Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Skema
Încărcat de
fizikkopuDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Skema
Încărcat de
fizikkopuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Latihan Muatan Haba Pelakuran
Haba
1.
Diagram 1.1 and Diagram 1.2 shows a set-up of apparatus to determine the specific latent heat of
fusion of ice.
Rajah 1.1 dan Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan susunan radas untuk menentukan haba pendam tentu
pelakuran bagi ais.
Experiment set up
control set up
Radas eksperimen
Radas kawalan
Diagram 1.1 / Rajah 1.1
When the power supply is switched on, water will dripped out of the filter funnels. As soon as the
dripping is at a constant rate, beaker A and beaker B are placed underneath the filter funnels and
stopwatch is started simultaneously.
Apabila bekalan kuasa dihidupkan, air akan menitis dari corong turas. Sebaik sahaja titisan pada
kadar seragam, bikar A dan bikar B diletakkan di bawah corong turas dan jam randik dimulakan
serentak.
(a) What is the meaning of specific latent heat of fusion?
(b)
Heat absorbed to change 1kg of solid to liquid without any change of temperature[1 mark]
What is the purpose of having a control set-up?
To determine the mass of water collected due to the melting of ice at room temperature
(c)
[1 mark]
After 5 minutes, the mass of water collected in beaker A and B are measured.
Selepas 5 minit, jisim air yang dikumpulkan dalam bikar A dan B itu disukat.
Table 1 shows the data collected from the experiment.
Jadual 1 menunjukkan data yang diperolehi daripada eksperimen tersebut.
Latihan Muatan Haba Pelakuran
Haba
Mass of water collected in beaker A, / g
112
Jisim air yang dikumpulkan dalam bikar A, / g
Mass of water collected in beaker B, / g
12
Jisim air yang dikumpulkan dalam bikar B, / g
Amount of heat supplied, Q / kJ
50
(c)
Jumlah haba dibekalkan, Q / kJ
What is the mass of ice melted by the energy supplied by the power supply?
(d)
100g
Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of the ice.
[1mark]
[2
(e)
(f)
marks]
Give a reason why the value in 1(c) is higher than the actual value.
Heat loss to surrounding
[1mark]
Suggest one way to get a more accurate value.
The heater must be fully immersed in ice
2.
[1 mark]
Diagram 2.1 shows two beaker A and B containing water at 0OC, with beaker A containing some
pieces of ice.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan dua buah bikar A dan B yang berisi air pada 0OC, dengan bikar A
mengandungi beberapa ketul ais.
Diagram 2.1 / Rajah 2.1
diagram 2.2 / Rajah 2.2
Latihan Muatan Haba Pelakuran
Haba
Diagram 2.2 shows the temperature of the water in beaker A and beaker B after 10 minutes.
Rajah 2.2 menunjukkan suhu bagi air dalam bikar A dan bikar B selepas 10 minit.
(a) What is the meaning of temperature?
Degree of hotnesss
(b)
(i)
Name the physical quantity involved in the melting of the ice.
Latent heat of fusion
(ii)
[1mark]
[1mark]
Using the kinetic theory of matter:
Dengan menggunakan teori kinetic jirim:
Explain why the temperature of the water in beaker A remains constant at 0OC.
Heat is used to break the bonds between ice molecules // weaken the force
of attraction between molecules
Kinetic energy of the ice molecules remains unchanged.
Explain why the temperature of the water in beaker B has risen.
Heat is used to increase the kinetic energy of the water molecules
(c)
Temperature depends on kinetic energy
[4 marks]
Relate the temperature increase of a substance to its specific heat capacity. Use this
relationship toexplain why a piece of iron becomes hotter than a piece of wood of the same
mass when both absorb the same amount of heat.
Substance with higher heat capacity requires more heat to change the temperature of
1OC.
the higher the specific heat capacity, the smaller the temperature change
specific heat capacity of wood is higher / vice versa
if the amount of heat absorb is the same, the change in temperature for wood is smaller /
(d)
vice versa
Diagram 2.3 shows food being fried in a wok of cooking oil.
[4 marks]
Rajah 2.3 menunjukkan makanan digoreng dalam sebuah kuali yang mengandungi minyak
masak.
Latihan Muatan Haba Pelakuran
Haba
Diagram 2.3 / Rajah 2.3
Suggest and explain how the food to be fried can be cooked in a short time based on the
following aspect of the material of the wok and the cooking oil.
Cadang dan terangkan bagaimana makanan yang digoreng boleh menjadi masak dalam masa
yang singkat berdasarkan aspek-aspek berikut mengenai bahan kuali dan minyak masak.
Material of the wok
Bahan kuali:
(i) Specific heat capacity /Muatan haba tentunya
Low reason: can heat up faster / temperature increase faster
(ii) Thermal conductivity /Kekonduksian termanya
High reason: can conduct heat faster
(iii) Melting point / Takat leburnya
High reason: can withstand high temperature
3.
Cooking oil :
Minyak masak :
(iv) Specific heat capacity / Muatan haba tentunya
Low reason: heat up faster
(v) Boiling point / Takat didihnya
High reason: it will not change to vapour easily.
[10 marks ]
As many people strive to live a healthier lifestyle and eat a healthier diet, many new diets call for
steamed vegetables. The easiest method for cooking food in this way is to use a food steamer.
Diagram 3.1 shows an electric food steamer.
Semakin ramai orang berusaha untuk mengamalkan gaya hidup dan cara pemakanan yang sihat.
Oleh itu, mengukus ialah cara memasak yang semakin digemari. Cara paling mudah untuk mengukus
makanan adalah dengan menggunakan pengukus makanan. Rajah 3.1 menunjukkan sebuah
pengukus makanan elektrik.
Lower level containing water
Tingkat bawah yang mengandungi
air
Diagram 3.1 / Rajah 3.1
Latihan Muatan Haba Pelakuran
Haba
(a)
(i)
What is the meaning of specific latent heat of vaporisation?
(ii)
Amount of heat required to boil one unit mass of liquid to gas at its boiling point,
without change in temperature
[1 mark]
Explain how food is cooked by the food steamer in Diagram 3.1 in terms of the transfer of
heat.
(b)
(i)
Heat from the heater transfers to the water
Water changes to steam
Steam condenses on food
Steam transfers high latent heat to food
[4 marks]
Sharon poured 0.50 kg of water at room temperature in the lower compartment of the
steamer. Find the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of the water to 100
C. [Specific heat capacity of water, c = 4200 J kg1OC1, room temperature = 25 C]
(ii)
E = (0.50)(4200)(100-25)
= 157 500 J
The food in the steamer needs 4.5 105 J of heat to be steamed.
[2 marks]
Calculate the mass of water that was converted to steam during the steaming of the food.
[Specific latent heat of vaporisation of water, l = 2.3 106 J kg1]
[2
(iii)
marks]
State one assumption that you have made in 3(b) (i).
No heat loss to the surrounding
(c)
[1 mark]
Diagram 3.2 shows a cooler bag which can be used to keep food cool or warm.
Rajah 3.2 menunjukkan sebuah beg sejuk yang boleh digunakan untuk mengekalkan kesejukan
atau kepanasan makanan.
Inner lining
Pelapik dalam
Diagram 3.2 / Rajah 3.2
Latihan Muatan Haba Pelakuran
Haba
Table 11 shows the characteristics of four different cooler bags.
Jadual 11 menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi empat beg sejuk yang berlainan.
Cooler bag
Thermal
Specific heat
Density of the
Material of the
Beg sejuk
conductivity of
capacity
bag
inner lining
the bag
of the bag / J kg-
Ketumpatan beg
Bahan
Kekonduksian
1 C-1
terma beg
Muatan haba
pelapik dalam
tentu
P
Low
beg / J kg-1 C-1
900
Rendah
Low
Aluminium foil
Rendah
Kerajang
High
900
High
aluminium
Plastic
Tinggi
High
387
Tinggi
Low
Plastik
Plastic
Tinggi
Low
387
Rendah
Low
Plastik
Aluminium foil
Rendah
Kerajang
Rendah
aluminium
Table 3 / Jadual 3
Low
As heat insulator// prevent heat loss/ heat gain
Low
Absorbs less heat from the food // Lower final temperature
Low
Light
Aluminium foil
Reflects heat back to the food// help transfer escaped heat back to the food// contains the
heat within the cooler bag as long as it remains closed// Metallic material
S
cooler bag with low thermal conductivity, low specific heat capacity,
low density, aluminium foil as inner lining
[10 marks]
Latihan Muatan Haba Pelakuran
Haba
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Phy S1 Heat (Fixed Version)Document12 paginiPhy S1 Heat (Fixed Version)Holdon ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skema Latihan HabaDocument10 paginiSkema Latihan HabafizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal GuideDocument34 paginiThermal GuideMazinÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY VIII P2 BEFORE MID 2nd SemsDocument10 paginiPHY VIII P2 BEFORE MID 2nd SemsShahidul Hassan MontiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 21 PDFDocument3 paginiWorksheet 21 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- DSE Physics Past DSE Questions - HeatDocument29 paginiDSE Physics Past DSE Questions - HeatTsz Wun CHOWÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soalan Heat 2 QualitiDocument10 paginiSoalan Heat 2 QualitiShahrir DoralimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Properties of WaterDocument4 paginiPhysical Properties of WaterLuk Ee RenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phyf4 Chap4Document71 paginiPhyf4 Chap4Mohd AzlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter4 Enrichment (Answer)Document5 paginiChapter4 Enrichment (Answer)Siti Arbaiyah AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 4.3Document3 paginiExercise 4.3Anonymous w7ujq3cH2FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument71 paginiChapter 4 HeatYusfalina Mohd YusoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Exercise 16 AugDocument4 paginiHeat Exercise 16 AugAngie Kong Su MeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 0heat 130415001626 Phpapp01Document14 pagini4 0heat 130415001626 Phpapp01sherlyn may lolÎncă nu există evaluări
- CalorimetryDocument5 paginiCalorimetryVenu GopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bonus Session Thermometers and SP Heat CapDocument10 paginiBonus Session Thermometers and SP Heat CapTimothy SeyaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- E302: Heat and CalorimetryDocument5 paginiE302: Heat and CalorimetryPJ BundalianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Measurements PPQDocument4 paginiThermal Measurements PPQMichael Harrichandsingh100% (1)
- L. The Set-Up Is Shown in The Following Figure.: GlassDocument4 paginiL. The Set-Up Is Shown in The Following Figure.: GlassHanis ZafriÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADocument20 paginiAShu85Încă nu există evaluări
- Specific Heat CapacityDocument7 paginiSpecific Heat Capacitykeeesh4100% (1)
- 2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Document4 pagini2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Raistlin Chan Ching KitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 21Document3 paginiWorksheet 21Dariya IsmagilovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM 2021 Heat QuestionsDocument9 paginiSPM 2021 Heat QuestionskokseemailÎncă nu există evaluări
- What We Have Already LearntDocument13 paginiWhat We Have Already Learnt'Shyam SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 3Document6 paginiCh. 3Sandy ShohdyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic: (Chapter 4) HEAT: (4.2) Specific Heat Capacity Highlight: (30 Minutes)Document7 paginiTopic: (Chapter 4) HEAT: (4.2) Specific Heat Capacity Highlight: (30 Minutes)RusnizaARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Capacity and Latent Heat QuestionsDocument2 paginiHeat Capacity and Latent Heat QuestionstuvvacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Capacity 3: Questions: Q1Document3 paginiHeat Capacity 3: Questions: Q1heheheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Properties of Matter: ExperimentDocument4 paginiPhysical Properties of Matter: Experimentch chÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS IX 4th Sem AftermidDocument12 paginiPHYSICS IX 4th Sem AftermidShahidul Hassan MontiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 4 Chapter 4: Heat: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocument10 paginiForm 4 Chapter 4: Heat: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumbatrisyiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics HOTS KBAT QuestionsDocument29 paginiPhysics HOTS KBAT QuestionsNoor95% (21)
- W37 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat CapacityDocument12 paginiW37 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat CapacityBiid HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRADE 11 D AssignmentDocument4 paginiGRADE 11 D AssignmentPaul MunsakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dps Sts Schol: Explanetion - Ioskttsy.Nstsisal..W:M..Slst..The..Block... Snd..Esna. Hect - Jles...Document17 paginiDps Sts Schol: Explanetion - Ioskttsy.Nstsisal..W:M..Slst..The..Block... Snd..Esna. Hect - Jles...Why is LivingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specific and Latent Heat MsDocument6 paginiSpecific and Latent Heat MsDeepika DevarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.0 Title of Experiment: DKK2771 Chemical Reaction Engineering LaboratoryDocument9 pagini1.0 Title of Experiment: DKK2771 Chemical Reaction Engineering LaboratoryFarah -HÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW1 Solutions ME321Document2 paginiHW1 Solutions ME321R02Încă nu există evaluări
- Grade 11 First Six Weeks TestDocument7 paginiGrade 11 First Six Weeks TestTanieka PowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 - May 2023 - 065328Document1 paginăAssignment 2 - May 2023 - 065328lawrence munya jarichaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Exercise 5Document26 paginiPhysics Exercise 5Law Jing SeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.0 Title of Experiment: BKF2741 Chemical Reaction Engineering Laboratory IDocument9 pagini1.0 Title of Experiment: BKF2741 Chemical Reaction Engineering Laboratory IWeng KhimÎncă nu există evaluări
- X Physics emDocument116 paginiX Physics emPhani KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quest 6-Additional ExerciseDocument7 paginiQuest 6-Additional Exercisebimbel onlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiling PointDocument3 paginiBoiling PointaeneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeDocument11 paginiName: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeChrise RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal Cup With Cotton Wool Layer: Table ADocument2 paginiMetal Cup With Cotton Wool Layer: Table AhahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Markscheme SL Paper2Document41 pagini3 Markscheme SL Paper2maddiemads562Încă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Specific Latent HeatDocument8 paginiUnderstanding Specific Latent HeatNoraidah Harun100% (1)
- Temperature and HeatingDocument4 paginiTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 2 TheoryDocument6 paginiPart 2 TheoryGiorgioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Sec B (Thermal Physics and The Kinetic Theory) - Graded WorksheetDocument5 paginiPhysics - Sec B (Thermal Physics and The Kinetic Theory) - Graded Worksheetjonroman795Încă nu există evaluări
- RevisionWsheet 5054 ThermalPropertiesofMatterDocument4 paginiRevisionWsheet 5054 ThermalPropertiesofMatterHem HemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geothermal Energy: Sustainable Heating and Cooling Using the GroundDe la EverandGeothermal Energy: Sustainable Heating and Cooling Using the GroundÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Intensification for Sustainable Energy ConversionDe la EverandProcess Intensification for Sustainable Energy ConversionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fizik Tingkatan 5Document56 paginiFizik Tingkatan 5Sakinah Ridzuan0% (1)
- Radioactive Table PDFDocument4 paginiRadioactive Table PDFfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radioactive Table PDFDocument4 paginiRadioactive Table PDFfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnergyDocument4 paginiEnergyfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trial SPM Melaka 2014 - SoalanDocument72 paginiTrial SPM Melaka 2014 - SoalanfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huraian Sukatan Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Document57 paginiHuraian Sukatan Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Nadiah RaffiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 1Document8 paginiScience Form 1Kathija BanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add MathDocument5 paginiAdd MathfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
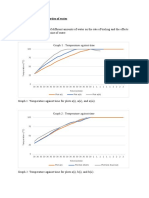
- 2.2 Motion GraphsDocument20 pagini2.2 Motion GraphsfizikkopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Linear MotionDocument27 pagini2.1 Linear MotionkhodijahaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jelovnik / MenuDocument15 paginiJelovnik / MenuervinpoljakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roohafza 150420234337 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument27 paginiRoohafza 150420234337 Conversion Gate02 PDFKhubaib ImtiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pippa and Pop Pippa and Pop Teacher Book 1 U5 9781108928298 Sample ContentDocument27 paginiPippa and Pop Pippa and Pop Teacher Book 1 U5 9781108928298 Sample ContentMelissa ParedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Do You Need NattoDocument13 paginiWhy Do You Need NattoGwyneth100% (1)
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W9Document2 paginiDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W9Rucelle Mae Fernandez ArbolerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethnic Culture of The Khasia and Mendi: Prof. Dr. Ashit Boran PaulDocument17 paginiEthnic Culture of The Khasia and Mendi: Prof. Dr. Ashit Boran PaulWorld's GalleryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homemade Choco Tacos - A Cozy KitchenDocument3 paginiHomemade Choco Tacos - A Cozy KitchenWDIV/ClickOnDetroitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2 Assignment: Cnidaria and Porifera BIOL 2P92 - 09 Romil Patel (5844196) TA: Fiona Tuesday, January 24, 2017Document8 paginiLab 2 Assignment: Cnidaria and Porifera BIOL 2P92 - 09 Romil Patel (5844196) TA: Fiona Tuesday, January 24, 2017RomilPatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises For Passive VoiceDocument6 paginiExercises For Passive VoicechondrokoukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upt Laboratorium Lingkungan BantenDocument2 paginiUpt Laboratorium Lingkungan BantenPandeglang laboratoriumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hussain Kapadawala 1Document56 paginiHussain Kapadawala 1hussainkapda7276Încă nu există evaluări
- OIV Annual Assessment-2023Document30 paginiOIV Annual Assessment-2023fanghao19980816Încă nu există evaluări
- Tanay Rizal Day Tour Itinerary and Tips - Tara Lets AnywhereDocument1 paginăTanay Rizal Day Tour Itinerary and Tips - Tara Lets AnywhereShiela Marie MalanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Owner's Manual: Microwave Oven Household Use Only Model NoDocument22 paginiOwner's Manual: Microwave Oven Household Use Only Model NoAlfonso CalderonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUNGGODocument17 paginiMUNGGOJenny Joy B. Fortin100% (2)
- ResepDocument58 paginiResepErwin R. PrasajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travefy Free Itinerary TemplateDocument5 paginiTravefy Free Itinerary TemplateAman kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pis D10Document2 paginiPis D10Mohammed AyazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplified Keys To Soil Series PampangaDocument29 paginiSimplified Keys To Soil Series Pampangaa24gianÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Alcohol DistillationDocument3 paginiHistory of Alcohol DistillationLester MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Perception and Distribution Chanel of HulDocument76 paginiCustomer Perception and Distribution Chanel of HulShariq KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EjerciciosPresentTenses 210907 171536Document10 paginiEjerciciosPresentTenses 210907 171536Andrea Martinez JiménezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recipe For A Healthy Fruit Salad Activity CardDocument4 paginiRecipe For A Healthy Fruit Salad Activity CardboobooÎncă nu există evaluări
- FinancialStatement 2014 Tahunan BUDI PDFDocument224 paginiFinancialStatement 2014 Tahunan BUDI PDFafidatul fitriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia: Dr. Tutik Harjianti, SP PDDocument47 paginiAnemia: Dr. Tutik Harjianti, SP PDsujidahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Milk Adulteration Using MID-IR SpectrosDocument6 paginiAnalysis of Milk Adulteration Using MID-IR SpectrosEditor IJRITCCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective Skin Care For WomenDocument7 paginiEffective Skin Care For WomenFeirniadoll100% (1)
- 5 Forces Model - Vinamilk - K20405CDocument19 pagini5 Forces Model - Vinamilk - K20405CNga Nguyễn Thị HảiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TQM of Pepsi ColaDocument22 paginiTQM of Pepsi Colapooja42980% (10)
- 4ds0315e P2 (F)Document1 pagină4ds0315e P2 (F)nagravÎncă nu există evaluări