Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CH 22
Încărcat de
Mark ReyesTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CH 22
Încărcat de
Mark ReyesDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
22
Gausss Law
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric
Charge distributions
Systems with symmetry
Systems without symmetry
Gausss Law makes E-field
calculation easier.
Gausss Law also applies but more
difficult.
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
What is Gausss Law?
relationship between electric charges and electric fields
imaginary surface
What is the Electric field
(on the surface)?
applicable for both continuous and discrete charge distribution
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Objectives
1. Evaluate the electric flux through a surface given the electric
field
2. Relate the electric flux thru a closed surface to the total charge
inside and outside the surface
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Electric Flux and Enclosed Charge
Note: Electric field does not flow.
points out of the surface
points into of the surface
Inward electric flux
Outward electric flux
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Electric Flux and Enclosed Charge
3 cases in which there is zero net charge inside a box and
no net electric flux through the surface of the box.
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Electric Flux and Enclosed Charge
Main points:
The net electric flux due to a charge distribution inside a closed surface is
independent of the size and shape of the closed surface.
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Electric Flux and Enclosed Charge
Main points:
The net electric flux due to a charge distribution inside a closed surface
depends only on the net charge inside.
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Qualitative Statements of Gausss Law
1.
Whether there is a net outward or inward electric flux through a closed surface
depends on the sign of the enclosed charge.
2.
Charges outside the closed surface do not give a net electric flux through
the surface.
3.
The net electric flux is directly proportional to the net amount of charge
enclosed within the surface but is otherwise independent of the size of the
closed surface.
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
10
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Example:
Charge +2q is at the center of two cubes of different side lengths L and
2L as shown. The total flux through the small and big cubes are small
and big, respectively. Also Esmall and Ebig are the magnitudes of the
electric field passing through the corners of the small and big cubes,
respectively. Which of the following relations is/are true?
A. small = big; Esmall = Ebig
B. small > big; Esmall > Ebig
C. small < big; Esmall = Ebig
D. small = big; Esmall < Ebig
E. small = big; Esmall > Ebig
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
11
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
General definition of electric flux
where
Uniform Electric Field
Non-uniform Electric Field
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
12
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Flux of a Uniform Electric Field
Define:
: electric flux
number of field lines crossing a surface
(electric flux for uniform
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
, flat surface)
13
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Note:
Case 1.
: unit vector perpendicular to A
Case 2.
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
Case 3.
14
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
15
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Example:
A uniform electric field given by
is incident on a flat square sheet lying on the xy-plane. If the
length of the sides is 3 m, what is the absolute value of the
electric flux through the sheet?
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
16
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Objective
1. Express Gausss law verbally and mathematically
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
17
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Gausss Law
alternative to Coulombs Law
a different way of expressing the relationship between electric charge
and electric field
formulated by Carl Friedrich Gauss
Recall:
Gausss Law
(qualitative)
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
18
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Point Charge inside a Spherical Surface
Consider a point charge +q placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface with radius R.
: Outward and perpendicular to any point on the Gaussian surface
+q
R
has the same value at any point on the surface.
(Flux is independent of radius R of sphere)
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
19
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
2 spheres with radii R and 2R centered on the point charge +q
4dA
dA
q
2R
The same number of field lines and the same flux
pass through bothJ. Manuel
of these
area elements.
Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
20
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Point Charge inside a Non-spherical Surface
For irregular surface:
If enclosed charge is positive (+q):
+q
Holds for any size or shape of closed surface
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
21
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Point Charge inside a Non-spherical Surface
For irregular surface:
If enclosed charge is negative (-q):
-q
Holds for any size or shape of closed surface
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
22
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Point Charge inside a Non-spherical Surface
For irregular surface:
If there is no enclosed charge:
Holds for any size or shape of closed surface
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
23
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
General form of Gausss Law
q1
q2
qn
Enclosed charge
Electric field
on Gaussian surface
Electric flux
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
24
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
General form of Gausss Law
q1
q2
qn
Gausss Law
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
25
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Example:
A positive point charge Q is located at the center of a cube of
side-length L. In addition, six other identical positive point
charges q are positioned symmetrically around Q, as shown
in the figure. What is the electric flux through one face of the
cube?
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
26
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Seatwork (for 2 minutes):
Which of the following closed surfaces has the most positive
electric flux through it?
A. S1
B. S5
S2
C. S2
S5
D. S3
S3
Legend:
+q
-q
S4
S1
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
27
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Homework (due tomorrow):
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
28
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Homework (due tomorrow):
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
29
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Homework (due tomorrow):
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
30
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Objective
1. Use Gausss law to calculate the electric field generated at a
point by highly symmetrical charge distributions.
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
31
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Gausss Law
valid for any distribution of charges and for any closed surface
Two applications:
1. Symmetric charge distribution + evaluate integral = electric field
2. Electric field + Gausss Law = knowledge of charge distribution
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
32
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
For a solid conductor
any excess charge must
reside on the surface
inside
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
33
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
34
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Seatwork (for 2 minutes):
Consider a solid spherical conductor of radius R and charge
+Q at electrostatic equilibrium shown below. Which is the
correct ranking of the Points A, B, C, and D according the
value of the electric field at their locations?
A. D > C > B > A
B. D > C > B = A
C. D = C > B = A
D. C > D > B = A
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
35
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
36
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
37
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
38
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Seatwork (for 3 minutes):
A Gaussian cube of side s is placed inside a uniformly charged
insulating sphere of radius 2s and charge Q. What is the
electric flux on the Gaussian cube?
A. 3Q/(32o)
Hint:
B. 32Q/(3o)
C. 3Q/(32o)
D. 32Q/(3o)
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
39
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
40
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Gausss Law
valid for any distribution of charges and for any closed surface
Two applications:
1. Symmetric charge distribution + evaluate integral = electric field
2. Electric field + Gausss Law = knowledge of charge distribution
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
41
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Objective
1. Predict the charge distribution induced on the surface of a
conductor in the presence of a static charge and external
electric field
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
42
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Charges on a conductor
For a solid conductor in electrostatic situation,
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
43
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
Question:
But what if there is a cavity inside the
conductor?
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
44
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Charges on a conductor
For a conductor with internal cavity,
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
45
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Charges on a conductor
If we insert an isolated charge q inside the cavity,
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
46
22
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
47
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Seatwork (for 3 minutes):
A spherical conducting shell S1 is placed inside another spherical
conducting shell S3. The space between S1 and S3 is filled by an
uncharged insulator S2. The isolated charge within the cavity is +2Q. If
the net charge of S1 is 4Q and the net charge of S3 is 4Q, what is the
net charge of the following surfaces?
Inner surface of S1
A. Q
B. +Q
C. +2Q
D. 2Q
Outer surface of S1
A. Q
B. +6Q
C. +4Q
D. Q
Inner surface of S3
A. 6Q
B. +3Q
C. +4Q
D. 3Q
B. +3Q
C. +2Q
D. 4Q
Outer surface of S3
A. Q
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
48
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Example:
A small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is
concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and
outer radius d. The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the
outer shell has charge +4q.
Calculate the electric field magnitude in terms of k, q and r from the
common center of the spheres.
1. r < a
2. a < r < b
3. b < r < c
4. c < r < d
5. r > d
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
49
Charge and Electric Flux
Calculating Electric Flux
Gausss Law
Applications of Gausss Law
Charges on Conductors
22
Example:
Which of the following can be true regarding the figure shown below?
I. The electric field at S is stronger than at P.
II. There is a point charge at point Q.
III. There are negative charges at point L.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
I only
I and II only
II and III only
I and III only
I, II and III
J. Manuel Physics 72 2nd Sem AY13-14
50
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Quiz 1Document1 paginăQuiz 1Mark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 55 3rd Exam Exercises PDFDocument3 paginiMath 55 3rd Exam Exercises PDFMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Piercing Point Edit ThisDocument5 pagini8 Piercing Point Edit ThisMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interference: Physics 72 8:45-9:45 PM May 8, 2015 TWHFR-XDocument27 paginiInterference: Physics 72 8:45-9:45 PM May 8, 2015 TWHFR-XMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thin Lenses: Physics 72 8:45-9:45 AM May 6, 2015 TWHFR-XDocument30 paginiThin Lenses: Physics 72 8:45-9:45 AM May 6, 2015 TWHFR-XMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Z Axes at Equal Distances D From The Origin. What Is TheDocument2 paginiZ Axes at Equal Distances D From The Origin. What Is TheMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 72-TWHFW-x Recitation Quiz 4: K C J by I Z Ax E K C J by I Z Ax EDocument3 paginiPhysics 72-TWHFW-x Recitation Quiz 4: K C J by I Z Ax E K C J by I Z Ax EMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 29 Electromagnetic InductionDocument59 paginiChapter 29 Electromagnetic InductionMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 30 InductanceDocument59 paginiChapter 30 InductanceMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 35 InterferenceDocument54 paginiChapter 35 InterferenceMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 26 Direct Current CircuitsDocument61 paginiChapter 26 Direct Current CircuitsMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 27 Magetic Field and Magnetic ForcesDocument85 paginiChapter 27 Magetic Field and Magnetic ForcesMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
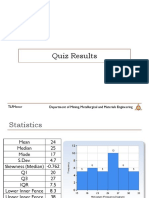
- Quiz Results: Department of Mining, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering TlfmenorDocument70 paginiQuiz Results: Department of Mining, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering TlfmenorMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 26 Chain Rule and Implicit Differentiation PDFDocument17 pagini26 Chain Rule and Implicit Differentiation PDFMark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass Moment of Inertia v2Document27 paginiMass Moment of Inertia v2Mark ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Shadan Zolghani - 9 Ag Displacement and VelocityDocument12 paginiShadan Zolghani - 9 Ag Displacement and Velocityapi-531290004Încă nu există evaluări
- Yang Et Al. (2017)Document11 paginiYang Et Al. (2017)Francisco OppsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engine Control SystemDocument7 paginiEngine Control SystemFaisal Al HusainanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBS10 PPT MTB Ch04 ProbabiltyDocument37 paginiBBS10 PPT MTB Ch04 ProbabiltyAgenttZeeroOutsiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signals & Systems (Solved Problems)Document7 paginiSignals & Systems (Solved Problems)Lohith CoreelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Semester Latest 21Document75 pagini2nd Semester Latest 21Mugars Lupin ArseneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kobold Flow SensorDocument4 paginiKobold Flow SensorjilaypandyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes - Transformation (Enlargement)Document5 paginiNotes - Transformation (Enlargement)Samhan Azamain0% (1)
- Basics of Mining and Mineral ProcessingDocument179 paginiBasics of Mining and Mineral Processingminerales&materiales100% (6)
- SPE Swab Surge Field Validations PDFDocument5 paginiSPE Swab Surge Field Validations PDFAbhayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insta Grid Products PamphletDocument2 paginiInsta Grid Products PamphletShawn Paul BoikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gate FTDocument51 paginiGate FTjayavardhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2: Chemicals, Apparatus, and Unit Operations of Analytical ChemistryDocument28 paginiChapter 2: Chemicals, Apparatus, and Unit Operations of Analytical Chemistryangela100% (2)
- MIT16 842F15 Ses 8 Sys IntDocument42 paginiMIT16 842F15 Ses 8 Sys IntssvivekanandhÎncă nu există evaluări
- LNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Document24 paginiLNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Ram Charan Konidela100% (1)
- NA Curve FittingDocument31 paginiNA Curve FittingRadwan HammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- All1 58Document61 paginiAll1 58arisÎncă nu există evaluări
- FredHymans TheoryRopeTraction Part1Document11 paginiFredHymans TheoryRopeTraction Part1WojciechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 CoordinatesDocument13 paginiChapter 8 CoordinatesWei ZhaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 371JB Lecture 3Document38 paginiECE 371JB Lecture 3yassinebouazziÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hubbard Coil MatrixDocument4 paginiThe Hubbard Coil MatrixAna Luisa Lynce100% (1)
- Flexibility FactorsDocument61 paginiFlexibility FactorsCarlos BorgesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BlastingDocument138 paginiBlastingcklconÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Efficiency Coalescers For Gas Processing OperationsDocument9 paginiHigh Efficiency Coalescers For Gas Processing OperationsAndri SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC2Document92 paginiRC2Chrisneil DelosreyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Sheets de Todos Cabos Da ListaDocument20 paginiData Sheets de Todos Cabos Da ListaLaercio ChissicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Downhill Simplex AlgorithmDocument2 paginiDownhill Simplex AlgorithmKtk ZadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 6 Translating Solving EquationsDocument8 paginiLab 6 Translating Solving Equationsapi-389057247Încă nu există evaluări
- My IT 2Document56 paginiMy IT 2sentaljohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Contractor, Supplier, Independent Survey, Ship Service & IndustrialDocument24 paginiGeneral Contractor, Supplier, Independent Survey, Ship Service & IndustrialNicoÎncă nu există evaluări