Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Anatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDF
Încărcat de
Angel KimDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Anatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDF
Încărcat de
Angel KimDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
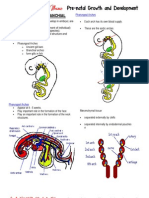
ANATOMY: ANTERIOR TRIANGLE OF THE
NECK
RELATIONS:
SUPERIOR: Inferior border of the mandible (completed by
an imaginary line drawn from the angle of the mandible to
the mastoid process
INFERIOR: Superior border of the clavicle with the
suprasternal notch
ANTERIOR: Median line of the neck
POSTERIOR: Sternocleidomastoid
EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEINS
Palpable structures within the Anterior Triangle of the Neck:
Hyoid Bone
o Lies below the inferior border of the
mandible
Laryngeal Prominence
o Aka PROMINENTIA LARYNGEA, POMMUM
ADAMI, ADAMS APPLE
o Pointed anteriorly
! Projecting the superior angular
process of the thyroid cartilage
o Thyrohyoid Membrane " membrane
between the hyoid bone and thyroid
cartilage
Cricoid Cartilage
o Narrow strip of cartilage below the thyroid
cartilage
o Shaped like a signet ring
! Narrow anteriorly and expands as
it moves posteriorly
o The only complete ring among the
cartilages of the neck
o Carotid tubercle
! Transverse process of the 6th
cervical vertebrae
! Lies lateral to the cricoids
cartilage
! Where the pulsations of the
common carotid artery can be felt
o Cricothyroid cartilage " membrane
between the thyroid cartilage and cricoid
cartilage
Tracheal cartilages
o Cartilages that lie posterior to the thyroid
gland
SUBCUTANEOUS CERVICAL FASCIA
Layer which contains the superficial structures of
the neck including:
o Platysma muscle
o External Jular Vein (EJV)
o Anterior Jugular Vein
o Cervical Plexus
o Superficial Cervical Lymph Nodes
PLATYSMA
Thin sheet of muscle fibers extending from the
anterior chest wall
o Anterior portion of the 2nd rib level
Its fibers reaches up to the inferior labial muscles
and join their insertion to the skin of the lower lip
Innervated by the cervical branch of the Facial
Nerve
Voluntary contraction of muscles: stretch the
overlying skin
o Strong contractions: pulls down the angles
of the lips
Formed by the union of the Posterior division of the
retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular
vein
Commencement: behind the angle of the mandible
Course: crosses vertically downward over the
surface of the SCM, piercing the investing layer of
the deep cervical fascia and drain into the
subclavian vein
Termination: behind the middle portion of the
clavicle
**SUPERFICIAL CERVICAL LYMPH NODES nodes are
closely related to the EJV
ANTERIOR JUGULAR VEINS
Pair of slender veins on each side of the median
line
Drains the veins on the chin
Course: Descends vertically to pierce the investing
layer of the deep cervical fascia above the jugular
notch to join the EJV or subclavian vein
Jugular Arch anastomis of the 2 anterior jugular
veins which lies above the jugular notch
CERVICAL PLEXUS
All branches of the cervical plexus arise behind the
middle part of the SCM and hooks to its posterior
side to emerge anteriorly
Comprised by the anterior rami of C1- C4
o C1 only has a motor component
o C2-C4 are purely sensory nerves
Branches of the Cervical Plexus
o Lesser Occipital Nerve
! C2
! Course: travels upwards along the
posterior border of the SCM to the
apex of the posterior triangle
! Innervates the occipital area
behind the auricle
o Greater Auricular Nerve
! C2 C3
! Course: crosses over the surface
of the SCM
! Innervates:
Angle of the mandible
Mastoid process
Auricle (skin)
Parotid gland
Transverse Cervical/ Anterior Cutaneous
Nerve of the Neck
! C2 C3
! Course: crosses the external
surface of the SCM horizontally
! Innervates the skin of the anterior
neck
Supraclavicular Nerves
! C3 C4
! Course: Courses superficially as a
single stem behind the posterior
border of the SCM, crossing the
lower part of the posterior triangle
! Divides into medial, intermediate
and lateral branches to innervate
skin along the clavicle up to the
pectoralis
DEEP CERVICAL FASCIA
3 layers of the deep cervical fascia:
o Investing layer
o Pretracheal layer
o Prevertebral layer
Composed of fribro-elastic tissue that forms a colar
around the neck
Functions:
o Maintain the relative positions of the
structures
o Prevents the spread of infection to deeper
layers
o Allows mobility of the neck
o Separate different structures of the neck
! Important in surgery to gauge the
depth of the incision made
INVESTING LAYER OF THE DEEP CERVICAL FASCIA
Bony attachments:
o Superior: Hyoid bone and the lower
border of the mandible
o Inferior: Upper border of the manubrium,
along the clavicle to the acromion and
spine of the scapula
! Supraclavicular Space/ Burns
space " located at the
manubrium which contains the
sterna heads and anterior jugular
vein
** PAROTIDEO-MASSETERIC FASCIA ! extension of the
investing layer, covering the side of the face
Structures within the investing layer:
o Sternocleidomastoid
o Trapezius muscle
o Parotid gland
o Submandibular gland
o Lower portion of the Anterior jugular vein
and jugular arch
PRETRACHEAL LAYER OF THE DEEP CERVICAL FASCIA
Attachments:
o Superior: Hyoid bone
Inferior: Descends to the thoracic cavity
to blend with the adventia of great vessels
and the fibrous pericardium
Known as the dangerous area of the neck
because of its direct continuation to the
pericardium
Functions to firmly hold the thyroid gland to the
cartilages lying posterior to it
o Berrys Ligament/ Lateral Thyrohyoid
Ligament " attaches the thyroid gland to
the cartilage; arises from the pretracheal
layer
Extensions of the Pretracheal Layer:
o Carotid Sheath
! Envelops:
Common Carotid Artery
Internal Jugular Vein
Vagus Nerve
! Reaches the base of the skull and
inferiorly into the thoracic cavity
Only the internal carotid
artery carries the carotid
sheath covering
The ECA has no carotid
sheath covering.
o Prethyroid Lamina
! Ensheaths the infrahyoid muscles
and the thyroid gland
! It blends with the pretracheal
layer inferiorly which descends
into the thoracic cavity
o
**The pretracheal fascia blends with the BUCCOPHARYNGEAL FASCIA along this location.
PREVERTEBRAL LAYER OF THE DEEP CERVICAL FASCIA
Deep layer covering the muscles and
neurovascular structures in the posterior triangle
of the neck
Attachment:
o Superior: basilar part of the occipital
bone
o Inferiorly: Joins the fascia of the
posterior mediastinum in the thoracic
cavity
Axillary Sheath " encloses the brachial plexus and
the subclavian artery; arises from the prevertebral
fascia
**The prevertebral layer also blends with the BUCCOPHARYNGEAL FASCIA and the PHARYNGO-BASILAR
FASCIA.
SUBMANDIBULAR TRIANGLE
Relations:
o Superior: Lower border of the mandible
o Inferior: posterior belly of the digastric
and stylohyoid
o Roof: Mylohoid
**The mylohyoid muscle also comprises the floor of the
mouth.
**The bellies of the posterior digastric and stylohyoid
separate the submandibular triangle from the carotid
triangle.
Contents of the Submandibular Triangle:
o Submandibular gland
o External Carotid artery
Submental Triangle:
Small insignificant triangle bound by the two
anterior bellies of the digastrics muscle
The only significance of the submental triangle is
that it contains lymph nodes, fats and small veins
that unite to form the anterior jugular vein
o Commencement of AJV: submental
triangle
CAROTID TRIANGLE
Relations:
o Superior: bellies of the posterior digastric
and stylohyoid
o Posterior: Anterior border of the SCM
o Anterior: Anterior belly of the omohyoid
Contents of the Carotid Triangle
o Common Carotid Artery medially located
o Internal Jugular Vein laterally located
o Vagus Nerve posteriorly located
EXTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY
Lies more antero-medially than the Internal Carotid
Artery
Bifurcation of the Common Carotid Artery "
superior border of the thyroid cartilage
o Termination of Common Carotid Artery:
superior border of the thyroid cartilage
o Commencement of ECA: Superior border
of the thyroid cartilage
Branches of the ECA (8):
o Superior Thyroid Artery
o Facial Artery
o Lingual Artery
o Occipital Artery
o Posterior Auricular Artery
o Ascending Pharyngeal Artery
o Superficial Temporal Artery
o Maxillary Artery
Termination of the ECA: neck of the mandible
o When it gives rise to its 2 terminal
branches, superficial temporal artery and
the maxillary artery
**The ICA does give off any branches externally, only when
it courses through the Carotid Canal of the skull where it
starts to give off branches supplying the brain.
INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
Deeper, more posterior branch
Carotid Sinus slight dilatation located at its
commencement
o Commencement: superior border of
thyroid cartilage
Carotid Bodies/ Glomus Caroticum
o Nestling in between the ECA and ICA
Commencemet: dilated bulb in the jugular fossa
Course: Starts off as a dilated bud in the jugular
fossa. It then descends lateral and superficial to
the common carotid artery and external carotid
artery.
Termination: At the level of T1 vertebrae, superior
to the sternoclavicular joint
Drains the deeper veins of the head, common
facial vein and the superior and middle thyroid
veins.
The IJV then joins the subclavian vein that will then
drain into the brachiocephalic vein
Internal(Jugular(Vein(
Subclavian(Vein(
B(rachiocephalic(
Vein(
VAGUS NERVE
INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY
Composed of chemoreceptor cells
(baroreceptors) from the parasympathetic
nerves of CNIX and sympathetic nerves
from the superior cervical ganglion
Baroreceptors
are
affected
by
hemoconcentrations of O2 and CO2
pressures
which
influences
blood
pressure, cardiac and respiratory rate.
Emerges from the jugular foramen with the CN IX
and XI
Mixed nerve with fibers:
o Afferent and efferent parasympathetic
fibers to the pharynx, esophagus, larynx,
trachea and lungs
! With special fibers to the heart
and abdominal viscera
o Receives efferent fibers from the cranial
portion of CN XI for the innervations of
most voluntary muscles of the larynx and
pharynx
The main trunk of the vagus nerver lies between
the carotid arteries and the internal jugular vein in
the carotid sheath
Gives off 2 branches, superior and inferior cardiac
branches
o Participates in the cardiac plexus
2 ganglia within the jugular fossa:
o Superior ganglion
! Gives off a meningeal and
auricular branch
o Inferior ganglion
! Gives off:
Phayrngeal branch
participates
in
the
pharyngeal plexus (with
CN
IX)
and
also
innervates the pharynx
and soft palate (with
cervical plexus)
Superior Laryngeal Nerve
2 branches of the vagus nerve related to the neck:
o Superior Larnygeal Nerve
o Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
! Right recurrent laryngeal nerve "
hooks to the subclavian artery
! Left recurrent laryngeal nerve "
hooks to the arch of the aorta
o
o
Suprahyoid group of muscels
Infrahyoid group of muscles
Mylohyoid
Thyrohyoid
Hyoglossys
Sternothyroid
Geniohyoid
Sternohyoid
Stylohyoid
Omohyoid
Superior Laryngeal Nerve:
Descends deep to the ICA which divides into:
o Internal Laryngeal Nerve
! Larger branch
! Afferent fibers from dorsum of
tongue, internal mucosa, pharynx,
larynx and vocal folds
o External Laryngeal Nerve:
! Smaller branch
! Descends alongside the superior
laryngeal artery and superior
laryngeal vein
! Innervates the cricothyroid and
inferior constrictor muscles of the
pharynx
HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE
Composed of motor fibers for the lingual muscles
Course: emerges from the hypoglossal canal and
descends with the ICA and IJV to the level of the
posterior belly of the digastric and stylohyoid where
it joins 1st and 2nd spinal nerves. It then twists
anteriorly, passing above the ECA and ICA to enter
the oral cavity where it distributes its branches to
the different lingual muscels.
Descendens Hypoglossi" The fibers from C1 and
C2 separate from the hypoglossal nerve to
descend lateral to the carotid sheath.
Descendends Cervicalis " fibers forming C2 and
C3
Ansa Cervicalis:
o Union of the descendens hypoglossi and
descendens cervicalis
o Supplies the infrahyoid group of muscles
MUSCULAR TRIANGLE
Pretracheal of Infrahyoud muscles or often
referred to as STRAP MUSCLES
o Flat, thin, narrow slips that cover the
thyroid cartilage and gland
o Ensheathed by the pretracheal layer of the
deep cervical fascia
Contents of the muscular triangle:
o Sternohyoid
o Omohyoid
o Sternothyroid
o Thyrohoid
o Thyroid gland
o Parathyroid gland
Thyroid cartilage, cricoids and tracheal
rings
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
Digastric
**All the muscles of the infrahyoid group of muscles are
innervated by the ansa cervicalis EXCEPT the thyrohyoid
muscle which is innervated by C1 of hypoglossal nerve.
THYROID GLAND
H-shaped or butterly-shapedgland
Encapsulated
Attached to the sides of the thyroid, cricothyroid
and upper tracheal cartiages via the prethyroid
layer of fascia
Each of the 2 conical lobes taper into apices that
reaches up to about the middle portion of the
lateral thyroid laminae
Isthmus
o Narrow glandular strip which connects the
2 lobes
o Normally positioned in front of the 2nd and
3rd tracheal cartilage
o Base of the isthmus: in front of the lower
border of the 4th tracheal cartilage
Pyramidal Lobe
o Located slightly to the left of the median
plane
o Attached above the hyoid bone
o Levator glandula thyroidea muscle "
smooth
muscular
tissue
which
impregnates the pyramidal lobe
Blood Supply:
o Superior Thyroid Artery
! Supplies the upper and middle
parts of the thyroid gland on each
side
! Branch of the ECA
o Inferior Thyroid Artery
! Branch of the thyrocervical
branch of the subclavian artery
! Course: from the thyrocervical
trunk of the subclavian artery, it
approaches the posterior border
of the gland at its middle part
! Supplies the inferior portion of
the gland
o Thyroidea Ima
! Arising either from the arch of the
aorta or brachiocephalic trunk
! Supplies the isthmus and base of
the gland
Venous Drainage:
o Superior Thyroid Vein and Middle Thyroid Vein
! Drains into the IJV
o Inferior Thyroid Vein
! Located at the base of the isthmus
! Drains into the brachiocephalic vein
PARATHYROID GLANDS
Oval or circular masses located within the capsule at the posterior border of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland
Innervated by the superior and middle cervical ganlgiia
CRICOID CARTILAGE
Located below the thyroid cartilage and in front of the 6th cervical vertebra
Articulates with the inferior horn of the thyroid cartilage and is attached by:
o Cricothyroid muscles
! Fibers directed obliquely upwards and is attached to the lower border of the thyroid cartilage
o Cricothyroid membrane
! Connects the 2 cartilages
! A fold of this membrane turns inwards to form the vocal membrane which participates in the formation
of the vocal folds
RECURRENT LARYNGEAL NERVE
Paired slender nerves lodged between the thyroid gland and tracheoesophageal tubes
o Right recurrent laryngeal nerve hooks at the subclavian artery
o Left recurrent laryngeal nerve hooks at the arch of the aorta
Related to the inferior thyroid artery
Innervates the intrinsic muscles of the larynx which move the vocal folds
LYMPHATICS
Located superficial at the lateral side of the cricoids and tracheal cartilages
o Higher nodes receive lymph from the head, parotid and sumandibular and pharynx
o Lower nodes receive lymph from the base of the neck, axilla and upper pectoral area and mammary glands
These two efferent vessels unite and drain into:
o Right Subclavian Vein " drains the right side
o Thoracic Duct " drains the left side
MUSCLES OF THE NECK:
ORIGIN
Sternocleidomastoid
Sternal head
Clavicular
head
Platysma
Anterior surface
manubrium
INSERTION
INNERVATION
ACTION
of
Superior surface of the
medial third of the
clavicle
Fascia of the pectoralis
major and deltoids
Mastoid process and lateral
half of the superior nuchal
line
Spinal Accessory Nerve
Can twist and flex head
on
one
side
or
forwards; 2 muscles in
action
can
raise
thoracic inlet
Inferior border of the
mandible and skin of lower
face
Cervical
branch
Trigeminal nerve
of
Mandibular
branch
trigeminal nerve
of
C2 and C3proprioception
Draws skin of neck
superiorly when teeth
are clenched
Digastric
Ant. Belly
Digastic
mandible
fossa
of
Post. Belly
Mastoid process
Intermediate
tendon
attached to the hyoid bone
Stylohyoid
Styloid process
Hyoid bone
Sternohyoid
Manubrium
Hyoid bone
Depresses
mandible
the
Facial Nerve
Depresses
mandible
the
Ansa cervicalis
Depresses hyoid after
elevation
during
Muscular branch of Facial
nerve
swallowing
Omohyoid
Near the jugular notch
Hyoid bone
Sternothyroid
Psoterior surface
manubrium
Oblique line
cartilage
Thyrohyoid
Oblique line of thyroid
cartilage
of
of
thyroid
Hyoid bone
Ansa cervicalis
Depresses,
retracts
and stedies the hyoid
Ansa cervicalis
Depresses hyoid and
larynx
C1 of CN XII
Depresses hyoid and
elevates larynx
**Injury to the SCM can lead to TORTICHOLIS
**The intermediate tendon of the digastrics arises from the pretracheal layer of the deep cervical fascia
IMPORTANT NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES
COMMENCEMENT
TERMINATION
External Jugular Vein
Behind the angle of the mandible
Posterior part of the middle portion of the clavicle
Anterior Jugular Vein
Area of the submental triangle
Above the jugular notch
Internal Jugular Vein
Jugular fossa as a dilated bulb of the
skull
At the level of T1 vertebrae, superior to the
sternoclavicular joint
Right Common Carotid
Artery
Sternoclavicular joint (site of the division
of the right brachiocephalic trunk into
the subclavian and common carotid
arteries
Superior border of the thyroid cartilage
Left Common Carotid
Artery
manubrium
Superior border of the thyroid cartilage
External Carotid Artery
Superior border of the thyroid cartilage
Neck of the mandible
Internal Carotid Artery
Superior border of the thyroid cartilage
Petrous part of the temporal bone
BRANCHES OF THE ECA:
COURSE
Superior Thyroid Artery
Emerging from the anterior side, it descends into the apex of the
thyroid gland
SUPPLIES:
Thyroid gland
Accompanied by the external laryngeal nerve
Facial Artery
Arising deep in the submandibular gland
face
Lingual Artery
Occipital Artery
Emerges from the posterior side close to the posterior border of the
posterior belly of the digastric which ascends to the mastoid
Posterior Auricular Artery
Arising from the posterior side at a higher level that the occipital
artery, proceeding towards the auricle of the ear
Occipital part of the skull
Auricles of the ear and
adjacent parts
Maxillary Artery
Superficial Temporal
Artery
Ascending
PharyngealArtery
Internal Laryngeal Artery
Branch of the superior thyroid artery
Accompanied by the internal laryngeal nerve as it pierces the thyrohyoid membrane to supply internal tissues of the
larynx
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Being Mortal: Medicine and What Matters in The EndDocument15 paginiBeing Mortal: Medicine and What Matters in The EndEsteban0% (19)
- Music Education (Kodaly Method)Document4 paginiMusic Education (Kodaly Method)Nadine van Dyk100% (2)
- Eye HistologyDocument9 paginiEye HistologyGrace Shan BernusÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Inguinal Canal PDFDocument58 pagini3-Inguinal Canal PDFN A0% (1)
- PATHO 4-3 Diseases of The EsophagusDocument7 paginiPATHO 4-3 Diseases of The EsophagusMiguel Cuevas DolotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTDocument108 paginiHistology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTVernadel ApolloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ana 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Document119 paginiAna 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Favour OnyeaboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arterial Supply of Head and NeckDocument41 paginiArterial Supply of Head and NeckKhadija VasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Histology of Respiratory SystemDocument66 paginiComplete Histology of Respiratory Systemhassam qaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Pectoral Region and Axilla PDFDocument4 paginiAnatomy - Pectoral Region and Axilla PDFAngel KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal Tract PathologyDocument12 paginiGastrointestinal Tract PathologyTurinawe Bin ByensiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal Cavity, Peritoneum, Abdominal EsophagusDocument4 paginiAbdominal Cavity, Peritoneum, Abdominal EsophagusMlcnd TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Bat NotesDocument1.048 paginiAll Bat NotesAfk SystemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Femoral Sheath and Femoral TriangleDocument23 paginiFemoral Sheath and Femoral TriangleSamiha Haq100% (2)
- Osteology Lower Limb, by DR IramDocument76 paginiOsteology Lower Limb, by DR IramimmmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System HistologyDocument32 paginiRespiratory System HistologyMohib HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pelvis and Perinium 2019Document59 paginiPelvis and Perinium 2019Vuluwa GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Face and Scalp ANATOMYDocument60 paginiFace and Scalp ANATOMYpuliyogareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bilaminar and Trilaminar Germ DiscDocument40 paginiBilaminar and Trilaminar Germ DiscjabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zone Raiders (Sci Fi 28mm)Document49 paginiZone Raiders (Sci Fi 28mm)Burrps Burrpington100% (3)
- Anatomy of Hypopharynx and LarynxDocument39 paginiAnatomy of Hypopharynx and LarynxArjun NambiarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NeckDocument94 paginiNeckSathvika BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Branchial ArchesDocument4 paginiDevelopment of Branchial ArchesFidz Lianko100% (1)
- Special SensesDocument33 paginiSpecial SensesDICKSONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gestroresectional SyndromesDocument18 paginiGestroresectional SyndromesAna CotomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of The FaceDocument76 paginiDevelopment of The Facedr parveen bathla100% (1)
- Osta Diagrams Facial Part of HeadDocument22 paginiOsta Diagrams Facial Part of HeadslyfoxkittyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgical Anatomy of Fascial SpacesDocument61 paginiSurgical Anatomy of Fascial SpacesDR NASIM100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachDocument82 paginiClinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachmackieccÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Process in The Philippine SettingDocument3 paginiGroup Process in The Philippine Settingthelark50% (2)
- Abdominal Wall Edited WordDocument13 paginiAbdominal Wall Edited WordKennie RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories and Paradigms in SociologyDocument10 paginiTheories and Paradigms in SociologyAngel KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk AssessmentDocument38 paginiRisk AssessmentYasar arafat SHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper LimbDocument54 paginiUpper LimbMar YÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salivary GlandsDocument36 paginiSalivary GlandsNithish Reddy100% (1)
- Renal PathDocument71 paginiRenal PathSuha AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PerineumDocument4 paginiPerineumwiwin09Încă nu există evaluări
- BcqsDocument38 paginiBcqsAdnan MaroofÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Chapter 3Document29 pagini10 Chapter 3felefel100% (1)
- Upper Limb: Organization FunctionDocument33 paginiUpper Limb: Organization FunctionAhmed Nabiel El-Jaliel100% (1)
- Documents - Pub Surgical Anatomy of Breast Management of Advanced Carcinoma BreastDocument53 paginiDocuments - Pub Surgical Anatomy of Breast Management of Advanced Carcinoma BreastРоман ПолежаевÎncă nu există evaluări
- MInor To ContractsDocument28 paginiMInor To ContractsDakshita DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study On TQMDocument20 paginiCase Study On TQMshinyshani850% (1)
- Tumours of Larynx: A Clinicopathological StudyDe la EverandTumours of Larynx: A Clinicopathological StudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Superior and Mediastinal Structures PDFDocument3 paginiAnatomy - Superior and Mediastinal Structures PDFAngel KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Head, Neck & Spine (163Qs)Document69 paginiAnatomy Head, Neck & Spine (163Qs)rajvikram87Încă nu există evaluări
- The Gut Tube and Body CavitiesDocument31 paginiThe Gut Tube and Body CavitiesGeoffreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases of Blood Vessels Dr. Fe A. Bartolome, Maed, FpasmapDocument15 paginiDiseases of Blood Vessels Dr. Fe A. Bartolome, Maed, FpasmapJayesh MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A&P 2 Respiratory Lecture NotesDocument31 paginiA&P 2 Respiratory Lecture NotesBethanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Image Interpretation 4Document93 paginiImage Interpretation 4NanaJaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryo NotesDocument52 paginiEmbryo NotesSharona Avgush100% (1)
- Blood Supply Head and NeckDocument6 paginiBlood Supply Head and Necksahana2791Încă nu există evaluări
- Embryology Session 6 Development of The Kidneys and Urinary TractDocument6 paginiEmbryology Session 6 Development of The Kidneys and Urinary TractMuhammadBasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xray AbdominalDocument38 paginiXray Abdominalrizki sanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esophagus: - Development ofDocument14 paginiEsophagus: - Development ofJonathan00711Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Middle Mediastinum PDFDocument5 paginiAnatomy - Middle Mediastinum PDFAngel Kim100% (1)
- Anatomy I MCQ PDFDocument10 paginiAnatomy I MCQ PDFRishabhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphatic Drainage of Abdomen: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 paginiLymphatic Drainage of Abdomen: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Vascular SystemDocument51 paginiCardiac Vascular SystemYasir Altaf WaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCALP: (Keith L Moore)Document5 paginiSCALP: (Keith L Moore)rajtanniruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology Exam IV Review Part 2Document26 paginiHistology Exam IV Review Part 2ashdmb217Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7 ThermoregulationDocument30 paginiLecture 7 ThermoregulationLouella Artates100% (1)
- ANATOMY: Pelvic 2Document16 paginiANATOMY: Pelvic 2Nur Liyana MohamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- EAR MCQs Points Rida NaqviDocument6 paginiEAR MCQs Points Rida NaqviÅli Raza ChaudaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypercholesterolemia PDFDocument7 paginiHypercholesterolemia PDFkookiescreamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyDocument29 paginiAbdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyRathnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PELVISDocument68 paginiPELVISDevsya DodiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy MCQSDocument13 paginiAnatomy MCQSdrpnnreddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery Fluids & Electrolytes-1Document9 paginiSurgery Fluids & Electrolytes-1Aimie DagaleaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal Trauma: Fatin Amirah KamaruddinDocument29 paginiAbdominal Trauma: Fatin Amirah Kamaruddinvirz23Încă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Mentor: Policy ForumDocument6 paginiVirtual Mentor: Policy ForumAngel KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Middle Mediastinum PDFDocument5 paginiAnatomy - Middle Mediastinum PDFAngel Kim100% (1)
- Anatomy - Posterior Triangle of The Neck PDFDocument4 paginiAnatomy - Posterior Triangle of The Neck PDFAngel Kim100% (1)
- Anatomy - Upper GI Tract PDFDocument8 paginiAnatomy - Upper GI Tract PDFAngel KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Scalp PDFDocument3 paginiAnatomy - Scalp PDFAngel Kim100% (1)
- Anatomy - Anterior Forearm and Palm PDFDocument5 paginiAnatomy - Anterior Forearm and Palm PDFAngel Kim100% (2)
- MK Slide PDFDocument26 paginiMK Slide PDFPrabakaran NrdÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF Certificacion 3dsmaxDocument2 paginiPDF Certificacion 3dsmaxAriel Carrasco AlmanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbal Reasoning TestDocument3 paginiVerbal Reasoning TesttagawoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Beginner 2nd GradeDocument12 pagini2 Beginner 2nd GradesebÎncă nu există evaluări
- BrookfieldDocument8 paginiBrookfieldFariha Naseer Haral - 28336/TCHR/JVAITÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Development Life CycleDocument70 paginiSoftware Development Life CycleChaitanya MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplified Cost Accounting Part Ii: Solutions ManualDocument58 paginiSimplified Cost Accounting Part Ii: Solutions ManualAnthony Koko CarlobosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introductory EconomicsDocument22 paginiIntroductory Economicswedjefdbenmcve100% (1)
- (Applied Logic Series 15) Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Auth.), Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Eds.) - Fuzzy Sets, Logics and Reasoning About Knowledge-Springer NeDocument420 pagini(Applied Logic Series 15) Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Auth.), Didier Dubois, Henri Prade, Erich Peter Klement (Eds.) - Fuzzy Sets, Logics and Reasoning About Knowledge-Springer NeAdrian HagiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNS Drugs Pharmaceutical Form Therapeutic Group: 6mg, 8mgDocument7 paginiCNS Drugs Pharmaceutical Form Therapeutic Group: 6mg, 8mgCha GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Đại Từ Quan Hệ Trong Tiếng AnhDocument5 paginiĐại Từ Quan Hệ Trong Tiếng AnhNcTungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan in PED 12Document10 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in PED 12alcomfeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Magical Number SevenDocument3 paginiThe Magical Number SevenfazlayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Durability Problems of 20 Century Reinforced Concrete Heritage Structures and Their RestorationsDocument120 paginiDurability Problems of 20 Century Reinforced Concrete Heritage Structures and Their RestorationsManjunath ShepurÎncă nu există evaluări
- They Cried MonsterDocument13 paginiThey Cried MonstermassuroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Early Pregnancy and Its Effect On The Mental Health of Students in Victoria Laguna"Document14 paginiEarly Pregnancy and Its Effect On The Mental Health of Students in Victoria Laguna"Gina HerraduraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read Online 9789351199311 Big Data Black Book Covers Hadoop 2 Mapreduce Hi PDFDocument2 paginiRead Online 9789351199311 Big Data Black Book Covers Hadoop 2 Mapreduce Hi PDFSonali Kadam100% (1)
- Secant Method - Derivation: A. Bracketing MethodsDocument5 paginiSecant Method - Derivation: A. Bracketing MethodsStephen Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Listening 2Document5 paginiReading Listening 2Lisbet GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH 7S eIIaDocument8 paginiMATH 7S eIIaELLA MAE DUBLASÎncă nu există evaluări
- 105-0004 - Significant Characteristics For Compliance With Emission RegulationsDocument5 pagini105-0004 - Significant Characteristics For Compliance With Emission RegulationsthisisjineshÎncă nu există evaluări