Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BKTK II Sifat Sifat Zat Padat
Încărcat de
dikimstTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BKTK II Sifat Sifat Zat Padat
Încărcat de
dikimstDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
26/09/2016
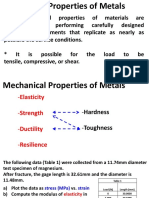
SIFAT-SIFAT MEKANIK (MECHANICAL
PROPERTIES)
SIFAT-SIFAT ZAT PADAT
Stress
Strain
Modulus of elasticity
Tensile strength
Yield strength
Elongation (Ductility)
Hardness
Lukhi Mulia S
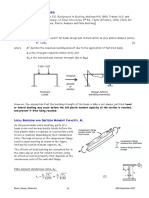
CONCEPTS OF STRESS AND STRAIN
Stress (tegangan) : perbandingan antara gaya terhadap luas
penampang benda
Simbol stress
Secara matematis dapat dituliskan :
=
CONCEPTS OF STRESS AND STRAIN
Strain (regangan) : Perbandingan antara pertambahan
panjang terhadap panjang mula-mula
F : besar gaya tekan/tarik (N)
A : luas penampang (m 2 )
: tegangan (N/m 2 )
26/09/2016
ELASTIC DEFORMATION
Deformation in which stress and strain are proportional
a plot of stress (ordinate) versus strain (abscissa) results in a
linear relationship, as shown in Figure 6.5
MODULUS OF ELASTICIT Y (YOUNGS
MODULUS)
Hookes law relationship between engineering stress and
engineering strain for elastic deformation (tension and
compression)
=
Figure 6.5 Schematic stressstrain
diagram showing linear
elastic deformation for loading and
unloading cycles
MODULUS OF ELASTICIT Y (YOUNGS
MODULUS)
26/09/2016
STRENGTH (KEKUATAN)
STRESS-STRAIN DIAGRAM
Strength : tegangan maksimal yang dapat ditahan oleh bahan
Yield strength (kekuatan luluh), terjadi pada titik dimana
bahan mulai mengalami deformasi plastik (tidak dapat
kembali ke panjang asal)
Tensile strength, T S : kekuatan tarik maksimum
Deformasi plastik terjadi setelah bahan terkena tegangan
yang melebihi kekuatan luluh
Fracture terjadi setelah bahan terkena tegangan yang melebhi
TS
Figure 6.11 Typical engineering stressstrain behavior to fracture, point F. The tensile strength
TS is indicated at point M. The circular insets represent the geometry of the deformed specimen at various
points along the curve
26/09/2016
DUCTILIT Y
Figure 6.13 Schematic representations of tensile stressstrain behavior for brittle and ductile materials loaded to
fracture
DUCTILIT Y
Ductility dapat dinyatakan sebagai persen perpanjangan bahan
atau persen pengurangan luas
l f = the fracture length (panjang ketika patah)
l 0 = the original gauge length (panjang mula-mula)
%EL = percent elongation (% perpanjangan )
Percent reduction in area % RA
A 0 = the original cross-sectional area (luas mula-mula)
A f = the cross-sectional area at the point of fracture (luas ketika
patah)
Bahan dikatakan brittle jika %EL < 5%
26/09/2016
QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
1)
A specimen of copper having a rectangular cross section
15.2 mm x 19.1 mm (0.60 in. 0.75 in.) is pulled in tension
with 44,500 N (10,000 lb ) force, producing only elastic
deformation. Calculate the resulting strain.
2) An aluminum bar 125 mm (5.0 in.) long and having a square
cross section 16.5 mm (0.65 in .) on an edge is pulled in
tension with a load of 66,700 N (15,000 lb f ), and
experiences an elongation of 0.43 mm (1.7 x 10 -2 in.).
Assumingthat the deformation is entirely elastic, calculate
the modulus of elasticity of the aluminum.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Rebar Buckling Model GOpazoDocument10 paginiRebar Buckling Model GOpazoD Toño ToroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultimate Strength and Deformation of Concrete Members Strengthened by Jacketing With Various MaterialsDocument14 paginiUltimate Strength and Deformation of Concrete Members Strengthened by Jacketing With Various MaterialsAhmad MensaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taglio Sez Circ 2Document3 paginiTaglio Sez Circ 2mariorossi_4Încă nu există evaluări
- Aluru Wen Shen J Mech 2010Document6 paginiAluru Wen Shen J Mech 2010abraham silva hernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.0 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Tension Compression Shear TorsionDocument40 pagini6.0 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Tension Compression Shear TorsionWilliams AkandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of Steel Plate Shear Walls Including Shear and Bending Deformations - 1992 PDFDocument9 paginiNonlinear Dynamic Analysis of Steel Plate Shear Walls Including Shear and Bending Deformations - 1992 PDFciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Opening On The Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Beam I011275261Document10 paginiEffects of Opening On The Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Beam I01127526101010Încă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument25 paginiMeasuring Mechanical Properties of MaterialsUmesh ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument26 paginiMechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsAli AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Softened Truss Model For RC Torsional Members Under Combined ActionDocument8 paginiSoftened Truss Model For RC Torsional Members Under Combined ActionMinaksheePhutkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyclic Strut & Tie Modelling of Simple Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument8 paginiCyclic Strut & Tie Modelling of Simple Reinforced Concrete StructuresGloomsyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple StrainDocument6 paginiSimple StrainKhan ToothÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument25 paginiMechanical PropertiesUmesh ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static Resistance Bolted Circular Flange JointsDocument9 paginiStatic Resistance Bolted Circular Flange JointsBálint Vaszilievits-SömjénÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Strength of Materials - GDLC - 8851 PDFDocument12 paginiAdvanced Strength of Materials - GDLC - 8851 PDFabdullahaafaq33% (3)
- Characteristic Withdrawal Capacity and Stiffness of Threaded RodsDocument13 paginiCharacteristic Withdrawal Capacity and Stiffness of Threaded RodsAndrej SørensenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Mit OpencoursewareDocument4 pagini3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Mit OpencoursewareMohan BangaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deflection of Simply-Supported Beams: Title of The ExperimentDocument21 paginiDeflection of Simply-Supported Beams: Title of The Experimentopeyemi71Încă nu există evaluări
- Columns 6Document113 paginiColumns 6d584cnÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 323/ BES 222 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Chapter 2 - StrainDocument6 paginiCE 323/ BES 222 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Chapter 2 - StrainNadlor Gasco OzausÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 07Document12 paginiCH 07Madeline NgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geas FormulaDocument29 paginiGeas Formularoy016Încă nu există evaluări
- 221 Lab 1 - Tensile Testing of Metals (2017W)Document8 pagini221 Lab 1 - Tensile Testing of Metals (2017W)Abdul HafieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures 1Document13 paginiFatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures 1Telma VarelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TensileDocument5 paginiTensileTharinya SellathuraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument16 paginiMechanical Properties of MetalsShione T MundawararaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Physical and Mathematical Modelling in Underground ExcavationsDocument8 paginiApplication of Physical and Mathematical Modelling in Underground ExcavationsrannscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Behaviour and modelling of flat slab-column connectionsDocument8 paginiBehaviour and modelling of flat slab-column connectionsrogin737Încă nu există evaluări
- Shear Behavior of Unbonded Post-TensionedDocument10 paginiShear Behavior of Unbonded Post-TensionedAnonymous eB2AZT3Încă nu există evaluări
- p10 PDFDocument4 paginip10 PDFakash kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- QLM of SOMDocument4 paginiQLM of SOMatulkumargaur26Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 Mechanics of DBDocument20 paginiModule 2 Mechanics of DBJohnny King ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument33 paginiMechanical Properties of MaterialsAaron Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nonlinear Analysis of RC Elements with Pronounced Bond-SlipDocument8 paginiNonlinear Analysis of RC Elements with Pronounced Bond-SlipGenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torsional StressesDocument48 paginiTorsional StressesKory EstesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Material ModelsDocument8 paginiSteel Material ModelspirazorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument13 paginiMechanical Properties of MetalsIvyy Joyce BuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Large Footings For One Way ShearDocument8 paginiDesign of Large Footings For One Way ShearAsad SohailÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Paper Must Be Cited As:: Document Downloaded FromDocument52 paginiThis Paper Must Be Cited As:: Document Downloaded FromTesfa HunderaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beam Design Lecture NotesDocument24 paginiBeam Design Lecture Notesyyanan1118Încă nu există evaluări
- MARA University of Technology Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument12 paginiMARA University of Technology Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringAdiela Syuhada Roslan100% (1)
- Pengaruh Rasio Tulangan-Balok T - AkmaluddinDocument13 paginiPengaruh Rasio Tulangan-Balok T - Akmaluddinakmal2k4Încă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Approach To Predict Nonlinear Parameters For Dynamic Analysis of Structures Applied To Blast LoadsDocument19 paginiAnalytical Approach To Predict Nonlinear Parameters For Dynamic Analysis of Structures Applied To Blast LoadscemadaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kecman Bending Collapse of Rectangular and Square Section Tubes 1983 International Journal of Mechanical SciencesDocument14 paginiKecman Bending Collapse of Rectangular and Square Section Tubes 1983 International Journal of Mechanical SciencesNhật Vũ100% (2)
- 36b73ed7-6794-4c83-9d92-6b3676675211Document20 pagini36b73ed7-6794-4c83-9d92-6b3676675211muralihare100% (1)
- Concerns On Seismic Moment-Shear Connections Using Available Indian Hot-Rolled I-SectionsDocument16 paginiConcerns On Seismic Moment-Shear Connections Using Available Indian Hot-Rolled I-SectionsGautam PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 PDFDocument22 paginiChapter 8 PDFمشعل العليÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge Isolation With High-Damping Rubber BearingsDocument15 paginiBridge Isolation With High-Damping Rubber Bearingslucassn14Încă nu există evaluări
- The Brazier Effect for Finite Composite CylindersDocument22 paginiThe Brazier Effect for Finite Composite CylindersAscanio BarbosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Material (Stress and Strain)Document31 paginiStrength of Material (Stress and Strain)Mg SicsicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Structures Tension Members 2Document24 paginiSteel Structures Tension Members 2Nafi AykutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear-Transfer Strength of Reinforced ConcreteDocument11 paginiShear-Transfer Strength of Reinforced ConcretePremasiri KarunarathnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arm301 QBDocument6 paginiArm301 QBKunal KhandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- JCSR 2364 - Lateral-Torsional Buckling of Coped Beams PDFDocument17 paginiJCSR 2364 - Lateral-Torsional Buckling of Coped Beams PDFShamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue of Textile and Short Fiber Reinforced CompositesDe la EverandFatigue of Textile and Short Fiber Reinforced CompositesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainDe la EverandStrength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionDe la EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionEvaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (4)
- Chemical Engineer Cover LetterDocument1 paginăChemical Engineer Cover LetterdikimstÎncă nu există evaluări
- China Powder Sodium Nitrate (NaNO3) With CAS - 7631-99-4 - China Sodium Nitrate, Price Sodium NitrateDocument1 paginăChina Powder Sodium Nitrate (NaNO3) With CAS - 7631-99-4 - China Sodium Nitrate, Price Sodium NitratedikimstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodium Nitrate Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size and Forecast, 2018 To 2026Document1 paginăSodium Nitrate Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size and Forecast, 2018 To 2026dikimstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Konsentrasi Natrium Nitrat Dan Natrium Dehidrogen Fosfat Pada Media Walne Terhadap Konsentrasi Biomassa Dan Protein Nannochloropsis OculataDocument10 paginiPengaruh Konsentrasi Natrium Nitrat Dan Natrium Dehidrogen Fosfat Pada Media Walne Terhadap Konsentrasi Biomassa Dan Protein Nannochloropsis OculatadikimstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proses Industri Natrium KarbonatDocument3 paginiProses Industri Natrium KarbonatdikimstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canon 60dDocument1 paginăCanon 60ddikimstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengenalan Teknik KimiaDocument26 paginiPengenalan Teknik KimiakioÎncă nu există evaluări
- SetDocument2 paginiSetdikimstÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Algorithms For Real-Time DSP - EMBREEDocument125 paginiC Algorithms For Real-Time DSP - EMBREELuiz Carlos da SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 6 - Potentiometer & Servo MotorDocument7 paginiLab 6 - Potentiometer & Servo MotorChristy CheriyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- KG Per HR To MMSCFD & BBL Into m3phDocument6 paginiKG Per HR To MMSCFD & BBL Into m3phsathishÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIT2 29S15 Lecture10Document26 paginiMIT2 29S15 Lecture10Ihab OmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadratics CH 4Document48 paginiQuadratics CH 4yddapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Second Law AnalysisDocument2 paginiNewton's Second Law AnalysisJamiel CatapangÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Social Sciences in the PhilippinesDocument19 paginiHistory of Social Sciences in the PhilippinesHAZEL JANE ABAPOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fried BergDocument3 paginiFried BergneedmyscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ontology Reasoning With Deep Neural NetworksDocument38 paginiOntology Reasoning With Deep Neural NetworksYamine KliouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementing Logic Gates Using Neural Networks (Part 1) - by Vedant Kumar - Analytics Vidhya - MediumDocument3 paginiImplementing Logic Gates Using Neural Networks (Part 1) - by Vedant Kumar - Analytics Vidhya - Mediumhelen leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Sky Network Revenue ManagementDocument10 paginiBlue Sky Network Revenue Managementp3im4nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me53 Design of Machine Elements L T P CDocument2 paginiMe53 Design of Machine Elements L T P CajithjkingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Sem 4 Electrical Engineering Syllabus For WB PolytechnicDocument35 pagini3rd Sem 4 Electrical Engineering Syllabus For WB PolytechnicParthasarothi SikderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Birational Geometry Caucher Birkar PDFDocument35 paginiBirational Geometry Caucher Birkar PDFhuangrj9Încă nu există evaluări
- 2022 Year 9 Yearly Report: Nick Diles Subjects StudiedDocument11 pagini2022 Year 9 Yearly Report: Nick Diles Subjects StudiedNick DilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convex FunctionsDocument93 paginiConvex FunctionsAntonio Villagómez ChiluisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recall The Innis Investments Problem Chapter 2 Problem 39 Letting S Units Purchased in The PDFDocument4 paginiRecall The Innis Investments Problem Chapter 2 Problem 39 Letting S Units Purchased in The PDFCharlotte0% (1)
- Theories of OrganizationsDocument21 paginiTheories of Organizations1921 Pallav Pali100% (1)
- The Numbers Have An End: Mohamed Ababou Strengthens His Proof of a Finite Digit TheoryDocument15 paginiThe Numbers Have An End: Mohamed Ababou Strengthens His Proof of a Finite Digit TheoryFredÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSYS SimplorerDocument2 paginiANSYS Simplorerahcene2010Încă nu există evaluări
- 15 Traveling Salesman Problem: AuthorDocument25 pagini15 Traveling Salesman Problem: AuthorRama Krishna MuttavarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Game Theory1Document15 paginiGame Theory1Vishwas tomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pursuing MS in ML to Advance ResearchDocument3 paginiPursuing MS in ML to Advance ResearchSangabattulaLokeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MasterProgramming - in - BCA C Programing Assignment 2021Document79 paginiMasterProgramming - in - BCA C Programing Assignment 2021Debnath SahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculus 1 with Dr. Janet Semester 1 SyllabusDocument100 paginiCalculus 1 with Dr. Janet Semester 1 SyllabusTrần Xuân QuỳnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Book Three-DimensionalModelAnalysis PDFDocument434 pagini2010 Book Three-DimensionalModelAnalysis PDFJhoan Sebastian Tenjo GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet (1) - Fluid Mechanics IIDocument3 paginiSheet (1) - Fluid Mechanics IIAhmed Rabie Abd ElazeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Numbers: Numbers and Number LineDocument30 paginiUnderstanding Numbers: Numbers and Number LinerajatÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR 9 Math Unit 1 Notes WebDocument29 paginiGR 9 Math Unit 1 Notes WebMohamed Ali100% (1)
- Itae 002 Test 1 2Document5 paginiItae 002 Test 1 2Nageshwar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări