Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Communicable Diseases: in The Philippines
Încărcat de
Mitchie CallosTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Communicable Diseases: in The Philippines
Încărcat de
Mitchie CallosDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Communicable
Diseases
in the Philippines
Submitted By: Ma. Veatriz L
Ilagan
VIII-Genesis
The top 10 communicable diseases in the Philippines, based
on World Health Organization data, include tuberculosis,
dengue fever, pneumonia, malaria, diarrhea, bronchitis,
influenza, acute febrile illness, HIV and lower respiratory
tract infections. Based on data from 2008, eight of the top
10 causes of morbidity in the Philippines were communicable
diseases.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia (new-MOH-nee-ah), or pneumonitis, refers to any infection
in the lungs. Most pneumonias are caused by bacterial infections.
However, some are viral, fungal, or protozoan in origin, individuals
with AIDS commonly are infected with a protozoan. Pneumocystis
carinii, which causes pneumocystis pneumonia. Symptoms of
pneumonia include fever, chest pain, fluid in the lungs, and difficulty in
breathing.
Influenza (FLU) CO-90373
Influenza (in-flew-EN-zah) or flu is a highly contagious viral infection of
the respiratory tract. It is caused by a myxovirus. Three main strains
have been identified: Type A, B, and C. New strains of the virus
continually evolve hence why yearly vaccinations with the current
prevalent virus is recommended, especially for the very young, the
elderly, and the debilitated person at risk. The strains are usually
named for either the area (Asian flu) or the organism from which the
strain evolved (bird flu). Symptoms include fever and chills, sore
throat, cough, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. The virus is
transmitted in airborne droplets.
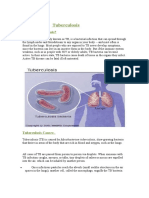
(TB)
Tuberculosis (too-ber-kew-LOH-sis) or TB is a chronic bacterial infection
that usually affects the lungs. It is caused by the bascillus bacterium
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can be transmitted by the ingestion or
inhalation of infected droplets. The bacterium can also infect other
organs of the body such as the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, bone
marrow, as well as the meninges of the central nervous system. Early
symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis include chest pain, fever, loss of
appetite with accompanying weight loss, and pleurisy. The tissue of the
lungs react to the presence of the bacterium by producing cells that
phagocytize the organism forming, tubercles, hence, the name
tuberculosis. If untreated the tubercles can enlarge and merge forming
clumps of dead tissue filling the lung cavity. This results in the patient
coughing up blood.
Malaria
Malaria is caused by the injection of a protozoan, Plasmodium, by a
female Anopheles mosquito. the microorganisms spends part of its life
cycle in the erythrocytes, eventually destroying them. Chills and fever
are produced by toxins released when the RBCs ruptures.
Rabies
Rabies is an acute viral, fatal disease that affects the CNS. It is
transmitted to humans through a bite with virus-containing saliva of an
infected mammal like unvaccinated dogs or cats or through the bite of
wild animals. The virus travels to the brain and other organs. Symptom
includes fever, headache, and muscle pain. If untreated, it results in
encephalitis, severe muscle spasms, seizures, paralysis, coma, and
eventually death. Treatment includes a series of vaccine injections
administered intramuscularly. Prevention is trough regular rabies shots
to our domesticated cats and dogs. Since dogs with rabies are afraid of
water and refuse to drink, the name hydrophobia (fear of water) is also
used for the disease.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea (dye-ah-REE-ah) literally means a flowing through. It occurs
when the mucosa of the colon is unable to maintain its usual levels of
water absorption and secretes larger than normal amounts of water,
ions, and mucus. Food poisoning with bacteria of the salmonella group,
certain viral infections like those that cause intestinal flu, and
protozoan infections with the amoeba. Entamoeba histolytica caused
by drinking untreated water causes bouts of severe diarrhea called
dysentery. These organisms invade the intestinal lining and destroy
the normal cells that carry on the absorption of water. The excessive
loss of water caused by bouts of diarrhea can lead to serious
dehydration. Without proper treatment, a victim could die. Diarrhea is
a common cause of death in young children in poor, undeveloped
countries.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Treatment: Chest Tube (Chest Drain or Tube Thoracostomy) Is A Flexible Plastic Tube That Is InsertedDocument7 paginiTreatment: Chest Tube (Chest Drain or Tube Thoracostomy) Is A Flexible Plastic Tube That Is Insertedmegrace_martinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocument30 paginiMicrobial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemChristopher Eria Santiañez0% (1)
- II ME NRP B SS 26. Human Health and DiseaseDocument9 paginiII ME NRP B SS 26. Human Health and DiseaseAmit RavindhraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Project by Mohini SagarDocument14 paginiBiology Project by Mohini Sagarsagarankit9977762Încă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument8 paginiPneumoniaNader Smadi100% (2)
- Pathogens & Microbiological Risk Assessment: CEGE2008 - Environmental PollutionDocument43 paginiPathogens & Microbiological Risk Assessment: CEGE2008 - Environmental PollutionmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HealthDocument10 paginiHealthAthul ShajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument1 paginăPneumoniaJozepf AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology: PneumoniaDocument7 paginiPathophysiology: PneumoniaCindy Mae de la TorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic: - Disease: Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test SeriesDocument10 paginiTopic: - Disease: Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test SeriesHarshaWakodkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On Human Diseases: PathogenDocument8 paginiProject Report On Human Diseases: PathogenPandit Shikhar TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To InfluenzaDocument6 paginiAn Introduction To InfluenzaMuchtazam MulsiansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microorganismos, Vocabulario en InglésDocument3 paginiMicroorganismos, Vocabulario en InglésAna María BedoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Jergen Blanche V. Domero Iv-Bsed-Bio - SciDocument3 paginiName: Jergen Blanche V. Domero Iv-Bsed-Bio - SciJergen Blanche DomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoology: Epidemiology of Parasitic DiseasesDocument19 paginiZoology: Epidemiology of Parasitic DiseasesEmraan EmmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penda Hulu AnDocument8 paginiPenda Hulu AnWahyu Kurnia putriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-8 Human Health and Diseases ContinuationDocument9 paginiChapter-8 Human Health and Diseases ContinuationKeerthana D SÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Communicable DiseasesDocument3 pagini10 Communicable DiseasesPauline de VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Health NotesDocument17 paginiHuman Health NotesGayathri Nandana M.SÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 8 - Human Health and Diseases - NottesDocument61 paginiCH 8 - Human Health and Diseases - NottesGopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Hand in 1Document14 paginiFinal Hand in 1lauraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assingment in MapehDocument1 paginăAssingment in MapehVictorino Victorino ButronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacterial Disease 1. Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument7 paginiBacterial Disease 1. Pulmonary TuberculosiskanishqcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hiv and AidsDocument5 paginiHiv and AidsMhie RecioÎncă nu există evaluări
- BronchitisDocument3 paginiBronchitisMagheswaran GovindasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignements 2024Document5 paginiAssignements 2024singhxraman00Încă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia WrittenDocument12 paginiPneumonia WrittenFereli Joy SupanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health, Common Diseases in Human and Immunity PYQ Part 1Document33 paginiHealth, Common Diseases in Human and Immunity PYQ Part 1ANKITA GAYENÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLAGUEDocument5 paginiPLAGUEHpu JogindernagerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious Diseases-Dr - Mohammad Suliman - 15102010Document2 paginiInfectious Diseases-Dr - Mohammad Suliman - 15102010jordanmedicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholera Is An Infection in The Small Intestine Caused by The Bacterium Vibrio Cholerae. TheDocument3 paginiCholera Is An Infection in The Small Intestine Caused by The Bacterium Vibrio Cholerae. ThebbhoeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia: Pneumococcus. A Serious Complication of Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Meningitis, Is AssociatedDocument7 paginiPneumonia: Pneumococcus. A Serious Complication of Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Meningitis, Is AssociatedHannah YtacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micropara 1Document30 paginiMicropara 1Myla OrlandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syndrom of Consolidated Pulmonary Tissue. Pneumonia. Athelectasis. Andrei IchimDocument114 paginiSyndrom of Consolidated Pulmonary Tissue. Pneumonia. Athelectasis. Andrei IchimYan Sheng Ho100% (1)
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Is A Disease in Which Individuals Who Have NotDocument5 paginiCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Is A Disease in Which Individuals Who Have NotxoxojylÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis (T.B) : What Is TB?Document16 paginiTuberculosis (T.B) : What Is TB?Usman MirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TP 1Document8 paginiTP 1nitesh tirkeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scan 16 May 2021 at 8.20 PMDocument8 paginiScan 16 May 2021 at 8.20 PMGringgo PanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW2 Ese150 GiananDocument9 paginiHW2 Ese150 GiananTyrone GiananÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Tuberculosis?Document10 paginiWhat Is Tuberculosis?samira_666Încă nu există evaluări
- Causes of PneumoniaDocument4 paginiCauses of Pneumoniailke akdenizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikDocument37 paginiName: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikChintiya PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Pneumonia?Document12 paginiWhat Is Pneumonia?rose angela0% (1)
- E.coli Causes Food Poisoning and Urinary Tract Infections. Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument32 paginiE.coli Causes Food Poisoning and Urinary Tract Infections. Mycobacterium TuberculosisTina WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- BACTERIADocument33 paginiBACTERIASchola De san joseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giardia: PROTOZOA Is A Group of Phyla That Comprises The Single-Celled Microscopic Animals, WhichDocument5 paginiGiardia: PROTOZOA Is A Group of Phyla That Comprises The Single-Celled Microscopic Animals, WhichAilah OtaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of PneumoniaDocument4 paginiDefinition of PneumoniaEmylia Ananda PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scarlet Fever: Caused by Group A StreptococciDocument24 paginiScarlet Fever: Caused by Group A StreptococciThomas GealonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument59 paginiHuman Health and Diseasesaryan aggarwal100% (1)
- Enteric Gram-Negative Rods (Enterobacteriaceae) : Prepared by Assistant Professor Dr. Khawaja Shakeel AhmedDocument26 paginiEnteric Gram-Negative Rods (Enterobacteriaceae) : Prepared by Assistant Professor Dr. Khawaja Shakeel AhmedZheemo ArshavinÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument2 paginiPneumoniaMargaret EricksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mapeh 9 DTDocument3 paginiMapeh 9 DTSantos JewelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung, Especially ofDocument14 paginiPneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung, Especially ofNar Patrick PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orDocument6 paginiPneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orOtrebron BatisanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Siti Suryatun Nikmah Class: Parkit NIM: AOA0160817 The Task of Improving English InfluenzaDocument3 paginiName: Siti Suryatun Nikmah Class: Parkit NIM: AOA0160817 The Task of Improving English InfluenzaAzulÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is LeptospirosisDocument18 paginiWhat Is LeptospirosisLuphly TaluvtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disease Uni 2Document20 paginiDisease Uni 2Aishwarya KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesDe la EverandThe Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!De la Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Viral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensDe la EverandViral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tropical AnemiaDocument315 paginiTropical AnemiaRajesh BholaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dengue Fever Case Pre WordDocument26 paginiDengue Fever Case Pre WordBjörn DaamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock Ospe (10 Q Questions) Me 211Document11 paginiMock Ospe (10 Q Questions) Me 211sahirbuleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health: Quarter 4 - Module 4A Prevention of Substance Use and AbuseDocument15 paginiHealth: Quarter 4 - Module 4A Prevention of Substance Use and AbuseJhun Mark100% (1)
- Metabolic Bone DisordersDocument24 paginiMetabolic Bone Disordersbpt20% (1)
- How To Get Hard and Stay Hard Longer NaturallyDocument2 paginiHow To Get Hard and Stay Hard Longer NaturallyRahul GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPC Marbonor 100 MLDocument6 paginiSPC Marbonor 100 MLJelena TerzicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Association Between Breastfeeding Patterns and Type 1 Diabetes Among ChildrenDocument6 paginiAssociation Between Breastfeeding Patterns and Type 1 Diabetes Among ChildrenHarun joel tatipataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Therapy AssignmentDocument4 paginiExercise Therapy AssignmentApoorvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credentialing and PrivilegingDocument113 paginiCredentialing and PrivilegingRobert Montuya100% (1)
- Breast Cancer Risks RecommendationsDocument2 paginiBreast Cancer Risks RecommendationsYohannes GirmawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Related Literature:Aloe Vera Gel As An Anti Blood CoagulantDocument8 paginiReview of Related Literature:Aloe Vera Gel As An Anti Blood CoagulantDanica Bondoc50% (2)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument49 paginiChronic Kidney Diseasesarguss1471% (7)
- Lipids Review QuestionsDocument10 paginiLipids Review QuestionsDavid TamayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- End of Report : Mr. Sumit GargDocument1 paginăEnd of Report : Mr. Sumit Gargsumit1234ggÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annotated Bibliography 3Document2 paginiAnnotated Bibliography 3api-486757147Încă nu există evaluări
- Blood VesselsDocument7 paginiBlood VesselsRohee TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Horizontal Guided Bone Regeneration On Knife Edge Ridges: A Retrospective Case-Control Pilot Study Comparing Two Surgical TechniquesDocument12 paginiHorizontal Guided Bone Regeneration On Knife Edge Ridges: A Retrospective Case-Control Pilot Study Comparing Two Surgical TechniquesFelix SchweppeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kode Pintar Icd 10Document25 paginiKode Pintar Icd 10Yusraa ZaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symmetry of Skin TemperatureDocument4 paginiSymmetry of Skin TemperaturepenfoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Manual For PubliC HealtH Dentistry and PraCtiCal reCorD Book PDFDocument322 paginiClinical Manual For PubliC HealtH Dentistry and PraCtiCal reCorD Book PDFSweet SumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstructed Labour (OL)Document34 paginiObstructed Labour (OL)ruhulcoc1Încă nu există evaluări
- IAU Logbook Core 6weeksDocument7 paginiIAU Logbook Core 6weeksbajariaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Physiology MCQsDocument24 paginiCardiovascular Physiology MCQsKlarens Affana63% (8)
- Vegad Pathology - PDFDocument602 paginiVegad Pathology - PDFSharafudheen KaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ophthalmology LastDocument28 paginiOphthalmology LastJamal Kadir100% (2)
- (S.C. Rastogi) Essentials of Animal Physiology, 4t (BookSee - Org) 250Document1 pagină(S.C. Rastogi) Essentials of Animal Physiology, 4t (BookSee - Org) 250Indah Rizka AprilianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument2 paginiCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interdisciplinary Treat Planning ChapterDocument56 paginiInterdisciplinary Treat Planning ChapterJulio César Huayllasco de la Cruz0% (1)
- The Thyroid Reset Diet 3 ChaptersDocument71 paginiThe Thyroid Reset Diet 3 ChaptersjovaneticÎncă nu există evaluări