Vs Wireshark OverviewHa Dinh ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- EduRoam 07102017 v3.0Document17 paginiEduRoam 07102017 v3.0mtawritÎncă nu există evaluări
- MNP SolutionDocument6 paginiMNP SolutionmtawritÎncă nu există evaluări
- One-MNP 16 DatasheetDocument4 paginiOne-MNP 16 DatasheetmtawritÎncă nu există evaluări
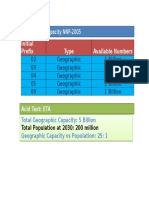
- Geographic Capacity NNP-2005: Initial Prefix Type Available NumbersDocument1 paginăGeographic Capacity NNP-2005: Initial Prefix Type Available NumbersmtawritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number Portability v2.0Document34 paginiNumber Portability v2.0mtawritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To SDHDocument44 paginiIntroduction To SDHCaring PankajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Guide Vm134-k8076 UkDocument16 paginiQuick Guide Vm134-k8076 UkCapsule CorpÎncă nu există evaluări
- NT11 NT21: Programmable TerminalsDocument4 paginiNT11 NT21: Programmable TerminalsSetija BudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV Agung Permana (Juni 2019)Document1 paginăCV Agung Permana (Juni 2019)Agung PermanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Word DocumentDocument17 paginiMicrosoft Word DocumentJeannand MarcialÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAB - 1st Quarter - Project BasisDocument38 paginiRAB - 1st Quarter - Project BasisPedro Lazaro O. PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COBOL Basics Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument2 paginiCOBOL Basics Questions and Answers - SanfoundryHarshu PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-II Array, Functions and StringDocument34 paginiUNIT-II Array, Functions and Stringvilasrao DeshmukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cake - Classifying, Associating & Knowledge Discovery An Approach For Distributed Data Mining (DDM) Using Parallel Data Mining Agents (Padmas)Document6 paginiCake - Classifying, Associating & Knowledge Discovery An Approach For Distributed Data Mining (DDM) Using Parallel Data Mining Agents (Padmas)MOHAMMAD WASEEMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amity School of Distance Learning Post Box No. 503, Sector-44 Noida - 201303 E-Commerce Assignment A Marks 10 Answer All QuestionsDocument9 paginiAmity School of Distance Learning Post Box No. 503, Sector-44 Noida - 201303 E-Commerce Assignment A Marks 10 Answer All QuestionsseemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acm IcpcDocument3 paginiAcm IcpcSivaramakrishna Markandeya GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mercedita M. Vergara: Personal DataDocument2 paginiMercedita M. Vergara: Personal DataAtienza JohnrehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auto-Income Bot: What Is This Guide About: AbsolutelyDocument9 paginiAuto-Income Bot: What Is This Guide About: AbsolutelyCat RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erp QuestionnaireDocument3 paginiErp Questionnaireviji_kichuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Guide To Enhanceing ElmDocument10 paginiQuick Guide To Enhanceing ElmmarkyrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To SuperMap IDesktopDocument36 paginiIntroduction To SuperMap IDesktopArif W. SunarsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challlengebrains Blogspot Com IMportantDocument23 paginiChalllengebrains Blogspot Com IMportantAbid SaifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Juliet SlidesCarnivalDocument39 paginiJuliet SlidesCarnivalelrechoncito 734Încă nu există evaluări
- History of Apple IncDocument26 paginiHistory of Apple IncKamal KhoobchandaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of PracticalsDocument6 paginiList of Practicalsshankarcr50% (2)
- Core Java Interview Questions (Ganesh)Document51 paginiCore Java Interview Questions (Ganesh)ganesh.compmumbai288Încă nu există evaluări
- Running PHP On Embedded DevicesDocument46 paginiRunning PHP On Embedded Deviceskaplumb_aga100% (4)
- Presentation KPMG Industry 4 0 Digital SCM For Enabling Growt 2019Document43 paginiPresentation KPMG Industry 4 0 Digital SCM For Enabling Growt 2019JhonathaÎncă nu există evaluări
- L4004N - 0920 - Nilfisk - Robotic-brochure-Liberty SC60Document12 paginiL4004N - 0920 - Nilfisk - Robotic-brochure-Liberty SC60Lucianderson Marques FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dump StateDocument8 paginiDump Statemusthasan0786Încă nu există evaluări
- WM ConfigDocument3 paginiWM ConfigasadshoaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 1 - Introduction To Computer and Network SecurityDocument66 paginiCHP 1 - Introduction To Computer and Network SecurityharizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read This First: Setting DefaultDocument42 paginiRead This First: Setting DefaultmathoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClusterDocument172 paginiClusterankit boxerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCCloneEX User Guide - ENGDocument14 paginiPCCloneEX User Guide - ENGjeanhertzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Plug Installation GuideDocument9 paginiSmart Plug Installation GuideFrancisco GuerreroÎncă nu există evaluări