Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
TENSES
Încărcat de
Yumanraya NohoDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TENSES
Încărcat de
Yumanraya NohoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1.
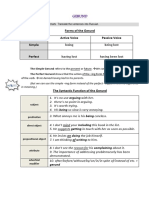
GRAMMAR
Simple present tense
Function of simple present tense
The simple present tense is used for an action that is repeated or usual. The action can be a habit, a
hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. It is also used for future
planned events.
Here are some examples of simple present tense:
Fact (or something we believe to be true)
Beijing is the capital of China.
Exxon and Royal Dutch Shell are very big oil companies.
All my friends live in Gorontalo
Opinion:
A job in the oil industry has a good future.
I think that is a good idea.
Habit:
My husband usually gets up at 6.00 oclock every day.
We always have lunch at 12.30pm.
We normally go to the market on Saturdays.
Timetables, schedules and rosters:
The plane from Darwin arrives at 9.00am.
Your shift begins at 8.30am.
Future: for future events or programmes
The meeting starts at 9.00am tomorrow.
The bus leaves at 10 oclock.
Structure of present tense
The verb to be is irregular:
Subject
I
he/she/it
we/you/they
Verb
am
is
are
For all other verbs, we put s, es or ies on the third person singular form.
Where the verb ends in y we delete the y and add ies
carry
carr+ies
carries
Where the verb ends in o or an s-like sound (x, z, ss, ch, or sh), we add es
go
fix
buzz
miss
catch
wash
=
=
=
=
=
=
goes
fixes
buzzes
misses
catches
washes
There is only one irregular form
have
has
Present continuous tense
Present continuous for present time
We use the present continuous tense for an action that is happening now or around now. It is
unfinished and not permanent or habitual. To show we are talking about the present time, we can use
time phrases such as: now, at the moment, currently, at present, nowadays.
I am living in Gorontalo at the moment.
They are going to the meeting. (now)
I am reading a motorcycle magazine.
Marcos is repairing his motorcycle.
At the moment I am teaching English.
At present we are negotiating a new contract with the Government.
Present continuous for future
Present continuous can also be used for an action happening in the future. In this case we may add a
future word, for example: this afternoon, tomorrow, next week/month/year.
We are going shopping tomorrow.
My brother is going to Australia next week.
My friend is coming back to Timor next year.
Construction of present continuous tense
Subject
+ verb to be
+ main verb + ing
I
He/she/it
We/you/they
+ am
+ is
+ are
+ walk
+ walk
+ walk
+ ing
+ ing
+ ing
Present continuous spelling
When the verb ends in e, delete the e and add ing.
ache
drive
wave
=
=
=
ach+ing
driv+ing
wav+ing
=
=
=
aching
driving
waving
For all other verbs, add ing.
stay
try
carry
=
=
=
staying
trying
carrying
Present continuous exceptions
We do not usually use the following verbs in the continuous tense.
Emotion and thought:
believe
imagine
love
realize
suppose
wish
dislike
know
hate
recognize
understand
doubt
Like
prefer
remember
want
Sense:
appear
seem
taste
Hear
Smell
see
sound
Belong
contain
deserve
involve
Matter
Own
concern
cost
fit
lack
need
possess
Other:
be
consist
depend
include
look
owe
For all these verbs, we do not use present continuous. Instead we must use simple present tense.
Incorrect: Present continuous
I am knowing your friend.
He is not understanding the teacher.
I am remembering your birthday.
Correct: Simple present
I know your friend.
He does not understand the teacher.
I remember your birthday.
Simple Past Tense
Function of simple past tense
The simple past tense is used to describe actions that happened at a past time, which have been
completed at the time of speaking.
We can use a time phrase when we use the past tense, for example: yesterday, last week, two weeks
ago, last night.
Last night I watched television with my family.
I started my new job yesterday.
My brother bought a new motor cycle last week.
I lived there many years ago.
Structure of past tense
The verb to be is irregular:
Subject
I/he/she/it
we/you/they
Verb
Was
Were
Where the verb ends in a consonant plus y we delete the y then add ied.
carry
dry
=
=
carr+ied
dr+ied
=
=
carried
dried
For all other verbs, add ed.
employ
walk
start
=
=
=
employed
walked
started
Some verbs are irregular. These needs to be learned. There is a list of irregular verbs in section 8.9
Pronunciation
The pronunciation of final ed depends on the last sound in the verb.
If it is t or d, then the sound is ed.
started
decide
started
decided
If it is any other voiceless consonsant (p, k, s, ch, sh), then the sound is t.
Word
helped
asked
missed
watch
wished
Pronunciation
helpt
askt
mist
watcht
wisht
If it is a vowel or any other voiced consonant (b, g, z, v, l, m, n, r, w, y) then the sound is d.
Word
Tie
Bag
received
Mill
Form
Turned
Answered
Flow
Toy
Pronunciation
Tied
Bagd
Receivd
Mild
Formd
Turnd
Answerd
Flowd
Toyd
Present Perfect (V3)
Function of present perfect
The present perfect is used when talking about a past event which is still relevant now. The
action in the past has a result now.
Marcos has lost his mobile phone. (He lost it, and still hasnt found it.)
Exxon Mobil has discovered a new oil field in the Timor Sea. (They discovered oil, and
hope it will make them rich.)
We also can use present perfect when we talk about a period of time that continues from the past
until now.
I have been here for about a year.
I have been here since 2011. (i.e. from 2011 to now)
I havent seen my friend since last week.
I have been busy this week. (From Monday until now; this week has not yet finished.)
We can use the present perfect with adverbs such as just, yet, already.
I havent found a job yet.
She has just finished breakfast.
I have already finished the report.
Structure of present perfect
Subject
+ verb have + past participle
He/she/it
Has
walked
I/we/you/they
Have
walked
The past participle for regular verbs is the same as the simple past (verb + ed), but for irregular
verbs it must be memorized.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Filipinism IIIDocument19 paginiFilipinism IIIJaniceÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar All You Need To KnowDocument22 paginiEnglish Grammar All You Need To KnowDavid Fueter0% (1)
- Basic Hindi - Lesson 1 - IntroductionDocument50 paginiBasic Hindi - Lesson 1 - IntroductionCulture Alley100% (1)
- 11 Plus Scheme of WorkDocument1 pagină11 Plus Scheme of Worknabhan07Încă nu există evaluări
- Verb 2Document3 paginiVerb 2Rajeev RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Introduction To TensesDocument34 paginiBasic Introduction To TensesPriti PritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESP I Verbs & TensesDocument16 paginiESP I Verbs & TensesmurpicantikbangetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common MistakesDocument12 paginiCommon Mistakesnailul-abrorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Has Have HadDocument5 paginiHas Have Hadvanilla_42kp100% (2)
- Grammar For IELTSDocument25 paginiGrammar For IELTSZahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Going Away PART 2: It S +adjective +toDocument12 paginiGoing Away PART 2: It S +adjective +toMirla Mojica100% (1)
- Sva RulesDocument2 paginiSva Ruleskayra dale larrauriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cause and Effect - Key IELTS Vocabulary Because: NotesDocument18 paginiCause and Effect - Key IELTS Vocabulary Because: NotesBharti Dogra100% (1)
- 7 Grammar Rules You Need To Get A Higher IELTS Score - FluentU IELTS BlogDocument19 pagini7 Grammar Rules You Need To Get A Higher IELTS Score - FluentU IELTS Blogmandaliya umeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS General Writing Task 1 - Advanced Vocabulary For LettersDocument7 paginiIELTS General Writing Task 1 - Advanced Vocabulary For LettersShalva SamkharadzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conjunction Rules in English Grammar PDFDocument4 paginiConjunction Rules in English Grammar PDFMhadz B.A.Încă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Vocabulary - Psychology & Cognitive Science - Psychological ConceptsDocument1 paginăIELTS Vocabulary - Psychology & Cognitive Science - Psychological ConceptsChinonso Nelse NwadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Misconception About IELTSDocument4 paginiMisconception About IELTSMosharraf Hossain SylarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 88 IELTS Speaking Part 2 Cue Cards With Audio Final-4-94 2Document91 pagini88 IELTS Speaking Part 2 Cue Cards With Audio Final-4-94 2Nedarafiei100% (1)
- Gerund StsDocument43 paginiGerund StsMustafa ÇamÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Masterclass Handout Updates FinalDocument32 paginiIELTS Masterclass Handout Updates FinalMd.DulalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Writing Task 2Document2 paginiIELTS Writing Task 2lauraningsih50% (2)
- SAT Vocabulary BookDocument282 paginiSAT Vocabulary BookkattantestprepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Verb InversionDocument2 paginiSubject Verb InversionisabelmcostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free IELTS General Training Writing Test - Task 1Document5 paginiFree IELTS General Training Writing Test - Task 1kunta_kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vocabulary - Collocations Topic Environment For Writing Task 2 - IELTS Practice Online (Band 9)Document3 paginiVocabulary - Collocations Topic Environment For Writing Task 2 - IELTS Practice Online (Band 9)Sarah JaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdjectivesDocument6 paginiAdjectivesBabita SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Let's Spell Words Ending - TionDocument27 paginiLet's Spell Words Ending - TioncarrycarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 12: Health: Essay TopicsDocument5 paginiTopic 12: Health: Essay Topicsnitin ujjainwal100% (1)
- Pronoun Shortcut RulesDocument3 paginiPronoun Shortcut RulesnilvemangeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- V3 - IELTS INTENSIVE SPEAKING 24hrs - LESSON 1 FinalDocument18 paginiV3 - IELTS INTENSIVE SPEAKING 24hrs - LESSON 1 Finalshophanguc. VnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topics Vocabulary-DucVuDocument81 paginiTopics Vocabulary-DucVuĐức VũÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adverb Shortcut RulesDocument2 paginiAdverb Shortcut Rulesnilvemangesh100% (1)
- Use of AdverbsDocument14 paginiUse of AdverbsAntony PandiarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Task 1 ProcessDocument8 paginiIELTS Task 1 ProcessHafiz AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Speaking 1Document52 paginiIELTS Speaking 1vit1306abcÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Verb Tenses EngvidDocument4 paginiEnglish Verb Tenses EngvidbintangwirawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phrasal Verbs PART 2 PDFDocument31 paginiPhrasal Verbs PART 2 PDFelena6pshennikovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 31 High Score Ielts Speaking PDFDocument368 pagini31 High Score Ielts Speaking PDFIris NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Grammar: Present Perfect ContinuousDocument1 paginăIELTS Grammar: Present Perfect ContinuousLogdi JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Cô Nguyêt CA) .Jump Ielts - Writing Task 1 & 2 (Abazar Alizadeh)Document140 pagini(Cô Nguyêt CA) .Jump Ielts - Writing Task 1 & 2 (Abazar Alizadeh)Hong HoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- @IELTSmaterials IdeasDocument52 pagini@IELTSmaterials IdeasmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- SpeakingDocument55 paginiSpeakingBảo Lê QuốcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ielts EssayDocument4 paginiIelts EssaySunil GAireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giving OpinionDocument6 paginiGiving OpinionRenan Barbosa QueirozÎncă nu există evaluări
- English CapsuleDocument41 paginiEnglish CapsuleVipul Priya KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Writing SamplesDocument23 paginiIELTS Writing SamplesalirehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vocabulary For Ielts Speaking Ielts Spea PDF FreeDocument48 paginiVocabulary For Ielts Speaking Ielts Spea PDF Freejohnny waveÎncă nu există evaluări
- The GERUND AndcompoundnounDocument7 paginiThe GERUND AndcompoundnounJannice Coscolluela CanlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Can /can't: Ability PermissionDocument21 paginiCan /can't: Ability PermissionRocio Condeña Hilario100% (1)
- Linking Words For IELTS Essay WritingDocument6 paginiLinking Words For IELTS Essay WritingRajiv RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELTS Speaking Frequently Asked Questions: 1-How Many Parts Are There To The IELTS Speaking Test?Document23 paginiIELTS Speaking Frequently Asked Questions: 1-How Many Parts Are There To The IELTS Speaking Test?هندسة الإنتاج والتصميم الميكانيكيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ielts SynonymsDocument36 paginiIelts SynonymsOmer AtiqiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentence Transformation & Sentence CombinationDocument16 paginiSentence Transformation & Sentence CombinationMinh Thư Huỳnh100% (1)
- IELTS Speaking Part 2 Topics Summer 2017Document12 paginiIELTS Speaking Part 2 Topics Summer 2017Mansoor MAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nominalization: The Charity Walk Raised AED 10,000 For Dubai CaresDocument2 paginiNominalization: The Charity Walk Raised AED 10,000 For Dubai CaresGary O'NeillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 1 - Flow ChartDocument18 paginiTask 1 - Flow Chartnavigator290679Încă nu există evaluări
- Acdemic IELTS Reading Test 86Document9 paginiAcdemic IELTS Reading Test 86PrabhjotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantifiers With Countable and Uncountable Nouns PDFDocument6 paginiQuantifiers With Countable and Uncountable Nouns PDFNicolás CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Common Error RulesDocument11 paginiEnglish Common Error RulesWahid AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential GRAMMAR SECTIONDocument38 paginiEssential GRAMMAR SECTIONVahid Alizadeh100% (2)
- Teacher King’s English Speaking Course Book 1: Italian EditionDe la EverandTeacher King’s English Speaking Course Book 1: Italian EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giao An Tieng Anh 6 Friends PlusDocument135 paginiGiao An Tieng Anh 6 Friends PlusTrần Khải Phương 9/2Încă nu există evaluări
- Gateway B2 Practice Online PDFDocument9 paginiGateway B2 Practice Online PDFNuria GLÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th PT in English g9Document3 pagini4th PT in English g9Melany A. ManrizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4: What Do We Do During The Week and at The Weekend?Document29 paginiUnit 4: What Do We Do During The Week and at The Weekend?Marisa MontesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tes HiraganaDocument5 paginiTes Hiraganadisya18Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 English Grammar and Punctuation Test 1: Each ExampleDocument4 paginiYear 5 English Grammar and Punctuation Test 1: Each Examplesylvie05Încă nu există evaluări
- P1 - Gramma in Use (There Is Are) Things in The ClassroomDocument4 paginiP1 - Gramma in Use (There Is Are) Things in The ClassroomYan WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- FG - Types of Thematic Progression (Group 6)Document10 paginiFG - Types of Thematic Progression (Group 6)Tata regitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Language Skills-II (5660)Document17 paginiLanguage Skills-II (5660)Shaukat Hussain AfridiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cial or TialDocument1 paginăCial or TialAndyBrookeÎncă nu există evaluări
- University Grammar of English: Quirk, GreenbaumDocument17 paginiUniversity Grammar of English: Quirk, Greenbaumnora khaledÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Commas To Set Off Introductory PhrasesDocument3 paginiUsing Commas To Set Off Introductory PhrasesMelinda SuharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ks2 English 2015 Grammar Punctuation Spelling Paper 1 Short Answer QuestionsDocument32 paginiKs2 English 2015 Grammar Punctuation Spelling Paper 1 Short Answer QuestionsBharat Manjibhai BhadaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Yearly Plan For Year 6Document8 paginiEnglish Yearly Plan For Year 6Masnizan Binti HamdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Close Test With CluesDocument54 paginiClose Test With CluesChandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phrases For RecitationDocument10 paginiPhrases For RecitationJon ToresÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUBJECT-VERB AGREEMENT All Rules With ActivitiesDocument87 paginiSUBJECT-VERB AGREEMENT All Rules With ActivitiesVicky Condino BilardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complex Sentences PracticeDocument4 paginiComplex Sentences PracticeRaniaGFÎncă nu există evaluări
- fl2 4Document24 paginifl2 4Gwen Sula LacanilaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hakim Dekkar Hakim DekkarDocument2 paginiHakim Dekkar Hakim DekkarAyat FzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Figurative Language Final Quiz. No AnswerpptxDocument49 paginiFigurative Language Final Quiz. No AnswerpptxTon RJ IdoÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument12 paginiNew Microsoft Word DocumentBurning RoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airline Security: Pre-Reading Activities 1 VocabularyDocument3 paginiAirline Security: Pre-Reading Activities 1 Vocabularynermin özÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sonja Poulsen. Grammatical CollocationsDocument10 paginiSonja Poulsen. Grammatical CollocationsCennet EkiciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Bank: Should For Advice Should: InformationDocument1 paginăGrammar Bank: Should For Advice Should: InformationKatia LuizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TESTSDocument4 paginiTESTSBegoña García Acevedo100% (1)