Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pre-IGCSE Problem Set 1
Încărcat de
Anas ElgaudDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pre-IGCSE Problem Set 1
Încărcat de
Anas ElgaudDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Solved Problems IGCSE Physics
Mr. Anas Elgaud
Attempt the questions before checking the answers:
1. State the three basic quantities of Physics, and their SI units
1. Length (meter); Mass (kilogram); Time (second)
2. Convert the following length to metres:
1500 cm; 150 cm; 15 cm; 1.5 cm
2. 15 m, 1.5 m, 0.15 m; 0.015 m
3. A student records the time taken for 20 complete swings of a pendulum to
be 32 seconds. What is the period of the pendulum?
3. 32 seconds/20 swings = 1.6 seconds per swing
4. How many bricks of size 5 cm x 2 cm x 3 cm would a child need to build a
rectangular block of dimensions 15 cm x 15 cm x 10 cm?
4. Volume of smaller blocks is a three-dimensional value, which is 30 cm3.
Volume of large rectangular block is 2250 cm3. Therefore the answer is
2250/30=75 blocks.
5. Circle the correct SI unit of density
g/cm2; g/m3; kg/m3; kg/cm3
6. A block of ice has dimensions 2 cm x 2 cm x 2 cm and a mass of 7.36 g.
Calculate the density of the ice.
6. Mass = 7.36 g. Volume = 8 cm3. Density = Mass / Volume = 0.92 g/cm3
7. The density of air is 1.3 kg/m3. What is the mass of air in a room of
dimensions 3 m x 4 m x 2.5 m?
7. Mass =? Volume = 30 m3. Density = 1.3 kg/m3. Density = Mass / Volume.
Therefore Mass = Density x Volume = 39 kg.
8. A metal spanner has a mass of 200 g. It is lowered into a measuring
cylinder of water until it is completely submerged. If the original level of the
water was 50 cm3 and the final level is 75 cm3, calculate: the volume of the
metal; the density of the metal
8. Volume of metal = 75 cm3 - 50 cm3 = 25 cm3
Density of metal = Mass / Volume = 200g/25cm3 = 8 g/cm3
9. Give the weight of the following masses. Take the acceleration of free fall to
be 10 m/s2.
15 kg; 50 g; 0.3 g
9. 150 N; 0.5 N; 0.003 N
Dont Panic
Solved Problems IGCSE Physics
Mr. Anas Elgaud
10. On the Earth the acceleration of free fall is about 10 m/s2. On the moon the
acceleration of free fall is about 1.6 m/s2 (which is about one-sixth the
acceleration on the Earth).
A man weighs 800 N on the Earth. Give his mass measured on the moon, and
the weight measured on the Moon
10. Weight on the Earth = 800 N. W = mg, therefore m = W/g = 80 kg. Mass on
the Earth = Mass on the Moon = 80 kg;
Weight measured on the moon = m x g on moon = 128 N
11. A mass of 0.5 kg extends a spring by 10 cm. When an unknown mass M, is
hung on the spring, the extension is 15 cm. What is the value of M?
11. A mass of 0.5 kg extends a spring by 10 cm, from this use F = kx, solve
for k. k = F / x. My F here is the force of weight (W =mg=5N)
Then, k = 5N/0.1m=50N/m.
Now I have my k, I can use it with an extension of 15 cm, to find the required
weight (from which I find the required mass)
F = k x = 50 N/m x 0.15 m = 7.5 N; Mass of weight 7.5 N is 0.75 kg
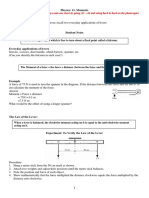
12. Which see-saw in the diagram below is balanced? In which direction will
the unbalanced see-saw tip?
12. To solve any problems containing moments, we start by finding the
moments in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions, and then we
compare them.
A. CW = 10 N x 2.5 m = 25 Nm; CCW = 150 N x 2.5 m = 375 Nm
CCW moment is larger than CW moment. Therefore it tips in CCW direction
B. CW = 200 N x 2 m = 400 Nm; CCW = 150 N x 2.5 m = 375 Nm
CW moment is larger than CCW. Therefore it tips in CCW direction
C. CW = 300 Nm. CCW = 300 Nm. CW = CCW. Therefore it is balanced.
D. CW = 350Nm. CCW = 375 Nm. Tipping in CCW
Dont Panic
Solved Problems IGCSE Physics
Mr. Anas Elgaud
13. A dog pulls a sledge across a flat snowfield for a distance of 500 m.
Calculate the work done if the dog exerts a steady force of 120 N on the
sledge.
13. Work done = force x distance moved = 120 N x 500 m = 60 KJ (Note: work
done = energy transferred)
14. An electrical appliance has a power input of 500 W. If it transfers energy
at a rate of 350 W, calculate its efficiency. What happens to the lost energy?
14. Efficiency = 70%; Lost energy is not really lost, its transferred to nonuseful heat.
15. A man lifts a weight of 60 N through a vertical distance of 1.2m. How
much work is done? If the man takes 2 minutes to lift 16 boxes each of weight
60 N vertically through 1.2 m, at what power is he working?
15. Work done = energy transferred = force x distance = mg x h = 60 N x 1.2 m
= 72 Joules.
For 16 boxes, the work (energy) is 72 J x 16 = 1152 J. Time is 120 seconds.
Hence, power = 1152 J per 120 seconds = 1152J/120s=9.6 Watt
16. A lift raises a load of 9000 N to a height of 20 m in 15 seconds. Calculate
the work done, and the power of the lift
16. Work = 180Kilojoules. Power= 12Kilowatt
17. A 3 kg mass falls with its terminal velocity. Which of the combinations A to
E gives its weight, the air resistance and the resultant force acting on it?
Answer is D, the body feels weightless in free-fall at terminal velocity because
the forces balance on it. So its velocity is not increasing, but it is still moving
(at constant velocity, i.e. the terminal velocity)
Dont Panic
Solved Problems IGCSE Physics
Mr. Anas Elgaud
18. Which one of the following statements is not true?
A
Pressure is the force acting on unit area.
B
Pressure is calculated from force/area.
C
The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa) which equals 1 newton per
square metre (1 N/m2).
D
The greater the area over which a force acts the greater is the
pressure.
E
Force = pressure area.
Answer: This is an easy one; clearly it is D since P = F / A, if we increase A, P
decreases (Logic 101)
19. A woman cycles, along a level road, a distance of 2.4 km in 10 minutes.
What is the womans average speed? The woman does work during her cycle
ride. Against what force has this work been done?
19. Average speed = Total distance / time taken = 2400 m / 600 s = 4 m/s;
work has to be done against friction between the wheels and the road.
20. A bus starts from rest and accelerates smoothly. After 10 s the bus reaches
a speed of 8 m/s, a) find the acceleration of the bus. b) If the bus continues to
travel at 8 m/s and then decelerates smoothly as it approaches a bus stop,
and the deceleration is 8 m/s2, find the time over which the bus decelerates
before it comes to rest
20. a) a = (v-u) / t = (8m/s 0m/s) / 10 s = 0.8 m/s2.
b) a now = - 8 m/s2. Since the bus is coming to a stop (decelerating).
a = (v-u) / t; HENCE, t = (v-u) / a = (0m/s 8m/s) / (-8 m/s2) = 1 s
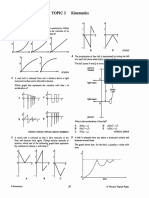
21. In the following page, a graph showing at the top the distance-time graph
for a girls bicycle ride and the bottom you are given the axes for the
corresponding speed-time graph.
(i) What is happening to the distance from the starting point between A and
B?
(ii) What can you say about the speed of the bicycle?
(iii) On the speed-time axes on the bottom graph, draw a thick line that could
show the speed during AB.
(iv) Find the speed during BC and CD; and draw the lines for the speed-time
portions accordingly
Dont Panic
Solved Problems IGCSE Physics
Mr. Anas Elgaud
- Graphs for question 21
21. Distance is increasing between A and B, and speed is constant. Since the
distance returned back to zero, it is clear that the cyclist returned to the
original position. For the speed, if it was constant, the lines are horizontal, no?
Dont Panic
Solved Problems IGCSE Physics
Mr. Anas Elgaud
22. Define Brownian motion, with a scribble of a graph. SB-P72
23. Describe Bimetallic strip with a sketch. SB- P82
24. Write formulas of Specific heat capacity SB- P88, and specific latent heat
(SB-P92) Can you describe experiments to measure both c and L? If its not
any trouble, of course.
Comment: These are some general revision questions that should help
consolidate your understanding of our current coursework in Physics. If you
have any points to be clarified reach me on our deserted fb group.
Mr. Anas Elgaud
IGCSE Physics
4/4/2016
Dont Panic
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Motion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625Document11 paginiMotion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625IGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- Forces Worksheet-2 (Ol)Document5 paginiForces Worksheet-2 (Ol)Shabbir H. Khan100% (1)
- Work For The Week of Oct 2009Document3 paginiWork For The Week of Oct 2009ftnmrd7Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers To End-Of-chapter Questions CambDocument2 paginiAnswers To End-Of-chapter Questions CambJetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0580 Straightlinegraphs Teaching Pack v1Document71 pagini0580 Straightlinegraphs Teaching Pack v1Karela KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Learner Guide For As and A Level PhysicsDocument4 paginiCambridge Learner Guide For As and A Level PhysicsVarshLokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers To Worksheet 4Document1 paginăAnswers To Worksheet 4Azeem iftikhar100% (1)
- 4.1 - Further MechanicsDocument28 pagini4.1 - Further MechanicsEmperor Saladin100% (1)
- Full Mock - 1 Paper-2Document16 paginiFull Mock - 1 Paper-2Dewan Olin ChotepadaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 9.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion - AHLDocument57 paginiTopic 9.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion - AHLPaul Amezquita100% (2)
- Igcse PhysicsDocument2 paginiIgcse PhysicsJay D PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 KinematicsDocument17 pagini04 KinematicsMilan LawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentiation Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1Document15 paginiDifferentiation Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1Sri Devi NagarjunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Level Physics Topic 3 Kinematics Lessons 1 2 WorksheetsDocument9 paginiAs Level Physics Topic 3 Kinematics Lessons 1 2 Worksheetsapi-183882946Încă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 2.2: Acceleration ProblemsDocument3 paginiWorksheet 2.2: Acceleration ProblemsTrúc HồÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper and Lower Bounds Gcse 9 1 Practice Questions 30213Document21 paginiUpper and Lower Bounds Gcse 9 1 Practice Questions 30213bhooshan ramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Most Commonly Asked Questions Paper 2-8Document61 paginiPhysics Most Commonly Asked Questions Paper 2-8Sayuri De AlwisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade KinematicsDocument13 paginiGrade KinematicsVarshLokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equations of Motion - Summative Quiz - IB 11 HLDocument5 paginiEquations of Motion - Summative Quiz - IB 11 HLpixelhoboÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Electrical Systems-StudentDocument53 pagini2014 Electrical Systems-StudentKim TaehyungÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Percentages: Exercise 2 - Determining The PercentageDocument4 paginiGCSE Percentages: Exercise 2 - Determining The PercentageSally VakhtangishviliÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementDocument7 paginiIGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementKyi Nue KhinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 Multiple Choice MS (Forces)Document39 paginiTopic 2 Multiple Choice MS (Forces)John VaitsÎncă nu există evaluări
- WorkEnergy P2Document26 paginiWorkEnergy P2dhairya gandhi100% (1)
- Edexcel GCSE Math Higher Revision Guide - Page 11Document1 paginăEdexcel GCSE Math Higher Revision Guide - Page 11farahgraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths HL InductionDocument10 paginiMaths HL InductionKadar PathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MomentsDocument5 paginiMomentsPichakorn100% (1)
- Electric&Magnetic Fields ExamZone AnswersDocument4 paginiElectric&Magnetic Fields ExamZone AnswersIllia Surya Afifuddin100% (4)
- GCSE Physcis WorksheetsDocument11 paginiGCSE Physcis WorksheetsMuhammad Talha SubhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3d TrigonometryDocument16 pagini3d TrigonometryHet J SanjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Skate Park WorksheetDocument4 paginiEnergy Skate Park WorksheetKiLlmEEEplz XD100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 23.1Document2 paginiIGCSE Physics Worksheet 23.1Alex DatsyukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wave PropertiesDocument2 paginiWave PropertiesAshok Kumar Dondati100% (1)
- GCSE VectorsDocument28 paginiGCSE VectorsKenanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1997 June Paper 1Document15 pagini1997 June Paper 1Rahique ShuaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9702 w17 QP 13 PDFDocument20 pagini9702 w17 QP 13 PDFDhito PramudyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternating CurrentDocument15 paginiAlternating CurrentUcok PandapotanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 3 - Mass and WeightDocument23 paginiPhysics 3 - Mass and WeightHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Level 2 Physics Mechanics Revision Booklet 2012Document26 paginiLevel 2 Physics Mechanics Revision Booklet 2012ctremblaylcsd150Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 MomentumDocument6 paginiChapter 6 MomentumAbdulaziz AlMuallimÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE MATHS PAST PAPER 580 - 2004 - QP - 3Document16 paginiIGCSE MATHS PAST PAPER 580 - 2004 - QP - 3Hassan mahmud100% (3)
- Edexcel IGCSE Physics Double Award Equations New SyllabusDocument1 paginăEdexcel IGCSE Physics Double Award Equations New Syllabusshaikh Mohammad ElahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cie Igcse p2 MergedDocument901 paginiCie Igcse p2 Mergedneelam goelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Classified Paper 1Document234 paginiPhysics Classified Paper 1Maaz Rashid0% (2)
- 10 IGCSE Physics Test 1 2014Document12 pagini10 IGCSE Physics Test 1 2014pixelhoboÎncă nu există evaluări
- BearingsDocument5 paginiBearingsNitin KatkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equations Involving Algebraic Fractions Lesson PlanDocument1 paginăEquations Involving Algebraic Fractions Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet O Levels Physics PressureDocument30 paginiWorksheet O Levels Physics PressureHZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Business Studies 0450/11 May/June 2021Document21 paginiCambridge IGCSE™: Business Studies 0450/11 May/June 2021Imran Ali100% (1)
- A Level PhysicsDocument157 paginiA Level Physicsvinod_kumarranÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Physics Workbook Answers: 1 Measurement and MotionDocument16 paginiIGCSE Physics Workbook Answers: 1 Measurement and MotionBasratul RafidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0580 IGCSE 22 MARCH 2024 FullDocument17 pagini0580 IGCSE 22 MARCH 2024 FullArminda Sofia AzevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VELOCITY: 1) What Is The Speed of ADocument25 paginiVELOCITY: 1) What Is The Speed of Armoanriy100% (1)
- PHYSICSDocument7 paginiPHYSICSCherryl FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science FormulaeDocument9 paginiScience FormulaeNoel Cunningham50% (2)
- AQA GCSE Physics Equation Practice Paper 2 Recall and Applyv1.1Document16 paginiAQA GCSE Physics Equation Practice Paper 2 Recall and Applyv1.1wasif.hello123100% (1)
- Class 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7Document4 paginiClass 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7tamishraza26Încă nu există evaluări
- Ngel of God, My Guardian Dear, To Whom God's Love Commits Me Here, Ever This Day, Be at My Side To Light and Guard, To Rule and GuideDocument10 paginiNgel of God, My Guardian Dear, To Whom God's Love Commits Me Here, Ever This Day, Be at My Side To Light and Guard, To Rule and GuideClaire Valdeavilla - DudasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rev2, ENGR 62, StanfordDocument40 paginiRev2, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasDocument42 paginiCCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasAnas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pilots A5 Folded Flyer V2-Oct16Document2 paginiPilots A5 Folded Flyer V2-Oct16Anas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corner Ning 161017Document44 paginiCorner Ning 161017Anas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCSEC25 Maths Syllabus Examination-2015 EnglishDocument96 paginiSCSEC25 Maths Syllabus Examination-2015 EnglishAnas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW2 - EE211 - Circuits TheoryDocument6 paginiHW2 - EE211 - Circuits TheoryAnas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alice Munro Short Story To Reach JapanDocument18 paginiAlice Munro Short Story To Reach JapanAnas Elgaud100% (2)
- Digital Signal Processing Basic ReviewDocument34 paginiDigital Signal Processing Basic ReviewAnas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Systems Homework 1Document2 paginiLinear Systems Homework 1Anas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System - Position Control SystemDocument4 paginiControl System - Position Control SystemAnas Elgaud100% (1)
- Prove Trig IdentitiesDocument2 paginiProve Trig IdentitiesAnas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Italy and New Libya Between Continuity and Change: Arturo VarvelliDocument7 paginiItaly and New Libya Between Continuity and Change: Arturo VarvelliAnas ElgaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Quiz 2 4Document4 paginiFinal Quiz 2 4Erick GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strouhal ADocument8 paginiStrouhal Asivaaero41Încă nu există evaluări
- PIDE Presentation Part 1 PDFDocument7 paginiPIDE Presentation Part 1 PDFGilmar DemenekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deflection Considerations in Two-Way Reinforced CoDocument13 paginiDeflection Considerations in Two-Way Reinforced CoHamid HassanzadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eqps + Notes (TCS)Document92 paginiEqps + Notes (TCS)vinayak pawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Package Survival': R Topics DocumentedDocument185 paginiPackage Survival': R Topics DocumentedFlorencia FirenzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 256 Statistics Spring 2011Document5 paginiMath 256 Statistics Spring 2011Laksamana NusantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Versatile Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer For VibDocument318 paginiA New Versatile Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer For Vibssunil7432Încă nu există evaluări
- CDMA Simulation: Alison Hightman Elaine Chung Alejandra GalvanDocument30 paginiCDMA Simulation: Alison Hightman Elaine Chung Alejandra GalvanericnaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimum Design PrinciplesDocument3 paginiOptimum Design PrinciplesJen Chavez100% (1)
- A Case Study in Ow Assurance of A Pipeline-Riser System Using OLGADocument10 paginiA Case Study in Ow Assurance of A Pipeline-Riser System Using OLGAAhmed BedhiefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Absolutely Continuous Functions of Several VariablesDocument16 paginiNotes On Absolutely Continuous Functions of Several VariablesSufyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quay Walls DesignDocument12 paginiQuay Walls DesignAdrian Frantescu100% (1)
- JEXPO MathsDocument6 paginiJEXPO MathsAvijit Das.Încă nu există evaluări
- XYZ Data Analysis ReportDocument14 paginiXYZ Data Analysis ReportAshwini Kumar Maurya100% (1)
- MA-345 NMC: 1 Root Finding MethodsDocument5 paginiMA-345 NMC: 1 Root Finding MethodsZakir HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gann Time Price SquareDocument5 paginiGann Time Price Squareanudora0% (1)
- Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Based On Fuzzy Sets With Orthogonal Teaching-Learning-Based OptimizationDocument13 paginiMultimodal Medical Image Fusion Based On Fuzzy Sets With Orthogonal Teaching-Learning-Based OptimizationtirupalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jaime Sandoval Real EstateDocument3 paginiJaime Sandoval Real EstateJaime R. SandovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Statistics Course SyllabusDocument7 paginiAdvanced Statistics Course SyllabusKristina PabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- D-Wave Articulo Prof Venegas Del de Youtube PDFDocument31 paginiD-Wave Articulo Prof Venegas Del de Youtube PDFMarco A. ErazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Machine Learning: Pembelajaran Mesin D4 Ti IFY IT Del 2019Document17 paginiIntro To Machine Learning: Pembelajaran Mesin D4 Ti IFY IT Del 2019Hanzel ArdeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE5143 Tutorial1Document5 paginiEE5143 Tutorial1Sayan Rudra PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog To DigitalDocument46 paginiAnalog To DigitalSaleem HaddadÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Objectives: S10FE-llg-50Document10 paginiI. Objectives: S10FE-llg-50John Loreto MentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of OscillationDocument4 paginiStudy of OscillationPHƯỚC DƯƠNG THANHÎncă nu există evaluări
- SimuPlot5 ManualDocument25 paginiSimuPlot5 Manualikorishor ambaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimal Agricultural Land Use: An Efficient Neutrosophic Linear Programming MethodDocument7 paginiOptimal Agricultural Land Use: An Efficient Neutrosophic Linear Programming MethodScience DirectÎncă nu există evaluări
- National PDFDocument168 paginiNational PDFDINESH100% (1)