Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
AP Physics B Formulas
Încărcat de
José Luis Salazar EspitiaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AP Physics B Formulas
Încărcat de
José Luis Salazar EspitiaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
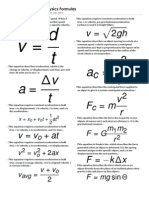
AP Physics B Formula Study Sheet
NEWTONIAN MECHANICS
displacement is a change in
Δx = area under v-t graph position; velocity is the rate
Kinematics of change of displacement,
Δv = area under a-t graph acceleration is the rate of
change of velocity
the sum of all forces is
Net Force Fnet = ma proportional to mass x
acceleration
the friction force is
Friction force Ff = μFN proportional to the coefficient
of friction x the normal force
the acceleration of an object
v2
centripetal acceleration ac =
r
experiencing UCM is equal to
the speed2 / the radius
torque is equal to the
torque τ = rF perpendicular distance x the
force
momentum is equal to mass x
momentum p = mv velocity
impulse is equal to the change
impulse J = FΔt = mΔv in momentum
1 kinetic energy is ½ mass x
kinetic energy K= 2 mv2 velocity2
gravitational potential gravitational potential energy
Ug = mgh is mass x gravitational field x
energy height
work is the energy done by an
mechanical work W = FΔx external force moving
through a displacement
power (general Wnet power is the rate of energy
P= transfer
definition) ∆t
power in terms of power is the rate at which an
P = Fv external force moves through
velocity a displacement
the force in a spring is equal
to the spring constant x the
spring force Fs = kΔx amount of stretch or
compression of the spring
1
the energy stored in a spring
spring potential energy Us = 2 kΔx2 = ½ x spring constant x the
stretch or compression
the period of a spring depends
m
period of a spring Ts = 2π
k
on mass and spring constant
(not amplitude)
the period of a pendulum
l
period of a pendulum Tp = 2π
g
depends on length and
gravitational field
relationship between period and 1 period and frequency are
frequency T= f reciprocals of each other
any two masses exert a
gravitational force between Gm 1 m 2
any two objects with mass
FG = r2
gravitational force on each
other
gravitational potential energy any 2-mass system near has
Gm 1 m 2 potential energy
between any two objects with UG = r
mass
FLUID MECHANICS AND THERMAL PHYSICS
absolute pressure in a
P = P0 + ρgh
fluid
gage pressure P = ρgh
buoyant force Fbouy = ρVg
fluid flow continuity A1v1 = A2v2
volume flow rate A1v1
1
P + ρgy + 2 ρv2 =
Bernoulli’s principle
constant
pressure (general F
P=
definition) A
ideal gas law PV = nRT = NkBT
3
internal energy in a gas Kavg = 2 kBT
velocity of a gas 3RT 3k B T
vrms = = µ
molecule M
W = PΔV or area under
thermal work
graph
change in internal
ΔU = Q + W
energy
Wnet
efficiency (general) e= Qin
TH − TC
ideal (Carnot) efficiency ec = TH
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
kq1 q 2
Electrostatic force Fe = r2
kq1
Electrostatic field E= r2
Electrostatic potential kq 1q 2
Ue =
energy r
kq 1
Electrostatic potential V= r
Charge on a capacitor Q = VC
ε0 A
Capacitance C= d
Energy stored in a
UC = ½ QV = ½ CV2
capacitor
∆Q
Current (definition) I= ∆t
ρl
Resistance of a wire R= A
Ohm’s Law V = IR
V2
Power in a circuit P = IV = R
= I2R
Equivalent resistor for
Req = R1 + R2 + …
series
Equivalent resistor for 1 1
−1
Req =
R + R +...
parallel 1 2
Equivalent capacitance for 1 1
−1
Ceq =
C + C +...
series 1 2
Equivalent capacitance for
Ceq = C1 + C2 +…
parallel
Magnetic force on a
moving charge in a FB = qvBsinθ
magnetic field
Magnetic force on a
current carrying wire in FB = BIlsinθ
a magnetic field
Magnetic field around a µ0 I
B= 2πr
current carrying wire
Magnetic flux Φm = BAcosθ
Average EMF generated ∆ Φm
by a changing magnetic −
εavg = ∆t
field
EMF generated by a
loop moving into or out ε = Blv
of a magnetic field
Force BIl’s qvB
ε Blvd when the flux is changing.
Take ast
WAVES AND OPTICS
Velocity of a wave v = fλ
c
Index of refraction n= v
Snell’s Law n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
n1sinθ1 = n2sin90 or
Critical angle n2
sinθc = n1
1 1 1
Mirror & lens equation +
si s o
=
f
hi s
Magnification M= =− i
ho so
Focal length in terms of R
f=
radius of curvature 2
Diffraction pattern path
mλ = dsinθ
difference
Diffraction pattern mλL
xm =
spacing d
ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
Energy of a photon E = hf = pc
Maximum kinetic energy
-φ + hf = Kmax
of an emitted electron
deBroglie wavelength of h
λ=
an emitted electron p
Rest energy of a mass ΔE = (Δm)c2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Understanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsDe la EverandUnderstanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionDe la EverandA Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Document2 paginiO Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Taha Maroof100% (1)
- 9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMTDocument4 pagini9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMT王涛Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 paginiPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 paginiPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap Physics ReveiwDocument18 paginiAp Physics ReveiwPaul Mitchell100% (1)
- AP Physics Question BankDocument99 paginiAP Physics Question BankElianne Gabbay100% (2)
- AP Physics ReviewDocument96 paginiAP Physics Reviewderekcal100% (6)
- AP Physics C Mechanics Review Lecture Notes - AllDocument29 paginiAP Physics C Mechanics Review Lecture Notes - AllAnanda WiselyÎncă nu există evaluări
- High School Physics Cheat SheetDocument7 paginiHigh School Physics Cheat SheetM J Rhoades50% (4)
- AP Study Guide PhysicsDocument96 paginiAP Study Guide PhysicsRajiv KabadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8185physics Unit 3 and 4 Cheat Sheet MHSDocument4 pagini8185physics Unit 3 and 4 Cheat Sheet MHSSyed Mairaj Ul Haq100% (1)
- All Physics Formula and Glossary - GCE Study Buddy - The Best O Level Revision ResourceDocument13 paginiAll Physics Formula and Glossary - GCE Study Buddy - The Best O Level Revision ResourceVei Adoptante100% (2)
- Work and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Document13 paginiWork and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Mansoor Al TunijiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 252 Page Notes AP Physics 1 2016 17Document7 pagini252 Page Notes AP Physics 1 2016 17Michelle MariposaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics B 2013 Practice WorkbookDocument401 paginiAP Physics B 2013 Practice WorkbookGabby Tanaka0% (1)
- AP Physics 1 - Motion QuestionsDocument14 paginiAP Physics 1 - Motion QuestionsAnonymous RzU94z100% (1)
- Complete AP Physics Study GuideDocument98 paginiComplete AP Physics Study GuideGAT TutoringÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP AP Success PhysicsDocument336 paginiAP AP Success Physicsnomejodas2100% (9)
- AP Physics Study GuideDocument96 paginiAP Physics Study GuideBenjamin GroffÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics Test ReviewDocument21 paginiAP Physics Test ReviewAnish KalappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics B ReviewDocument65 paginiAP Physics B Reviewsky5725100% (1)
- Physics ResourcesDocument7 paginiPhysics ResourcesDevon SamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics C Review and Calculus ReviewDocument11 paginiAP Physics C Review and Calculus ReviewJohnny WoodsÎncă nu există evaluări
- High School Chemistry PDFDocument12 paginiHigh School Chemistry PDFAleph ContinuumÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics 1 - Review Expressing Motion Visually MathmaticallyDocument7 paginiAP Physics 1 - Review Expressing Motion Visually MathmaticallyBUG100% (1)
- Absolute Holy GrailDocument597 paginiAbsolute Holy GrailHarley BaustianÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP PhysicsDocument336 paginiAP Physicsbeks100% (1)
- Physics Formula SheetDocument2 paginiPhysics Formula SheetExtremeVelocity67% (6)
- AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based: Free-Response QuestionsDocument18 paginiAP Physics 1: Algebra-Based: Free-Response QuestionsAnitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics B Exam Cram Sheet (Ver. 5.01) General Reminders: X X y y ResultantDocument8 paginiAP Physics B Exam Cram Sheet (Ver. 5.01) General Reminders: X X y y Resultantkirsten hutchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Cheat Sheet - MotionDocument1 paginăPhysics Cheat Sheet - MotionKurt50% (2)
- 7 WavesDocument65 pagini7 WavesDalia MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Student WorkbookDocument483 paginiPhysics Student WorkbookR. K Gupta100% (1)
- Physics Resources V 4Document10 paginiPhysics Resources V 4Bip Rilly100% (2)
- Ap Physics 1 Course and Exam Description PDFDocument236 paginiAp Physics 1 Course and Exam Description PDFManya Punjabi100% (1)
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDocument16 paginiAP Calculus BC Study GuideBrimwoodboy100% (3)
- Physics FormulaDocument26 paginiPhysics Formulachhor tithmesa100% (1)
- AP1 Student WorkbookDocument358 paginiAP1 Student WorkbookThe vegetal saiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCAT Physics FormulasDocument6 paginiMCAT Physics Formulasjetone472100% (2)
- 22 - The Nuclear AtomDocument10 pagini22 - The Nuclear AtomEdgardo LeysaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 07Document27 paginiCH 07Jessica Ibarreta100% (1)
- Physics Exam Cheat SheetDocument3 paginiPhysics Exam Cheat SheetJib Bros100% (4)
- A Level Physics Waves Topic GuideDocument17 paginiA Level Physics Waves Topic Guideshanadil10Încă nu există evaluări
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 paginiAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- AP Physics 1 Exam Solution GuideDocument11 paginiAP Physics 1 Exam Solution GuideBUG67% (3)
- Physics Key Points and FormulaeDocument35 paginiPhysics Key Points and FormulaeAt TanwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP® Statistics Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + OnlineDe la EverandAP® Statistics Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + OnlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics 1 Practice Questions: High Yield AP Physics 1 Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDe la EverandAP Physics 1 Practice Questions: High Yield AP Physics 1 Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schaum's Outline of College Physics, 11th EditionDe la EverandSchaum's Outline of College Physics, 11th EditionEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 2, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDe la EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 2, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regents Physics--Physical Setting Power Pack Revised EditionDe la EverandRegents Physics--Physical Setting Power Pack Revised EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- AP® Calculus AB & BC All Access Book + OnlineDe la EverandAP® Calculus AB & BC All Access Book + OnlineEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- AP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDe la EverandAP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crash Course: QM MathDocument6 paginiCrash Course: QM MathJosé Luis Salazar EspitiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Units of Chapter 10: BarometerDocument28 paginiUnits of Chapter 10: BarometerJosé Luis Salazar EspitiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Eigenvector/Eigenvalue RuleDocument1 pagină5 Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Eigenvector/Eigenvalue RuleJosé Luis Salazar EspitiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics B CH 4 ReviewDocument29 paginiAP Physics B CH 4 ReviewJosé Luis Salazar EspitiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics B CH 1-2Document18 paginiAP Physics B CH 1-2José Luis Salazar EspitiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Calculus TextbookDocument526 paginiContemporary Calculus TextbookJosé Luis Salazar Espitia100% (2)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at InfinityDocument11 paginiCalculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at Infinityapi-1192241886% (7)
- 1998 AP Physics B & C ExamsDocument234 pagini1998 AP Physics B & C ExamsJosé Luis Salazar Espitia100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Solutions To The AP Physics B Exam 1993Document16 paginiMultiple Choice Solutions To The AP Physics B Exam 1993José Luis Salazar EspitiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amnaya Sutra (English)Document458 paginiAmnaya Sutra (English)Assam Bhakti SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF en Iso 5167-6-2019Document22 paginiNF en Iso 5167-6-2019Rem FgtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improve On-Time DeliveriesDocument24 paginiImprove On-Time DeliveriesUdayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Cost EstimateDocument21 paginiStandard Cost EstimateMOORTHYÎncă nu există evaluări
- GROSS Mystery of UFOs A PreludeDocument309 paginiGROSS Mystery of UFOs A PreludeTommaso MonteleoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dual Op Amp and Voltage Reference Ap4310/ADocument12 paginiDual Op Amp and Voltage Reference Ap4310/AМихаил ЯненкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCPL 316J 000eDocument34 paginiHCPL 316J 000eElyes MbarekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main Girders: CrossDocument3 paginiMain Girders: Crossmn4webÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanta V12 Data SheetDocument2 paginiAdvanta V12 Data SheetJuliana MiyagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Climate ChangeDocument3 paginiEffects of Climate Changejiofjij100% (1)
- Immigrant Italian Stone CarversDocument56 paginiImmigrant Italian Stone Carversglis7100% (2)
- Prestige Institute of Management & Research: Guided By:-Submitted By: - Prof. Arpit Loya Sumeet RattanDocument21 paginiPrestige Institute of Management & Research: Guided By:-Submitted By: - Prof. Arpit Loya Sumeet RattanSumeet700005Încă nu există evaluări
- Paediatric Intake Form Modern OT 2018Document6 paginiPaediatric Intake Form Modern OT 2018SefÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMDWLab Book AnswersDocument44 paginiDMDWLab Book AnswersNarpat Makwana Pune100% (1)
- Biology Accel Syllabus 2011-2012Document3 paginiBiology Accel Syllabus 2011-2012Mike DeleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gypsum Plasterboard: National Standard of The People'S Republic of ChinaDocument15 paginiGypsum Plasterboard: National Standard of The People'S Republic of ChinaGarry100% (2)
- Tugas 2-TRK Lanjut Kelompok 3 Andre-Arief-IstiaDocument18 paginiTugas 2-TRK Lanjut Kelompok 3 Andre-Arief-IstiaAndre Fahriz Perdana HarahapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric EmergenciesDocument47 paginiPediatric EmergenciesahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Specification - 077154C-000-JSS-1700-009 - DDocument13 paginiMaterial Specification - 077154C-000-JSS-1700-009 - DStructures ProductionÎncă nu există evaluări
- 123 09-Printable Menu VORDocument2 pagini123 09-Printable Menu VORArmstrong TowerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Halfen Cast-In Channels: HTA-CE 50/30P HTA-CE 40/22PDocument92 paginiHalfen Cast-In Channels: HTA-CE 50/30P HTA-CE 40/22PTulusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cynosure Starlux 500 Palomar Technical Service ManualDocument47 paginiCynosure Starlux 500 Palomar Technical Service ManualJF SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Runyankore-Rukiga Dictionary Launch: President Yoweri Museveni's SpeechDocument28 paginiRunyankore-Rukiga Dictionary Launch: President Yoweri Museveni's SpeechThe New Vision50% (2)
- Manual Wire Rope Winches Wall-Mounted Wire Rope Winch SW-W: Equipment and ProcessingDocument1 paginăManual Wire Rope Winches Wall-Mounted Wire Rope Winch SW-W: Equipment and Processingdrg gocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clevo W940tu Service ManualDocument93 paginiClevo W940tu Service ManualBruno PaezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dual Shield 7100 Ultra: Typical Tensile PropertiesDocument3 paginiDual Shield 7100 Ultra: Typical Tensile PropertiesDino Paul Castro HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On 4G TechnologyDocument23 paginiPresentation On 4G TechnologyFresh EpicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated Factory Profile of Aleya Apparels LTDDocument25 paginiUpdated Factory Profile of Aleya Apparels LTDJahangir Hosen0% (1)
- Managing Diabetic Foot Ulcers ReadingDocument21 paginiManaging Diabetic Foot Ulcers Readinghimanshugupta811997Încă nu există evaluări
- NAT-REVIEWER-IN-PHYSICAL EDUCATIONDocument4 paginiNAT-REVIEWER-IN-PHYSICAL EDUCATIONMira Rochenie CuranÎncă nu există evaluări