Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tut11 Solution PDF
Încărcat de
AboNawaF0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări3 paginiTitlu original
tut11-solution.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări3 paginiTut11 Solution PDF
Încărcat de
AboNawaFDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
King Saud University
College of Computer and Information Sciences
Department of Computer Engineering
Tutorial No: 340 CEN/ 11.
Date: 19/10/1436.
No of questions:2
3582
3421
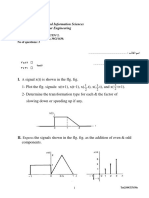
I.
:
:
Consider a LTI system with impulse response:
h(t) = e-t u(t)
a)
b)
c)
d)
Determine if the system is causal or not.
Find its Laplace transform and name it
Plot the pole-zero pattern of H(s).
Draw the conclusion about the causality and the stability of this system.
Solution
a) Determine if the system is causal or not.
Yes the system is causal since it is = 0 for t<0 {due to multiplication by u(t)}.
b) Find its Laplace transform.
Re{s}> - 1
H (s) is called: System function or Transfer function.
Tut 11/340CEN/56s
c) Sketch the pole-zero plot of H (s).
There is one pole only (when Re{s} = - 1).
d) Conclusion:
- Laplace transform is rational and the ROC is to the right of rightmost pole.
This is consistent with the statement that the causality of system with rational
system functions is equivalent to the ROC being to the right of the rightmost
pole.
- The system is stable: The pole is in the left-half of the s-plane, that is ROC
includes j axis.
Note: From the impulse function it is seen that the system is stable since it is
integrable.
II. Find the Transfer function for flg. system.
Solution:
Y(s) = H1(s) E(s)
2
Tut 11/340CEN/56s
E(s) = X(s) - Z(s)
And:
Z(s) = H2(s) Y(s)
From which we obtain the relation:
Y(s) = H1(s)[X(s) - H2(s) Y(s)]
Consequently the Transfer function is:
H(s) = Y(s) / X(s)
= H1(s) / 1 + H1(s) H2(s)
Tut 11/340CEN/56s
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Explaining Convolution Using MATLABDocument10 paginiExplaining Convolution Using MATLABRupesh VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signals Systems Lab 2Document5 paginiSignals Systems Lab 2ahmad.a.touseefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel College of Engineering For WomenDocument4 paginiExcel College of Engineering For Womenk_m_deepaÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument1 paginăKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- S and S Examination PaperDocument3 paginiS and S Examination Paperzeeshanahmad12030Încă nu există evaluări
- Closed Form FormDocument14 paginiClosed Form FormManiRoopÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIEN462 A1Document4 paginiBIEN462 A1Eileen FuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec6303 - Ss QB (Part - A & B) 2Document10 paginiEc6303 - Ss QB (Part - A & B) 2Maheshwaran MahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4: Linear Time-Invariant Systems and Representation: ObjectivesDocument6 paginiLab 4: Linear Time-Invariant Systems and Representation: ObjectivesFahad AneebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 06 PDFDocument7 paginiLab 06 PDFAbdul Rehman AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec6303 - Signals and Systems Question Bank Unit - I: 2 MarksDocument10 paginiEc6303 - Signals and Systems Question Bank Unit - I: 2 MarksPrasanna Kumar BÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC6303-Signals and Systems PDFDocument10 paginiEC6303-Signals and Systems PDFlakshman donepudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enee 660 HW #7Document2 paginiEnee 660 HW #7PeacefulLion0% (1)
- FLab-04 EXP4Document20 paginiFLab-04 EXP4Carl Kevin CartijanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- If Student Proven Dishonest or Make A Cheating, They Will Get E ScoreDocument5 paginiIf Student Proven Dishonest or Make A Cheating, They Will Get E ScoreGhozi AlbiziaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2EC6303-Signals and Systems QBDocument10 pagini2EC6303-Signals and Systems QBShyla RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- EECE 301 Note Set 10 CT ConvolutionDocument11 paginiEECE 301 Note Set 10 CT ConvolutionrodriguesvascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roll No:15011A0411Document41 paginiRoll No:15011A0411ChanjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document47 paginiLecture 2Houssam moussaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ss QBDocument7 paginiSs QBTapan Kumar PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convolution SumDocument5 paginiConvolution SumAniket SankpalÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC208 Important QuestionsDocument7 paginiEC208 Important QuestionsHariharan VigneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- T F 2 O S: Ransfer Unctions AND Rder YstemsDocument9 paginiT F 2 O S: Ransfer Unctions AND Rder YstemsSohaib SajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signals and Systems Model - 1Document2 paginiSignals and Systems Model - 1sharanyameen2704Încă nu există evaluări
- Signals and SystemsDocument2 paginiSignals and SystemsJanani MunisamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Manual 1 To 5Document23 paginiControl System Manual 1 To 5Eashan PendseÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELCE301 Lecture5 (LTIsystems Time2)Document31 paginiELCE301 Lecture5 (LTIsystems Time2)Little VoiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity No. 3 The Transfer Function and System ResponseDocument3 paginiActivity No. 3 The Transfer Function and System ResponseChester Kyles ColitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 5 - Part2 - DT Signals & SystemsDocument51 paginiChapter - 5 - Part2 - DT Signals & SystemsReddy BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System IDocument12 paginiControl System IKhawar RiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ransfer Unction Epresentation: ObjectivesDocument14 paginiRansfer Unction Epresentation: ObjectivesSohaib SajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System IDocument13 paginiControl System Ishiko nemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Modeling & ExamplesDocument16 paginiSystem Modeling & ExamplesahmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematical ModellingDocument36 paginiMathematical ModellingMohd Fazli100% (2)
- Transfer FunctionDocument26 paginiTransfer FunctionRacheal KirbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- R13 - December, 2014 - Regular ExaminationsDocument3 paginiR13 - December, 2014 - Regular ExaminationsmushahedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cce330 (B) L: Matlab Applications in Signals and (Bio) Systems: American University of Science & TechnologyDocument7 paginiCce330 (B) L: Matlab Applications in Signals and (Bio) Systems: American University of Science & TechnologyDani Hajj Ali SleimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- S6 Ei Control Sys 2 May2014 (O)Document3 paginiS6 Ei Control Sys 2 May2014 (O)shilpa.1595Încă nu există evaluări
- Signals and Systems Model 1&2 FINAL22Document10 paginiSignals and Systems Model 1&2 FINAL22GiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- B. Tech Control SystemsDocument2 paginiB. Tech Control SystemsAnant VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC6303-Signals and SystemsDocument10 paginiEC6303-Signals and SystemssumathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Control Systems Lab File: Name: Prateek Pandey Enroll. No: 43113204918 Batch: EEE 4 YrDocument26 paginiAdvance Control Systems Lab File: Name: Prateek Pandey Enroll. No: 43113204918 Batch: EEE 4 YrCharanpreet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y (N) X (N) H (N) - Y (N) Sigma of (Product of X (K) and H (N-K) ) (K 0 To n-1)Document26 paginiY (N) X (N) H (N) - Y (N) Sigma of (Product of X (K) and H (N-K) ) (K 0 To n-1)G.Sai Karthik ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signals and Systems Question BankDocument4 paginiSignals and Systems Question BankVimal RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Domain Representation of Linear Time Invariant (LTI) SystemsDocument54 paginiTime Domain Representation of Linear Time Invariant (LTI) SystemsLai Yon PengÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS331 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 2003Document3 paginiCS331 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 2003Chandru SekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lamplace Transform SignalDocument2 paginiLamplace Transform SignalAHMAD HAFIZUDDIN BIN HASHIM STUDENTÎncă nu există evaluări
- ps3 (1) From MAE 4780Document5 paginips3 (1) From MAE 4780fooz10Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2Document7 paginiAssignment 2ue06037Încă nu există evaluări
- Linear Systems: Prof. Dr. João Edgar Chaves Filho Mestrado em Eng. ElétricaDocument49 paginiLinear Systems: Prof. Dr. João Edgar Chaves Filho Mestrado em Eng. ElétricaAndré AraújoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete-Time Signals & Systems COME480: Dr. Abdul Rahman El Falou BAUDocument39 paginiDiscrete-Time Signals & Systems COME480: Dr. Abdul Rahman El Falou BAUMahmoud AbdouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computers and Mathematics With Applications: Yan Li, Yangquan Chen, Igor PodlubnyDocument12 paginiComputers and Mathematics With Applications: Yan Li, Yangquan Chen, Igor PodlubnykarpagasenthilpandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - State SpaceDocument15 paginiLab - State SpaceSohaib Sajid100% (1)
- Systems and Control PDFDocument9 paginiSystems and Control PDFHamid Farhan0% (1)
- UntitledDocument32 paginiUntitledMasudur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euler'S Method For Coupled Differential Equations RLC CircuitsDocument10 paginiEuler'S Method For Coupled Differential Equations RLC CircuitsEpic WinÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument1 paginăKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument1 paginăKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument1 paginăKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument1 paginăKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tut8 PDFDocument1 paginăTut8 PDFAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument2 paginiKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.003 (Fall 2011) Quiz #1: October 5, 2011Document7 pagini6.003 (Fall 2011) Quiz #1: October 5, 2011AboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument2 paginiKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument2 paginiKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringDocument2 paginiKing Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer EngineeringAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEN214 Chapter5 P3 Modified PDFDocument60 paginiCEN214 Chapter5 P3 Modified PDFAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 - Memory Basics: Logic and Computer Design FundamentalsDocument38 paginiChapter 8 - Memory Basics: Logic and Computer Design FundamentalsAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEN214 - Asynchronous Circuit PDFDocument85 paginiCEN214 - Asynchronous Circuit PDFAboNawaFÎncă nu există evaluări