Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
How to realize a thermal oil plant with open tank
Încărcat de
PierluigiBusettoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
How to realize a thermal oil plant with open tank
Încărcat de
PierluigiBusettoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
No.
031/2004
HOW TO REALIZE A THERMAL OIL PLANT WITH OPEN TANK
1)
APPLICATION FIELD:
The present precept is applied to thermal oil plants.
2)
SYMBOL:
DENOMINATION
Heating surface
Thermal efficiency
Volume
Fluid contents
Bulk capacity
Temperature
Sliding point
Distillation starting point
Pressure
Steam tension
Output
Kinematics viscosity
Specific heat
Total thermal capacity
Specific thermal load in combustion chamber
Heat conduction
Angular speed
Breaking unitary load
3.
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS:
3.2
PRESSURE
3.2.1
WORKING PRESSURE
SYMBOL
S
V
Q
T,t
p
Pvs
P
v
c
C
SI UNIT
m
m
Kg
m/s
K
K
K
Pa
Pa
kW
m/s
KJ/(Kg-K)
kJ/K
OTHER UNIT
m
m
Kg
m/h
C
C
C
Kgf/cm
mmHg
Kcal/h
cST
Kcal/(Kg.C)
Kcal/C
kW/m
W/(m.K)
rad/s
N/m
Kcal/(h.m)
Kcal/(h.mC)
giri/min
Kgf/mm
Working pressure of single parts of the system is the addition of static pressure due to the head of oil circulation pump.
3.2.2
MAXIMUM PRESSURE ALLOWED
Is the maximum pressure on which the circuit is designed and tested.
3.3
TEMPERATURES
Are considered the different temperatures of thermal oil in different sections of the circuit.
3.3.1
FLUID TEMPERATURES
Is the thermal oil temperature checked in the middle of the piping.
3.3.2
OUTLET TEMPERATURE
Is the thermal oil temperature checked outside the heater.
3.3.3
INLET TEMPERATURE
Is the thermal oil temperature just before entering the heater.
3.3.4
WORKING TEMPERATURE
Is the outlet temperature of the oil that must be below the design temperature.
Working temperature is one of the points to value the fluids long life.
3.3.5
DESIGN TEMPERATURE
Maximum temperature allowed by design of plant.
This temperature must be higher than the working temperature.
3.3.6
EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURE
Is the temperature of the flue gas at the heaters exit.
3.3.7
EXHAUST GAS OVERTEMPERATURE ALLOWED
Is the difference between the flue gas temperature and the thermal oil temperature.
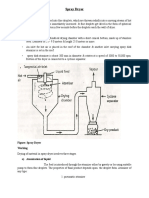
ELEMENTS OF THE PLANT:
The principal components of the plant are:
-
Thermal oil heater
Combustion plant - burner
Expantion tank
Drain tank
Oil circulation pump
Oil barrel pump
Valves
Filters
Level indicators
Piping
Instruments
4.1
THERMAL OIL HEATERS CHARACTERISTICS
For each heater must be indicated the following data:
-
4.1.2
Capacity at maximum load
Capacity at economical load
Design pressure
Maximum working pressure
Maximum thermal oil temperature
Temperature fall between outlet and inlet
Nominal viscosity and type of oil to be used
Furnace volume
Specific thermal load
Heating surface
Efficiency at maximum and at economical load
Exhaust gas temperature
Gas head loss
Minimum capacity of thermal oil allowed according to the working temperature
Thermal oil content
EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURE
Exhaust gas temperature must not be higher than the value deduced from the following formula: TF = TL + TS
TF
TL
TS
Ts
in
C
=
=
=
Exhaust gas temperature
Outlet temperature of the oil
Over temperature allowed according to the following diagram
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
700
1400
Pc in kW
4.1.3
INSPECTION
The heater must be able to be easily inspected inside.
4.2
EXPANTION TANK
Thermic plants, using diathermic oil at high temperature, must be provided with a tank built dimensioned and installed in order to
grant its two main functions:
* To allow oil contained dilatation in whole plants
* To guarantee to the system the right hydrostatic constant head
4.2.1
HOW TO DIMENSION EXPANTION TANK
The expantion tank must have a minimum capacity equal to 30% of the oil volume contained in the whole plant.
4.3
OIL TANK
The main function is to receive the total amount of the oil contained in the plant.
4.3.1
HOW TO DIMENSION OIL TANK
The tank must be able to receive about 150% of the plants total volume.
4.4
OIL CIRCULATION PUMPS
For diathermic oil circulation at high temperature must be used special pumps designed and built for this duty in order to
guarantee a correct work.
4.5
BARREL PUMPS
Being a matter of fluid at room temperature are suggested gear pumps.
4.6
REGULATION, CHECK AND THREE WAY VALVES
Must be designed and built to work with fluid at high temperature.
It is forbidden to use and allow copper.
4.7
FILTERS
Filters are necessary to keep possible impurity or ageing products contained in the air in order to guarantee a normal
transmission of the heat.
Filters either help valves in their work.
4.7.1
Each filter must be equipped with a couple of manometers that indicate the obstruction condition.
4.8
OIL LEVEL INDICATORS
Oil level indicators must be suitable to work at the provided temperatures considering the special characteristics of the used fluid.
The taps must be legible in their "open" and "close" positions.
4.9
All pipes connecting parts in thermal oil plants must be in steel.
For temperatures below 300 C it is allowed to use pipes not in steel.
4.10
INSTRUMENTS
Safety and control devices:
*
*
*
*
*
Burner regulator thermostat
Maximum temperature thermostat
Differential pressure switch
Burner block in case the oil circulation pump stops to work
Block or alarm devices for minimum level in the expantion tank.
DIATERMIC OIL:
Diathermic oil are mineral oils coming from oil distillation and refining, provided with a good thermic stability and rust-proof at
high working temperature.
5.1
CHARACTERISTICS
The characteristics that the diathermic oil producer should provide are:
*
*
*
*
*
Viscosity at 50 C
Viscosity at 20 C
Sliding point
Bulk at 15 C
Maximum working temperature
On request can be provided the following characteristics:
*
*
*
*
*
6.3
Initial distillation point at normal atmospheric pressure
Specific heat at 15 C
Heat conduction
Tension of steam at outlet temperature
Viscosity at outlet temperature
EXPANTION TANK:
Expantion tank, in atmospheric plans, is the only part of the system where the thermal oil can join the oxygen in the atmosphere,
because the oxidation process is very reduced until the temperature does not go above 60 C.
The plan should be realized to guarantee these conditions. Further to this point is a role to prefer a vertical cylindrical shape and
to install the expantion tank outdoor. If the winter weather conditions and the characteristics of the thermal oil excludes the
possibility to freeze. The expantion tank should be installed on a high that will guarantee the necessary head on the circulation
pump.
6.3.1
The connection between the expantion tank and the circuit must be realized before the circulation pump.
Piping connection must have a diameter between 1" e 2", should not be insulated and the oil temperature inside the pump
should not go over 60 C.
6.4
STORAGE TANK FOR THERMAL OIL
Storage tank should be placed in a position that allows discharge of all the fluid by gravity.
Must be provided with a hand pump or motor pump, in order to transfer thermal oil in the circuit.
Must be provided with a ventilation system communicating with the atmosphere and with suitable connection to the plan.
If the tank is installed in a visible and accessible position, out from the ground, must be provided with a level indicator.
6.5
PIPING
Equipments and piping to use to realize the connections for plant with thermal oil must be according to the point 4.9.
Piping, in which is circulating the fluid at high temperature, must be insulated.
For piping disposition you must take care to correct slope in order to avoid air formation;
Anyway it is always better to provide right blow down valve and air hole.
6.5.1
PIPING DILATION
Designing and realizing the connections is indispensable to take care of the thermic dilation of pipings, which importance
increases with the rise of the working temperature, power and dimension of the plant.
It is necessary to avoid that dilations induce to much on the main equipments, like heat generators and valves; except in the case
of small diameter not always the piping elasticity allows to absorb dilations without inducing to much stress.
You must provide right exaution joints suitable for this use.
One of the most critical points, especially in case of big dimension and many equipments, is the one in connection to the
circulation pump and in connection to the automatic regulation three way valve.
Piping must be, of course, provided of adequate fixed points.
6.6
SAFETY AND CONTROL DEVICES FOR THE THERMAL OIL
The plant and all equipments must be designed and realized in order to avoid:
* Temperature rising, even if it is casual, over maximum working temperature.
* Contact between air-oil at temperature above 60 C.
6.7
AIR HOLES
The plant must be provided with air holes, to be placed in the highest point of the piping, in order to allow the separation and
elimination of gas and steam produced during starting or work.
6.8
BLOW DOWN
The plant must be provided with blow down, properly dimensioned and placed in a suitable position to eliminate all materials
deposited that must be removed.
6.9
BLOW DOWN
The plant must be provided with blow down properly dimensioned, placed in all lower points directed to the storage tank in order
to empty completely and quickly the whole fluid.
BOILER ROOMS:
Boiler rooms in which are installed hot oil heaters must satisfy the low according to certification issued by fire-men.
7.1
BOILER ROOMS
Buildings, in which are installed heat generators and all equipments, are preferably separated from the main building and should
be at ground level.
7.1.1
OPENING
The boiler house must be provided with easy accessible exits with fire proof doors; at least one exit must approach to open-air.
7.1.2
VENTILATION
It is very important to take care about ventilation, that besides to assure the primary air for combustion must also prevent that
temperature increases and becomes noxious for the staff, for automatic control and safety equipments.
START AND PLAN OPERATIONS:
8.1
HYDRAULIC TEST
Hydraulic test of the heater and of the whole plan must be done with oil or compressed air with pressure at least at 6 bar.
All air in the plan must be eliminated.
8.2
FILLING
Filling should be done from the lower point of the circuit through an auxiliary pump due to avoid air formation.
During the filling airvant valves must be opened until the oil starts to leak.
Filling must be stopped when the expantion tank reaches the minimum level.
After filling is advisable to let the oil circulate for 4 hours in order to eliminate all the air.
8.3
START UP
The oil heating must be done gradually increasing the temperature not more than 40 C/h.; between 90 and 120 C the
temperature increase must be not over 10 + 15 C/h.
Start up is finished after you have joint and maintained the temperature for 6 hours at the normal working temperature.
After heating you must leave the oil cool down and discharge, possibly filtering it.
Then you must control and clean all filters.
8.4
CHARGE
8.4.1
OIL TEST
Periodically you must check the oil in order to verify if is not necessary to change it for the following reasons:
* First check on the new charge
* A check at 1.000 working hours or after two months
* Two checks after 2.000 working hours or after six months.
* Further checks after 3.000 working hours or after one year.
Samples must be taken cool at a temperature not above 30 C and not less than 1 Kg.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 240-61227631 Piping and Instrumentation Diagram Standard Rev 1Document69 pagini240-61227631 Piping and Instrumentation Diagram Standard Rev 1AdventurerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leaflet For Inclining TestDocument9 paginiLeaflet For Inclining TestPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Aluminiumal Loyand Steel MaterialDocument8 paginiComparison of Aluminiumal Loyand Steel MaterialBablu SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Dimensions Chart Rev Jan 2012Document1 paginăPipe Dimensions Chart Rev Jan 2012snake13Încă nu există evaluări
- Army WeldingDocument757 paginiArmy WeldingKenn FerroÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Batch Convert Your IDWDocument6 paginiHow To Batch Convert Your IDWPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Dimensions Chart Rev Jan 2012Document1 paginăPipe Dimensions Chart Rev Jan 2012snake13Încă nu există evaluări
- Choosing the Right Thermal Fluid Heater <40Document6 paginiChoosing the Right Thermal Fluid Heater <40PierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legend SymbolsDocument21 paginiLegend SymbolsFaJar FieLdenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimum Design of Pressure Vessel Subjected To Autofrettage ProcessDocument6 paginiOptimum Design of Pressure Vessel Subjected To Autofrettage ProcessPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Offshore Instrumentation Design CriteriaDocument63 paginiOffshore Instrumentation Design CriteriaedgardoboieroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Fluid Heat Technology M1 PDFDocument8 paginiThermal Fluid Heat Technology M1 PDFPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pid Legend PDFDocument1 paginăPid Legend PDFSocMed Dtk UI0% (1)
- Legend SymbolsDocument21 paginiLegend SymbolsFaJar FieLdenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006 Int Ansys Conf 134Document15 pagini2006 Int Ansys Conf 134bamboolÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.metal Forming Bending-1Document4 pagini7.metal Forming Bending-1Victor NalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- XXI Paper 025 PDFDocument8 paginiXXI Paper 025 PDFPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convective Heat Transfer 1Document7 paginiConvective Heat Transfer 1xaaabbb_550464353Încă nu există evaluări
- Heat Balance Sheet - Heat Exchanger PerformanceDocument1 paginăHeat Balance Sheet - Heat Exchanger PerformancePierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Complete Design of Ship Propellers Using The New Computer SystemDocument6 paginiA Complete Design of Ship Propellers Using The New Computer SystemPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Affecting Ship Resistance Calculation with CFDDocument9 paginiFactors Affecting Ship Resistance Calculation with CFDPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ab Heatec 1977 Marine Application of Thermal Fluid HeatingDocument17 paginiAb Heatec 1977 Marine Application of Thermal Fluid HeatingPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pad Eyes PDFDocument1 paginăPad Eyes PDFPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VTO Options in Scope of Supply DIN4754 FigA1 Systems PDFDocument1 paginăVTO Options in Scope of Supply DIN4754 FigA1 Systems PDFPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 RACM-E-Hot Water Draft PDFDocument24 pagini2013 RACM-E-Hot Water Draft PDFPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cargo Oil Heating Requirements For An FSO Vessel Conversion PDFDocument11 paginiCargo Oil Heating Requirements For An FSO Vessel Conversion PDFPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correlations ListDocument6 paginiCorrelations ListSyed Rafat FaysalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer Fluid for Concentrated Solar SystemsDocument51 paginiHeat Transfer Fluid for Concentrated Solar SystemsPierluigiBusettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Heavy Fuel Oil 1984Document68 paginiNotes On Heavy Fuel Oil 1984mohdfadhirulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- AD 251 - Equivalent Uniform Moment Factor, M (Italic)Document1 paginăAD 251 - Equivalent Uniform Moment Factor, M (Italic)symon ellimacÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20comm Um003 - en PDocument270 pagini20comm Um003 - en PRogério BotelhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- D2DDocument2 paginiD2Dgurjit20Încă nu există evaluări
- Institutional Competency Assessment Instrument (ICAI)Document12 paginiInstitutional Competency Assessment Instrument (ICAI)Bea EtacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Approval List by FSSAIDocument16 paginiComplete Approval List by FSSAIAnkush Pandey100% (1)
- 740 (Q50, V40, Awa 4Document10 pagini740 (Q50, V40, Awa 4rawat2583Încă nu există evaluări
- Horizontal Machining Centers: No.40 Spindle TaperDocument8 paginiHorizontal Machining Centers: No.40 Spindle TaperMax Litvin100% (1)
- Defining Public RelationsDocument4 paginiDefining Public RelationsKARTAVYA SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- NewTrendsInLeadershipandManagement ArikkokDocument32 paginiNewTrendsInLeadershipandManagement Arikkoksocofem288Încă nu există evaluări
- CA-Endevor Quick EditDocument31 paginiCA-Endevor Quick Editmariela mmascelloniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultimate Guide To Construction SubmittalsDocument10 paginiUltimate Guide To Construction SubmittalsDavid ConroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Pathogenic Basis of Malaria: InsightDocument7 paginiThe Pathogenic Basis of Malaria: InsightRaena SepryanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dryers in Word FileDocument5 paginiDryers in Word FileHaroon RahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulated Robot Football Team Uses Neural Networks to LearnDocument8 paginiSimulated Robot Football Team Uses Neural Networks to LearnKishore MuthukulathuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Results For: "Multiple-Choice Questions: B": DelayDocument4 paginiYour Results For: "Multiple-Choice Questions: B": DelayawairmalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer InsulationDocument14 paginiTransformer InsulationcjtagayloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6Document226 paginiManual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6rsp filmes100% (1)
- Activity 2Document5 paginiActivity 2Kier VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubik Clock Solution 1Document2 paginiRubik Clock Solution 1Ionel PaunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparing Financial Performance of Conventional and Islamic BanksDocument9 paginiComparing Financial Performance of Conventional and Islamic BanksIkbal HardiyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP SD Course Content PDFDocument4 paginiSAP SD Course Content PDFshuku03Încă nu există evaluări
- HCCM System Technical Specification v1Document12 paginiHCCM System Technical Specification v1Ankita ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA 5921 and RA 10918Document32 paginiRA 5921 and RA 10918Hani Loveres100% (1)
- Anatomy 090819Document30 paginiAnatomy 090819Vaishnavi GourabathiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOS 22402 Winter 19th I SCHEME Paper Model Answer PaperDocument25 paginiTOS 22402 Winter 19th I SCHEME Paper Model Answer Paperirshadmirza753Încă nu există evaluări
- L P 10Document13 paginiL P 10Bình Minh HoàngÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA For Installation & Dismantling of Loading Platform A69Document15 paginiRA For Installation & Dismantling of Loading Platform A69Sajid ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toki PonaDocument2 paginiToki PonaNicholas FletcherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive E-Coat Paint Process Simulation Using FEADocument20 paginiAutomotive E-Coat Paint Process Simulation Using FEAflowh_100% (1)
- Asus X553MA Repair Guide Rev2.0Document7 paginiAsus X553MA Repair Guide Rev2.0UMA AKANDU UCHEÎncă nu există evaluări