Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
My Second Tutorial in WaterCad Modeling PDF
Încărcat de
EdDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
My Second Tutorial in WaterCad Modeling PDF
Încărcat de
EdDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
4/13/2014
Water Pipe Networks
Second Tutorial in WaterCad
Hydraulic Modeling of WellField vi WaterCad
By: Dr. Mohamed Elgamal
Introduction to Borehole Pumps
Calculations of Operating Point for borehole
pumps in a well.
4/13/2014
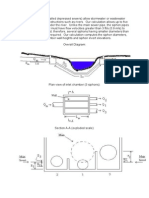
Typical Borehole Pump in a Well
Top of casing
casing
Riser
Stages
Intake
Motor
Multi-stages borehole
submerged pump
Well Idealization
Idealization of a Well (First Approach)
Actual Case
Model
Idealization
Hp
Top of casing
Hs
Q
Static Level
Hs
Dynamic Level
Problem with this idealization:
What happen if Q Changed?
4/13/2014
System of a Well (First Approach-Cont.)
Actual Case
Model
Idealization
Hp new
Top of casing
Hs new
Qnew
Hs new
Hs
Changing Q will result in changing drawdown and thus Hs
Idealization of a Well (Second Approach)
Hp
Actual Case
Hs
Model
Idealization
Q
Top of casing
Hs
Static Level
(s)
Dynamic Level
There is no problem with this idealization:
What happen if Q Changed?
4/13/2014
Idealization of a Well (Second Approach)
Hp
Actual Case
Hs
Model
Idealization
Q
Top of casing
Hs
Static Level
(s)
Dynamic Level
There is no problem with this idealization:
What happen if Q Changed?
Idealization of a Well (Second Approach)
Hp new
Model
Idealization
Actual Case
Hs
Qnew
Top of casing
Hs
Static Level
(s)
Dynamic Level
Changing Q will result in changing drawdown and thus Hs
You do not need to update Hs in this approach
4/13/2014
Second Tutorial in WaterCad
Objectives
The purpose of this Tutorial is to train the trainees
how to:
-Open then run an existing WaterCad model,
-Model groundwater well pumps in WaterCad,
-Determine the suitable pump head for an existing system,
-Check conservation of mass,
-Set two pumps in parallel.
Second Tutorial in WaterCad
Problem Statement
Awajan well field is an existing pipe transmission
system that consists of four existing wells connected
together as shown in figure below. The extracted water
is conveyed to a collector tank in a pump station.
The pump station in its turn pumps water to another
distribution tank far downstream.
Distribution Tank
Requirement:
To satisfy the future expansion needs of the
community, it has been decided to dig a
new well and connect it to the existing
system. From the groundwater studies it
was shown that the most suitable place for
a new well is as the shown figure.
Pump
Station
4/13/2014
Steps for Tutorial #2
#2
1. Open the existing file:
File Open
Browse and select:
Awajan Extention Well.wtg
Exploring Existing WaterCad Model
2. Run the Model
Make sure that the model run
successfully
4/13/2014
Exploring Existing WaterCad Model
3. Explore the results of the existing system:
Determine the flow of each well.
Click Flex Table Icon and select Pumps
Exploring Existing WaterCad Model
4. Explore the results of the existing system:
Determine the flow out of the pump station.
4/13/2014
How can I make sure that
Qin =Qout or in other words, mass
is conserved?
Exploring Existing WaterCad Model
5. Make Sure that Qin =Qout at the Pump Station.
5.1 Activate pipe Annotation for this regard:
Under Element Symbology: R-Click over Pipe New Annotation
4/13/2014
Exploring Existing WaterCad Model
5. Make Sure that Qin =Qout at the Pump Station.
5.2 Enter the Following Annotation Properties:
Field Name: Select Flow;
Set Y Offset: -4m;
Set Height Multiplier: 2;
Exploring Existing WaterCad Model
5. Make Sure that Qin =Qout at the Pump Station.
Now we can easily check the mass balance
4/13/2014
Exploring Existing WaterCad Model
6. Save the file as "AwajanWithNewWell.
File Save As
Adding A New Well to the Model
7. Add the new well (well 25) as follow:
7.1 Zoom in to the well location
10
4/13/2014
Adding A New Well to the Model
7.2 draw a schematic presentation of the well
system (refer to the Figure below): Use Icon
Reservoir represents the
groundwater aquifer
Virtual Pipe Connector
Well
Pump
Junction represents
wells Top of casing
Well actual location
Adding A New Well to the Model
7.3 Assign then enter data of the new well (well 25):
- Well Top of Casing (TOC) level = 585.5;
- Well riser length = 95.5m;
- Dynamic GWL (including drawdown) = 524.0;
Set Water Level in
Reservoir =524.0
Wells Top of casing
Set Elev.=585.5
11
4/13/2014
Adding A New Well to the Model
How to Assign a Length for a Pipe?
The default in WaterCad is the automatic identification of the
length of the pipe based on the backdrop scale.
In order to assign a length to a pipe, do the following:
- Double click the pipe;
- Has User Defined Length: Select True;
- Enter Pipe Length;
Adding A New Well to the Model
7.3 Assign then enter data of the new well (well 25):
- Well Top of Casing (TOC) level = 585.5;
- Well riser length = 95.5m;
- Dynamic GWL (including drawdown) = 524.0;
- Well is located 40m far from the nearby transmission line;
- Elevation of connecting junction (J-28) = 586.5
Set Water Level in
Reservoir =524.0
Set Length of virtual pipe =1m
Set Pipe
Length =40m
Wells Top of casing
Set Elev.=585.5
Set Junction Elevation =586.5m
12
4/13/2014
Adding A New Well to the Model
How to Enter Pump Data?
a- Pump Elevation;
= TOC Riser Length
= 585.5 95.5 = 490.0m
Adding A New Well to the Model
How to Enter Pump Data?
b- Pump Definition;
Select Edit Pump Definition
13
4/13/2014
Adding A New Well to the Model
How to Enter Pump Data?
c- Pump Definition;
Add New Pump
Rename it as Pump Well25
Adding A New Well to the Model
How to Enter Pump Data?
d- Pump Definition Type;
Select Design Point (1 Point)
14
4/13/2014
Adding A New Well to the Model
How to Enter Pump Data?
e- Pump Definition Type;
Enter Design Flow =70 m3/hr
Enter any estimate of head:
say 100m, will be checked later
Please Note that up till now we have defined a new pump
type (Pump Well25) However we did not yet assign this
type to well 25.
Adding A New Well to the Model
How to Enter Pump Data?
f- Assign Pump to well 25;
Double Click the Pump of well 25
Pump Definition:
Select Pump Well 25
15
4/13/2014
Adding A New Well to the Model
Run the Model
Check all errors
Adding A New Well to the Model
Run the Model
Check all errors
This does mean that no numerical
error or no missing data.
This does not mean that the
solution is physically accepted.
16
4/13/2014
Adding A New Well to the Model
Check if the assume head of Pump Well 25 is sufficient
R Click on the Pump and Select: System Head Curve
Fine Tuning for the Suitable Pump
Check if the assume head of Pump Well 25 is sufficient
Click the Compute icon to construct the System
Head Curve
Pump
Curve
System
Curve
17
4/13/2014
What Does the System Curve
Mean?
Fine Tuning for the Suitable Pump
Check if the assume head of Pump Well 25 is sufficient
The well will pump at Q > 70 m3/hr (safe Yield)
Pump
Curve
System
Curve
18
4/13/2014
Fine Tuning for the Suitable Pump
To Solve this Problem, we need to have a pump with
lower head. An approximate value could be obtained
from the system head at the required max flow
The required Pump Head is close to 70m
Pump
Curve
System
Curve
Fine Tuning for the Suitable Pump
To get the exact system head at Q=70 m3/hr
Click Data Tap
19
4/13/2014
Fine Tuning for the Suitable Pump
Lets go and correct the pump head accordingly
Fine Tuning for the Suitable Pump
Re-Run the Model
Check the Operating Point
YesI have got
the right Pump
20
4/13/2014
Mass Balance Comparison
Lets Check the Mass Conservation in the new
Case.
Balanced
Un-Balanced
Existing Condition
After Adding Well 25
Why weve got an unbalanced
flow at the Pump Station?
21
4/13/2014
Problem Diagnostic
After adding Well 25, the total extracted flow has
increased from 338 399 m3/hr which exceeds
the pump capacity.
The solution of the problem is one of the following:
-To replace the pumping unit located at the PS by a
more power-full pump with bigger capacity;
-To add a new pump to work in parallel with the
existing one.
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
Zoom
in to the Pump Station
22
4/13/2014
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
Plot
the System Curve
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
Determine
the required system head to get
the required Q to be pumped (Q=399
(Q=399 m3/hr)
Required
New Operating Pt.
Virtual Curve of
2 Pumps in Parallel
QnewPump
System Curve
Existing
Operating Pt.
Q=399
m3/hr
Existing One
Pump Curve
Qnew pump 70-80
m3/hr
23
4/13/2014
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
Shift
the existing pump to allow some
room for the new pump
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
Geometrically
add the new pump in parallel.
24
4/13/2014
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
For
the new pipes PP-66
66,, PP-67 use the same
data as PP-49 and PP-59
59..
Use the same pump level (not head)
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
Use
the following Pump Definition.
25
4/13/2014
Adding a Pump in Parallel to Exiting One
Check
that Qin=Qout and change Pump Q if
necessary till satisfying Qin=Qout.
Now it is
Balanced
26
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Design of Water Based Fire Protection SystemsDocument43 paginiDesign of Water Based Fire Protection SystemsKumararaja Konikki94% (33)
- Design of Water Based Fire Protection SystemsDocument43 paginiDesign of Water Based Fire Protection SystemsKumararaja Konikki94% (33)
- Hydraulic Structures SpillwaysDocument36 paginiHydraulic Structures SpillwaysLim BoonchinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrological Procedure No 27 (HP 27) PDFDocument64 paginiHydrological Procedure No 27 (HP 27) PDFAgungNurFauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewage and Drainange System Theories and CalculationDocument19 paginiSewage and Drainange System Theories and CalculationSopi Labu0% (1)
- Guidance Note On The Design of Thrust BlocksDocument1 paginăGuidance Note On The Design of Thrust BlocksLi Tsz ChunÎncă nu există evaluări
- AK - Design of Diversion Weir and Intake Works Jan 2020Document50 paginiAK - Design of Diversion Weir and Intake Works Jan 2020Manoj100% (1)
- hw11 DallasonnekommtDocument2 paginihw11 DallasonnekommtDan Yapp0% (1)
- My First Tutorial in WaterCad HandoutDocument16 paginiMy First Tutorial in WaterCad HandoutMathiTwadC100% (1)
- Hec RasDocument4 paginiHec RasGerman D Gutierrez ManzanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highway Drainage Design Manual HydrologyDocument338 paginiHighway Drainage Design Manual HydrologyBernard OwusuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewerage and Sewage Treatment of Panvel, Maharashtra (Presentation) PDFDocument38 paginiSewerage and Sewage Treatment of Panvel, Maharashtra (Presentation) PDFDhruv MudgalÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Step by Step Guide To EPANET SimulationsDocument23 paginiA Step by Step Guide To EPANET Simulations17018 Md. Shahariar KabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dam HydraulicDocument307 paginiDam HydraulicSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epa SWMM TutorialDocument16 paginiEpa SWMM TutorialHassan Abib BasalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hytran+ TutoDocument5 paginiHytran+ TutoMohamed BenrahmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- REG 265-Surface DrainageDocument43 paginiREG 265-Surface DrainageAdam Chow Wen YanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProfessionalPractice - FAQ (For BEM's Website) PDFDocument17 paginiProfessionalPractice - FAQ (For BEM's Website) PDFgilbert850507Încă nu există evaluări
- Hec RasDocument453 paginiHec RasED Ricra CapchaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Hydrologic Principles in Storm Sewage 1Document18 paginiApplication of Hydrologic Principles in Storm Sewage 1Balanlan PenalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics PDFDocument18 paginiHydraulics PDFDeepak_pethkar100% (1)
- Epanet DescriptionDocument17 paginiEpanet Descriptionamhosny64Încă nu există evaluări
- Old Exam 4307Document6 paginiOld Exam 4307rizwan ghafoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intake StructuresDocument29 paginiIntake Structureshardeep SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverted SiphonsDocument6 paginiInverted SiphonsRaju ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADOT - Bridge Hydraulics GuidelinesDocument10 paginiADOT - Bridge Hydraulics GuidelinesbobbyccwÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 Sewers DesignDocument11 paginiCH 4 Sewers DesignmavessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fet Ci Lecture Notes Prof Quamrul Hassan Design-WeirDocument53 paginiFet Ci Lecture Notes Prof Quamrul Hassan Design-WeirVEDANT SHARMA 129Încă nu există evaluări
- Below Ground DrainageDocument9 paginiBelow Ground Drainagepatrick kivutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyTran Training Hill ChartDocument31 paginiHyTran Training Hill ChartAyanilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics Training Lesson 10Document22 paginiHydraulics Training Lesson 10sponky05100% (1)
- Bentley Water SolutionsDocument86 paginiBentley Water Solutionsmoraru727Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of ManholesDocument6 paginiTypes of ManholesEvonYongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Service Installation ManualDocument15 paginiWater Service Installation ManualSumit MardaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 Storage Structures ReservoirDocument33 paginiLecture 2 Storage Structures ReservoirNguyen Hong HaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Stormwater NetworkDocument14 paginiDesign Stormwater NetworkAhmad SanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Parts of Culvert DesignDocument6 paginiImportant Parts of Culvert DesignER Rajesh MauryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report PaperDocument14 paginiReport PaperAlreen-Nadzrif L. SakandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- WaterCAD Theory DocumentDocument49 paginiWaterCAD Theory DocumentMohammed SohailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1. Flow in Open Channel: BFC21103 HydraulicsDocument41 paginiChapter 1. Flow in Open Channel: BFC21103 HydraulicsdibaelleyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1B Mat FoundationsDocument17 paginiChapter 1B Mat Foundationsmohamed hassan adenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-1 Introduction To Hydrologic Methods PDFDocument41 pagini3-1 Introduction To Hydrologic Methods PDFSubija IzeiroskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thrust Force CalculationDocument2 paginiThrust Force CalculationlfpachecoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETL 1110-2-231 Initial Reservoir FillingDocument44 paginiETL 1110-2-231 Initial Reservoir Fillingsksibal100% (1)
- WaterNetGenManual 2011 10 13Document19 paginiWaterNetGenManual 2011 10 13MwabutwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Ogee SpillwayDocument32 paginiDesign of Ogee SpillwayBenson NkyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization of Water Distribution NetworksDocument10 paginiOptimization of Water Distribution NetworksBenny Aryanto SihalohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Hydraulic Structures: B.Tech Civil Credit Hours: 03Document16 paginiDesign of Hydraulic Structures: B.Tech Civil Credit Hours: 03Suleman FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hobas Sand Trap eDocument3 paginiHobas Sand Trap ekhaimatsahÎncă nu există evaluări
- SWMM 4 ManualsDocument720 paginiSWMM 4 ManualsFatmah El WardagyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture3 - Uniform Flow 2Document18 paginiLecture3 - Uniform Flow 2Kaaviyan ThirunyanamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Hammer in Pumped Sewer MainsDocument45 paginiWater Hammer in Pumped Sewer MainsManikandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE404 Seepage TheoriesDocument50 paginiCE404 Seepage Theoriesanuragsatyarth86% (7)
- Culvertmaster Readme PDFDocument6 paginiCulvertmaster Readme PDFHector Mayol NovoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Manual For Small Wastewater Works 2009-2Document52 paginiDesign Manual For Small Wastewater Works 2009-2VichekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravity DamDocument26 paginiGravity DamKalyani SurywanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wet Retention Ponds: AdvantagesDocument7 paginiWet Retention Ponds: AdvantagesEugene MarcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week-1 Lec-2-Introduction To Water Supply System DesignDocument38 paginiWeek-1 Lec-2-Introduction To Water Supply System DesignMuhammad UsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Storm Water Management Design Manual Culverts and BridgesDocument14 paginiStorm Water Management Design Manual Culverts and Bridgesfox360Încă nu există evaluări
- Classic Energy Problem in Open-Channel Flow - Wikiversity PDFDocument31 paginiClassic Energy Problem in Open-Channel Flow - Wikiversity PDFAlaa AbdulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design—Operation Interactions at Large Treatment Plants: Proceedings of a Workshop Held in ViennaDe la EverandDesign—Operation Interactions at Large Treatment Plants: Proceedings of a Workshop Held in ViennaS. H. JenkinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Schedule Weight Sheet Norwegian Piping PDFDocument2 paginiPipe Schedule Weight Sheet Norwegian Piping PDFKiran Kumar KondapalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- UFH Installation Guide PDFDocument96 paginiUFH Installation Guide PDFEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Flow Friction Factor CalculationsDocument10 paginiPipe Flow Friction Factor CalculationspanchitasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projekti Elektrik PDFDocument15 paginiProjekti Elektrik PDFEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heating System Chapter6 PDFDocument26 paginiHeating System Chapter6 PDFbekir kurtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projekti Elektrik PDFDocument15 paginiProjekti Elektrik PDFEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underfloor Heating/Cooling: Technical InformationDocument206 paginiUnderfloor Heating/Cooling: Technical InformationNataLeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF71 Guide To Underfloor HeatingDocument40 paginiNF71 Guide To Underfloor Heatingngocdhxd92Încă nu există evaluări
- Epanet Vs WatergemsDocument9 paginiEpanet Vs WatergemsEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- CYPECAD - User's Manual PDFDocument141 paginiCYPECAD - User's Manual PDFBelak1Încă nu există evaluări
- WaterGems WorkDocument41 paginiWaterGems WorkSameerMinhaj100% (2)
- WaterGems PlanDocument5 paginiWaterGems PlanEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heating & Cooling Load Calculation Program - CLTD/CLF/SCL MethodDocument43 paginiHeating & Cooling Load Calculation Program - CLTD/CLF/SCL MethodSenthilnathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- VRF PDFDocument37 paginiVRF PDFJohn DaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rev It Piping and PlumbingDocument12 paginiRev It Piping and PlumbingEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Capacity HVAC CalculationDocument12 paginiPower Capacity HVAC CalculationEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heating Cooling Guide FINAL 9-4-09Document24 paginiHeating Cooling Guide FINAL 9-4-09chakks_99Încă nu există evaluări
- IPWE2014 Tunnel Ventilation and SafetyDocument56 paginiIPWE2014 Tunnel Ventilation and SafetyDurgesh GovilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wer Tert WertDocument1 paginăWer Tert WertEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wert Wet Wet WetDocument2 paginiWert Wet Wet WetEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flood Risk Assessment ChecklistDocument9 paginiFlood Risk Assessment ChecklistEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tunnel EngineeringDocument134 paginiTunnel EngineeringEd100% (2)
- HYDROLOGY BY RATIONAL FORMULA (English or Metric Units)Document1 paginăHYDROLOGY BY RATIONAL FORMULA (English or Metric Units)jherwindo895Încă nu există evaluări
- Fire Alarm Detection SystemsDocument70 paginiFire Alarm Detection SystemsEdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema 8. Quantum Mechanics 1D - 2P - 2019Document29 paginiTema 8. Quantum Mechanics 1D - 2P - 2019Eduardo Junior Hernandez RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue Analysis of Wing-Fuselage Lug Section of A Transport AircraftDocument9 paginiFatigue Analysis of Wing-Fuselage Lug Section of A Transport Aircraftaz1az100% (1)
- Q3 MathDocument28 paginiQ3 MathKennedy EscanlarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 12 Tutorial 10 KSP CalculationsDocument12 paginiChemistry 12 Tutorial 10 KSP CalculationsrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics V LP 1ST To 4TH GradingDocument220 paginiMathematics V LP 1ST To 4TH GradingsweetienasexypaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument8 paginiSciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectÖğr. Gör. Yasin BEKTAŞÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stability Analysis of Tunnel Keyblock: A Case Study: I.-M. Lee and J.-K. ParkDocument10 paginiStability Analysis of Tunnel Keyblock: A Case Study: I.-M. Lee and J.-K. ParkBastian AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variabel ModeratDocument26 paginiVariabel ModeratraudhahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice - Circle The Correct ResponseDocument7 paginiMultiple Choice - Circle The Correct ResponsesharethefilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cavidad PrediccionDocument9 paginiCavidad PrediccionLuis MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOA Matrix Ibrahim WrongDocument109 paginiTOA Matrix Ibrahim WrongSobhan DasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infocad Ifc ManualDocument8 paginiInfocad Ifc ManualMarian DragosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Syllabus:: Department of Textile EngineeringDocument3 paginiDetailed Syllabus:: Department of Textile EngineeringProf Dr Md Saifur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer in Olga 2000Document11 paginiHeat Transfer in Olga 2000Akin MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Kid Abacus Learning Private LimitedDocument9 paginiSmart Kid Abacus Learning Private Limitedhong lyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT and JFET Frequency ResponseDocument16 paginiBJT and JFET Frequency ResponseVert WheelerÎncă nu există evaluări
- USFS Timber Cruising Handbook PDFDocument268 paginiUSFS Timber Cruising Handbook PDFJeffTaborÎncă nu există evaluări
- From Monopoles To Textures: A Survey of Topological Defects in Cosmological Quantum Field TheoryDocument7 paginiFrom Monopoles To Textures: A Survey of Topological Defects in Cosmological Quantum Field TheoryDamian SowinskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Domino Effect AnalysisDocument16 paginiDomino Effect Analysisapi-270822363Încă nu există evaluări
- Fei Zeng PosterDocument1 paginăFei Zeng PosterNaida AdemovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prob-4 5Document8 paginiProb-4 5Vinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asymptotes WorksheetDocument2 paginiAsymptotes WorksheetjosephmwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inductive Reasoning RefresherDocument7 paginiInductive Reasoning RefresherAnne Masangkay50% (2)
- Switched - Capacitor by Ken MartinDocument30 paginiSwitched - Capacitor by Ken MartinSumeet SauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment 01 - Introduction To Descrete Probability: Probability of Cyan - GeneralizedDocument2 paginiAssessment 01 - Introduction To Descrete Probability: Probability of Cyan - Generalizedashishamitav123Încă nu există evaluări
- Semi-Variogram - Nugget, Range and Sill - GIS GeographyDocument8 paginiSemi-Variogram - Nugget, Range and Sill - GIS GeographyhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graph Sheet V.2Document13 paginiGraph Sheet V.2youssef amrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Functions in PI 7.0 - Process Integration - Community WikiDocument34 paginiStandard Functions in PI 7.0 - Process Integration - Community Wikifziwen100% (1)
- Module 2 Laplace TransformsDocument36 paginiModule 2 Laplace TransformsErnie Mark Patosa MaratasÎncă nu există evaluări