Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Mixing Station
Încărcat de
Prudencio Almonte IIIDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Mixing Station
Încărcat de
Prudencio Almonte IIIDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing
Fab 3 17K Implanter Cleanroom Expansion Project
1.2
MIXING STATION
The testing and commissioning of these units involve the following.
1.2.1
Mixing Station Schematics
The schematic diagram is necessary as it gives a simple illustration of the water
distribution.
1.2.2
Pump Performance
The performance of the pump is verified against the pump curve produced by the
manufacturer. The water flow rate and the head are significance. Measurements of water
flow through the secondary balancing valves and pressure gauge reading across the
pump, plotted on the pump curve, show the performance of the pump.
Pump shut-off condition is also verified by closing the discharge valve fully and
recording the pressure gauge readings across the pump.
1.2.3
Chilled Water Balancing
Chilled water flowing through the secondary balancing valve is throttled according to the
requirement of the dry coil. The primary balancing valve is also adjusted to allow about
one-third the amount of water required by the dry coils.
The secondary valve adjustment is necessary to ensure the correct amount of water flows
through to the dry coil. The primary valve adjustment is necessary the right mixing
amount to achieve the intended dry coil supply water temperature.
Takasago (S) Pte. Ltd.
Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing
Fab 3 17K Implanter Cleanroom Expansion Project
1.2.2
PUMP PERFORMANCE
Objective:
To check the pump shut-off condition.
To verify pump water capacity and head.
Procedure:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Ensure that all valves at dry coil are opened fully
Ensure that all bypass valves are closed and all 3-way control valves stems are up.
Close the primary loops valves.
Open fully the balancing valve at secondary loop.
Hook up measuring instrument to balancing valve at secondary loop.
Run one pump.
Slowly, shut off the pump discharge valve completely.
Record readings of pressure gauges across the pump to calculate the head at zero
flow.
9. Measure and record reading of running ampere.
10. Open the pump discharge valve slowly, until the specified pump head is reached.
11. Measure and record water flowrate and pressure drop across the balancing valve.
12. Measure and record reading of running ampere and speed of motor.
13. Plot reading of flows and head on pump curve.
14. Repeat for the other pump.
Results:
From the results obtained, the performances of the pumps is within acceptable limits of
10%.
The flowrate capacity of the pumps differs from the -1%to+0.7%. This small differences
can be attributed to the accuracy of the achieving the pump head during measurement, as
it is only dependent on the visual reading of the pressure gauges, Since the required flow
is much less than this difference, the pumps still has some capacity for future upgrade.
All pumps meet the shut-off condition.
Takasago (S) Pte. Ltd.
Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing
Fab 3 17K Implanter Cleanroom Expansion Project
1.2.3
CHILLED WATER BALANCING
Objective:
To balance the amount of water flow into the mixing station.
Procedure:
1. Ensure that all valves at dry coil are opened fully.
2. Ensure that all bypass valves are closed and all 3-way and 2-way control valve
stems are up.
3. Open fully the balancing valve at secondary loop.
4. Open fully all valves at primary loop except the bypass valve.
5. Hook up measuring instrument to primary balancing valve.
6. Ensure pump discharge valve is opened fully.
7. Run one pump.
8. Throttle the primary balancing valve to the required flow.
9. Measure and record water flowrate and pressure drop across the balancing valve.
Results:
From the balancing results, the valves have been acceptably adjusted to the required flow.
Takasago (S) Pte. Ltd.
Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing
Fab 3 17K Implanter Cleanroom Expansion Project
1.3.2
CHILLED WATER BALANCING
Objectives:
To balance the amount of water flow into the dry coil.
Procedure:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Ensure that all valves at dry coil are opened fully.
Ensure that all bypass valves are closed and all 3-way control valve stems are up.
Ensure only one pump is running.
Check initial flow in all the dry coils in the pump system.
Calculate the total l flow to establish that the initial in the coil is equivalent to the
flow in the balanced secondary loop.
6. Identify the branch with the highest to lowest flow.
7. Start balancing the dry coils from the branch with the highest flow.
8. Adjust the last coil (n) to the required flow.
9. Next, adjust the 2nd last coil (n-1) to the required flow.
10. Check back the flow in the last coil. Re-adjust, if necessary.
11. Check back the flow in the 2nd last coil. Re-adjust if necessary.
12. Next, adjust the 3rd last coil (n-2) to the required flow.
13. Continue checking back the coils in the order of n, n-1, n-2.
14. Then proceed to adjust the next coil to the required flow.
15. Repeat procedure until the adjustment and checking back is done to the 1st coil in
the branch.
16. Record all readings of flow for that branch.
17. Find the branch with the next highest flow and proceed to balance the dry coils in
the same manner as described above.
Results:
The dry coils have been balanced to the design flowrate and the result can be tabulated as
such:
Takasago (S) Pte. Ltd.
Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing
Fab 3 17K Implanter Cleanroom Expansion Project
1.3
DRY COIL BALANCING
The testing and commissioning of these units involved the following:
1.3.1 Dry Coil Layout
The layout plan is necessary as it gives a clear illustration of the
arrangement of the dry coils, the zones affected and the water distribution.
1.3.2 Chilled Water Balancing
The dry coil system is balanced in a logical sequences. The branch with the
highest proportion of the flow is balanced first, thereby gradually forcing the
water into the areas with bad circulation.
However, when the balancing dry coils on that branch, the flow in the last
coil is adjusted first. Subsequently, the following 2nd last coil is adjusted.
Using only 1 measuring instrument, coils already adjusted have to be
checked back to confirm that the adjustment downstream do not change its
flow. Final flow measurement and recording is done when all coils in the
branch are adjusted and balanced.
Takasago (S) Pte. Ltd.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Number CardsDocument21 paginiNumber CardsCachipún Lab CreativoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Bosch KE-Jetronic System DescriptionDocument3 paginiBosch KE-Jetronic System DescriptionJack Tang50% (2)
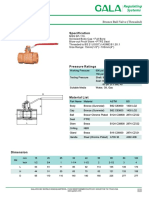
- GALA Valves PDFDocument14 paginiGALA Valves PDFPrudencio Almonte IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dayco-Timing Belt Training - Entrenamiento Correa DentadaDocument9 paginiDayco-Timing Belt Training - Entrenamiento Correa DentadaDeiby CeleminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation of Plumbing and HVAC Systems PDFDocument128 paginiInstallation of Plumbing and HVAC Systems PDFPrudencio Almonte IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schmidt Hammer TestDocument5 paginiSchmidt Hammer Testchrtrom100% (1)
- HVAC System Functional Design Description - Commentes - Gusto - 110202 PDFDocument28 paginiHVAC System Functional Design Description - Commentes - Gusto - 110202 PDFPrudencio Almonte III67% (3)
- Powerplant QuestionsDocument19 paginiPowerplant QuestionsAshok KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lub OIl Flushing Procedure PDFDocument44 paginiLub OIl Flushing Procedure PDFSubrahmanyam100% (1)
- 3.6 LPG Supply SystemDocument5 pagini3.6 LPG Supply SystemPrudencio Almonte IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probe Card Room: Design SpecificationDocument1 paginăProbe Card Room: Design SpecificationPrudencio Almonte IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual - SMG Battery - UPS PDFDocument15 paginiManual - SMG Battery - UPS PDFPrudencio Almonte III100% (1)
- Gen - Battery Description UPS PDFDocument2 paginiGen - Battery Description UPS PDFPrudencio Almonte IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- En DAY4 David Chen Building The AI Computing Platform For Pervasive Intelligence enDocument8 paginiEn DAY4 David Chen Building The AI Computing Platform For Pervasive Intelligence endieuwrignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Car Parking DesignDocument6 paginiCar Parking Designcharler kinyuajÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE-23113-SP-902-R01-00 Asset SpecificationDocument14 paginiCE-23113-SP-902-R01-00 Asset SpecificationСветлана ФайберÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Unseen Passage For Class 5 in EnglishDocument7 pagini1st Unseen Passage For Class 5 in EnglishVibhav SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tekla SoakwayDocument2 paginiTekla SoakwayBalaji Naik100% (1)
- Make Yeast StarterDocument2 paginiMake Yeast StarterAlexandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Engineering & Processing: Process Intensi Fication: ArticleinfoDocument9 paginiChemical Engineering & Processing: Process Intensi Fication: Articleinfomiza adlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Study On Analysis of Plain and RC Beam Using AbaqusDocument9 paginiComparative Study On Analysis of Plain and RC Beam Using Abaqussaifal hameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Programs Using Kit: Exp No: Date: Arithmetic Operations Using 8051Document16 pagini8051 Programs Using Kit: Exp No: Date: Arithmetic Operations Using 8051Gajalakshmi AshokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling Jigs Italiana FerramentaDocument34 paginiDrilling Jigs Italiana FerramentaOliver Augusto Fuentes LópezÎncă nu există evaluări
- S25580 MSDS Corn Starch FisherchiDocument6 paginiS25580 MSDS Corn Starch FisherchiProcurement ProlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- 61annual Report 2010-11 EngDocument237 pagini61annual Report 2010-11 Engsoap_bendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Markets Strategically: Professor Noel CaponDocument49 paginiManaging Markets Strategically: Professor Noel CaponChristiandeuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE Uno Downlight Backlit BLDocument2 paginiGE Uno Downlight Backlit BLChen KengloonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NiftDocument3 paginiNiftMegha Nair PillaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22 Thành NG Quen Thu C Trên Ielts - FirefighterDocument2 pagini22 Thành NG Quen Thu C Trên Ielts - FirefighterNinh NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dpb6013 HRM - Chapter 3 HRM Planning w1Document24 paginiDpb6013 HRM - Chapter 3 HRM Planning w1Renese LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Worksheets MYSQLDocument33 paginiAll Worksheets MYSQLSample1Încă nu există evaluări
- Aicte Internship Approval Pending 1Document7 paginiAicte Internship Approval Pending 1Anisha KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 Uco 578Document20 pagini19 Uco 578roshan jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- GL Career Academy Data AnalyticsDocument7 paginiGL Career Academy Data AnalyticsDeveloper GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- KARAKTERISTIK GEOTERMAL SUMUR EKSPLORASI AT-1, LAPANGAN PANAS BUMI ATADEI, KABUPATEN LEMBATA NTT. Kastiman Sitorus Dan Arif Munandar SUBDIT PANAS BUMIDocument7 paginiKARAKTERISTIK GEOTERMAL SUMUR EKSPLORASI AT-1, LAPANGAN PANAS BUMI ATADEI, KABUPATEN LEMBATA NTT. Kastiman Sitorus Dan Arif Munandar SUBDIT PANAS BUMIItTo MakinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS3501 Compiler Design Lab ManualDocument43 paginiCS3501 Compiler Design Lab ManualMANIMEKALAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ateneo de Naga University: Professional Training For Teacher 4.0Document10 paginiAteneo de Naga University: Professional Training For Teacher 4.0Rosemarie BrionesÎncă nu există evaluări