Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Yeaa
Încărcat de
Michael LeungDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yeaa
Încărcat de
Michael LeungDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
In this experiment, you will investigate the extension of one of the springs supporting a load
as the load is varied. (Nov 09/P33)
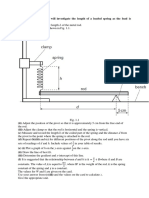
The apparatus has been partly assembled. Complete the assembly by suspending the mass hanger
(with no masses on it) from the central loop, as shown in Fig. 1.1. In this experiment, you will
investigate the extension of one of the springs supporting a load as the load is varied.
The apparatus has been partly assembled. Complete the assembly by suspending the mass hanger
(with no masses on it) from the central loop, as shown in Fig. 1.1.
Fig. 1.1
Note that two marks 0.100 m apart have been made on the string.
(a) Record the suspended mass M (the mass of the mass hanger).M = .............................. kg
(b) (i) Measure the length l of the coiled section of spring A, as shown in Fig. 1.1. l = .............. m
(ii) Hence calculate the extension x of the spring (the unloaded length is written on a card).
x = ....m
(c) Measure the heights of the marks above the bench and use these to find the vertical
separation v of the marks (see Fig. 1.1). Show your working. v = ................................ m
(d) Add more mass to the hanger and repeat (a), (b) and (c) until you have six sets of
readings for M, l, x and v. Include values of in your table.
(e) (i) Plot a graph of on the y-axis against x on the x-axis.
(ii) Draw the line of best fit.
(iii) Determine the gradient and y-intercept of the line of best fit.
(f) The quantities M, v and x are related by the equation
, where q is a constant, k
is the spring constant (the value of k is written on a card) and C is the tension required for the
initial separation of the springs coils. Using your answers from (e)(iii), determine the value of C.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Drwaing f4Document2 paginiDrwaing f4Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini PhysDocument10 paginiMini PhysMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- UplinkDocument2 paginiUplinkMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- g8 NotesDocument6 paginig8 NotesMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Constant MassDocument4 paginiFor Constant MassMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- M A Grams, Where A Is The Mass Nucleonnumber of The ElementDocument1 paginăM A Grams, Where A Is The Mass Nucleonnumber of The ElementMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethics and The Law in Social WorkDocument4 paginiEthics and The Law in Social WorkMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disp MethodDocument3 paginiDisp MethodMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyn g12 ws22Document5 paginiDyn g12 ws22Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Known Function New Function Transformation: A X F yDocument2 paginiKnown Function New Function Transformation: A X F yMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9702 P5 Q1Document4 pagini9702 P5 Q1Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic Learning OutcomesDocument3 paginiTopic Learning OutcomesMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Form Iv 1. (A) Write Down The Readings BelowDocument26 paginiTest Form Iv 1. (A) Write Down The Readings BelowMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Power Output Electrical Power Supplied: Paper 5 Revision QuestionsDocument5 paginiMechanical Power Output Electrical Power Supplied: Paper 5 Revision QuestionsMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 9702 Paper 5 Skill Breakdown of MarksDocument12 paginiPhysics 9702 Paper 5 Skill Breakdown of MarksMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- A TubesDocument7 paginiA TubesMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRI Student WorksheetDocument1 paginăMRI Student WorksheetMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opt D1Document2 paginiOpt D1Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name School Name Class/Section: Physics October 2015Document12 paginiName School Name Class/Section: Physics October 2015Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronDocument12 paginiCurrent Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Physics QuestionsDocument9 paginiO Level Physics QuestionsMichael Leung75% (4)
- Is The Weight of The Rod, Is The SpringDocument1 paginăIs The Weight of The Rod, Is The SpringMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)