Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lab - Creating A Dichotomous Key To Identify Species of Beetles
Încărcat de
api-328915544Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lab - Creating A Dichotomous Key To Identify Species of Beetles
Încărcat de
api-328915544Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lab: Creating a Dichotomous Key To Identify Species of Beetles
Name:___________________________ Period:____ Date:__________________
Lab Partner:_______________________________________________________
24
Introduction: If you find an insect you have never seen before, how could you discover its identity?
Many field guides help you match up the characteristics of your specimen with those of
similar organisms using a dichotomous key. This identification key uses a series of paired
comparisons to sort organisms into smaller and smaller groups.
Purpose: To construct a dichotomous key to identify species of beetles.
Pre-Lab Questions:
1. What characteristics do all insects have in common? (2 marks)
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. Name two characteristics that scientists use to tell insects apart. (2 marks)
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. How can you use the characteristics of beetles to classify them? Give examples. (3 marks)
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
Method:
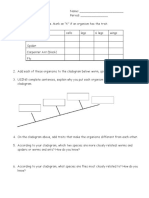
1. Use the diagram (Figure 1) of the dichotomous tree on the next page as a reference to create your
dichotomous key for classifying beetles. You should copy this diagram onto a separate piece of paper.
2. Study the illustration of 18 beetles on the page given to you.
3. Select one characteristic and sort the beetles into two groups based on whether they have the
characteristic or not.
Lab: Creating a Dichotomous Key To Identify Species of Beetles (continued)
Page 2
Method: (continued)
Figure 1: A dichotomous tree structure.
4. List each beetles number under either group 1 or group 2 on your diagram of the dichotomous tree.
5. Record the characteristic that identifies each group.
6. Select another characteristic of each subgroup, and repeat steps 4 and 5 for the next level down on your
diagram.
7. Continue to subdivide the groups until you have 18 groups with one beetle in each. Give your
dichotomous tree an appropriate title following this method: Figure 1: Title which describes
figure. (2 marks)
8. Using the characteristics shown on your diagram, construct a dichotomous key that someone could use
to identify any beetle from the original large group. Give your dichotomous key an appropriate title
following this method: Table 1: Title which describes table. (4 marks)
a) To do this, create a series of numbered steps with the first step showing the first characteristic used.
b) At each step, off two choices for classifying the beetle based on a single characteristic. For
example, you may have use the characteristic antennae longer than front legs as your first
dividing characteristic. The first numbered step in your key would be (1a) antennae longer than
front legs or (1b) antennae not longer than front legs.
c) Use the sample keys you have in your notes and in the lab on Using a Dichotomous Key for the
classification of the salamander species.
9. Exchange your key with another lab group. Use the other lab groups key to classify one beetle, and
record all the characteristics of the species you chose.
Lab: Creating a Dichotomous Key To Identify Species of Beetles (continued)
Page 3
Analyze and Interpret:
1. Did the other lab group produce a dichotomous key identical to yours? Explain why or why not.
(2 marks)
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. Which beetle characteristics were not useful for creating your key? Explain why. (2 marks)
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Discussion:
1. Why does a key offer two choices at each step and not more than two? (2 marks)
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. In your own words, define dichotomous key. (1 mark)
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Lab: Creating a Dichotomous Key To Identify Species of Beetles (continued)
Page 4
Communication: (4 marks)
o
o
o
o
Printing and writing is neat and legible or word processed.
Tables and figures are neatly drawn with ruler or word processed. Printing used in tables and figures.
Tables and figures are numbered and have a proper title.
Spelling and grammar is correct. Complete sentences are used.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Create Your Own Dichotomous Key - Protist Mug ShotsDocument4 paginiCreate Your Own Dichotomous Key - Protist Mug ShotsMike LuchÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEEP LEARNING TECHNIQUES: CLUSTER ANALYSIS and PATTERN RECOGNITION with NEURAL NETWORKS. Examples with MATLABDe la EverandDEEP LEARNING TECHNIQUES: CLUSTER ANALYSIS and PATTERN RECOGNITION with NEURAL NETWORKS. Examples with MATLABÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM AssignmentsDocument4 paginiDM AssignmentsKaustubh KhareÎncă nu există evaluări
- DATA MINING and MACHINE LEARNING: CLUSTER ANALYSIS and kNN CLASSIFIERS. Examples with MATLABDe la EverandDATA MINING and MACHINE LEARNING: CLUSTER ANALYSIS and kNN CLASSIFIERS. Examples with MATLABÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - Classifying Flying SpeciesDocument3 paginiLab - Classifying Flying Speciesapi-328915544Încă nu există evaluări
- Plant Vs Animal Cells: Clear Image of Cells)Document5 paginiPlant Vs Animal Cells: Clear Image of Cells)Xuan Quoc Nguyen100% (1)
- Notice in This Class. Derive Firstclass, Ladies, General, Luggage Classes From The CompartmentDocument2 paginiNotice in This Class. Derive Firstclass, Ladies, General, Luggage Classes From The CompartmentPriyankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section A (42 Marks) : St. Joseph's Anglo-Chinese School F.1 Integrated Science (Sample)Document10 paginiSection A (42 Marks) : St. Joseph's Anglo-Chinese School F.1 Integrated Science (Sample)LEO NGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction of A Dichotomous KeyDocument6 paginiConstruction of A Dichotomous KeyMayhaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dichotomous Key Activity GeneralDocument5 paginiDichotomous Key Activity General27zjjfb68fÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution Lab CladogramsDocument13 paginiThe Evolution Lab Cladogramsapi-372548146Încă nu există evaluări
- Classification WorksheetDocument2 paginiClassification WorksheetPaul Williams Maravillas100% (1)
- Review 8 Sem 1 ExamDocument11 paginiReview 8 Sem 1 Examcayden.hattanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells Exploration ActivitiesDocument16 paginiCells Exploration ActivitiesMorticia VizactyhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template - Bio 31A Exercise 1 WorksheetsDocument7 paginiTemplate - Bio 31A Exercise 1 WorksheetsJocelle TondingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactive Notebook 3 Plant Cells and Animal CellsDocument11 paginiInteractive Notebook 3 Plant Cells and Animal Cellsapi-241062194100% (1)
- Lab 2 Online Worksheet 2021 - The WormsDocument12 paginiLab 2 Online Worksheet 2021 - The WormsKahelia CampbellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Bio WorksheetsDocument15 paginiScience 10 Bio WorksheetsMemmy KidnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Cells and Microscopy Note PacketDocument13 paginiIntro To Cells and Microscopy Note Packetdanijela cetkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Building A Dichotomous Key Take HomeDocument5 paginiLab Building A Dichotomous Key Take HomeKaren SinorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dichotomous KeyDocument5 paginiDichotomous KeyKim SolisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characterization of Semester Unknown - Part IDocument4 paginiCharacterization of Semester Unknown - Part Izahids2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Act Sheet1 LevelsDocument3 paginiAct Sheet1 LevelsRodel AzaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Candy Dichotomous KeyDocument4 paginiCandy Dichotomous KeyKaren SinorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eggs, Bungee Jumping, and Algebra: An Application of Linear ModelingDocument9 paginiEggs, Bungee Jumping, and Algebra: An Application of Linear Modelingjmgoette13Încă nu există evaluări
- Classification WorksheetDocument2 paginiClassification Worksheetapi-24272777350% (4)
- Mesquite Users GuideDocument16 paginiMesquite Users GuideHikaru Stark100% (1)
- Form 1 Integrated Science Time: 1H 30minDocument10 paginiForm 1 Integrated Science Time: 1H 30minNg Lay HoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- E1990 Activity 2 Generate A Dichotomous KeyDocument3 paginiE1990 Activity 2 Generate A Dichotomous Keycdshgg12Încă nu există evaluări
- Biodiversity & Classification - Advanced Student VersionDocument13 paginiBiodiversity & Classification - Advanced Student VersionTeachLABScIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biodiversity & Classification Lab: (Standard Version)Document10 paginiBiodiversity & Classification Lab: (Standard Version)TeachLABScIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis PrelabDocument4 paginiMitosis Prelabapi-247664759Încă nu există evaluări
- 4th SeminarDocument3 pagini4th SeminarDoinita ConstantinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cladogram WorksheetDocument2 paginiCladogram WorksheetHolli Grant100% (1)
- Activity ClasworkDocument2 paginiActivity Clasworkapi-711484810Încă nu există evaluări
- Congratulations Dear Students On Your Weekly Accomplishments! Keep Up The Great Work!!Document2 paginiCongratulations Dear Students On Your Weekly Accomplishments! Keep Up The Great Work!!LowelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22 Restriction Enzyme SimDocument6 pagini22 Restriction Enzyme SimS. Spencer0% (1)
- Cop2800 s13 Exam2 AnswerkeyDocument5 paginiCop2800 s13 Exam2 AnswerkeyethelfajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomy - Advanced Student VersionDocument13 paginiTaxonomy - Advanced Student VersionTeachLABScIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mains (Sesson 2)Document7 paginiMains (Sesson 2)Alejandra LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 2 Exam Paper 2023 NEWDocument9 paginiYear 2 Exam Paper 2023 NEWMariayee PerumalÎncă nu există evaluări
- QUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Document1 paginăQUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Tego Shei Harumi100% (1)
- Lab - Gum Lab Copy Used 2014Document6 paginiLab - Gum Lab Copy Used 2014api-264731832Încă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 1 - Model QuestionDocument7 paginiScience Form 1 - Model Questionuminoriah68% (25)
- Performance Task: Honeycombs: Outside As We Start To Build Our HiveDocument6 paginiPerformance Task: Honeycombs: Outside As We Start To Build Our HiveKyla FerrerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1.2: How Small Is Small?: Name: - DateDocument7 paginiLesson 1.2: How Small Is Small?: Name: - DateRick WuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sciences Cells and Cell Structures/plant and Animal Cells Total: 50Document7 paginiSciences Cells and Cell Structures/plant and Animal Cells Total: 50JoanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Science: Biology Unit Test PracticeDocument7 paginiGrade 10 Science: Biology Unit Test PracticeB BizzleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 86ab6cbd - 1 16667079393835 3817Document2 pagini86ab6cbd - 1 16667079393835 3817Tahmid FarhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Short TestDocument2 paginiBiology Short TestAvantika KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC Paper 2 Yr 5 (2022)Document6 paginiSC Paper 2 Yr 5 (2022)SHEELA A/P ARUMUGAM MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision 3Document4 paginiRevision 3xfd n8Încă nu există evaluări
- WS 2 IG I BiologyDocument4 paginiWS 2 IG I BiologyRaj MalkanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle Square Patterns - Unit 1 Lesson 3Document2 paginiCircle Square Patterns - Unit 1 Lesson 3RileyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam - Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument7 paginiFinal Exam - Object Oriented Programmingdj_eqc7227100% (2)
- Toaz - Info Year 8 Exam Paper PRDocument13 paginiToaz - Info Year 8 Exam Paper PRNormanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handling Data - Year 5 - Revision WorksheetDocument4 paginiHandling Data - Year 5 - Revision WorksheetRabia MoeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2Document8 paginiLab 2alyssa cambaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Lab WorksheetDocument6 paginiCell Lab WorksheetBri HookerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brief COPE QuestionnaireDocument3 paginiBrief COPE QuestionnairerajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCB Pbis HandbookDocument21 paginiGCB Pbis Handbookapi-256174152100% (1)
- The Challenge of Identifying Gifted/Learning Disabled Students Linda A. Krochak Thomas G. RyanDocument11 paginiThe Challenge of Identifying Gifted/Learning Disabled Students Linda A. Krochak Thomas G. RyanAlwin AsuncionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jim Dine Tool RubricDocument1 paginăJim Dine Tool Rubricapi-375325190Încă nu există evaluări
- Theory U1t2 UnlockedDocument11 paginiTheory U1t2 Unlockedcarlos santanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories of Nursing PracticeDocument2 paginiTheories of Nursing PracticeShanilyn BiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cheat Sheet For Literary AnalysisDocument2 paginiCheat Sheet For Literary AnalysisLiteracy RootsÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.No Uid Name Session Group Coursety Pename Coursename Linkedin Activated/No T Activated Linkedin Course Progress Percentage As On 27-03-2023Document30 paginiS.No Uid Name Session Group Coursety Pename Coursename Linkedin Activated/No T Activated Linkedin Course Progress Percentage As On 27-03-2023RW AKSHATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 15 - Measuring HappinessDocument17 paginiClass 15 - Measuring HappinessPaul O'ConnorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angel SyllabusDocument5 paginiAngel SyllabusJundee L. CarrilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- TSLB3083 Teaching of Grammar in The Primary ESL L3Document12 paginiTSLB3083 Teaching of Grammar in The Primary ESL L3Syarah ImaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parenting Questionnaire (PQ)Document15 paginiParenting Questionnaire (PQ)DijuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edu 404 PDFDocument41 paginiEdu 404 PDFSiti Mashasanah MunsirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Success Factors For Stakeholder Management: Construction Practitioners' PerspectivesDocument9 paginiCritical Success Factors For Stakeholder Management: Construction Practitioners' PerspectiveswhyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Parenting and TodayDocument12 paginiSingle Parenting and Todaygelli joy corpuz67% (3)
- Article DesignDocument24 paginiArticle DesignJ.C.VÎncă nu există evaluări
- EAPP MediaDocument2 paginiEAPP MediaJaemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tpack Lesson 1Document4 paginiTpack Lesson 1api-334063815Încă nu există evaluări
- Brochure Are Your Emotions Too Difficult To HandleDocument2 paginiBrochure Are Your Emotions Too Difficult To HandleAguz PramanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Will in Psychotherapy - Alberto Alberti PDFDocument8 paginiThe Will in Psychotherapy - Alberto Alberti PDFWill NoyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ResultDocument3 paginiResultQuỳnh HoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poem Analysis PracticeDocument1 paginăPoem Analysis PracticeJalal AshqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Test (Read & Speak) NotesDocument4 paginiOral Test (Read & Speak) NotesAzimi AzminÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Value of Social Interaction in The Development of Good Work Ethics Amongst Young PeopleDocument1 paginăThe Value of Social Interaction in The Development of Good Work Ethics Amongst Young PeopleViolet Evergarden100% (5)
- Why Is Reading ImportantDocument15 paginiWhy Is Reading ImportantGe LoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Men Against Fire AnalysisDocument4 paginiMen Against Fire Analysisdina100% (1)
- Determinism VS. Free Will: Philo0 01 Ms - Jhohanah R. Bediones DPRO Olivarez CollegeDocument20 paginiDeterminism VS. Free Will: Philo0 01 Ms - Jhohanah R. Bediones DPRO Olivarez CollegeCd LeonorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erich Fromm Sane Society PDFDocument2 paginiErich Fromm Sane Society PDFJackieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ehrenberg 1974 AdvertisingDocument10 paginiEhrenberg 1974 AdvertisingNicholas Yeoh Chee Guan0% (2)
- Oral Communication SpeechDocument1 paginăOral Communication SpeechLeonel LiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDe la EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDe la EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDe la EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (397)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDe la EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDe la EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDe la EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (52)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDe la EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (812)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)De la EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (411)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDe la Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (33)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDe la EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDe la EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDe la EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (65)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDe la EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDe la EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (216)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDe la EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (16)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDe la EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (66)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueDe la EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (38)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDe la EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildDe la EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (44)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldDe la EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (596)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDe la EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (115)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouDe la EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (62)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindDe la EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (93)