Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Skema Latihan Haba
Încărcat de
fizikkopuDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Skema Latihan Haba
Încărcat de
fizikkopuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
1.
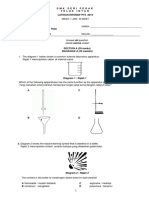
Diagram 1 shows an uncalibrated mercury thermometer placed in pure melting ice and steam to determine ice
point and steam point.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan sebatang termometer merkuri yang belum ditentukur dimasukkan ke dalam ais tulen yang
sedang melebur dan stim untuk menentukan takat ais dan takat stim.
Diagram 1 / Rajah 1
(a)
(b)
(c)
2.
State the working principle of the thermometer.
[1mark]
Principle of thermal equilibrium
Based on the Diagram 1:
Berdasarkan Rajah 1:
explain why the thermometer is placed in the steam above the boiling water instead of putting in
(i)
the boiling water?
[1mark]
0
To ensure the temperature of steam is at 100 C
determine the distance between the ice point and the steam point along the thermometer? [1mark]
(ii)
6.5cm
The mercury thermometer is then used to measure the temperature of liquid M. When the bulb of the
thermometer is immersed in liquid M, the length of the mercury column is 45 cm. Calculate the
temperature of liquid M.
[2marks]
= [(4.5 2.5) / 6.5] x 100 = 30.8 0C
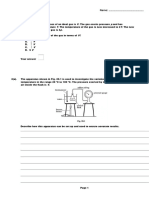
Diagram 2.1 shows a 800 W immersion heater being used to heat water of mass 300 g in a beaker which is on an
electronic balance. The initial temperature of water is 28 0C.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan suatu pemanas rendam 800 W yang digunakan untuk memanaskan air berjisim 300 g
dalam bikar yang berada di atas neraca elektronik. Suhu awal air adalah 280C.
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
Diagram 2.1 / Rajah 2.1
(a)
(b)
3.
State the transformation of energy involved while the water is heated with an immersion heater. [1 mark]
Electrical energy Heat energy
Calculate the heat energy absorbed by the water to reach its boiling point.
Hitung tenaga haba yang diserap oleh air itu untuk mencapai takat didih.
( Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 oC-1)
(Muatan haba tentu bagi air = 4200 J kg-1 oC-1)
[2marks]
0.3 x 4200 x (100-28)
90720J
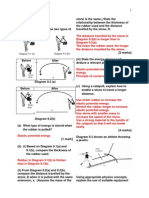
Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2 show two identical frying pan filled with cooking oil of different amount used to
fry an identical fish on a gas stove. The cooking oil has low specific heat capacity.
Rajah 3.1 dan Rajah 3.2 menunjukkan dua buah kuali yang serupa berisi minyak masak dalam kuantiti yang
berbeza digunakan untuk menggoreng seekor ikan yang serupa di atas sebuah dapur gas. Minyak masak itu
mempunyai muatan haba tentu yang rendah.
Diagram 3.1/Rajah 3.1
Diagram 3.2 / Rajah 3.2
After a few minutes, it was observed that the fish in Diagram 3.1 is scorched and the fish in Diagram 3.2 is wellcooked even though was fried under the same state of flame.
Selepas beberapa minit, dapat diperhatikan ikan dalam Rajah 3.1 hangus dan ikan dalam Rajah 3.2 masak
sempurna walaupun digoreng di bawah keadaan api yang sama
(a) What is the meaning of specific heat capacity?
[1mark]
Quantity of heat required by 1 kg of mass to increase the temperature by 1 0C
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
(b)
(c)
(d)
Using Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2, compare:
Menggunakan Rajah 3.1 dan Rajah 3.2, bandingkan:
(i)
The mass of the cooking oil used
[1mark]
Mass of cooking oil in Diagram 9.1 < Diagram 9.2 // vice- versa
(ii)
The quantity of heat supplied
[1mark]
Quantity of heat is equal / same
(iii)
The final temperature of the cooking oil
[1mark]
final temperature in Diagram 9.1 > Diagram 9.2
Relate the mass of the cooking oil with the state of fishes to deduce the relationship between mass and an
increase in temperature.
[2marks]
When mass of cooking oil is small, the fish is overcooked /scorched // vice-versa
When mass is small, increase in temperature is high // mass inversely proportional to
increase in temperature
Diagram 3.3 shows a boy at the sea shore.
Rajah 3.3 menunjukkan seorang budak lelaki berada di tepian pantai
Diagram 3.3 / Rajah 3.3
(e)
He feels the sea is cooler than land during the day but is warmer during the night. Explain why. [4marks]
During the day, the sea and the land receive the same amount of heat from the sun
Land heated to a high temperature because land has low specific heat capacity // vice-versa
During night, air above the land and sea release heat
Temperature of the sea decreases slowly because water has low specific heat capacity // vice
versa
Diagram 3.4 shows a car engine radiator.
Rajah 3.4 menunjukkan satu radiator enjin kereta.
Diagram 3.4 / Rajah 3.4
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
You are required to design a car engine radiator which can function effectively, based on the following
aspects:
Anda ditugaskan untuk mereka bentuk sebuah radiator enjin kereta yang dapat berfungsi dengan
berkesan, berdasarkan aspek-aspek berikut:
[10marks]
Aspect
Explanation
Size of fan big
More wind to blow to cool the hot water faster
Number of fins many
Can cool the engine faster
Cooling liquid is water
High specific heat capacity // high boiling point
//cheap //easily available //does not react with the
inner part of engine
Liquid that has high specific heat capacity
Transfer large quantity of heat with small increase
in temperature
Liquid of high boiling point
Not easy to vapor when absorb heat from the
engine
4.
Diagram 4 shows a doctor used a thermometer to measure the body temperature of a girl.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan seorang doktor menggunakan sebuh termometer untuk mengukur suhu badan seorang
budak perempuan.
Diagram 4 / Rajah 4
(a)
(b)
(c)
What is the meaning of temperature?
[2 marks]
Degree of hotness
Explain in terms of thermal equilibrium, how the thermometer reads the body temperature of the girl.
[4 marks]
The thermometer is put under the tongue
The heat is transferred from the body to the thermometer
Mercury expand until it reaches a state of thermal equilibrium
The temperature of the thermometer is the same as the body.
Table 4 shows the characteristics of five termometers, A, B, C and D.
Jadual 4 menunjukkan ciri-ciri empat termometer, A, B, C dan D.
Thermometer
Liquid used
Glass walled
Diameter capillary
Termometer
Cecair yang
bulb
tube
digunakan
Dinding bebuli
Diameter tiub kapilari
kaca
A
Mercury
Thin
Big
Merkuri
Nipis
Besar
B
Alcohol
Thick
Small
Glass-bore stem and
cross section
Lubang batang kaca
dan keratas rentas
Thick and curved
Tebal dan melengkung
Thin and plane
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
Alkohol
C
Mercury
Merkuri
D
Alcohol
Alkohol
Aspect
Liquid used is mercury
(d)
Tebal
Thin
Nipis
Thick
Tebal
Kecil
Small
Kecil
Big
Besar
Nipis dan satah
Thick and curved
Tebal dan melengkung
Thin and plane
Nipis dan satah
Explanation
Expands uniformly // sensitive to changes in
temperature
More sensitive to heat
Get a wider range // more sensitive to heat
Not easily to break // easy to read
Thin glass walled bulb
Small diameter of capillary tube
Glass-bore stem and cross section: thick and
curved
C
Mercury, thin, small and thick and curved
A thermometer which is not calibrated has a mercury column of length 5.0 cm. When the temperature is
00C and 25.0 cm when the temperature is 1000 C. The mercury column is 12.0 cm when put in liquid X.
Sebuah termometer yang belum ditentukurkan mempunyai panjang turus 5.0 cm apabila suhu adalah 0 0 C
dan 25.0 cm apabila suhu adalah 1000 C. Turus merkuri adalah 12.0 cm apabila diletakkan ke dalam
cecair X.
(i)
Determine the temperature of liquid X.
( l -l0) x 100
( l100 - l0)
[3 marks]
( 12 - 5 ) x 100
( 25 - 5 )
(ii)
(iii)
= 35 0C
Determine the temperature of liquid X in Kelvin
( 273 + 35 ) K = 308K
State a thermometric property used when making of a thermometer.
Volume expand with temperature
[1 mark]
[1 mark]
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
Latihan Keseimbangan Terma dan Muatan Haba Tentu Haba
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Advanced Taxation Tutorial 4Document15 paginiAdvanced Taxation Tutorial 4kk k100% (1)
- English - (UASA) F3 - ENGLISH MODEL 1 - 2023Document11 paginiEnglish - (UASA) F3 - ENGLISH MODEL 1 - 2023MIZA BATRISYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crude Oil Emulsions - Petroleum Engineers Handbook PDFDocument34 paginiCrude Oil Emulsions - Petroleum Engineers Handbook PDFMichael Grayson100% (3)
- Quick Notes Form 2 (Science)Document11 paginiQuick Notes Form 2 (Science)FishGlobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ambank GroupDocument8 paginiAmbank Groupainhamzah22Încă nu există evaluări
- Form 2: Heir ConditioningDocument36 paginiForm 2: Heir ConditioningSafwan Salleh100% (1)
- Effect of Different Quantities of Water Intake On Urine OutputDocument2 paginiEffect of Different Quantities of Water Intake On Urine OutputJin Ming50% (2)
- English SPM Module 1Document18 paginiEnglish SPM Module 1Mohd Yusoff TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Percubaan SPM 2023Document20 paginiPercubaan SPM 2023KALAI SELVI A/P CHENDERAN MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Going Green MalaysiaDocument7 paginiGoing Green MalaysiaezlynxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guideline On Answering Questions in Chemistry Paper 3Document4 paginiGuideline On Answering Questions in Chemistry Paper 3pkrajenpillaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skema Fizik Kertas 2Document8 paginiSkema Fizik Kertas 2hakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM 2022 Chemistry Paper3 Kerja AmaliDocument28 paginiSPM 2022 Chemistry Paper3 Kerja Amali22 LEE KE YIN 李科莹Încă nu există evaluări
- Peka Report Experiment 4.8 Effects of Acid and Alkali On LatexDocument2 paginiPeka Report Experiment 4.8 Effects of Acid and Alkali On LatexHOOI PHING CHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Tips For PT3 English ListeningDocument3 pagini6 Tips For PT3 English ListeningdeasaadiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Note Chemistry Forn 5-Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument16 paginiShort Note Chemistry Forn 5-Chapter 2 Carbon Compoundssalamah_sabri100% (10)
- Pentaksiran Tingkatan Dua: Bahasa Inggeris Pemahaman 1 Jam 15 MinitDocument16 paginiPentaksiran Tingkatan Dua: Bahasa Inggeris Pemahaman 1 Jam 15 MinitNur Hafeza100% (1)
- F3 Poem - Poisoned TalkDocument28 paginiF3 Poem - Poisoned TalkErica8899100% (1)
- React 2.0 Module JPN PerakDocument166 paginiReact 2.0 Module JPN PerakKureen FreddieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematic Form 2 APRIL 2019 Pre-Mid Year ExaminationDocument10 paginiMathematic Form 2 APRIL 2019 Pre-Mid Year ExaminationNurhashimahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 294 Latihan Intensif PT3 2019 Sains PDFDocument23 pagini294 Latihan Intensif PT3 2019 Sains PDFNorulfarrah binti Jaafar Teb3092Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Peka Sains SPMDocument15 paginiSample Peka Sains SPMNor Azizah100% (1)
- (Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Document12 pagini(Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Aizzat BahiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of Salt EssayDocument2 paginiPreparation of Salt EssayzhuzaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkaliDocument38 paginiScience Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkalinurafziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 2 Chapter 6 Air PressureDocument6 paginiForm 2 Chapter 6 Air Pressurelccjane8504Încă nu există evaluări
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Document6 paginiIT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Titim MohdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument10 paginiAcids, Bases and Saltsshehryar khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRSM-Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009Document36 paginiMRSM-Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Investigating Sustainable Practices in The Malaysian Office Building DevelopmentsDocument21 paginiInvestigating Sustainable Practices in The Malaysian Office Building Developmentscrystal1991Încă nu există evaluări
- Borang Rekod Transit Tingkatan 1Document43 paginiBorang Rekod Transit Tingkatan 1Halizah RamthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry SPMDocument20 paginiChemistry SPMJacob ChowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kertas Model PT3 PDFDocument16 paginiKertas Model PT3 PDFAnonymous hSFsADEFK0% (1)
- Ethnic Composition of The Malaysian PopulationDocument74 paginiEthnic Composition of The Malaysian PopulationNoorasmad Mat RipinÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT Chem F4 Topical Test 2 (BL)Document8 paginiIT Chem F4 Topical Test 2 (BL)NORAZIAH AHMAD ZULKIPLIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Practical Operational Definition Form 4 & 5Document1 paginăChemistry Practical Operational Definition Form 4 & 5Danny VoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE CHAPTER 7 Form 3Document21 paginiMODULE CHAPTER 7 Form 3Nurul Shafiah Mustafa KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT3 Essay 2 (MasterVocab)Document18 paginiPT3 Essay 2 (MasterVocab)nasirah shamshulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physic Lab Report 5Document2 paginiPhysic Lab Report 5Salazar ZawawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Kimia Tingkatan 4,5 - Paper3 - 20170420112820Document4 paginiSPM Kimia Tingkatan 4,5 - Paper3 - 20170420112820nurzatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 5: Food Technology and ProductionDocument2 paginiScience Form 5: Food Technology and Productionwaris636756360% (1)
- Complete Debate Transcript of Grandfinal of WSDC 2023 Between Usa VS CanadaDocument31 paginiComplete Debate Transcript of Grandfinal of WSDC 2023 Between Usa VS CanadaAdimarta TeguhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logistics in MalaysiaDocument11 paginiLogistics in MalaysiaVishyataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Folio Form 5 VariationDocument12 paginiBiology Folio Form 5 VariationSentoash NaiduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Pt3Document30 paginiModel Pt3Sean Larson100% (4)
- Skema Paper 2 ChemDocument11 paginiSkema Paper 2 ChemFarah Shafiqah AmiruddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peka Sains Form 5Document3 paginiPeka Sains Form 5quraisahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Averaging Strategy and DebtDocument5 paginiAveraging Strategy and DebtJiah Mohd DaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- F2 Science Chapter Summary Form 2Document12 paginiF2 Science Chapter Summary Form 2Cerdik CekapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics HOTS KBAT QuestionsDocument29 paginiPhysics HOTS KBAT QuestionsNoor95% (21)
- SkemaDocument7 paginiSkemafizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bonus Session Thermometers and SP Heat CapDocument10 paginiBonus Session Thermometers and SP Heat CapTimothy SeyaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- E302: Heat and CalorimetryDocument5 paginiE302: Heat and CalorimetryPJ BundalianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Capacity 3: Questions: Q1Document3 paginiHeat Capacity 3: Questions: Q1heheheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics HOTS KBAT QuestionsDocument29 paginiPhysics HOTS KBAT QuestionskwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2 Section B and C Sample QuestionsDocument30 paginiPaper 2 Section B and C Sample Questionscikgusuriyati100% (4)
- Phys 161Document5 paginiPhys 161Collins BichiyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik SPM 2016Document59 paginiBengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik SPM 2016Suriyati Yusoff100% (2)
- Soalan Heat 2 QualitiDocument10 paginiSoalan Heat 2 QualitiShahrir DoralimÎncă nu există evaluări
- W37 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat CapacityDocument12 paginiW37 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat CapacityBiid HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- OCR Gas Laws Revision Questions & MSDocument29 paginiOCR Gas Laws Revision Questions & MS17guoxiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radioactive Table PDFDocument4 paginiRadioactive Table PDFfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fizik Tingkatan 5Document56 paginiFizik Tingkatan 5Sakinah Ridzuan0% (1)
- EnergyDocument4 paginiEnergyfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radioactive Table PDFDocument4 paginiRadioactive Table PDFfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trial SPM Melaka 2014 - SoalanDocument72 paginiTrial SPM Melaka 2014 - SoalanfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- SkemaDocument7 paginiSkemafizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 1Document8 paginiScience Form 1Kathija BanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add MathDocument5 paginiAdd MathfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huraian Sukatan Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Document57 paginiHuraian Sukatan Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Nadiah RaffiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Linear MotionDocument27 pagini2.1 Linear MotionkhodijahaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Motion GraphsDocument20 pagini2.2 Motion GraphsfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic StructureDocument71 paginiAtomic StructureGowri ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analogy RLC en Mass Spring Dash PotDocument26 paginiAnalogy RLC en Mass Spring Dash Potjef_aernoutsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 004-The Stability of A Floating BodyDocument10 pagini004-The Stability of A Floating BodyHafizah Fadil100% (1)
- 101 Things You Don't Know About Science and No One Else Does Either PDFDocument388 pagini101 Things You Don't Know About Science and No One Else Does Either PDFSubramanya ByndoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetism SC L4-5Document12 paginiMagnetism SC L4-5Abhishek tiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Design MethodDocument19 paginiMagnetic Design MethodKataria GauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: K. Mahesh Associate Professor BVFRIT NarsapurDocument75 paginiPresented By: K. Mahesh Associate Professor BVFRIT NarsapurmaheshÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Gate 2001: 2 Marks) Ans. (D) Since The Diode Is Forward Biased, It Is Taken As Short Circuit. Writing KCLDocument3 pagini(Gate 2001: 2 Marks) Ans. (D) Since The Diode Is Forward Biased, It Is Taken As Short Circuit. Writing KCLSiva GuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- NDT Composite ComponentsDocument37 paginiNDT Composite ComponentsNarendra Palande100% (1)
- AAN036e Paints and CoatingsDocument6 paginiAAN036e Paints and CoatingsEyad AlsheiikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rock Mechanics AssignmentDocument8 paginiRock Mechanics AssignmentYibeltal FekaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decoherence-Free Entropic Gravity For Dirac FermionDocument23 paginiDecoherence-Free Entropic Gravity For Dirac Fermionubik59Încă nu există evaluări
- CLC Clear: %% Inputs %modulus of Elasticity (Gpa)Document5 paginiCLC Clear: %% Inputs %modulus of Elasticity (Gpa)Alaa MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 9: March 24, 2011Document4 paginiTutorial 9: March 24, 2011Overloaded SenseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illustrative Example: A Blending Process: An Unsteady-State Mass Balance For The Blending SystemDocument22 paginiIllustrative Example: A Blending Process: An Unsteady-State Mass Balance For The Blending SystemHermes Yesser Pantoja CarhuavilcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fender Analysis PDFDocument242 paginiFender Analysis PDFjay climacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument57 paginiStatics of Rigid BodiesAnna Louise WyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Statcom For Voltage Improvement in An Electric Power NetworkDocument14 paginiSimulation of Statcom For Voltage Improvement in An Electric Power NetworkOladeji Ifedayo RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard and Actual Vapor Compression CycleDocument19 paginiStandard and Actual Vapor Compression CycleJB LabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis: Symmetrical Components, Unbalanced Fault AnalysisDocument28 paginiPower System Analysis: Symmetrical Components, Unbalanced Fault Analysisسلطان العتيبيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sri Lanka Institute of Information Technology: Faculty of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument9 paginiSri Lanka Institute of Information Technology: Faculty of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringMuthuPabasaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter: Quantum Annealing With Manufactured SpinsDocument5 paginiLetter: Quantum Annealing With Manufactured SpinsnhdalkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 267: Advanced Thermodynamics I: Thermodynamic RelationsDocument73 paginiME 267: Advanced Thermodynamics I: Thermodynamic Relationsluzviminda ramosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermistor 50KDocument2 paginiThermistor 50Kfredjbps@gmail.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Quartz Crystals PDFDocument6 paginiUnderstanding Quartz Crystals PDFRAVINDERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework Electron ConfigurationDocument3 paginiHomework Electron ConfigurationRoman AchkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch04 PDFDocument4 paginich04 PDFAnderson Gomez CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment:02 Aim: Analysis of Time Response of Series RLC Circuit Using State Space Approach SOFTWARE: Scilab 5.2.2 TheoryDocument4 paginiExperiment:02 Aim: Analysis of Time Response of Series RLC Circuit Using State Space Approach SOFTWARE: Scilab 5.2.2 Theoryashishkhot5rÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 - SIM DN150 PN160 Valve 2 PDFDocument4 pagini02 - SIM DN150 PN160 Valve 2 PDFunnicyriacÎncă nu există evaluări