Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Paris Law Theory
Încărcat de
panbuuDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Paris Law Theory
Încărcat de
panbuuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
9/8/2016
ParisLawTheory
Theory
Lifepredictionforfatiguecrackswasmadeverymucheasierandfarmorequantitative,inthe1960'swhenParis[1]postulatedthat
therangeofstressintensityfactormightcharacterisesubcriticalcrackgrowthunderfatigueloadinginthesamewaythatK
characterisedcritical,orfastfracture.Heexaminedanumberofalloysandrealisedthatplotsofcrackgrowthrateagainstrangeof
stressintensityfactorgavestraightlinesonloglogscales.Thisimpliesthat:
Forthefirsttime,itbecamepossibletomakeaquantitativepredictionofresiduallifeforacrackofacertainsize.Thissimply
requiredfindinglimitsontheintegrationintermsofcracksize,whichcouldbedonebyfindingthefinalsizewhichcausedfast
fracturefromtherelationshipbetweenfracturetoughnessandcracksize:
SeparationofthevariablesaandNandsubstitutionfortherangeofstressintensitybytheequivalentequationintermsofstress
andcracksizegives:
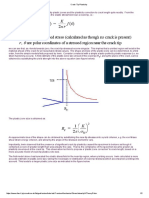
Itwaslaterrealisedthatthissocalled'law'appliedtogrowthratesintherangeofperhaps103 mm/cycleto106 mm/cycle,andthat
thefatiguecrackgrowthratecurvewassigmoidalinshapewhengrowthlowerandhigherthanthisrangewereincluded.Typical
dataforaustemperedductileironinair,asafunctionofstressratio(minimumstressincycledividedbymaximumstressincyclea
measureofmeanstressinthefatiguecycle)isshowninthefigurebelow.
https://www.fose1.plymouth.ac.uk/fatiguefracture/tutorials/FractureMechanics/Fatigue/FatTheory1.htm
1/3
9/8/2016
ParisLawTheory
Thelowergrowthrateregionistermedthethresholdregime,becausegrowthratesdropoffsteeplyandthecrackbecomes
essentiallynonpropagating.Thisrepresentsachangeinmechanismfromdoubleshearcontinuumgrowthtosingleshearnon
continuumgrowth.Thehighergrowthrateregimeiswherevaluesofmaximumstressintensityinthefatiguecyclearetending
towardsthefracturetoughnessandstaticmodesoffracture(cleavage,intergranular)areaddingtothefatigueinducedgrowth
rates.
TheParislawremainsaveryusefulrelationship,however,becauseitcoverstherangeofgrowthratesmostusefultoengineering
structures,andbecauseanextrapolationintothethresholdregimegivesaconservativeestimatefortheremaininglife.This
developmentwascrucialtotheadoptionofdefecttoleranceconceptsandtheimplementationofaretirementforcausephilosophy.
Furtherinformationfromsomeearlypapersdealingwithcharacterisationoffatiguecrackgrowthratesinfracturemechanicsterms
canbefoundinreferences2to6.Thereareanumberofmoderntextswhichdealwithfatigue,andausefulstartingpointis
reference7.
References:
1.PParisandFErdogan(1963),Acriticalanalysisofcrackpropagationlaws,JournalofBasicEngineering,Transactionsof
theAmericanSocietyofMechanicalEngineers,December1963,pp.528534.
2.TCLindley,CERichardsandRORitchie(1976),Mechanicsandmechanismsoffatiguecrackgrowthinmetals:areview,
MetallurgiaandMetalForming,September1976,pp.268280.
3.JSchijve(1978),Fourlecturesonfatiguecrackgrowth,EngineeringFractureMechanics,Vol.11No.1pp.169206.
4.RPWei(1978),Fracturemechanicsapproachtofatigueanalysisindesign,JournalofEngineeringMaterialsand
Technology,April1978,Vol.100,pp.113120.
https://www.fose1.plymouth.ac.uk/fatiguefracture/tutorials/FractureMechanics/Fatigue/FatTheory1.htm
2/3
9/8/2016
ParisLawTheory
5.RORitchie(1980),Applicationoffracturemechanicstofatigue,corrosionfatigueandhydrogenembrittlement,Analytical
andExperimentalFractureMechanics,ProceedingsoftheInternationalConferenceheldinRome,June1980,GCShih
(editor),SijthoffandNordhoff.
6.RJAllen,GSBoothandTJutla(1988),Areviewoffatiguecrackgrowthcharacterisationbylinearelasticfracture
mechanics(LEFM)Parts1and2,FatigueandFractureofEngineeringMaterialsandStructures,Vol.11No.1pp.4569and
No.2p.71108.
7.SSuresh(1998),FatigueofMaterials2ndedition,CambridgeUniversityPress,Cambridge,England.
CloseWindow
https://www.fose1.plymouth.ac.uk/fatiguefracture/tutorials/FractureMechanics/Fatigue/FatTheory1.htm
3/3
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Water Tank DesignDocument37 paginiWater Tank DesignWrishad Zia95% (98)
- Circular Concrete Tanks Without PrestressingDocument32 paginiCircular Concrete Tanks Without PrestressingDampierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wellbore Stability - A Driller's Guide PDFDocument60 paginiWellbore Stability - A Driller's Guide PDFRubén Navas100% (2)
- Chapter - 1 Stress and Strain PDFDocument21 paginiChapter - 1 Stress and Strain PDFAnonymous rT6y7298% (44)
- CAE ATPL 2 Airframes and SystemsDocument352 paginiCAE ATPL 2 Airframes and SystemsAŞKIN FIRAT100% (5)
- A 586Document4 paginiA 586Gustavo SuarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue Design Recommendations (JIP FPSO)Document122 paginiFatigue Design Recommendations (JIP FPSO)Wilson KooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue TestingDocument10 paginiFatigue TestingMuhammed SulfeekÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effct of Loom Settings On Weaving ResistanceDocument8 paginiThe Effct of Loom Settings On Weaving ResistanceArslan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Rainflow Cycle Counting A Historical Perspective4Document8 pagini01 Rainflow Cycle Counting A Historical Perspective4Victor PuglieseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Impact Test PDFDocument9 paginiComplete Impact Test PDFKalKatu MaLam86% (22)
- Exercise 6 - State-Space Models - SolutionsDocument13 paginiExercise 6 - State-Space Models - Solutionspanbuu100% (1)
- Test Exams PDFDocument7 paginiTest Exams PDFShaheer Ahmed KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is 516 Part 1 Section 1Document19 paginiIs 516 Part 1 Section 1devendra choudhary80% (5)
- 10 1016@j Jmps 2006 01 007 PDFDocument17 pagini10 1016@j Jmps 2006 01 007 PDFAscanio BarbosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue Crack Growth Prediction Models For Metallic Materials PDFDocument15 paginiFatigue Crack Growth Prediction Models For Metallic Materials PDFkarpanaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of The Fracture Sizes by Using The Frequency Dependence of AnisotropyDocument7 paginiEvaluation of The Fracture Sizes by Using The Frequency Dependence of Anisotropymsmsoft90Încă nu există evaluări
- A Cohesive Model of Fatigue Crack GrowthDocument19 paginiA Cohesive Model of Fatigue Crack GrowthsenthilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling of Droplet Breakage Probabilities in An Oscillatory Baffled ReactorDocument12 paginiModelling of Droplet Breakage Probabilities in An Oscillatory Baffled ReactorjohanpenuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basis Info FatigueDocument13 paginiBasis Info FatigueMarnix BroerÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMFEADocument10 paginiDMFEANag RazzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creep TestingDocument19 paginiCreep Testingاقْرَأْ وَرَبُّكَ الْأَكْرَمُÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Outline of The Techniques Available For The Measurement of Skin Friction in Turbulent Boundary LayersDocument57 paginiAn Outline of The Techniques Available For The Measurement of Skin Friction in Turbulent Boundary LayersRaquel FariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Stress Analysis Prof. K. Ramesh Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument29 paginiExperimental Stress Analysis Prof. K. Ramesh Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, MadrastamizhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal Club For December 2016Document11 paginiJournal Club For December 2016Mousavi N SajadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 60 Kardom Carls FFEMSDocument13 pagini60 Kardom Carls FFEMSmankari.kamal.18022963Încă nu există evaluări
- Stress ConcentrationsDocument0 paginiStress Concentrations777894292Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 - Measurement of FrictionDocument5 pagini5 - Measurement of FrictionAbdulla CamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To The New SIDocument7 paginiAn Introduction To The New SIMárcio Leandro RotondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wrinkle Formations in Axi-Symmetrically Stretched Membranes: T E P J EDocument10 paginiWrinkle Formations in Axi-Symmetrically Stretched Membranes: T E P J EPablo CelmareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clamp PDFDocument12 paginiClamp PDFNeneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigation Into The Time-Dependent Crack PropagDocument11 paginiInvestigation Into The Time-Dependent Crack PropagyimrhaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Basis of Evolution Laws For Rate and State FrictionDocument13 paginiPhysical Basis of Evolution Laws For Rate and State FrictionBennet KuriakoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019-01 On Unified Crack Propagation Laws - PapangeloDocument8 pagini2019-01 On Unified Crack Propagation Laws - PapangelorhinemineÎncă nu există evaluări
- 88 m46 PDFDocument10 pagini88 m46 PDFHARSHVARDHAN SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture Mechanics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument19 paginiFracture Mechanics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchReeverse MasterminddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spe 89 Pa PDFDocument13 paginiSpe 89 Pa PDFSteeven RezabalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lefm NotesDocument8 paginiLefm NotesSolomon GracioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Geophysical Research1985SmalleyDocument7 paginiJournal of Geophysical Research1985SmalleysmalleyrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear Strength Concrete StructuresDocument18 paginiShear Strength Concrete Structuresmmendez113Încă nu există evaluări
- Bell e Mehta 1988Document39 paginiBell e Mehta 1988Nelson LondoñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part NoticeDocument13 paginiDefense Technical Information Center Compilation Part NoticeAllan FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clothing Pressure Modeling 2019Document14 paginiClothing Pressure Modeling 2019Yehualaw AyresamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 430 PDFDocument33 pagini430 PDFPeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravity-Driven Flow of Grains Through Pipes: A One-Dimensional ModelDocument8 paginiGravity-Driven Flow of Grains Through Pipes: A One-Dimensional Modelhilmy yusuf maulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- O F F P I R C E I P A R L I N T: The Effect of Machine Conditions and Furnish Properties On Paper CD Shrinkage ProfileDocument24 paginiO F F P I R C E I P A R L I N T: The Effect of Machine Conditions and Furnish Properties On Paper CD Shrinkage ProfileDebanjana ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 V65 How Finite Element Method Helps Explaining Fatigue Crack Growth Retardation & Acceleration-Maljaars & TangDocument40 pagini2020 V65 How Finite Element Method Helps Explaining Fatigue Crack Growth Retardation & Acceleration-Maljaars & TangOmar AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Developments and Applications of Skin-Friction Measuring TechniquesDocument14 paginiNew Developments and Applications of Skin-Friction Measuring TechniquesVyssionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Size-Scale E Ects On The Friction Coe CientDocument10 paginiSize-Scale E Ects On The Friction Coe CientSwapnil PawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Allal 2006Document9 paginiAllal 2006Manel KOUBAAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractality in The Threshold Condition of Fatigue Crack Growth: An Interpretation of The Kitagawa DiagramDocument10 paginiFractality in The Threshold Condition of Fatigue Crack Growth: An Interpretation of The Kitagawa DiagramFrancesco MontagnoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- G1 1973+bruneDocument30 paginiG1 1973+bruneMidhun MÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9an Explanation of The Different Regimes Os Friction and Wear Using Asperity Deformation Models PDFDocument15 pagini9an Explanation of The Different Regimes Os Friction and Wear Using Asperity Deformation Models PDFAnderson JuniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2008 - Lister Et Al. - Shape and Stability of Axisymmetric Levitated Viscous Drops - Journal of Fluid MechanicsDocument19 pagini2008 - Lister Et Al. - Shape and Stability of Axisymmetric Levitated Viscous Drops - Journal of Fluid MechanicsClaudio BiaginiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acharya FinalReportDocument46 paginiAcharya FinalReportGonzalokpo69Încă nu există evaluări
- Progress in The Development of A Reynolds Stress TDocument31 paginiProgress in The Development of A Reynolds Stress TSmith Diaz VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture Toughness Testing of Non Standard Specimens: Etienne Mfoumou Sharon Kao-WalterDocument17 paginiFracture Toughness Testing of Non Standard Specimens: Etienne Mfoumou Sharon Kao-WalteruzumakhinarutoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cased ChargesDocument10 paginiCased ChargeshezigrisaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1626-Article Text (.Docx, Max 100 MB) - 6145-1-10-20151224Document9 pagini1626-Article Text (.Docx, Max 100 MB) - 6145-1-10-20151224Anonymous ZC1ld1CLmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Of Matrix: Estimation Block Size Distribution in Naturally Fractured ReservoirsDocument52 paginiOf Matrix: Estimation Block Size Distribution in Naturally Fractured Reservoirstomk2220Încă nu există evaluări
- COMPLAS2017-30 - A New Creep Model DirectlyDocument12 paginiCOMPLAS2017-30 - A New Creep Model DirectlyDiogo Alvarenga GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Perspectives in Mercury PorosimetryDocument32 paginiNew Perspectives in Mercury PorosimetryMaurice PolitisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of The Air Pollution Control AssociationDocument6 paginiJournal of The Air Pollution Control Associationavisek_misrÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Tearing Test As A Means For Estimating The Ultimate Properties of RubberDocument17 paginiThe Tearing Test As A Means For Estimating The Ultimate Properties of RubberAndjela RoganovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of The Mechanics and Physics of Solids: Ryan S. Ginder, William D. Nix, George M. PharrDocument11 paginiJournal of The Mechanics and Physics of Solids: Ryan S. Ginder, William D. Nix, George M. PharrRaj Jung MahatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creep and Shrinkage InteractionDocument10 paginiCreep and Shrinkage Interactiondanielsu87Încă nu există evaluări
- Compaction Behavior of Continuous Carbon Fiber Tows An Experimental AnalysisDocument7 paginiCompaction Behavior of Continuous Carbon Fiber Tows An Experimental Analysisenkilee2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment of Rubber BlockDocument10 paginiExperiment of Rubber BlockM Zaid Akram50% (4)
- IJF Manuscript - For ShaunDocument18 paginiIJF Manuscript - For ShaunShaun Raphael LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Brittle SolidsDocument13 paginiSimulation of Brittle Solidsdr_kh_ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Misurata UniversityDocument11 paginiMisurata UniversityDustin EllisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculator For Stiffness and Compliance of Lamina 90Document3 paginiCalculator For Stiffness and Compliance of Lamina 90panbuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials Selection and TemperatureDocument2 paginiMaterials Selection and TemperaturepanbuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crack Tip PlasticityDocument2 paginiCrack Tip PlasticitypanbuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Transformation 1 PDFDocument14 paginiLinear Transformation 1 PDFpanbuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Linear TransformationDocument7 paginiIntroduction To Linear TransformationpanbuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pap ST3.2 Task 13 Sept 2011Document5 paginiPap ST3.2 Task 13 Sept 2011Kaltenbacher ZsoltÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection Chart For Waterproofing ProductsDocument20 paginiSelection Chart For Waterproofing ProductsKiran KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of FRC Tunnel Segments Considering The Ductility Requirements of The Model Code 2010Document23 paginiDesign of FRC Tunnel Segments Considering The Ductility Requirements of The Model Code 2010Freddie KooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fitness-for-Service Engineering Assessment Procedure: Quest Integrity October 2015Document7 paginiFitness-for-Service Engineering Assessment Procedure: Quest Integrity October 2015امينÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 29 - A 29M - 04 - Qti5l0eyou0Document5 paginiA 29 - A 29M - 04 - Qti5l0eyou0alokaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault Facies and Its Application To Sandstone ReservoirsDocument27 paginiFault Facies and Its Application To Sandstone Reservoirsc_b_umashankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Shear Connection Training - MoCDocument81 paginiComposite Shear Connection Training - MoCAbdifatah HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6Document27 paginiChapter 6E Cos LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subsize Charpy V SpecimenDocument8 paginiSubsize Charpy V SpecimennooneoveroneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation Defect Detection System ReportDocument38 paginiAutomation Defect Detection System ReportDaisyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aluminim Welding Filler Material PDFDocument20 paginiAluminim Welding Filler Material PDFvishal bailurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scad 2011 2 2 307 PDFDocument13 paginiScad 2011 2 2 307 PDFCarlos NievesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm A111Document3 paginiAstm A111deivisbtsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME8692-Finite Element Analysis - 03 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument122 paginiME8692-Finite Element Analysis - 03 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inSengutuvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Crack Modeling in Concrete StructuresDocument16 paginiDiscrete Crack Modeling in Concrete StructuresjahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment NO:6 Compression Test For Anisotropic MaterialDocument6 paginiExperiment NO:6 Compression Test For Anisotropic MaterialAraragi KoyomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Damage Evolution LawDocument15 paginiDamage Evolution LawRafael ZanettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Efeitos Mecanicos Da Fibra de Curauá em Cimento ExtrudadoDocument11 paginiEfeitos Mecanicos Da Fibra de Curauá em Cimento ExtrudadoEduardo Lima CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEM 3D Analysis of Rock Cone Failure Range DuringDocument8 paginiFEM 3D Analysis of Rock Cone Failure Range DuringFritz NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări