Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Calcium Dobesilate Monohydrate
Încărcat de
Mulayam Singh YadavDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Calcium Dobesilate Monohydrate
Încărcat de
Mulayam Singh YadavDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Calcium dobesilate monohydrate
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0
Barium. To 10 mL of solution S add 1 mL of calcium sulfate
Heavy metals (2.4.8) : maximum 20 ppm.
12 mL of solution S complies with test A. Prepare the reference solution R. After at least 15 min, any opalescence in the
solution is not more intense than that in a mixture of 1 mL of
solution using lead standard solution (2 ppm Pb) R.
distilled water R and 10 mL of solution S.
ASSAY
Iron (2.4.9) : maximum 7 ppm, determined on solution S.
Dissolve 0.280 g in 100 mL of water R and carry out the
Magnesium and alkali metals : maximum 0.3 per cent.
complexometric titration of calcium (2.5.11).
To
a mixture of 20 mL of solution S and 80 mL of water R add
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 14.70 mg
2 g of ammonium chloride R and 2 mL of dilute ammonia R1,
of CaCl2,2H2O.
heat to boiling and pour into the boiling solution a hot
solution of 5 g of ammonium oxalate R in 75 mL of water R.
LABELLING
The label states, where applicable, that the substance is suitable Allow to stand for 4 h, dilute to 200 mL with water R and lter
through a suitable lter. To 100 mL of the ltrate add 0.5 mL
for use in the manufacture of dialysis solutions.
of sulfuric acid R. Evaporate to dryness on a water-bath and
ignite to constant mass at 600 50 C. The residue weighs a
STORAGE
maximum of 5 mg.
In an airtight container.
Heavy metals (2.4.8): maximum 15 ppm.
01/2008:0707 12 mL of solution S complies with test A. Prepare the reference
corrected 6.0 solution using lead standard solution (2 ppm Pb) R.
CALCIUM CHLORIDE HEXAHYDRATE
Calcii chloridum
CaCl2,6H2O
[7774-34-7]
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 100 mL of water R. Carry out the
complexometric titration of calcium (2.5.11).
hexahydricum
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 21.91 mg
Mr 219.1 of CaCl2,6H2O.
DEFINITION
Content : 97.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent of CaCl2,6H2O.
CHARACTERS
Appearance : white or almost white, crystalline mass or
colourless crystals.
Solubility : very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol
(96 per cent).
It solidies at about 29 C.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Solution S (see Tests) gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
B. It gives the reactions of calcium (2.3.1).
C. It complies with the limits of the assay.
TESTS
Solution S. Dissolve 15.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R
prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 100 mL with the
same solvent.
Appearance of solution. Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not
more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2,
Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity. To 10 mL of freshly prepared solution S
add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R. If the solution is red,
not more than 0.2 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required
to discharge the colour and if the solution is colourless, not
more than 0.2 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to
turn it red.
Sulfates (2.4.13) : maximum 200 ppm.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R.
Aluminium. To 10 mL of solution S add 2 mL of ammonium
chloride solution R and 1 mL of dilute ammonia R1. Heat to
boiling. No turbidity or precipitate is formed.
If intended for use in the manufacture of dialysis solutions,
the above test is replaced by the following test for aluminium
(2.4.17) : maximum 1 ppm.
Prescribed solution. Dissolve 6 g in 100 mL of water R and add
10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R.
Reference solution. Mix 2 mL of aluminium standard solution
(2 ppm Al) R, 10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R and
98 mL of water R.
Blank solution. Mix 10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R
and 100 mL of water R.
General Notices (1) apply to all monographs and other texts
LABELLING
The label states, where applicable, that the substance is suitable
for use in the manufacture of dialysis solutions.
07/2008:1183
corrected 7.0
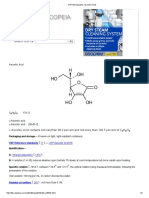
CALCIUM DOBESILATE
MONOHYDRATE
Calcii dobesilas monohydricus
C12H10CaO10S2,H2O
[20123-80-2]
Mr 436.4
DEFINITION
Calcium di(2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate) monohydrate.
Content : 99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance : white or almost white, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility : very soluble in water, freely soluble in anhydrous
ethanol, very slightly soluble in 2-propanol, practically
insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry
(2.2.25).
Test solution. Dissolve 0.100 g in water R and dilute to
200.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of this
solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Spectral range : 210-350 nm.
Absorption maxima : at 221 nm and 301 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum at 301 nm :
174 to 181.
B. Mix 1 mL of ferric chloride solution R2, 1 mL of a freshly
prepared 10 g/L solution of potassium ferricyanide R
and 0.1 mL of nitric acid R. To this mixture add 5 mL of
freshly prepared solution S (see Tests) : a blue colour and a
precipitate are immediately produced.
1733
Calcium folinate
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0
C. 2 mL of freshly prepared solution S gives reaction (b) of
calcium (2.3.1).
1 mL of 0.1 M cerium sulfate is equivalent to 10.45 mg of
C12H10CaO10S2.
TESTS
Solution S. Dissolve 10.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and
dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution. Solution S, when freshly prepared,
is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3): 4.5 to 6.0 for solution S.
Related substances. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Keep
all solutions at 2-8 C.
Buffer solution. Dissolve 1.2 g of anhydrous sodium dihydrogen
phosphate R in 900 mL of water for chromatography R, adjust
to pH 6.5 with disodium hydrogen phosphate solution R and
dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Test solution. Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined
in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a). Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to
100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to
10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b). Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to
be examined and 10 mg of hydroquinone R (impurity A) in
water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Dilute
1 mL of this solution to 100 mL with water R.
Column :
size : l = 0.25 m, = 4.6 mm ;
stationary phase : spherical end-capped octadecylsilyl silica
gel for chromatography R (5 m).
Mobile phase : acetonitrile R1, buffer solution (10:90 V/V).
Flow rate : 0.8 mL/min.
Detection : spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection : 10 L.
Run time : 2.5 times the retention time of dobesilate.
Relative retention with reference to dobesilate (retention
time = about 6 min) : impurity A = about 1.7.
System suitability : reference solution (b) :
resolution : minimum 8.0 between the peaks due to
dobesilate and impurity A.
Limits :
correction factor : for the calculation of content, multiply
the peak area of impurity A by 0.6 ;
impurity A : not more than the area of the principal peak
in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)
(0.1 per cent) ;
unspecified impurities : for each impurity, not more than the
area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained
with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent) ;
total : not more than twice the area of the principal peak
in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)
(0.2 per cent) ;
disregard limit : 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in
the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)
(0.05 per cent).
Heavy metals (2.4.8) : maximum 15 ppm.
1.0 g complies with test C. Prepare the reference solution using
1.5 mL of lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R.
Iron (2.4.9) : maximum 10 ppm, determined on 10 mL of
solution S.
Water (2.5.12) : 4.0 per cent to 6.0 per cent, determined on
0.500 g.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in a mixture of 10 mL of water R and 40 mL
of dilute sulfuric acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M cerium sulfate,
determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1734
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities : A.
A. benzene-1,4-diol (hydroquinone).
01/2009:0978
corrected 7.0
CALCIUM FOLINATE
Calcii folinas
C20H21CaN7O7,xH2O
Mr 511.5 (anhydrous substance)
DEFINITION
Calcium (2S)-2-[[4-[[[(6RS)-2-amino-5-formyl-4-oxo1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropteridin-6-yl]methyl]amino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioate.
Content :
calcium folinate (C20H21CaN7O7): 97.0 per cent to 102.0 per
cent (anhydrous substance) ;
calcium (Ca ; Ar 40.08) : 7.54 per cent to 8.14 per cent
(anhydrous substance).
It contains a variable quantity of water.
CHARACTERS
Appearance : white or light yellow, amorphous or crystalline,
hygroscopic powder.
Solubility : sparingly soluble in water, practically insoluble in
acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent).
The amorphous form may produce supersaturated solutions
in water.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification : A, B, D.
Second identification : A, C, D.
A. Specic optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation : discs.
Comparison : calcium folinate CRS.
If the spectra obtained show differences, dissolve the
substance to be examined and the reference substance
separately in the minimum volume of water R and add
dropwise sufcient acetone R to produce a precipitate.
Allow to stand for 15 min, collect the precipitate by
centrifugation, wash the precipitate with 2 small quantities
of acetone R and dry. Record new spectra using the
residues.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution. Dissolve 15 mg of the substance to be
examined in a 3 per cent V/V solution of ammonia R and
dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- FentanylDocument2 paginiFentanylMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Oil Components ChromatogramDocument3 paginiEssential Oil Components ChromatogramMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Oil Components ChromatogramDocument3 paginiEssential Oil Components ChromatogramMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kchristman Maltol Extraction and Purification Report 2Document6 paginiKchristman Maltol Extraction and Purification Report 2api-694290335100% (1)
- ANSI 173 Draft DS 2011 6B Targeted Verification 9-22-2011 DRAFTDocument42 paginiANSI 173 Draft DS 2011 6B Targeted Verification 9-22-2011 DRAFTMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring phosphorus in waterDocument17 paginiMeasuring phosphorus in waterMarcelino Putra PerdanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IR IntroductionDocument48 paginiIR IntroductionMuhammad Erik Rezakola Ahnaf100% (1)
- Colorful Solutions of Iron (II) and Iron (III) ComplexesDocument15 paginiColorful Solutions of Iron (II) and Iron (III) ComplexesAyii AlfredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coral CalciumDocument6 paginiCoral Calciumfariha farheenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phosphate Content PDFDocument5 paginiPhosphate Content PDFjuli_radÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages and Limitations of Iron Amino Acid Chelates As Iron Fortificants PDFDocument4 paginiAdvantages and Limitations of Iron Amino Acid Chelates As Iron Fortificants PDFI. Murali KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Molecules: WaterDocument34 paginiBiological Molecules: WaterYing ShuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purified Water DOCUMENTATION: S.No. Name of Document Full FormDocument34 paginiPurified Water DOCUMENTATION: S.No. Name of Document Full FormMulayam Singh Yadav100% (1)
- The Analysis of Phospholipids in Soy Lecithin by HPLCDocument2 paginiThe Analysis of Phospholipids in Soy Lecithin by HPLCReza Sadeghi100% (1)
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument51 paginiWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsClaudia TiffanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook For Analytical Quality Control in Water and Wastewater LaboratoriesDocument164 paginiHandbook For Analytical Quality Control in Water and Wastewater LaboratoriesCarlos OrionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conventional Drug Delivery Routes, Recent Developments and Future Prospects - Tugas SPO "Document21 paginiConventional Drug Delivery Routes, Recent Developments and Future Prospects - Tugas SPO "Niken Dwi100% (1)
- Calcium chloride dihydrate tests and propertiesDocument2 paginiCalcium chloride dihydrate tests and propertiesMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PDFDocument61 paginiIron Deficiency Anemia PDFbhat Library100% (1)
- Determination of Vitamin B6 in Foods by HPLCDocument6 paginiDetermination of Vitamin B6 in Foods by HPLCDaniel Dávila MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pi Is 1548559519301144Document20 paginiPi Is 1548559519301144hemer hadyn calderon alvites0% (1)
- Liposomes: Controlled Delivery SystemsDocument31 paginiLiposomes: Controlled Delivery SystemsDRx Sonali Tarei100% (1)
- Science 4 Diagnostic TestDocument3 paginiScience 4 Diagnostic TestManelyn Taga100% (3)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron With Orthophenanthroline PDFDocument5 paginiSpectrophotometric Determination of Iron With Orthophenanthroline PDFribotsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Documents List For Calibration LaboratoryDocument18 paginiDocuments List For Calibration LaboratoryMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Titrimetric Method for Carbonate and Bicarbonate in Water (AOAC 920.194Document1 paginăTitrimetric Method for Carbonate and Bicarbonate in Water (AOAC 920.194Vanessa HigueraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Determination of Citric AcidDocument4 paginiThe Determination of Citric AcidSoumya NeemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethanol (96 Per Cent) (1317)Document2 paginiEthanol (96 Per Cent) (1317)Mulayam Singh Yadav100% (1)
- British Pharmacopea - 02 PDFDocument1.345 paginiBritish Pharmacopea - 02 PDFYawanBasopataÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZN (Ii) With GlycineDocument17 paginiZN (Ii) With GlycinesyamandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubber Deterioration-Discoloration From Ultraviolet (UV) or UV/Visible Radiation and Heat Exposure of Light-Colored SurfacesDocument4 paginiRubber Deterioration-Discoloration From Ultraviolet (UV) or UV/Visible Radiation and Heat Exposure of Light-Colored SurfacesAndre Rodriguez SpirimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derivatives For HPLC AnalysisDocument68 paginiDerivatives For HPLC Analysismagicianchemist0% (1)
- Ortoic AcidDocument25 paginiOrtoic AcidSandy Wasfy100% (1)
- Magnesium Calcium PDFDocument3 paginiMagnesium Calcium PDFokikwmÎncă nu există evaluări
- LNG Safety and Security - CEEDocument56 paginiLNG Safety and Security - CEEErwin100% (1)
- Cipac H2oDocument3 paginiCipac H2omercuriusÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPPStartUp PDFDocument376 paginiIPPStartUp PDFSinan YıldızÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntihistaminDocument46 paginiAntihistaminVenerandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Oxidation Ponds & LagoonsDocument33 paginiOn Oxidation Ponds & LagoonsDevendra Sharma82% (22)
- Image Pro Plus ReferenceDocument784 paginiImage Pro Plus Referenceanhntran4850Încă nu există evaluări
- Soluble SilicatesDocument311 paginiSoluble SilicatesSomboon BoonsomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium stearate analysisDocument3 paginiCalcium stearate analysisRanndolf JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnesium Oxide USP Monograph AnalysisDocument2 paginiMagnesium Oxide USP Monograph AnalysisIfra AkhlaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silimarina Farmacopea FrancesaDocument4 paginiSilimarina Farmacopea FrancesaROBINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assay For Citric AcidDocument3 paginiAssay For Citric AcidLRahmawÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW - Chem.ucla - Edu Harding Ec Tutorials Tutorial28Document3 paginiWWW - Chem.ucla - Edu Harding Ec Tutorials Tutorial28asyiqqinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacopeia 1 (Autosaved)Document12 paginiPharmacopeia 1 (Autosaved)farooq shah shabbirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enve 208 Experiment 2.1 SonDocument10 paginiEnve 208 Experiment 2.1 Sonmihrican302Încă nu există evaluări
- Ferrous Glycinate (Processed With Citric Acid) : SynonymsDocument3 paginiFerrous Glycinate (Processed With Citric Acid) : SynonymsIfra AkhlaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment Estimation of Amino Acids: StructureDocument3 paginiExperiment Estimation of Amino Acids: StructureMàrwå Rägb ZäkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coral Disguised PDFDocument1 paginăCoral Disguised PDFSilviu AndoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- MT 18 Standard Waters: Miscellaneous Techniques and ImpuritiesDocument16 paginiMT 18 Standard Waters: Miscellaneous Techniques and ImpuritiesFelipe NavarreteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amino Acid Analysis Using ZORBAX Eclipse AAA ColumnsDocument10 paginiAmino Acid Analysis Using ZORBAX Eclipse AAA ColumnsMuhammad KhairulnizamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihistamines 101 Munich 06-05Document15 paginiAntihistamines 101 Munich 06-05pentruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Magnesium Oxide by HydroxyquinolineDocument8 paginiDetermination of Magnesium Oxide by Hydroxyquinolineamukti27Încă nu există evaluări
- Amine DerivatizationDocument5 paginiAmine DerivatizationOksana RotkajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infrared Theory PDFDocument9 paginiInfrared Theory PDFATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estrogens, ConjugatedDocument10 paginiEstrogens, ConjugatedJuan PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensitive Detection of 17 Organotin Compounds in Beverages by GC-MS/MSDocument24 paginiSensitive Detection of 17 Organotin Compounds in Beverages by GC-MS/MSiwonnascribdnomoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To ColorimetryDocument42 paginiA Guide To ColorimetryNgo TrangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knauer - Food PreservativesDocument1 paginăKnauer - Food PreservativesMaryanta HadisudiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulation, Characterization of Pellets of Duloxetine Hydrochloride by Extrusion and SpheronizationDocument28 paginiFormulation, Characterization of Pellets of Duloxetine Hydrochloride by Extrusion and SpheronizationHely PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- HPLC TitrationDocument7 paginiHPLC TitrationMelisa MonerrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- USP Monographs: Ascorbic AcidDocument2 paginiUSP Monographs: Ascorbic AcidIfra Akhlaq100% (1)
- USP Monographs - Magnesium Oxide CapsulesDocument2 paginiUSP Monographs - Magnesium Oxide CapsulesgirishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of DetergentsDocument13 paginiHandbook of DetergentsEmilyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cinchona BarkDocument2 paginiCinchona BarkAfra FitrianitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Method Development and Validation For Iron and Ascorbic Acid in Ferrous Bisglycinate Effervescent Tablets by Colorimetry and Reverse Phase-High-performance Liquid ChromatographyDocument7 paginiAnalytical Method Development and Validation For Iron and Ascorbic Acid in Ferrous Bisglycinate Effervescent Tablets by Colorimetry and Reverse Phase-High-performance Liquid Chromatographyshoaib naqviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thiamphenicol OkDocument4 paginiThiamphenicol OkJuan PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zinc AcexamateDocument2 paginiZinc AcexamateAlexi Del Castillo MustaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 5ed Sodium Carbonate MonohydrateDocument2 paginiEUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 5ed Sodium Carbonate MonohydrateMa IrmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium Folinate 1734Document3 paginiCalcium Folinate 1734Mulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodium HydroxideDocument1 paginăSodium HydroxideivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raw Material Requirement For Syrup Trial & Other RequirementsDocument2 paginiRaw Material Requirement For Syrup Trial & Other RequirementsMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Butterfly Ayurveda Private Limited 198, Sec-8, IMT Manesar, Gurgaon (Haryana)Document2 paginiButterfly Ayurveda Private Limited 198, Sec-8, IMT Manesar, Gurgaon (Haryana)Mulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addresses of Some Dealers in Medicinal PlantsDocument3 paginiAddresses of Some Dealers in Medicinal PlantsMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhupana KalpanaDocument3 paginiDhupana KalpanaMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Butterfly Ayurveda Private Limited 198, Sec-8, IMT Manesar, Gurgaon (Haryana)Document2 paginiButterfly Ayurveda Private Limited 198, Sec-8, IMT Manesar, Gurgaon (Haryana)Mulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of EquipmentsDocument10 paginiList of EquipmentsMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- FluconazoleDocument2 paginiFluconazoleMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affidavit: Witness With Full AdressDocument4 paginiAffidavit: Witness With Full AdressMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pkg. Checklist For PAncreofly CapsuleDocument2 paginiPkg. Checklist For PAncreofly CapsuleMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fludarabine PhosphateDocument3 paginiFludarabine PhosphateMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physicochemical Parameters TEASDocument4 paginiPhysicochemical Parameters TEASMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1.3. Efficacy of Antimicrobial Preservation: General Notices (1) Apply To All Monographs and Other TextsDocument2 pagini5.1.3. Efficacy of Antimicrobial Preservation: General Notices (1) Apply To All Monographs and Other TextsMonika BontongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nabl - Scope of IIIM JammuDocument28 paginiNabl - Scope of IIIM JammuMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fentanyl Citrate Impurities ChromatogramDocument2 paginiFentanyl Citrate Impurities ChromatogramMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- FluconazoleDocument2 paginiFluconazoleMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferrous Sulfate, DriedDocument2 paginiFerrous Sulfate, DriedMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate 2229Document2 paginiFerrous Sulfate Heptahydrate 2229Mulayam Singh Yadav100% (1)
- Ethylene Oxide and DioxanDocument2 paginiEthylene Oxide and DioxanMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fenoterol Hydrobromide 2220Document2 paginiFenoterol Hydrobromide 2220Mulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Famotidine 2211Document2 paginiFamotidine 2211Mulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eye care formulations guideDocument3 paginiEye care formulations guideMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethanol AnhydrousDocument2 paginiEthanol AnhydrousMulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etoposide (0823)Document4 paginiEtoposide (0823)Mulayam Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2004 Key Stage 3 Sats Science Level 3-6 Paper 1Document36 pagini2004 Key Stage 3 Sats Science Level 3-6 Paper 1SơnSơnÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE Has Done More Harm Than Good For The Overall Development of Mankind and SocietyDocument5 paginiSCIENCE Has Done More Harm Than Good For The Overall Development of Mankind and SocietyPib Mathers0% (1)
- Introduction To Environmental EngineeringDocument11 paginiIntroduction To Environmental EngineeringSheena Ann StonehillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improve Public Health With Proper Sanitation SystemsDocument33 paginiImprove Public Health With Proper Sanitation SystemsMathew VargheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dow Corning Molykote HP-870 GreaseDocument8 paginiDow Corning Molykote HP-870 GreaseEdgarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Application Value EngineDocument11 paginiWater Application Value EngineArul KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Servicio - LW C100plus (2020 - 08 - 20 02 - 50 - 44 UTC)Document112 paginiManual Servicio - LW C100plus (2020 - 08 - 20 02 - 50 - 44 UTC)Arnoldo FelixÎncă nu există evaluări
- KENT ROYD AYING BSEE 4-H AssignmentDocument4 paginiKENT ROYD AYING BSEE 4-H AssignmentEvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Flow Seperation Numerical Problem ExampleDocument6 paginiBase Flow Seperation Numerical Problem Exampletom meeteiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingersoll Rand Compressed Air FilterDocument4 paginiIngersoll Rand Compressed Air FilterSergiSerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fossil Powerplant Water Treatment BrochureDocument3 paginiFossil Powerplant Water Treatment BrochuresamarthÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 - English Version of MYM Membrane IntroductionDocument42 pagini15 - English Version of MYM Membrane IntroductionChrestella InggrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Life As A Drip: Water Cycle Story StarterDocument3 paginiMy Life As A Drip: Water Cycle Story StarterAnne GervaiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Fundamental Study of Chalcopyrite Flotation in Sea Water Using Sodium SilicateDocument6 paginiA Fundamental Study of Chalcopyrite Flotation in Sea Water Using Sodium SilicateEnoque MatheÎncă nu există evaluări
- River RestorationDocument60 paginiRiver RestorationShraddha BahiratÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDS-RIPSTAR 122-Part 2Document6 paginiMSDS-RIPSTAR 122-Part 2Ankita Baban GavadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bonderite® 958-EnDocument9 paginiBonderite® 958-EnGabriel BrăbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics IGCSE Past PaperDocument16 paginiPhysics IGCSE Past Paperjenny10040% (1)
- Activated Carbon MSDS PDFDocument6 paginiActivated Carbon MSDS PDFRIANG TRIANDONOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiography of Flowing Water: OutlineDocument12 paginiPhysiography of Flowing Water: OutlineHasaan WaheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modular Air Handling Unit IOM - (FASI03-2020,21A)Document20 paginiModular Air Handling Unit IOM - (FASI03-2020,21A)Jericho EstrellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Griha: Presented byDocument43 paginiGriha: Presented byvandy nehaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commercial Seawater Reverse Osmosis Watermaker SystemsDocument2 paginiCommercial Seawater Reverse Osmosis Watermaker SystemsMarco PoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 5 ST 1Document3 paginiScience 5 ST 1Nila Mae CalpoÎncă nu există evaluări