Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Genitourinary Neoplasms
Încărcat de
GerardLumDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Genitourinary Neoplasms
Încărcat de
GerardLumDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
jslum.
com | Medicine
Genitourinary Neoplasms
Neoplasms of GUT Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
Kidney Bladder Penis Clear Cell Carcinoma, Hypernephroma, Grawitz Tumour
Benign (Rare) Malignant TCC SCC Arise from Tubular Epithelium
Should be Adult Children Occurs in Parenchyma of Kidney
considered Renal Cell Nephroblastoma Epidemiology
Malignant Carcinoma (Wilm’s Tumour ) Most common type of Re nal Cancer
(if can clinically 3% of Adult Malignancy
recognized) Male ↑
Rare – Age <35 y/o
Benign Kidney Tumours
Fibroma
Adenoma 2 Forms (Structural Alterations of Short Arm of Chromosome 3 – 3p)
Villous Papillary Tumour Hereditary Non-Here ditary
Angioma von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome VHL gene is mutated in ↑ %
Angiomyolipoma (RCC Develop in 40% VHL Disease)
Hereditary Papillary Renal
Carcinoma (HPRC)
Familial Renal Oncocytoma (FRO)
Hereditary Renal Carcinoma (HRC)
Risk Factors
Cigarette smoking (25-30% case directly attributable to smoking)
Chronic Haemodialysis
Prolonged Estrogen Administration
Tubular Adenoma (Kidney) (induce Kidney Tumours in Animals, Questionable in Humans)
Neoplastic Tubular Epithelium Phenacetin (contain Analgesics)
Adenoma (Kidney)
Well Circumscribed Tumour Exposure to Asbestos, Cadmium, Gasoline
Patients who develop Cystic Disease
Nephroblast oma (Wilm’s Tumour) Clinical Features
Constitute 25-30% of Childhood Cancer Intermittent Hematuria If Classical Traid
Peak age 2-4 y/o Clot Colic (Carcinoma has Metastasized)
Arise from Primitive Blastema Cells (that may persists in outer part of kidney) Dragging Loin Pain • Hematuria
Genetic – Deletion of Short Arm of Chromos ome 11 Palpable Renal Swelling • Pain
Hereditary Rapidly developing Vericocele (Male) • Palpable Renal Swelling
• All Bilateral Wilms Persistent Pyrexia, LOW, LOA
• 1/3rd of Unilateral Wilms Polycythemia
Clinical Features Hypercalcemia
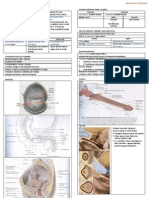
Large Abdominal Mass – unilateral or cross the midline when very large Renal Cell Carcinoma
Hematuria – Indicate Tumour has Burst into Renal Pelvis Occupies 1 Pole
Pain in Abdomen Well Circumscribed
Pyrexia Limited by Kidney Capsule
Pulmonary Metastasis
Wilms’ Tumour
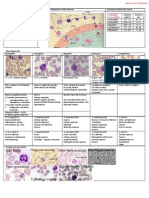
Large, Solitary, Well-circumscribed mass
Tumour
Soft, Homogenous, Tan → Gray, Foci of
Hemorrhage, Cystic Degeneration, Necrosis
Kidney – Adenocar cinoma Renal Cell Carcinoma
(Clear Cell Type) Large Uniform Cells
Cells in Solid Masses Abundant Glycogen
Occur in Acinar Arrangement
Stroma Scanty
Rich in Blood Vessels
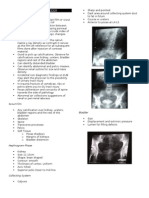
Staging for Diagnosis
Cystoscopy Computed Tomography (CT)
KUB Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Excretory Urogram (IVP) Renal Angiography
Wilm’s Tumour (Distortion of Calyces) Bone Scan
Nests, Sheets of Primitive Blastema Renal Ultrasound
Abortive Tubules Spread
Spindle Cell Stroma Local Distant
Abortive Glomeruli Medulla of Kidney Blood → Lungs, Bones, Brain, Liver
Striated muscles or other mesenchymal differentiation Renal Vein → IVC Lymphatics
Spread Perinephric Fat (Renal Capsule Bursts → Node s at
Blood (Early) → Lungs (common), Liver, Bone Kidney Hilum → Paraaortic Nodes)
Investigations
Principles of Treatment
AXR, U/S, CT Scan, Pyelography
Surgery (Radical Nephrectomy) – Localized Tumour, Renal Vein/ IVC Involved
Treatment
Radiation – Controversial
Immediate Nephrectomy, Postoperative Radiotherapy, Chemotherapy Chemotherapy – Ineffective
Prognosis Immunotherapy
90% Long Term Survival
• Lymphocyte Activated Killer (LAK) cells combine d with IL-2
• Alpha Antiferon
jslum.com | Medicine
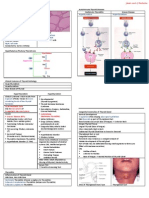
Bladder Carcinoma (Bladder Neoplasm) Carcinoma of Penis
Urothelial Origin (95%) Epidemiology
(eg. from Transitional Epithelium) Age 40-70 y/o
Common cancer in Malaysia Male Malignancies (10-20%) in Africa, Asia, South America
Benign counterpart – Rare Uncommon – Europe, US, Australasia
Villous Papilloma → Transitional Cell Carcinoma Circumcision Protective – Rare among Jews, Muslims
(TCC) (↓ likelihood of HPV infection due to circu mcision )
Causes
Villous Papilloma is similar to Papillary TCC except
Smoking-related Tumour
Thicker Epithelium
HPV Detectable in Cancer Cells (50% patients) – Types 16 > 18
↑ Numerous Mitoses
• ↓ common than in CIS (Bowen’s disease)
Epithelial cells Larger, more Deeply Stained
• HPV on its own cannot cause transformation
Villi Stunted – Closely Packed
Surface Ulcerate, Necrotic • Acts in concert with other carcinogenic influences (eg. Cigarette smoke)
Foci of Invasion/ Extension to Lymphatics Usually Arises on Glans or Inner Surface of Foreskin
Papillary or Flat – Papillary Lesions stimulate condylomata
Solid TCC – Raised plaque attaches to surface on broad base
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
TCC – Pathogenesis
Cigarette smokers (2-4X compared to non-s mokers)
↑ Risk if exposed to
• Azo dyes
• Pigments used in Textiles, Printing, Plastic, Rubber, Cable Industries
β-naphtylamine, 4-aminobiphenyl, 4-nitrobiphenyl, 4,4-diaminobiphenyl
L-Tryptophan metabolite
Cyclophospha mide
Schistoma Hematobium Infe ction
TCC – Clinical Features
Features
• Intermittent Painless Hematuria
• Urinary Tract Infection if Uretheral Orifice is involved
Staging
• 0 – Carcinoma in situ
• A – Invades Lamina Propria
• B – Involves Muscle
• C – Invades Perivesicle Region
Clinical
• D – Regional Metastasis Slow Growing, Locally Invasive
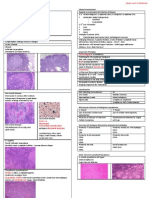
TCC – Macroscopy Often there for Years before presentation
Solid Type Papillary Type Classically Painless, unless Ulcerated/ Infected, Often Bleed
Early Nodal Spread (Inguinal/ Iliac), but Wide Dissemination uncommon
Prognosis (depend on Tu mour Stage)
Small Lesion, No Nodal Involvement 66% - 5 year Survival Rate
Nodal Involvement 27% - 5 year Survival Rate
Stage
T1 T2 T3 T4
Involve Infiltrate Infiltrate Full Muscle Fixed to
Subepithelial Muscle Thickness, Mobile Adjoining
Connective Tissue Organs
TCC – Histology
Transitional Cell Carcinomas (90%)
Squamous Cell Carcinomas (5%)
Adenocarcinomas (2%)
Classifications (WHO)\
Grade Growth Pattern
Low (Grade 1, 2) Papillary (70%)
High (Grade 3) Sessile, Pluque (20%)
Nodular (10%)
Microscopy
Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3
Management
Investigation Treatment
Urine Exfoliative Cystology Coagulative Diathermy (for small
Excretory Pyelography papillary lesion)
Cystoscopy (should be done on all Local DXT
cases of hematuria) Cystectomy
Biopsy
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument3 paginiSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDocument4 paginiPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDocument2 paginiPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Renal MCQ 2021Document27 paginiRenal MCQ 2021Shahriar Ahmed Sujoy100% (2)
- UROLOGYDocument222 paginiUROLOGYBeso DavitashviliÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThrombophiliaDocument3 paginiThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 paginiThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 paginiUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument3 paginiRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDocument2 paginiRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390Încă nu există evaluări
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 paginiSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 paginiPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument6 paginiSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 paginiPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 paginiProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 paginiPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 paginiOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDocument5 paginiPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDocument5 paginiPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 paginiPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Nsaids DrugsDocument2 paginiNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDocument4 paginiPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Leukocytes Benign DisordersDocument3 paginiLeukocytes Benign DisordersGerardLum100% (3)
- Nocturnal EnuresisDocument1 paginăNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymph Node PathologyDocument4 paginiLymph Node PathologyGerardLum0% (1)
- Myeloproliferative DisordersDocument2 paginiMyeloproliferative DisordersGerardLumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstructive UropathyDocument3 paginiObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Introduction To TransplantationDocument3 paginiIntroduction To TransplantationGerardLumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanism of MicturitionDocument4 paginiMechanism of MicturitionGerardLum100% (2)
- A Case Study of DIBH To Spare Abdominal Organs at Risk For Renal Cell Carcinoma MR-Guided RadiotherapyDocument14 paginiA Case Study of DIBH To Spare Abdominal Organs at Risk For Renal Cell Carcinoma MR-Guided Radiotherapyapi-525837437Încă nu există evaluări
- Kidney, Ureter, BladderDocument12 paginiKidney, Ureter, Bladdersarguss14100% (1)
- RENAL ScoreDocument5 paginiRENAL ScoreMurilo CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Cell Carcinoma Grand Case StudyDocument81 paginiRenal Cell Carcinoma Grand Case StudyAJIgama100% (1)
- Cystic Lesions of The Pituitary Clinicopathological Features Distinguishing Craniopharyngioma, Rathke - S Cleft Cyst, and Arachnoid Cyst, 1999Document11 paginiCystic Lesions of The Pituitary Clinicopathological Features Distinguishing Craniopharyngioma, Rathke - S Cleft Cyst, and Arachnoid Cyst, 1999CAMILO ARMANDO BENAVIDES BURBANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- CT KUB CN EditionDocument98 paginiCT KUB CN EditionphoenixibexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Ming Zhou and Huiying HeDocument20 paginiPathology of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Ming Zhou and Huiying Hesilvia hasibuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wilms Tumor Hank Baskin, MDDocument11 paginiWilms Tumor Hank Baskin, MDPraktekDokterMelatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mrcs UrologyDocument78 paginiMrcs UrologyAdebisiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney CancerDocument6 paginiKidney CancerAKHILÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaesthesia For Major Urological SurgeryDocument23 paginiAnaesthesia For Major Urological SurgeryDianita P Ñáñez VaronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intraperitoneal Vs RetroperitonealDocument36 paginiIntraperitoneal Vs RetroperitonealWahyudhy SajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney Cancer: By: Myra R. Abria & Karen HingadaDocument33 paginiKidney Cancer: By: Myra R. Abria & Karen Hingadamynoidanh19Încă nu există evaluări
- Medical Facts and MCQ'S - Urology MCQDocument15 paginiMedical Facts and MCQ'S - Urology MCQAhmed KassemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex-Clinton Twp. Trustee Dean Reynolds Lied About Cancer To Get Out of JailDocument12 paginiEx-Clinton Twp. Trustee Dean Reynolds Lied About Cancer To Get Out of JailDavid KomerÎncă nu există evaluări
- New England Journal Medicine: The ofDocument10 paginiNew England Journal Medicine: The ofmayracppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenvanix LenvatinibDocument1 paginăLenvanix Lenvatiniberfan alamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carcinoma KidneyDocument12 paginiCarcinoma KidneyFadhilla AnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidemiology and Factors Related To The Survival of Metastatic Kidney Cancers: Retrospective Study at The Mohamed VI Center For The Cancer Treatment in Casablanca, MoroccoDocument5 paginiEpidemiology and Factors Related To The Survival of Metastatic Kidney Cancers: Retrospective Study at The Mohamed VI Center For The Cancer Treatment in Casablanca, MoroccoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barry Thompson Book CHAPTER 8 Cantron - Extraordinary Antioxidant and Ingenious Cancer KillerDocument32 paginiBarry Thompson Book CHAPTER 8 Cantron - Extraordinary Antioxidant and Ingenious Cancer Killermonluck100% (2)
- Malignant Renal MassDocument42 paginiMalignant Renal MassZigmund Bryan CortezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIANDRA PARIKESIT Thrombus-Like - Tumor - of - Renal - Cell - Carcinoma - MimickDocument4 paginiDIANDRA PARIKESIT Thrombus-Like - Tumor - of - Renal - Cell - Carcinoma - MimickYulia DjatiwardaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology ProtocolsDocument33 paginiPathology ProtocolsLin AdutÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.MCQ Good PushDocument19 pagini3.MCQ Good Pushanderson ndabishakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Masses: Nick Tehrani, MDDocument77 paginiCardiac Masses: Nick Tehrani, MDNuha AL-YousfiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument9 paginiRenal Cell CarcinomaboianlinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal CancerDocument34 paginiRenal CancerArya100% (1)
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument3 paginiRenal Cell CarcinomaSenthil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări