Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Case Study Oligo
Încărcat de
mutiaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Case Study Oligo
Încărcat de
mutiaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
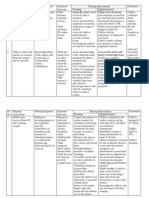
Case Study: Oligohydramnios
4.
Oligohydramnios
Severe reduction of amniotic fluid volume
(typically less than 500 ml at term); highly
concentrated urine.
Possibility of prolonged, dysfunctional labor
(usually beginning before term).
Fetal risk: renal anomalies, pulmonary
hyperplasia, hypoxia, increased skeletal
deformities, and wrinkled, leathery skin.
Causes
Exact cause is unknown.
Any condition that prevents the fetus from
making urine or that blocks urine from
going into the amniotic sac.
Contributing
factors:
uteroplacental
insufficiency, premature
rupture
of
membranes prior to labor onset, maternal
hypertension,
maternal
diabetes, intrauterine growth restriction,
postterm pregnancy, fetal renal genesis,
polycystic kidneys, and urinary tract
obstructions.
of
Nursing Interventions
closely,
and
including vital
fetal
status
signs and fetal
heart rate patterns.
2.
Monitor maternal weight gain pattern,
notifying the health care provider if weight
loss occurs.
3.
Provide
emotional
about
coping
5.
Instruct her about signs and symptoms
of labor, including those shell need to
report immediately.
6.
Reinforce the need for close supervision
and follow up.
7.
Assist with amnioinfusion as indicated.
8.
Encourage the patient to lie on her left
side.
9.
Ensure that amnioinfusion solution is
warmed to body temperature.
10. Continuously monitor maternal vital signs
and
fetal
heart
rate
during
the
amnioinfusion procedure.
11. Note the development of any uterine
contractions,
notify
the
health
care
strict sterile
technique during
amnioinfusion.
Treatment
Close medical supervision of the mother
and fetus.
Fetal monitoring
Amnioinfusion
(infusion
of
warmed
sterile normal saline or lactated Ringers
solution) to treat or prevent variable
decelerations during labor.
maternal
patient
measures if fetal anomalies are suspected.
12. Maintain
Test result
Ultrasonography reveals no pockets
amniotic fluid larger than 1 cm.
Monitor
the
provider, and continue to monitor closely.
Assessment
Asymptomatic
Lagging fundal height growth.
1.
Inform
support
during, and after ultrasonography.
before,
Oligohydramnios
When a woman has oligohydramnios, the
level of amniotic fluid surrounding the
baby is too low. To understand how this
can affect your health and the health of
your baby, it's helpful to first understand
the role amniotic fluid plays in a healthy
pregnancy.
What you need to know about
amniotic
fluid
The amniotic fluid that surrounds your
baby plays an important role in your
baby's growth and development. This
clear-colored liquid protects the baby and
provides it with fluids. Your baby breathes
this fluid into its lungs and swallows it.
This helps your baby's lungs and digestive
system grow strong. Your amniotic fluid
also allows the baby to move around,
which helps it to develop its muscles and
bones.
The amniotic sac that contains your baby
begins to form about 12 days after
conception. Amniotic fluid begins to form
at that time, too. In the early weeks of
pregnancy, amniotic fluid is mainly made
up of water supplied by the mother. After
about 20 weeks, your baby's urine makes
up most of the fluid.
The amount of amniotic fluid increases
until about 36 weeks of pregnancy. At that
time you have about 1 quart of fluid. After
that time, the level begins to decrease.
What you need to know about
oligohydramnios
Oligohydramnios (too little amniotic fluid)
occurs in about 4 out of every 100
pregnancies. It is most common in the last
trimester of pregnancy, but it can develop
at any time in the pregnancy. About 1 out
of 8 women whose pregnancies last 2
weeks past the due date develops
oligohydramnios.
This
happens
as
amniotic fluid levels naturally decline.
Oligohydramnios
is
diagnosed
with
ultrasound. The causes of this condition
are not completely understood. Some
pregnant
women
who
develop
oligohydramnios never know the cause.
Some causes are:
Certain birth defects in the baby
Ruptured membranes (breaks or
tears in the sac that holds the amniotic
fluid)
A pregnancy that goes 2 weeks
past the due date
A health condition in the pregnant
woman, such as high blood pressure,
diabetes or lupus
Birth defects involving the kidneys
and urinary tract can cause this
problem. That's because babies with
these birth defects produce less urine,
which makes up most of the amniotic
fluid.
Oligohydramnios may affect you, your
baby, and your labor and delivery in
different ways. The effects depend on the
cause, when the problem occurs, and how
little fluid there is.
In the first two trimesters, too little
amniotic fluid may result in birth defects
of the lungs and limbs. During this period,
oligohydramnios
increases
the
risk
of miscarriage, preterm birth and stillbirth.
When oligohydramnios occurs in the third
trimester, it is linked to poor fetal growth,
complications during labor and birth, and
increased risk of cesarean section.
Women
with
otherwise
normal
pregnancies who develop oligohydramnios
near their due date probably need no
treatment. Their babies are likely to be
born healthy. Even so, your provider may
want to watch you closely. When
treatment is needed, the amniotic fluid
may need to be replaced with an artificial
substitute.
What
you
can
do
The best thing you can do is to go to all
your prenatal
care appointments.
Your
health care provider can monitor the size
of your belly and how much amniotic fluid
is in your womb. If you have a problem,
your provider can take steps to help
prevent complications in you and your
baby.
Women with high blood pressure, diabetes
and lupus are at increased risk for
oligohydramnios. If you have any of these
conditions, be sure to let your health care
provider know.
If you have high blood pressure:
Talk to your health care provider before
pregnancy (or as soon as you think you
are
pregnant).
Be sure any medications you are taking
are
safe
during
pregnancy
Be sure your blood pressure is well
controlled.
If you have oligohydramnios, be sure to
eat a healthy and nutritious diet, drink lots
of fluids (water is best), get plenty of rest,
avoid smoking, and report any signs of
preterm labor to your health care provider
right
away.
MAS can affect the baby's breathing in a
number of ways, including chemical
irritation to the lung tissue, airway
obstruction by a meconium plug, infection,
and the inactivation of surfactant by the
meconium (surfactant is a natural
substance that helps the lungs expand
properly).
The severity of MAS depends on the
amount of meconium the baby inhales as
well as underlying conditions, such as
infections
within
the
uterus
or
postmaturity (when a baby is overdue, or
more than 40 weeks' gestational age).
Generally, the more meconium a baby
inhales, the more serious the condition.
MAS can happen before, during, or after
labor and delivery when a newborn inhales
(or aspirates) a mixture of meconium and
amniotic fluid (the fluid in which the baby
floats inside the amniotic sac). Meconium
is the baby's first feces, or poop, which is
sticky, thick, and dark green and is
typically passed in the womb during early
pregnancy and again in the first few days
after birth.
The inhaled meconium can partially or
completely block the baby's airways.
Although air can flow past the meconium
trapped in the baby's airways as the baby
breathes in, the meconium becomes
trapped in the airways when the baby
breathes out. And so, the inhaled
meconium irritates the baby's airways and
makes it difficult to breathe.
Normally, fluid is moved in and out of only
the trachea (the upper portion of the
airway) when there's breathing activity in
the fetus. Meconium can be inhaled into
the lungs when the baby gasps while still
in the womb or during the initial gasping
breaths after delivery. This gasping
typically happens when there has been a
problem (i.e., an infection or compression
of the umbilical cord) that causes the baby
to have difficulty getting enough oxygen in
the womb.
Causes
MAS is often related to fetal stress. Fetal
stress can be caused by problems in the
womb, such as infections, or by difficulties
during the labor process. A distressed
baby may experience hypoxia (decreased
oxygen), which may make the baby's
intestinal activity increase and may cause
relaxation of the anal sphincter (the
muscular valve that controls the passage
of feces out of the anus). This relaxation
then moves meconium into the amniotic
fluid that envelops the baby.
But meconium passage during labor and
delivery isn't always associated with fetal
distress. Occasionally, babies who aren't
distressed during the birth process pass
meconium before birth. In either case, a
baby that gasps or inhales meconium can
develop MAS.
Additional risk factors for MAS include:
a difficult delivery
advanced gestational age (or
postmaturity)
a mother who smokes cigarettes
heavily or who has diabetes,high blood
pressure (hypertension), or chronic
respiratory or cardiovascular disease
umbilical cord complications
poor intrauterine growth (poor
growth of the baby while in the uterus)
Prematurity is not a risk factor. In fact,
MAS is rare in babies born before 34
weeks.
Signs and Symptoms
At birth, the doctor will likely notice one or
more symptoms of MAS, including:
meconium or dark green streaks or
stains in the amniotic fluid
discoloration of the baby's skin
either blue (cyanosis) or green (from
being stained by the meconium)
problems
with
breathing
including rapid breathing (tachypnea),
labored
(difficulty)
breathing,
or
suspension of breathing (apnea)
low heart rate in the baby before
birth
low Apgar score (the Apgar test is
given to newborns just after birth to
quickly evaluate color, heartbeat,
reflexes, muscle tone, and breathing)
limpness in the baby
postmaturity (signs that a baby is
overdue such as long nails)
Diagnosis
If a baby is thought to have inhaled
meconium, treatment will begin during
delivery. If the baby has any depression in
breathing, the doctor taking care of the
baby will insert a laryngoscope into the
babys trachea to remove any meconium
that might be present. The doctor will also
probably listen to the baby's chest with a
stethoscope for sounds in the lungs that
are common in infants with MAS.
The doctor may also order tests a blood
test (called a blood gas analysis) that
helps determine if the baby is getting
enough oxygen and a chest X-ray that can
show patches or streaks on the lungs that
are found in babies with MAS.
Babies with MAS may be sent to a special
care nursery or aneonatal intensive care
unit (NICU) to be closely monitored for the
next few days. Treatments may include:
oxygen therapy by oxygen hood or
ventilation
antibiotics
use of surfactant
nitric oxide
obtaining
blood
routinely
to
determine if the baby is receiving
enough oxygen
Severe Aspiration
Babies who have severe aspiration and
require mechanical ventilation are at
increased risk for bronchopulmonary
dysplasia, a lung condition that can be
treated with medication or oxygen.
Another complication associated with MAS
is a collapsed lung. Also known as
pneumothorax, a collapsed lung is treated
by reinflating the lung (inserting a tube
between the ribs, allowing the lung to
gradually re-expand).
Although rare, a small percentage of
babies with severe MAS develop aspiration
pneumonia. If this occurs, the doctor may
recommend
advanced
lung
rescue
therapy.
Three therapies are currently used to treat
aspiration pneumonia and severe forms of
MAS:
1.
Surfactant therapy: An artificial
surfactant is instilled into the baby's
lungs, which helps to keep the air sacs
open.
2.
High-frequency oscillation: This
special ventilator vibrates air enriched
with extra oxygen into the baby's
lungs.
3.
Rescue therapy: Nitric oxide is
added to the oxygen in the ventilator. It
dilates the blood vessels and allows
more blood flow and oxygen to reach
the baby's lungs.
If one of these therapies (or a combination
of them) doesn't work, there is another
alternative. Extra corporeal membrane
oxygenation (ECMO) is a form of
cardiopulmonary bypass, meaning that an
artificial heart and lung will temporarily
take over to supply bloodflow to the
baby's body. ECMO reduces the fatality
rate for these severely distressed infants
from 80% to 10%. Not all hospitals are
ECMO centers, so babies that require
ECMO might need to be moved to another
hospital.
Babies with severe cases of MAS may
come home from the hospital on oxygen.
They may be more likely to have wheezing
and lung infections during their first year,
but lungs can regenerate new air sacs, so
the long-term prognosis for their lungs is
excellent.
It's important for a pregnant woman to tell
her doctor immediately if meconium is
present in the amniotic fluid when her
water breaks, or if the fluid has dark green
stains or streaks. Doctors also use a fetal
monitor during labor to observe the baby's
heart rate for any signs of fetal distress.
In some cases doctors may recommend
amnioinfusion, the dilution of the amniotic
fluid with saline, to wash meconium out of
the amniotic sac before the baby has a
chance to inhale it at birth.
Although MAS is a frightening complication
for parents to face during the birth of their
child, the majority of cases are notsevere.
Most infants are monitored for fetal
distress during labor, and doctors pay
careful attention to any signs that would
indicate meconium aspiration. If it does
occur, treatment will begin immediately.
For most infants who have inhaled
meconium, early treatment can prevent
further complications and help to reassure
anxious new parents.
oligohidramnion
Ketika
seorang
wanita
memiliki
oligohidramnion, tingkat cairan ketuban
yang mengelilingi bayi terlalu rendah.
Untuk memahami bagaimana hal ini dapat
Possible Long-Term Complications
Severely affected babies are at risk for
developing chronic lung disease and may
also have developmental abnormalities
and hearing loss. Babies diagnosed with
MAS will be screened at the hospital for
hearing problems or neurological damage.
mempengaruhi
kesehatan
Anda
dan
kesehatan bayi Anda, sangat membantu
untuk pertama memahami peran drama
cairan
ketuban
pada
kehamilan
yang
sehat.
Apa yang perlu Anda ketahui tentang
cairan ketuban
Although very rare, severe cases of MAS
may be fatal. Studies have indicated that
deaths
from
MAS
have
decreased
significantly through interventions such as
suctioning and reducing the number of
post-term births.
Cairan ketuban yang mengelilingi bayi
Anda memainkan peran penting dalam
pertumbuhan
Anda.
cairan
dan
perkembangan
bening
berwarna
bayi
ini
melindungi bayi dan menyediakan itu
Prevention
dengan cairan. Bayi Anda bernafas cairan
ini ke paru-paru dan menelannya. Hal ini
Ruptur membran (istirahat atau air mata
membantu
di
paru-paru
bayi
Anda
dan
kantung
yang
memegang
cairan
sistem pencernaan tumbuh kuat. cairan
ketuban)
ketuban Anda juga memungkinkan bayi
Sebuah kehamilan yang berlangsung 2
untuk bergerak di sekitar, yang membantu
minggu terakhir tanggal jatuh tempo
untuk mengembangkan otot dan tulang.
Kondisi kesehatan pada wanita hamil,
Kantung ketuban yang berisi bayi Anda
seperti tekanan darah tinggi, diabetes
mulai terbentuk sekitar 12 hari setelah
atau lupus
pembuahan.
Cacat lahir yang melibatkan ginjal dan
cairan
ketuban
terbentuk pada waktu itu juga.
mulai
Pada
saluran
kemih
dapat
menyebabkan
minggu-minggu awal kehamilan, cairan
masalah ini. Itu karena bayi dengan cacat
ketuban terutama terdiri dari air yang
lahir ini menghasilkan kurang urin, yang
disediakan oleh ibu. Setelah sekitar 20
membuat sebagian besar cairan ketuban.
minggu,
Oligohidramnion
urin
bayi
Anda
membuat
dapat
mempengaruhi
sebagian besar cairan.
Anda, bayi Anda, dan tenaga kerja dan
Jumlah meningkat cairan ketuban sampai
pengiriman dengan cara yang berbeda.
sekitar 36 minggu kehamilan. Pada saat
Efek tergantung pada penyebab, ketika
itu Anda memiliki sekitar 1 liter cairan.
masalah terjadi, dan betapa sedikit cairan
Setelah itu, tingkat mulai menurun.
yang ada.
Apa yang perlu Anda ketahui tentang
Di dua trimester pertama, terlalu sedikit
oligohidramnion
cairan ketuban dapat menyebabkan cacat
Oligohidramnion
(terlalu
sedikit
cairan
lahir dari paru-paru dan anggota badan.
ketuban) terjadi pada sekitar 4 dari setiap
Selama
100 kehamilan. Hal ini paling sering terjadi
meningkatkan risiko keguguran, kelahiran
pada trimester terakhir kehamilan, tetapi
prematur dan lahir mati.
dapat berkembang pada setiap saat dalam
Ketika
kehamilan. Sekitar 1 dari 8 wanita yang
trimester ketiga, hal ini terkait dengan
kehamilan berlangsung 2 minggu terakhir
pertumbuhan yang buruk janin, komplikasi
tanggal
selama
jatuh
tempo
berkembang
periode
ini,
oligohidramnion
persalinan
dan
oligohidramnion
terjadi
pada
kelahiran,
dan
oligohidramnion. Hal ini terjadi karena
peningkatan risiko operasi caesar.
tingkat
Wanita dengan kehamilan normal lain
cairan
ketuban
secara
alami
menurun.
yang
Oligohidramnion didiagnosis dengan USG.
dekat
Penyebab kondisi ini tidak sepenuhnya
mungkin tidak memerlukan pengobatan.
dipahami. Beberapa wanita hamil yang
bayi
mengembangkan
sehat.
pernah
tahu
oligohidramnion
penyebabnya.
penyebabnya adalah:
cacat lahir tertentu pada bayi
tidak
Beberapa
mengembangkan
tanggal
mereka
Meski
jatuh
oligohidramnion
tempo
kemungkinan
begitu,
mereka
akan
penyedia
lahir
Anda
mungkin ingin menonton Anda erat. Ketika
pengobatan dibutuhkan, cairan amnion
mungkin perlu diganti dengan pengganti
Jika Anda memiliki tekanan darah tinggi:
buatan.
Bicara dengan dokter Anda sebelum
Apa yang dapat Anda lakukan
hamil (atau segera setelah Anda pikir
Hal terbaik yang dapat Anda lakukan
Anda sedang hamil).
adalah pergi ke semua janji pemeriksaan
Pastikan setiap obat yang kita pakai
kehamilan
aman selama kehamilan
Anda.
penyedia
layanan
kesehatan Anda dapat memantau ukuran
Pastikan tekanan darah Anda terkontrol
perut Anda dan berapa banyak cairan
dengan baik.
ketuban dalam rahim Anda. Jika Anda
Jika
memiliki masalah, penyedia Anda dapat
pastikan untuk makan makanan sehat dan
mengambil
untuk
bergizi, minum banyak cairan (air yang
pada
terbaik), mendapatkan banyak istirahat,
membantu
langkah-langkah
mencegah
komplikasi
Anda dan bayi Anda.
Wanita
diabetes
dengan
dan
tekanan
lupus
Anda
memiliki
oligohidramnion,
menghindari merokok, dan melaporkan
darah
tinggi,
setiap tanda-tanda persalinan prematur
berada
pada
untuk penyedia layanan kesehatan Anda
peningkatan risiko untuk oligohidramnion.
Jika Anda memiliki kondisi ini, pastikan
untuk membiarkan dokter tahu.
segera
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Beta ThalaDocument2 paginiBeta ThalaAngie LamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live Preterm Baby Delivered NSDDocument13 paginiLive Preterm Baby Delivered NSDKristine Anne SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregestational DiabetesDocument7 paginiPregestational Diabetesraisya farah monicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaDocument3 paginiCase Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaToto RyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spontaneous AbortionDocument8 paginiSpontaneous Abortionsaber_fate_11Încă nu există evaluări
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryDocument5 paginiPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fetal Macrosomia UptodateDocument22 paginiFetal Macrosomia UptodateWinny Roman AybarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthalin InhalerDocument5 paginiAsthalin InhalerRajib MandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sub Arachnoid HaemorrageDocument46 paginiSub Arachnoid HaemorrageShitaljit IromÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case PresentationDocument50 paginiCase Presentationapi-19762967Încă nu există evaluări
- Case (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4Document36 paginiCase (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4EljhayrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- RLE 109 Group 4 Case Analysis in MastitisDocument20 paginiRLE 109 Group 4 Case Analysis in MastitisEugene MananganÎncă nu există evaluări
- PREECLAMPSIA Case ScenarioDocument2 paginiPREECLAMPSIA Case Scenariosabao kizuiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge PlanningDocument2 paginiDischarge PlanningAthena Irish LastimosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CASE STUDY TablesDocument9 paginiCASE STUDY TablesMicah MagallanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study - Incomplete Abortion Related To APSDocument8 paginiCase Study - Incomplete Abortion Related To APSRomeo ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Fetal DeathDocument9 paginiEvaluation of Fetal DeathVinisia TakaraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prevention of MeaslesDocument5 paginiPrevention of MeaslesJae Yong LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 paginiMedications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDarla JoyceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biliary AtresiaDocument8 paginiBiliary AtresiaBrooke MauriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyDocument1 paginăPregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of Honesty in MedicineDocument3 paginiImportance of Honesty in MedicineSuiweng WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationDocument5 paginiTriamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationMauricio Sv0% (1)
- Pyloric StenosisDocument5 paginiPyloric Stenosisensoooooooooo100% (1)
- Experiment 7Document7 paginiExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument14 paginiGestational Diabetes MellitusCzarina PorciunculaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stages of LaborDocument3 paginiStages of LaborCleo Pabilic100% (1)
- Case Study of Bacterial MeningitisDocument125 paginiCase Study of Bacterial MeningitisNap IchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ectopic Pregnancy - PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăEctopic Pregnancy - PathophysiologyMarimiel PagulayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addison's DiseaseDocument14 paginiAddison's Diseasedivya4nirmalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Flow Chart PretermDocument4 pagini4 Flow Chart PretermYeni PuspitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 - Abortion or MiscarriageDocument43 pagini5 - Abortion or Miscarriageasifdawar2011Încă nu există evaluări
- DR - Group CaseDocument62 paginiDR - Group CaseRon Lucernas MayugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Study and Discharge Plan Arnold and SelwynDocument17 paginiDrugs Study and Discharge Plan Arnold and SelwynArnold ZamoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Management of Woman With GDMDocument2 paginiNursing Care Management of Woman With GDMkimglaidyl bontuyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care PlanDocument4 paginiCare PlangopscharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6B Pregnant and Lactacting WomenDocument3 pagini6B Pregnant and Lactacting Womenmo'niqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Surgical Case Study On Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Page 1 of 29Document29 paginiA Surgical Case Study On Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Page 1 of 29Clyde R.OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP RiskDocument2 paginiNCP RiskNorries Jonell CaballarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report - For MaamDocument7 paginiReport - For MaamSherchen Antonio-CortesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evidence-Based Practice in Maternal & Child HealthDocument15 paginiEvidence-Based Practice in Maternal & Child HealthJan Oliver YaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument12 paginiNeonatal JaundiceJustine NyangaresiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minggu 5 LP THALASSEMIADocument14 paginiMinggu 5 LP THALASSEMIAMuhammad PanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Pathophysiology of PPROMDocument2 paginiThe Pathophysiology of PPROMNano KaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflective Journal 1Document4 paginiReflective Journal 1api-365605511Încă nu există evaluări
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: Prepared By: Bande, Kyla Marie O. Lorente, Alfie John CDocument22 paginiPostpartum Hemorrhage: Prepared By: Bande, Kyla Marie O. Lorente, Alfie John CNi Ki TaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hep B in PregnancyDocument42 paginiHep B in PregnancyAbraham ChiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH)Document3 paginiPregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH)Susan HepziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duphaston PDFDocument4 paginiDuphaston PDFmarcusjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Translational Research: Generating Evidence For PracticeDocument24 paginiTranslational Research: Generating Evidence For Practicebeer_ettaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan (Post CS)Document5 paginiNursing Care Plan (Post CS)Tony ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Med Template - NifedipineDocument2 paginiMed Template - NifedipineAshlee KeeferÎncă nu există evaluări
- 68 Abnormal PeuperiumDocument44 pagini68 Abnormal PeuperiumGodsonYeboah-AwudziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesDocument8 paginiSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesRyan Robert V. VentoleroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity Intolerance R/T Increased Energy Demands Due To Disease Condition and Increased Fetal Nutrient UptakeDocument8 paginiActivity Intolerance R/T Increased Energy Demands Due To Disease Condition and Increased Fetal Nutrient UptakeAbdelmar SusulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Filipino Culture, Values, and Practices in Relation To Difficult Childbearing and ChildrearingDocument8 paginiFilipino Culture, Values, and Practices in Relation To Difficult Childbearing and ChildrearingRheeanne AmilasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GastroschisisDocument19 paginiGastroschisiskunaidongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture NotesDocument11 paginiAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture Notes0912247251Încă nu există evaluări
- B Inggris Halim NCP Asma BronchialDocument28 paginiB Inggris Halim NCP Asma BronchialAbdul HlmÎncă nu există evaluări
- S Tahel 2005Document12 paginiS Tahel 2005Catherine MorrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implikasi Pasien Dengan Penyakit Paru Pada PenerbanganDocument47 paginiImplikasi Pasien Dengan Penyakit Paru Pada PenerbanganFebi Chyanx ElsanabiprilÎncă nu există evaluări
- CR Piopneumothoraks Nicky FIXdDocument62 paginiCR Piopneumothoraks Nicky FIXdPutri RahmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Incidentsduring Perioperative Period Sept 2011Document106 paginiCritical Incidentsduring Perioperative Period Sept 2011wellawalalasithÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATLS PretestDocument3 paginiATLS PretestDavid Reznick100% (5)
- Respiratory Status of Adult Patients in The Postoperative Period of Thoracic or Upper Abdominal SurgeriesDocument8 paginiRespiratory Status of Adult Patients in The Postoperative Period of Thoracic or Upper Abdominal SurgeriesDimitreÎncă nu există evaluări
- 990916 EUS教學 (14) 急診超音波在胸腔急症之應用Document63 pagini990916 EUS教學 (14) 急診超音波在胸腔急症之應用juice119Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Questions 3Document40 paginiFinal Exam Questions 3clarke skaikruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical VentilationDocument26 paginiMechanical VentilationNirupama Ks90% (10)
- Fcps IMMDocument22 paginiFcps IMMHaseeb Rasool0% (1)
- Concept Map CCDocument8 paginiConcept Map CCapi-402644703Încă nu există evaluări
- Stab Wound PathophysiologyDocument5 paginiStab Wound PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano86% (7)
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Hyaline Membrane Disease)Document98 paginiRespiratory Distress Syndrome (Hyaline Membrane Disease)Miraf MesfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intercostal Chest DrainageDocument6 paginiIntercostal Chest DrainageNovalis CrazyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trauma Thorax - Dr. Darmawan Ismail, SP - BTKV (K)Document33 paginiTrauma Thorax - Dr. Darmawan Ismail, SP - BTKV (K)Josafat PondangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lung Examination: Abnormal Arcot J. Chandrasekhar, M.D.: StepsDocument6 paginiLung Examination: Abnormal Arcot J. Chandrasekhar, M.D.: StepsadjcdaughtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Radiology For Dummies PDFDocument6 paginiChest Radiology For Dummies PDF0395Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For "HEMOTHORAX PNEUMOTHORAX"Document8 paginiNursing Care Plan For "HEMOTHORAX PNEUMOTHORAX"jhonroks78% (9)
- Piper N Abcde: Chest X-Ray GuideDocument3 paginiPiper N Abcde: Chest X-Ray GuideWinston TengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bates Outline of Chapter 8Document15 paginiBates Outline of Chapter 8KatherynSotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Venous ThromboebolismDocument15 paginiVenous ThromboebolismRashed ShatnawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lung ExaminationDocument14 paginiLung Examinationსალომე მუმლაძე “Slay” TMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tension PneumothoraxDocument3 paginiTension PneumothoraxariefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Assessment and Monitoring 28 Feb 2012 Final PDFDocument85 paginiRespiratory Assessment and Monitoring 28 Feb 2012 Final PDFRahiman Abd RahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchopleural Fistula 1frankDocument105 paginiBronchopleural Fistula 1frankroshjamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATLS Practice Questions FreeDocument4 paginiATLS Practice Questions Freeelcapitano vegetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency MedicineDocument150 paginiEmergency MedicineDev MartelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinesiología y Sus AlcancesDocument16 paginiKinesiología y Sus AlcancesEzequiel SosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trauma Nursing IntroductionDocument12 paginiTrauma Nursing Introductionanimesh pandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)De la EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Evaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDe la EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (29)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDe la EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDe la EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (81)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (328)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (42)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDe la EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDe la EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDe la EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (253)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.De la EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDe la EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDe la EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (61)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesDe la EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (1412)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingDe la EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDe la EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (59)