Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Polymer Bulk Morphology & Properties
Încărcat de
SorayaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Polymer Bulk Morphology & Properties
Încărcat de
SorayaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Polymermorphologyandpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymersolids
Amorphous
Semicrystalline
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Molten state
cooling
Crystalline structure
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Melting
Tm
V
Glasstransition
Tg
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Reptation is the snake-like thermal motion of very long linear,
entangled macromolecules in polymer melts or concentrated
polymer solutions
Reptationofpolymerchains
1
D 2
M
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Solvent evaporation
From solution
Solution cooling
Crystallization
Cooling the melt
From the melt
Heating the glassy phase
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
LDPE crystals precipitated from a xylene
solution (lamellar shaped)
LDPE spherulites (observed through CP)
obtained on cooling from the melt
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Fiber formation
The system becomes anisotropic
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Xray diffraction
Monocromatic Xray
beam
Braggs law
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
XRD pattern of isotactic PP
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Theories of Tg
The Free-Volume theory
Specific volume
V V0 V f
Vf
V f K ( R G )(T Tg )
K
V0
Tg
Temperature
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
The Kinetic theory
6-7oC shift in Tg per decade of time scale of the experiment
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
The Thermodynamic theory
The glass transition is a true second order transition, which takes
place at time scale infinitely long.
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Physical aging
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Factors which affect Tg:
Chain flexibility
Polyethylene Terephtalate
Tg= -123oC
Tg= +69oC
Tg= +185oC
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Presence of aliphatic side groups
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
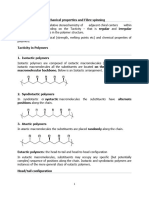
Tacticity
Tabla p. 409 Sperling
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Presence of stiff, bulky side groups
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Pressure
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Molecular weight
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Degree of crosslinking
In thermosets, Tg increases as the molecular weight between crosslinks decreases
TTT diagram
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Increase in number of
gell particles
Polymer bulk
First formation of infinite
network, theoretical gel point
Gel particles
Molecular weight increase
Polymermorphologyinthebulkstate
Modification of Tg by means of plasticizers
By copolymerization reactions or blending (internal plasticizesr)
1
w1 w2
Tg Tg1 Tg 2
Fox equation
By adding low MW compounds (external plasticizers)
Plasticizers must be:
-Compatible
-Miscible with the polymer
-Permanent, that is they need to have low diffusion coefficient and low vapour
pressure
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymer Viscoelasticity
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
l l0
l0
stress
A0
= E
Hookes law
ElasticSolid
deformation
stress
.
=
Newtons law
ViscousFluid
rateofdeformation
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymers are generally non-Newtonian, except over narrowly defined
ranges of strain rate.
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Three fundamental methods for characterizing the viscoelastic behavior of polymers:
Creep
Stress relaxation
Dynamic-mechanical analysis
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
In an idealized creep curve, we can distinguish four regions:
the initial elastic response region: Hookes law with zero-time modulus
a transition region: nonlinear increase in strain
an equilibrium region: strain increases linearly with time, characteristic of
viscous flow
And, on removal of the stress
a recovery region, characterized by an initial elastic retraction followed
by a strain decay.
Strain asymptotically approaches a non-zero value: permanent set
Data are generally reported as a time-dependent creep compliance:
(t )
J (t )
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
In the stress relaxation test, viscoelastic materials respond
with a stress which decays with time.
Stress relaxation data are commonly reported as timedependent stress relaxation modulus:
(t )
E (t )
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
A typical stress-strain curve for a polymer
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Necking: zone with a lower section, much more strained than
the neighbouring regions, characterized by chain orientation
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Polymerpropertiesinthebulkstate
Measurement of resilience
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ch3 Structure and Property PDFDocument29 paginich3 Structure and Property PDF임성민Încă nu există evaluări
- States of Order in PolymersDocument28 paginiStates of Order in PolymersMianHusnain IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Physical Chemistry of PolymerDocument172 paginiIntroduction To The Physical Chemistry of PolymerAmr Gamal100% (1)
- Polymers: Polymer: A Long Chain Organic Molecule Consisting ofDocument10 paginiPolymers: Polymer: A Long Chain Organic Molecule Consisting ofrossifam777Încă nu există evaluări
- Polymer TechnologyDocument16 paginiPolymer Technologykhubaib rahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Properties of PolymersDocument22 paginiPhysical Properties of PolymersSharifah Zulaikha BenYahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolymersDocument140 paginiPolymersNitin Nishant100% (2)
- ملخص بوليمرDocument47 paginiملخص بوليمرAhmad AlteeleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dental Polymers GuideDocument37 paginiDental Polymers Guideaboemadaldeen100% (1)
- Polymers and Elastomers For EngineersDocument153 paginiPolymers and Elastomers For EngineersVedant Prusty100% (1)
- ChE 543 W15 After Mid-Term ReviewDocument4 paginiChE 543 W15 After Mid-Term ReviewZohaib NarejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST - Ann'S College of Engineering & Technology Engineering Chemistry Unit - I Polymer TechnologyDocument18 paginiST - Ann'S College of Engineering & Technology Engineering Chemistry Unit - I Polymer TechnologyMaddu PavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everything You Need to Know About PolymersDocument64 paginiEverything You Need to Know About PolymersSpoodsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.properties of PolymerDocument25 pagini3.properties of PolymerNafis NahianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture - Engineeirng Materilas - Week 45678Document51 paginiLecture - Engineeirng Materilas - Week 45678Salar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 1Document23 paginiCHP 1Kerem Cengiz KılıçÎncă nu există evaluări
- All of PPDocument6 paginiAll of PPUmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch5 Characterization and Analysis-ADocument40 paginich5 Characterization and Analysis-A임성민Încă nu există evaluări
- Polymer Cha4Document57 paginiPolymer Cha4Galma DhugaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- L-3 Mee 241Document37 paginiL-3 Mee 241Promee Nafiza AnjumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materi-4-JENIS POLIMERDocument15 paginiMateri-4-JENIS POLIMERAnangSuryanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To PolymersDocument11 paginiIntroduction To PolymersAmir Aiman100% (1)
- Glass Transition Temperature, TGDocument13 paginiGlass Transition Temperature, TGSwe Zin Zaw MyintÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymer Properties Influenced by Electrostatic ForcesDocument26 paginiPolymer Properties Influenced by Electrostatic ForcesAditya PradiptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymer TacticityDocument28 paginiPolymer Tacticityowegibrian479Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Polymer ScienceDocument19 paginiIntroduction To Polymer ScienceAnshul GautampurkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolymersDocument106 paginiPolymersmambouhpriscaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae684 Coatings2Document116 paginiAe684 Coatings2Naresh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications and Processing of Polymers: Module-11Document20 paginiApplications and Processing of Polymers: Module-11Indranil BhattacharyyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymers QuestionsDocument15 paginiPolymers QuestionsOmar EzzatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument34 paginiLecture 1 PDFaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- CrystallinityDocument19 paginiCrystallinityMuhammad Abdur RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymers - 20Document60 paginiPolymers - 20MnkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymer Systems and Film Formation Mechanisms in HighDocument57 paginiPolymer Systems and Film Formation Mechanisms in HighUsama AwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymer PhysicsDocument4 paginiPolymer PhysicsThanga GanapathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Internship Program-2021 (OIP-2021) by Iiche: Subject: Chemical Process TechnologyDocument49 paginiOnline Internship Program-2021 (OIP-2021) by Iiche: Subject: Chemical Process TechnologyAngelapreethi 006Încă nu există evaluări
- Inorganic PolymersDocument189 paginiInorganic PolymersOmSilence2651100% (1)
- PolymerDocument48 paginiPolymerKhalnayak YtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristics, Applications, and Processing of Polymers: Meta Fitri Rizkiana, S.T., M.Sc. NRP. 760017111Document26 paginiCharacteristics, Applications, and Processing of Polymers: Meta Fitri Rizkiana, S.T., M.Sc. NRP. 760017111Dhea Kana ZhafiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Polymers: Definition, Classification, PropertiesDocument45 paginiUnderstanding Polymers: Definition, Classification, Properties21MEB358 Kunal AryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolymersDocument32 paginiPolymersCharles Emile McAnany100% (26)
- Polymer UiDocument27 paginiPolymer Uialfi alfathanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Lectures of Engineering Materials (CHEM)Document60 paginiTwo Lectures of Engineering Materials (CHEM)Rameen MasrurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of PolymerDocument36 paginiProperties of PolymerhedayatinluvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Properties: 5.1 Solubility and Solution PropertiesDocument32 paginiChemical Properties: 5.1 Solubility and Solution PropertiesUrmit ParmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5.2. POLYMERDocument12 paginiUnit 5.2. POLYMERAnusha PanchumarthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthesis of A New Side-Chain Type Liquid Crystal Polymer Poly (Dicyclohexyl Vinylterephthalate)Document3 paginiSynthesis of A New Side-Chain Type Liquid Crystal Polymer Poly (Dicyclohexyl Vinylterephthalate)FiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crystallinity of PolymersDocument24 paginiCrystallinity of Polymersakived100% (2)
- STruture and Properties of PolymersDocument35 paginiSTruture and Properties of PolymersWasif RazzaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymer Viscoelasticity: Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMADocument81 paginiPolymer Viscoelasticity: Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMAtayitooo100% (1)
- Phase Behavior: Melting PointDocument2 paginiPhase Behavior: Melting PointMarathi CalligraphyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure-Property Relationships in PolymersDocument55 paginiStructure-Property Relationships in PolymersPathikShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Polymerisation MethodDocument56 paginiChapter Polymerisation MethodwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymers: This Name Hints at How Polymers Are MadeDocument291 paginiPolymers: This Name Hints at How Polymers Are MadeshuklashreyanshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymers 2Document46 paginiPolymers 2Omed. HÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymer PPT FinalDocument22 paginiPolymer PPT Finalkbnarkhede100% (1)
- PolimerDocument22 paginiPolimerDhea Kana ZhafiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modified Polymers, Their Preparation and Properties: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth Bratislava Conference on Polymers, Bratislava, Czechoslovakia, 1-4 July 1975De la EverandModified Polymers, Their Preparation and Properties: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth Bratislava Conference on Polymers, Bratislava, Czechoslovakia, 1-4 July 1975A. RomanovEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- New Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. Ii the Chemistry of Initiation of Non-Ringed Monomers/CompoundsDe la EverandNew Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. Ii the Chemistry of Initiation of Non-Ringed Monomers/CompoundsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tips for Learning French QuicklyDocument2 paginiTips for Learning French QuicklySorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tips for Learning French QuicklyDocument2 paginiTips for Learning French QuicklySorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cae Information For Candidates 2016 Document PDFDocument15 paginiCae Information For Candidates 2016 Document PDFBeatriz LeoncioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument40 paginiMetal Forming ProcessesRyat AtmadjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AspenHYSYSDynModelV7 3 RefDocument224 paginiAspenHYSYSDynModelV7 3 RefThanh-Dat NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuchka 11262012Document28 paginiKuchka 11262012SorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM 650: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications To ChemistryDocument2 paginiCHM 650: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications To ChemistrySorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Manual For Introduction To Modern Statistical MechanicsDocument48 paginiSolutions Manual For Introduction To Modern Statistical MechanicsSong Bin Cui100% (4)
- Simplex OptimisationDocument44 paginiSimplex OptimisationSorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF Guia EconomiaDocument132 paginiPDF Guia EconomiaSorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 01 14Document105 paginiChapter 01 14SorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Researchpaper Modeling and Simulation of Styrene Monomer Reactor MathematicalDocument7 paginiResearchpaper Modeling and Simulation of Styrene Monomer Reactor MathematicalSorayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demanda CaprolactamDocument2 paginiDemanda CaprolactamSoraya100% (1)
- A Text Book of Physics (C.R. Dasgupta) (Z-Library)Document760 paginiA Text Book of Physics (C.R. Dasgupta) (Z-Library)toffee9soumavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Four-Node Plate Bending Element Based On Mindlin Reissner Plate Theory and A Mixed InterpolationDocument17 paginiA Four-Node Plate Bending Element Based On Mindlin Reissner Plate Theory and A Mixed InterpolationAdnan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Venturi MeterDocument8 paginiVenturi MeterSwati SachanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index: Combustion Technology: Essential of Flames and Burners, First Edition SDocument3 paginiIndex: Combustion Technology: Essential of Flames and Burners, First Edition SirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-Open Channel FlowDocument41 paginiChapter 1-Open Channel FlowhabtamuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lethabo Thermodynamic ModelDocument36 paginiLethabo Thermodynamic ModelSimba Emmanuel NdunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Element: Design of Biaxial Bending and CompressionDocument15 paginiReinforced Concrete Element: Design of Biaxial Bending and CompressionZefira WisnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Practices in Compressors Selection-Purdue UniversityDocument11 paginiBasic Practices in Compressors Selection-Purdue UniversityLuis Joel Ramos RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piping Hydrotest ProcedureDocument9 paginiPiping Hydrotest Procedurewendypost73100% (1)
- Rheological Characterization of Paints and CoatingsDocument10 paginiRheological Characterization of Paints and CoatingsRinox RachidÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProblemsDocument4 paginiProblemsbalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix H PDFDocument59 paginiAppendix H PDFarif_rubinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gases WorksheetDocument24 paginiGases WorksheetshasagailÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.1a Introduction To CementingDocument102 pagini6.1a Introduction To CementingSamuel OkezieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo - First Second LawDocument35 paginiThermo - First Second LawPengintaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Test PPR SD PN 10Document4 paginiPressure Test PPR SD PN 10Nharuto LintangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrostatic Bearing SystemsDocument71 paginiHydrostatic Bearing Systems1mmahoneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - 5 Gas Condensate Reservoirs - Aug06Document10 pagini3 - 5 Gas Condensate Reservoirs - Aug06Ashraf SeragÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To CFX: Domains and Boundary ConditionsDocument39 paginiIntroduction To CFX: Domains and Boundary Conditionsashoku2Încă nu există evaluări
- Rinkasan Materi Vane Shear TestDocument7 paginiRinkasan Materi Vane Shear TestAntariksa PrianggaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- XTRACT Analysis Report - Demonstration: Section DetailsDocument3 paginiXTRACT Analysis Report - Demonstration: Section DetailsLucas SeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antoine EquationDocument2 paginiAntoine EquationAlfrets Marade SianiparÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 16 Calibrating and Operating Coriolis Flow MetersDocument31 pagini2018 16 Calibrating and Operating Coriolis Flow MetersmochdimaskuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crack Propagation in Aluminum Sheets PDFDocument248 paginiCrack Propagation in Aluminum Sheets PDFvidal3213Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Copy Specific Heat Capacity ExperimentDocument3 paginiFinal Copy Specific Heat Capacity Experimentjoevic torrecampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Lab Manual GuideDocument100 paginiThermal Lab Manual GuideNegese TeklearegayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.5 Piping Thermal Expansion and FlexibilityDocument27 pagini2.5 Piping Thermal Expansion and FlexibilityJohn TinnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contherm® Core Scraped-Surface Heat ExchangerDocument2 paginiContherm® Core Scraped-Surface Heat ExchangerKhánh NgânÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saavedra 2001Document9 paginiSaavedra 2001raifelmbÎncă nu există evaluări
- KTA 3205 - 2 - Engl - 2018 - 10 PDFDocument35 paginiKTA 3205 - 2 - Engl - 2018 - 10 PDFMIKAEL HENRIOTÎncă nu există evaluări