Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
21B
Încărcat de
Raman LuxDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
21B
Încărcat de
Raman LuxDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
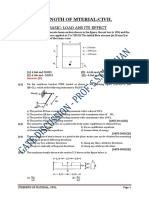
SUB: STRENGTH OF MATERIAL
MODULE-21B
MODULE-21B
Buckling of Column
1. The effective length of a column in a
reinforced concrete building frame, as
per IS: 456-2000, is independent of
the
(a) Frame type i.e., braced
sway) or un-braced (with sway)
(b) Span of the beam
(c) Height of the column
(d) Loads acting on the frame
(no
2. A long structural column (length = L)
with both ends hinged is acted upon
by an axial compressive load, P. The
differential equation governing the
bending of column is given by
where
is the structural lateral
deflection and EI is the flexural
rigidity. The first critical load on
column responsible for its buckling is
given by
(a) 2EI/L2
(b)
EI/L2
2
(c) 2 EI/L2
(d) 4 2EI/L2
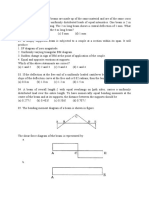
3. The buckling load
for the
column AB in the figure, as
KT approaches infinity, become
(a) 0.25 (b)1.00 (c) 2.05 (d) 4.00
4. A steel column, pinned at both ends,
has a buckling load of 200kN. If the
column is restrained against lateral
movement at its mid-height, its
buckling load will be
(A)
200kN (B) 283kN (C)
400kN
(D) 800kN
5. Cross-section of a column consisting
of two steel strips, each of thickness t
and width b is shown in the figure
below. The critical loads of the
column with perfect bond and without
bond between the strips are P and
P0respectively. The ration P/P0 is
, where is equal to
(A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 8
6. A rigid bar GH of length L is
supported by a hinge and a spring of
stiffness K as shown in the figure
JH Academy
SUB: STRENGTH OF MATERIAL
below. The buckling load, P
bar will be
for the
(A)
0.5 KL
(B)
0.8 KL
(C)
1.0KL
(D)
1.2KL
7. Consider the following statements for
a compression member:
I. The elastic critical stress in
compression increases with decrease
in slenderness ratio
II. The effective length depends on the
boundary conditions at its ends
III. The elastic critical stress in
compression is independent of the
slenderness ratio
IV.
The ratio of the effective
length to its radius of gyration is
called as slenderness ratio
The TRUE statements are
(A) II and III
(B)
III and IV
(C) II, III and IV (D) I, II and
IV
8. The effective length of a column of
length L fixed against rotation and
translation alone end and free al the
other end is
(A)0.5L(B) 0.7 L(C)1. 414L(D) 2L
9. The ratio of the theoretical critical
buckling load for a column with fixed
ends to that of another column with
the same dimensions and material, but
with pinned ends, is equal to
(A) 0.5 (B) 1.0 (C) 2.0 (D) 4.0
10. The sketch shows a column with a pin
at the base and rollers at the top. It is
subjected to an axial force P and a
JH Academy
MODULE-21B
moment M at mid-height.
reaction(s) at R is/are
The
(A) a vertical force equal to P
(B) a vertical force equal to P/2
(C) a vertical force equal to P and a
horizontal force equal to M/h
(D) a vertical force equal to P/2 and a
horizontal force equal to M/h
11. Two steel columns P (length
and
yield strength
) and Q
(length 2 and yield strength
) have the same crosssections and end-conditions. The ratio
of buckling load of column P to that of
column Q is:
(A) 0.5 (B) 1.0 (C) 2.0 (D) 4.0
12. A column of height H and area at top
A has the same strength throughout its
length, under its own weight and
applied stress
at the top. Density of
column material is . To satisfy the
above condition, the area of the
column at the bottom should be
a)
c) A
b)
d)
13. If the crushing stress in the material of
a mild steel column is 3300kg/
.
Eulers formula for crippling load is
applicable for slenderness ratio equal
to/greater than
SUB: STRENGTH OF MATERIAL
a) 40
b) 50
c)
d) 80
60
14. Which one of the following pairs is
not correctly matched?
Boundary
Conditions of
column
buckling
load
Eulers
MODULE-21B
Codes:
a) Both A and R are true and R is the
correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true but R is not
a correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false but R is true.
18. A short column of external diameter
and internal diameter
carries
an external load W. for no-tension
condition, the eccentricity will be
a) Pin-pin
b) Fixedend
c) Fixed-free
15. For a circular column having its ends
hinged, the slenderness ratio is 160.
The d ratio of the column is
a) 80
b) 57
c)
d) 20
16. A hollow circular column of internal
diameter d and external diameter
1.5d is subjected to compressive
load. The maximum distance of the
point of application of load from the
centre for no tension is
a) d/8
b) 13d/48
c)
d) 13d/96
d/4
17. Assertion (A): the buckling load for a
column of specified material, crosssection and end conditions calculated
as per Eulers formula varies inversely
with the column length.
Reason(R): Eulers formula takes
into account the end conditions in
determining the effective length of
column.
JH Academy
b)
c)
d)
d) Fixed-pin
40
a)
19. A column base is subjected to
moment. If the intensity of bearing
pressure due to axial load is equal to
stress due to the moment then the
bearing pressure between the base and
the concrete is
a) Uniform compression throughout
b) Zero at one end and compression
at the other end
c) Tension at one end and
compression at the other end
d) Uniform tension throughout
20. Assertion (A): Rankies theory is
generally used for finding out the
buckling load
of
intermediate
columns.
Reason (R): Eulers theory gives
higher values for buckling loads in
intermediate columns.
Codes:
a) Both A and R are true and R is the
correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true but R is not
a correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false but R is true.
SUB: STRENGTH OF MATERIAL
21. Which one of the following pairs is
NOT correctly matched?
a) Both ends hinged:
b) Both end fixed:
c) One end fixed and other end free:
MODULE-21B
d) 3
24. A circular column of external diameter
D, and internal diameter d, carries an
eccentric load such that tension is
developed nowhere. What shall be the
diameter of the core?
d) One end fixed and other hinged:
a)
22. The slenderness ratio of a compression
member in the context of Rankies
formula is defined as
b)
c)
d)
25. If the Euler load for a steel column is
1000KN and crushing load is
1500KN, the Rankine load is equal to
a)
b)
c)
a) 2500KN
b) 1500KN
c) 1000KN
d) 600KN
26. For the design of a cast iron member,
the most appropriate theory of failure
is
d)
23. Match list-I(end conditions of
columns)
with
list-II(effective
length, ) and select the correct
answer using the codes given below
the lists:
List-I
List-II
A. Both ends fixed
1. =2L
B. Both ends hinged
2.
a)
b)
c)
d)
Mohrs theory
Rankines theory
Maximum stress theory
Maximum shear energy theory
C. Oneendfixeotherfree3. =L
D. One end fixed
other hinged
4. = L
Codes:
A
a) 2
b) 3
c) 2
JH Academy
4
1
4
B
1
2
3
3
4
1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 7590 Letter Writing BookDocument51 pagini7590 Letter Writing BookDilip Varma100% (10)
- Periodic Table PtableDocument1 paginăPeriodic Table Ptableapi-239694539Încă nu există evaluări
- Afd 082516 33 1 37 1 PDFDocument74 paginiAfd 082516 33 1 37 1 PDFToots PomperadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ SOM Unit 3 Bending & Shear StressesDocument10 paginiMCQ SOM Unit 3 Bending & Shear Stressesrahul_patil8550% (2)
- Blender Art - 15 - March 2008Document75 paginiBlender Art - 15 - March 2008blackcougar100% (18)
- SSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For CIVILDocument14 paginiSSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For CIVILMaku RajkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Rack Design Philosophy (Continuous Pipe Racks)Document17 paginiPipe Rack Design Philosophy (Continuous Pipe Racks)Umer AleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spreadsheets To BS 8110: Single Column BaseDocument25 paginiSpreadsheets To BS 8110: Single Column BaseIr Ahmad AfiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASphericDocument5 paginiASpherickndprasad01Încă nu există evaluări
- 51 Industrial CrystallizationDocument23 pagini51 Industrial CrystallizationBoris DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specs For Permanent Ground Anchors For Retaining StructuresDocument21 paginiSpecs For Permanent Ground Anchors For Retaining StructuresMartin Sabah100% (1)
- Lecture 02 Energy-Rayleigh-Ritz 2015Document40 paginiLecture 02 Energy-Rayleigh-Ritz 2015Mustapha BelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate Analysis of Construction MaterialsDocument13 paginiRate Analysis of Construction MaterialsGino BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthquak Analysis in AnsysDocument14 paginiEarthquak Analysis in AnsysIgor GjorgjievÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Design of Jib Crane Type Rotating Derrick System" in EOT CRANE For Easy Lifting The Spare Parts During Heavy Maintenance in Confined SpaceDocument7 pagini"Design of Jib Crane Type Rotating Derrick System" in EOT CRANE For Easy Lifting The Spare Parts During Heavy Maintenance in Confined SpaceijsretÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 632 Earth PressureDocument18 paginiCE 632 Earth PressureBala Sutharshan100% (1)
- Strength of Material 2Document12 paginiStrength of Material 2mjdalenezi100% (1)
- Experiment 2 Lab ReportDocument11 paginiExperiment 2 Lab ReportVanessa Denise Aguilar50% (2)
- 21BDocument4 pagini21BJamie SchultzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gate 1533Document7 paginiGate 1533Darshit D RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories of ColumnDocument5 paginiTheories of ColumnShanmuga RamananÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16BDocument13 pagini16BBrynn AlexanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering SET ADocument16 paginiCivil Engineering SET Aishak789Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Mos FinalDocument12 paginiTest Mos FinalAbhishek Tiwari100% (1)
- GATE ColumnDocument2 paginiGATE ColumnbachayadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ese Som Pyq Chapter 1Document38 paginiEse Som Pyq Chapter 1Krishna GovindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarDocument7 paginiProblem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarYatharth KhicharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer Explanation: (A) Short ColumnDocument4 paginiAnswer Explanation: (A) Short ColumnUjjal Kalita 19355Încă nu există evaluări
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IDocument18 paginiIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IvishnupsudhakaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assigment 3Document8 paginiAssigment 3Zoheb ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45662597562obj CivilEngineering 2006paper IDocument18 pagini45662597562obj CivilEngineering 2006paper I94738183Încă nu există evaluări
- Civil 2001 Paper 1Document14 paginiCivil 2001 Paper 1Rajwinder Singh BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Open Book, Closed Notes, Do Not Write On This Sheet, Show All WorkDocument4 paginiFinal Exam Open Book, Closed Notes, Do Not Write On This Sheet, Show All Workandi suntoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Previous Papers2Document13 paginiCivil Engineering Previous Papers2Haresh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gate-2018 Test Series Strength of MaterialsDocument6 paginiGate-2018 Test Series Strength of Materialssushil.vgiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For CIVIL 5Document18 paginiSSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For CIVIL 5Agnibesh Dasgupta0% (1)
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IDocument18 paginiIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper ISudharsananPRSÎncă nu există evaluări
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2007 Paper IDocument15 paginiIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2007 Paper Iravi maharajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 55685698obj CivilEngineering 2005paper IDocument16 pagini55685698obj CivilEngineering 2005paper IAMIT KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac 1 (1) (1) .2Document20 paginiAc 1 (1) (1) .2Shyam K RautÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Stress and Strain Relationship: Stress and Strain in Two Dimensions, Principal Stresses, Stress Transformation, Mohr's CircleDocument67 paginiSimple Stress and Strain Relationship: Stress and Strain in Two Dimensions, Principal Stresses, Stress Transformation, Mohr's CircleMushini NagabhushanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apgenco (Mechanical) 2017-QpDocument16 paginiApgenco (Mechanical) 2017-QpSamresh GarnaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appsc 2012 Strength of MaterialsDocument8 paginiAppsc 2012 Strength of MaterialsKarthik Kala KondaÎncă nu există evaluări
- L-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013Document18 paginiL-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013MuradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiitjee 38Document5 paginiFiitjee 38BHAAJI0001100% (1)
- Strengh of Mateial Topic Wise Questions Sr. NoDocument28 paginiStrengh of Mateial Topic Wise Questions Sr. NoAd PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Stress StrainDocument8 paginiSimple Stress StrainJames Ortega33% (3)
- Strength of MaterialsDocument48 paginiStrength of Materialspankajkumarhans100% (1)
- QUIZ Without AnswersDocument24 paginiQUIZ Without AnswersSanjay TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap CEPAPER PDFDocument16 paginiAp CEPAPER PDFsanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP PGECET Civil Engg 2015 Question Paper & Answer Key DownloadDocument16 paginiAP PGECET Civil Engg 2015 Question Paper & Answer Key Downloadpavani83% (6)
- RC2 MeDocument11 paginiRC2 MeZelalem AberaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mace 60035Document7 paginiMace 60035eng_ayman_H_MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document7 paginiChapter 3Haftom GebreegziabiherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me601 HW1Document6 paginiMe601 HW1chinmayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current ElectricityDocument28 paginiCurrent ElectricitySatyanneshi ERÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE-IES-2012-obj Paper-IDocument21 paginiCE-IES-2012-obj Paper-IKunal KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deformation of SolidsDocument24 paginiDeformation of SolidsSaeed AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Columns & StrutsDocument4 paginiColumns & Strutsacharjeesneha68Încă nu există evaluări
- Machine Design GATE BitsDocument19 paginiMachine Design GATE BitsVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 623a5c67-4398-4e1b-8b41-da8a83ae2872Document9 pagini623a5c67-4398-4e1b-8b41-da8a83ae2872Vidhi ShekhawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutor Marked Assignment: BtwreDocument41 paginiTutor Marked Assignment: BtwrePranita JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The ClassDocument6 paginiME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The Classfatty acidÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ On MosDocument10 paginiMCQ On MosAkshayThakur0% (1)
- StructureDocument24 paginiStructureFrank StephensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 5 FinalDocument2 paginiTutorial 5 FinalAtul SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Physics 3Document5 paginiMCQ Physics 3Sugaraj SamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 308 CCW-Question-1 Rev1Document3 paginiCE 308 CCW-Question-1 Rev1SAKHI U 20MLCE11Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Practice Paper - 9 Term-1Document11 paginiPhysics Practice Paper - 9 Term-1JatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Pre 2013Document19 paginiCivil Engineering Pre 2013chanderp_15Încă nu există evaluări
- Free Test SOMDocument6 paginiFree Test SOMAbhishek MahtoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperbolic Structures: Shukhov's Lattice Towers - Forerunners of Modern Lightweight ConstructionDe la EverandHyperbolic Structures: Shukhov's Lattice Towers - Forerunners of Modern Lightweight ConstructionÎncă nu există evaluări
- TNPSC Aptitude Mental Ability Solved SumsDocument12 paginiTNPSC Aptitude Mental Ability Solved SumsRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- No 17 2021Document10 paginiNo 17 2021Raman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMMRC-Advertisement - Academic Co-ordinator-Feb 2021Document4 paginiEMMRC-Advertisement - Academic Co-ordinator-Feb 2021Raman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20mm-Thick Cement Plastering in Cement MortarDocument4 pagini20mm-Thick Cement Plastering in Cement MortarRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vestige Company: 7 Types of IncomeDocument2 paginiVestige Company: 7 Types of IncomeRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- 89 AhhDocument4 pagini89 AhhRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture10 5 PDFDocument9 paginiLecture10 5 PDFRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- 95 BssDocument2 pagini95 BssRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Resource-1Document7 paginiWater Resource-1Raman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Resource-1Document7 paginiWater Resource-1Raman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrology - 2Document8 paginiHydrology - 2Raman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- CXSDFDocument4 paginiCXSDFRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.4.4 Spatial Consistency CheckDocument7 pagini3.4.4 Spatial Consistency CheckRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydrologyDocument6 paginiHydrologyRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reded ReDocument2 paginiReded ReRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDDocument9 paginiSDRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3Document5 paginiLecture 3शेरसिंह खदावÎncă nu există evaluări
- KdsakdDocument5 paginiKdsakdRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- SdfreDocument2 paginiSdfreRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- XCSDFGDocument3 paginiXCSDFGRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsdqweDocument2 paginiAsdqweRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSC Report - LeanDocument143 paginiMSC Report - Leanbhuvanesh85Încă nu există evaluări
- 8013 10311 1 PBDocument14 pagini8013 10311 1 PBRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Chemistry IDocument60 paginiExperimental Chemistry IadminchemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Shuhairy SaidDocument23 paginiProject Shuhairy SaidRaman LuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unsteady Flow About A Sphere at Low Moderate Reynolds Number. Part Accelerated MotionDocument21 paginiUnsteady Flow About A Sphere at Low Moderate Reynolds Number. Part Accelerated Motionsamik4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost-Effective Skyhook ControlDocument9 paginiCost-Effective Skyhook Controlgloohuis463Încă nu există evaluări
- Enthalpimetric TitulationDocument3 paginiEnthalpimetric TitulationAlessandra Stangherlin OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Simulation Study For Switched Reluctance Motor Drives Based On Matlab6.5Document6 paginiThe Simulation Study For Switched Reluctance Motor Drives Based On Matlab6.5spnangraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 - Electricity and Magnetism Revision MC TestDocument30 pagini04 - Electricity and Magnetism Revision MC TestjaderainbowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adatlap PDFDocument12 paginiAdatlap PDFAnuradha SivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm A 101Document3 paginiAstm A 101RECEP ÇETİNKAYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Theory - Test PaperDocument3 paginiCircuit Theory - Test PapersvkchaudhuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Hooke - S Law SVDocument6 pagini11 Hooke - S Law SVTony GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alex Wouden SlidesDocument41 paginiAlex Wouden Slidesnjsmith5Încă nu există evaluări
- A Mathematical Model of Effects On Specific Joints During The Practice of Sun Salutation (SN, OMKAR 2011) PDFDocument8 paginiA Mathematical Model of Effects On Specific Joints During The Practice of Sun Salutation (SN, OMKAR 2011) PDFMarcelo NorisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traffic Flow Theory & Simulation: S.P. HoogendoornDocument41 paginiTraffic Flow Theory & Simulation: S.P. HoogendoornChiranjaya HulangamuwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ∫…Δi… M……b˜M…‰ §……§…… +®…Æ˙…¥…i…" ¥…t… (…"'ˆ: ¥…Y……x… ¥…t…∂……J……Document17 pagini∫…Δi… M……b˜M…‰ §……§…… +®…Æ˙…¥…i…" ¥…t… (…"'ˆ: ¥…Y……x… ¥…t…∂……J……YocobSamandrewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dcna Fixed Prosthodontics April 2004 PDFDocument236 paginiDcna Fixed Prosthodontics April 2004 PDFMiki FloreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Properties of PlywoodDocument9 paginiMechanical Properties of PlywoodJayant Kumar JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBM Probe 8Document1 paginăSBM Probe 8Haroon GhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terra Aqua Gabions Stable Slope Calculator Ver 1.0dDocument10 paginiTerra Aqua Gabions Stable Slope Calculator Ver 1.0dAna Mirella ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Quantum RobinDocument3 paginiThe Quantum RobinpresuraÎncă nu există evaluări