Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Demo!: Goal
Încărcat de
Ranjith Kumar GoudTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Demo!: Goal
Încărcat de
Ranjith Kumar GoudDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Demo!
GOAL:
Build an electronic combination lock with a reset
button, two number buttons (0 and 1), and an
unlock output. The combination should be 01011.
0
1
RESET
UNLOCK
STEPS:
1.Create state transition diagram for lock FSM
2.Write Verilog module(s) that implement FSM
3.Use MAX+plusII (synthesis, simulation)
4.Program FGPA, wire up buttons, give it a whirl!
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 1
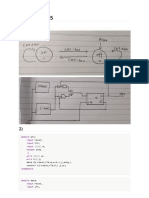
Step 1: State transition diagram
RESET
1
1
0
RESET
Unlock = 0
0
Unlock = 0
01
Unlock = 0
0
0
01011
Unlock = 1
0101
Unlock = 0
010
Unlock = 0
6.111 Fall 2004
66 states
states
33 bits
bits
Lecture 7, Slide 2
Step 2: Write Verilog
module lock(clk,reset_in,b0_in,b1_in,out);
input clk,reset,b0_in,b1_in;
output out;
// synchronize push buttons, convert to pulses
// implement state transition diagram
reg [2:0] state;
always @ (posedge clk)
begin
state <= ???;
end
// generate output
assign out = ???;
// debugging?
endmodule
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 3
Step 2A: synch buttons
// button -- push button synchronizer and level-to-pulse converter
// OUT goes high for one cycle of CLK whenever IN makes a
// low-to-high transition.
module button(clk,in,out);
out
input clk;
input in;
r1
r2
r3
in
D Q
D Q
D Q
output out;
clk
reg r1,r2,r3;
always @ (posedge clk)
synchronizer
state
begin
r1 <= in;
// first reg in synchronizer
r2 <= r1;
// second reg in synchronizer, output is in sync!
r3 <= r2;
// remembers previous state of button
end
// rising edge = old value is 0, new value is 1
assign out = ~r3 & r2;
endmodule
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 4
Step 2B: state transition diagram
// state assignments
parameter S_RESET = 0;
parameter S_0 = 1;
parameter S_01 = 2;
parameter S_010 = 3;
parameter S_0101 = 4;
parameter S_01011 = 5;
// implement state transition diagram
reg [2:0] state;
always @ (posedge clk)
begin
if (reset) state <= S_RESET;
else case (state)
S_RESET: state <= b0 ? S_0
: b1 ? S_RESET : state;
S_0:
state <= b0 ? S_0
: b1 ? S_01
: state;
S_01:
state <= b0 ? S_010 : b1 ? S_RESET : state;
S_010:
state <= b0 ? S_0
: b1 ? S_0101 : state;
S_0101: state <= b0 ? S_010 : b1 ? S_01011 : state;
S_01011: state <= b0 ? S_0
: b1 ? S_RESET : state;
default: state <= S_RESET; // handle unused states
endcase
end
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 5
Step 2C: generate output
// its a Moore machine!
Output only depends on current state
assign out = (state == S_01011);
Step 2D: debugging?
// hmmm.
What would be useful to know?
Current state?
led_decoder l(state,segments);
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 6
Step 2E: led_decoder
// led_decoder -- decode 4-bit input into 7-segment enables
module led_decoder(in,segments);
input [3:0] in;
output [6:0] segments;
wire a,b,c,d,e,f,g;
// the seven segments
// top segment
assign a = (in==0) || (in==2) || (in==3) || (in==5) || (in==6) || (in==7) || (in==8) ||
(in==9) || (in==10) || (in==14) ||(in==15);
// upper right segment
assign b = (in==0) || (in==1) || (in==2) || (in==3) || (in==4) || (in==7) || (in==8) ||
(in==9) || (in==10) || (in==13);
// lower right segment
assign c = (in==0) || (in==1) || (in==3) || (in==4) || (in==5) || (in==6) || (in==7) ||
(in==8) || (in==9) || (in==10) || (in==11) || (in==13);
// bottom segment
assign d = (in==0) || (in==2) || (in==3) || (in==5) || (in==6) || (in==8) || (in==11) ||
(in==12) || (in==13) || (in==14);
// bottom left segment
assign e = (in==0) || (in==2) || (in==6) || (in==8) || (in==10) || (in==11) || (in==12) ||
(in==13) || (in==14) || (in==15);
// upper left segment
assign f = (in==0) || (in==4) || (in==5) || (in==6) || (in==8) || (in==9) || (in==10) ||
(in==11) || (in==14) || (in==15);
// middle segment
assign g = (in==2) || (in==3) || (in==4) || (in==5) || (in==6) || (in==8) || (in==9) ||
(in==10) || (in==11) || (in==12) || (in==13) || (in==14) || (in==15);
// bundle results into a single 7-bit vector
assign segments = {g,f,e,d,c,b,a};
endmodule
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 7
Step 2: final Verilog implementation
module lock(clk,reset_in,b0_in,b1_in,out,segments);
input clk,reset_in,b0_in,b1_in;
output out;
output [6:0] segments;
wire reset,b0,b1;
button b_reset(clk,reset_in,reset);
button b_0(clk,b0_in,b0);
button b_1(clk,b1_in,b1);
// state assignments
parameter S_RESET = 0; parameter S_0 = 1; parameter S_01 = 2;
parameter S_010 = 3; parameter S_0101 = 4; parameter S_01011 = 5;
// implement state transition diagram
reg [2:0] state;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
if (reset) state <= S_RESET;
else case (state)
S_RESET: state <= b0 ? S_0 : b1 ? S_RESET : state;
S_0: state <= b0 ? S_0 : b1 ? S_01 : state;
S_01: state <= b0 ? S_010 : b1 ? S_RESET : state;
S_010: state <= b0 ? S_0 : b1 ? S_0101 : state;
S_0101: state <= b0 ? S_010 : b1 ? S_01011 : state;
S_01011: state <= b0 ? S_0 : b1 ? S_RESET : state;
default: state <= S_RESET; // handle unused states
endcase
end
6.111 Fall 2004
assign out = (state == S_01011);
led_decoder l(state,segments); // debugging!
endmodule
Lecture 7, Slide 8
Step 3A: set top level file
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 9
Step 3B: compile/synthesize/map
6.111 Fall 2004
select next error
locate error in source
Lecture 7, Slide 10
Step 3C: start waveform editor
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 11
Step 3D: add I/O nodes
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 12
Step 3E: set simulation end time
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 13
Step 3F: set input values, save
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 14
Step 3G: run simulation
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 15
Step 3H: examine simulation results
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 16
Step 4A: AssignDevice
6.111 Fall 2004
EPF10K10LC84 or EPF10K70RC240
EPC2LC20
Lecture 7, Slide 17
Step 4B: AssignPins
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 18
Step 4C: recompile
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 19
Step 4D: MAX+plusIIProgrammer
Set up JTAG chain
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 20
Step 4E: select programming file
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 21
Step 4F: Add to list
We program the EPC2 serial flash memory whose
contents is loaded into the Flex10K FPGA on power-up.
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 22
Step 4G: Attach ByteBlasterII cable
ByteBlasterII cable
EPC2LC20 serial flash RAM
Flex10K10LC84 FPGA
Header with AD bus
connections to FPGA pins
Connections to buttons
6.111 Fall 2004
1.8432Mhz XTAL wired to /AD0 which
connects to CLK input (pin 1) of FPGAs
FPGA I/Os wired to
7-segment display
Lecture 7, Slide 23
Step 4H: program device, cycle power
6.111 Fall 2004
Lecture 7, Slide 24
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Understanding The Stock MarketDocument53 paginiUnderstanding The Stock MarketvarathapandianÎncă nu există evaluări
- LB 502 Drafting, Pleadings, Full MaterialDocument153 paginiLB 502 Drafting, Pleadings, Full MaterialThakur Digvijay Singh100% (1)
- LB 502 Drafting, Pleadings, Full MaterialDocument153 paginiLB 502 Drafting, Pleadings, Full MaterialThakur Digvijay Singh100% (1)
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCDe la EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Storage Reservior and Balancing ReservoirDocument19 paginiStorage Reservior and Balancing ReservoirNeel Kurrey0% (1)
- Method StatementDocument11 paginiMethod StatementMohammad Fazal Khan100% (1)
- Sec of Finance Purisima Vs Philippine Tobacco Institute IncDocument2 paginiSec of Finance Purisima Vs Philippine Tobacco Institute IncCharlotte100% (1)
- City Gas Distribution ReportDocument22 paginiCity Gas Distribution Reportdimple1101100% (9)
- Sap Fi/Co: Transaction CodesDocument51 paginiSap Fi/Co: Transaction CodesReddaveni NagarajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- FTTH BookDocument197 paginiFTTH BookPrashant Agarwal100% (5)
- Verilog Dice GameDocument6 paginiVerilog Dice GameVishnu Sharma50% (2)
- Lab 2 ReportDocument9 paginiLab 2 Reportsherub wangdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demo!: GoalDocument24 paginiDemo!: GoalVaibhaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uday Intern Project Original 2Document42 paginiUday Intern Project Original 2Udaykiran PendemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog HDL: ModuleDocument9 paginiVerilog HDL: ModuleM Usman RiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog HDL: ModuleDocument9 paginiVerilog HDL: ModuleAvinash ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arithmetic and Logic UnitDocument6 paginiArithmetic and Logic UnitVikas KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPGA FINAL EXAM ANSWERS AND VHDL CODEDocument20 paginiFPGA FINAL EXAM ANSWERS AND VHDL CODEMinhaj FarooqiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI LaboratoryDocument10 paginiVLSI LaboratoryNitinÎncă nu există evaluări
- FSM Design for Vending Machine ProblemDocument6 paginiFSM Design for Vending Machine ProblemCheka CurativoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab10 Dice GameDocument10 paginiLab10 Dice GamePhuc Van NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- FSM Design Verilog HDL PDFDocument7 paginiFSM Design Verilog HDL PDFajayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Design and Synthesis: Fall 09Document35 paginiDigital Design and Synthesis: Fall 09Lua Dinh ThiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog HDLDocument14 paginiVerilog HDLAshokkumar GanesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interface Verilog CodeDocument21 paginiInterface Verilog CodeVishwanath B RajashekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab#1 2023 SimDocument6 paginiLab#1 2023 SimAltair Ibn La AhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lpic FLCDocument19 paginiLpic FLCLokesh DewanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 Sequence Detector: 1 ObjectivesDocument14 paginiExperiment 1 Sequence Detector: 1 ObjectivesEVD18I001 A BALAVIGNESHÎncă nu există evaluări
- KM Remote Control CodesDocument2 paginiKM Remote Control CodesdanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dataflow Modelling: 1) Logic GatesDocument39 paginiDataflow Modelling: 1) Logic Gateslilly jamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1202 Introduction To Programming CAT 1 2nd March 2022 With Marking GuideDocument4 pagini1202 Introduction To Programming CAT 1 2nd March 2022 With Marking Guidendunguloren96Încă nu există evaluări
- Design 8-func ALU FSM traffic ctrlDocument7 paginiDesign 8-func ALU FSM traffic ctrlMd Mejar Alam Liman 1912708643Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 6 DSDDocument12 paginiLab 6 DSDRohaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lumayaga Homework3Document9 paginiLumayaga Homework3Satoshi EugarnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog HDL Design of Moore and Mealy MachinesDocument8 paginiVerilog HDL Design of Moore and Mealy MachinesudayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bài giảng Kiến trúc máy tínhDocument22 paginiBài giảng Kiến trúc máy tínhĐinh Văn NamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shri Ramdeobaba College of Engineering andDocument18 paginiShri Ramdeobaba College of Engineering andAditya BelekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog HDL Synthesis and ImplementationDocument41 paginiVerilog HDL Synthesis and ImplementationAlexandru OleinicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vending Machine - Computer ArchitectureDocument11 paginiVending Machine - Computer ArchitecturenhungdieubatchotÎncă nu există evaluări
- fft256 Verilog CodeDocument3 paginifft256 Verilog CodeAdithyan JÎncă nu există evaluări
- LockDocument17 paginiLockRajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 수정 전 코드Document2 pagini수정 전 코드붕붕부릉부릉Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.design For 4:1 MuxDocument83 pagini1.design For 4:1 MuxKoushik GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Synthesis of Verilog Modules and CountersDocument35 paginiDesign Synthesis of Verilog Modules and Countersinwoman_249546987Încă nu există evaluări
- Verilog - Finite State MachinesDocument20 paginiVerilog - Finite State MachinesSharan ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog FSM Design and ImplementationDocument8 paginiVerilog FSM Design and ImplementationEr Pradip PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dice Game Controller Using SM ChartDocument43 paginiDice Game Controller Using SM ChartanjalisweÎncă nu există evaluări
- cs429 Lab4Document9 paginics429 Lab4YASH KUMAR SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- FSM LABDocument10 paginiFSM LABAbhay SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Corporation: Operating InstructionsDocument14 paginiInternational Corporation: Operating InstructionslittlebriÎncă nu există evaluări
- VERILOG Code For Up and Down Counter of Varying FrequencyDocument11 paginiVERILOG Code For Up and Down Counter of Varying FrequencyKartik VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7: Projects 2 and 3Document17 paginiLecture 7: Projects 2 and 3Sivasubramanian ManickamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate total marks and display using PL/SQL proceduresDocument12 paginiCalculate total marks and display using PL/SQL proceduressarjitgaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers Appendix PDFDocument30 paginiAnswers Appendix PDFhellojessica39Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical Exam - RonquilloDominicDocument9 paginiPractical Exam - RonquilloDominicCYCLONE 1020Încă nu există evaluări
- Homework 5: Pro Reset CLK N OutyDocument6 paginiHomework 5: Pro Reset CLK N OutyBan BanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Import Java - Awt.Event. Implements ActionlistenerDocument11 paginiImport Java - Awt.Event. Implements ActionlistenerAngel OlveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bach Khoa University of Technology: Digital Systems Laboratory Prelab 4 Finite State MachineDocument11 paginiBach Khoa University of Technology: Digital Systems Laboratory Prelab 4 Finite State MachineMờ LanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog Modules Implementing Logic Gates & FSMDocument4 paginiVerilog Modules Implementing Logic Gates & FSMsanjeewa29Încă nu există evaluări
- AssignmentDocument6 paginiAssignmentDEBERJEET USHAM 2K21/VLS/05Încă nu există evaluări
- VLSI Design Lab EC-16203 Experiment 5Document6 paginiVLSI Design Lab EC-16203 Experiment 5Brajesh SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog Code For SERIALDocument7 paginiVerilog Code For SERIALZulfiqar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECEN 248 Lab11 - ReportDocument7 paginiECEN 248 Lab11 - ReportRebecca Sontheimer100% (1)
- Fpga Lab Reports 1-8 2Document17 paginiFpga Lab Reports 1-8 2Sohail AfridiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VerificationDocument11 paginiVerificationNaved Sadat YaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 101 2 Digitalsystems Chap 05 2Document34 pagini101 2 Digitalsystems Chap 05 2thivyadharshiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 11Document4 paginiHW 11amku242461Încă nu există evaluări
- Linear Programming and Resource Allocation ModelingDe la EverandLinear Programming and Resource Allocation ModelingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Website Notice PDFDocument1 paginăWebsite Notice PDFRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Changing your Zyxel device passwordDocument10 paginiChanging your Zyxel device passwordVrushabh SahareÎncă nu există evaluări
- LawsuirsDocument1 paginăLawsuirsRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- FTTH Redefined for you with new Super Strong WiFiDocument2 paginiFTTH Redefined for you with new Super Strong WiFiRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT BOMBAY M.TECH ADMISSION BROCHUREDocument45 paginiIIT BOMBAY M.TECH ADMISSION BROCHURERashmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACME Quote-Word 2003Document4 paginiACME Quote-Word 2003Mutmainnah AGÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOHOWireless Routers (EU2-16Languages) - QIG - V1 PDFDocument79 paginiSOHOWireless Routers (EU2-16Languages) - QIG - V1 PDFGianfranco Di BaroneseÎncă nu există evaluări
- EWSD Subscriber and Tariff Administration GuideDocument38 paginiEWSD Subscriber and Tariff Administration GuideRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ciwp 2005 06Document17 paginiCiwp 2005 06api-27434403Încă nu există evaluări
- Ace Online Test Review for Communication SystemsDocument2 paginiAce Online Test Review for Communication SystemsRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- STV151Document2 paginiSTV151Ranjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- FHJKDocument2 paginiFHJKRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Select Question Out of 30: Online Test Review ForDocument2 paginiSelect Question Out of 30: Online Test Review ForRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Select Question Out of 30: Online Test Review ForDocument2 paginiSelect Question Out of 30: Online Test Review ForRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- EgerhDocument2 paginiEgerhRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Communication Systems Test 1Document2 paginiReview Communication Systems Test 1Ranjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Select Question Out of 30: Online Test Review ForDocument2 paginiSelect Question Out of 30: Online Test Review ForRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- AOLT CommandsDocument7 paginiAOLT CommandsRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Random Unrelated Words and PhrasesDocument1 paginăRandom Unrelated Words and PhrasesRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logical EffortsDocument223 paginiLogical EffortsMonalisa DebataÎncă nu există evaluări
- GPON Overview PDFDocument27 paginiGPON Overview PDFRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1278 Stock Market Basics GuideDocument11 pagini1278 Stock Market Basics Guideharsh143352Încă nu există evaluări
- FTTH OnM Manual PDFDocument25 paginiFTTH OnM Manual PDFRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ewewo J W W Riwe W Ier New Ewirw N Awme Ew Ew Mew (PFDocument1 paginăEwewo J W W Riwe W Ier New Ewirw N Awme Ew Ew Mew (PFRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- SerialnumbersDocument1 paginăSerialnumbersRanjith Kumar GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- FC Bayern Munich Marketing PlanDocument12 paginiFC Bayern Munich Marketing PlanMateo Herrera VanegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fleck 3150 Downflow: Service ManualDocument40 paginiFleck 3150 Downflow: Service ManualLund2016Încă nu există evaluări
- InvoiceDocument1 paginăInvoiceAnurag SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey Analyzes India's Toll Collection SystemsDocument15 paginiSurvey Analyzes India's Toll Collection SystemsmohitvermakspÎncă nu există evaluări
- Request Letter To EDC Used PE PipesDocument1 paginăRequest Letter To EDC Used PE PipesBLGU Lake DanaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liability WaiverDocument1 paginăLiability WaiverTop Flight FitnessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numark MixTrack Pro II Traktor ProDocument3 paginiNumark MixTrack Pro II Traktor ProSantiCai100% (1)
- Exp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsDocument1 paginăExp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsMuhammad ArslanÎncă nu există evaluări
- StrutsDocument7 paginiStrutsBatrisyialya RusliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentDocument17 paginiJodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentWMBF NewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 9. Wireless Communication Towers and Antennas 908.01 Purpose and IntentDocument12 paginiPart 9. Wireless Communication Towers and Antennas 908.01 Purpose and IntentjosethompsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- FZ16 9B 1KD2 (Patada) PDFDocument62 paginiFZ16 9B 1KD2 (Patada) PDFPanthukalathil Ram100% (1)
- CELF Final ProspectusDocument265 paginiCELF Final ProspectusDealBookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warranty Information Emea and CisDocument84 paginiWarranty Information Emea and CisHenriques BrunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S4H - 885 How To Approach Fit To Standard Analysis - S4HANA CloudDocument16 paginiS4H - 885 How To Approach Fit To Standard Analysis - S4HANA Cloudwai waiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Youtube AlgorithmDocument27 paginiYoutube AlgorithmShubham FarakateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppDocument1 paginăPass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppAnoop SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Skills:: Surabhi SrivastavaDocument3 paginiTechnical Skills:: Surabhi SrivastavaPrasad JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBM TS3500 Command Line Interface (CLI) ExamplesDocument6 paginiIBM TS3500 Command Line Interface (CLI) ExamplesMustafa BenmaghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)Document23 paginiCompany's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)ashairways100% (2)
- 10 Appendix RS Means Assemblies Cost EstimationDocument12 pagini10 Appendix RS Means Assemblies Cost Estimationshahbazi.amir15Încă nu există evaluări
- Exam Venue For Monday Sep 25, 2023 - 12-00 To 01-00Document7 paginiExam Venue For Monday Sep 25, 2023 - 12-00 To 01-00naveed hassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE Supplier Add Refresh FormDocument1 paginăGE Supplier Add Refresh FormromauligouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrepreneurship and EconomicDocument2 paginiEntrepreneurship and EconomicSukruti BajajÎncă nu există evaluări