Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Es 13 PS 1
Încărcat de
Reynald DaluzTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Es 13 PS 1
Încărcat de
Reynald DaluzDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ES 13: MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
2nd Sem AY 2015-16 | PROBSET 1
WFU1 [Junio]
Deadline: Feb. 15 (12 NN) | Pigeon Hole MH 102
General Instructions:
1. Answer the following questions on letter or A4-sized papers (preferably recycled). Only one
side of every sheet should be used to write your solutions to the problems. MAXIMUM of 2
problems in every sheet. Follow exam protocol on what details shall be written on the paper.
BOX or ENCIRCLE your final answers ONLY.
2. At the TOPMOST portion of the first page of your answer sheets, write the following academic
integrity pledge (and affix your signature):
I hereby certify that I have worked on this problem set by my own honest effort, without giving or
receiving any inappropriate help. I understand that any evidence which contradicts the foregoing
statement may be used against me, and I am prepared for the ensuing consequences thereof.
3.
Late submissions will NOT be accepted.
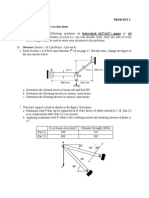
PROBLEM 1
An 8-kN force is applied to the front side of pin B. The diameter of pins A, B, and C is 16 mm.
The thickness of all members is 10 mm.
a) Determine the maximum normal stress in member AB. Indicate whether tension or
compression.
b) Determine the maximum normal stress in member BC. Indicate whether tension or
compression.
c) Determine the maximum average shear stress in pin B. (Hint: There are two shear
planes with different average shear stresses.)
d) Determine the average shear stress in pin C.
e) Determine the bearing stress between pin B and member AB.
ES 13: MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
2nd Sem AY 2015-16 | PROBSET 1
WFU1 [Junio]
Deadline: Feb. 15 (12 NN) | Pigeon Hole MH 102
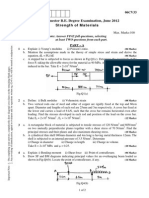
PROBLEM 2
The counter-clockwise moment M applied to the rigid L-bar B produces an axial strain of 0.004444 mm/mm in bar A and a shearing strain of 0.007 radians at E, and causes support F to
move by 2 mm. Determine the axial strain in bar C if there is a 0.5 mm clearance in the
connection between the triangular plate and the rigid L-bar D.
PROBLEM 3
A thin rectangular plate is deformed as shown.
The normal strains developed along the sides are
as follows:
AB = + 0.0022 mm/mm
BC = - 0.0030 mm/mm
CD = + 0.0050 mm/mm
Determine the following:
a) Horizontal displacement of B
b) Normal strain in AD
c) Shearing strain at A
d) Shearing strain at C
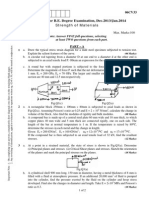
PROBLEM 4
Two blocks of rubber (G = 26 GPa), each having a height of 30 mm, width of 10 mm (out of
plane), thickness of 50 mm, and are bonded on fixed walls and to a rigid plate at the middle
(the whole mechanism is known as a Shear Spring). The rigid plate is connected to an
extensible steel cable (E = 200 GPa) with a 20-mm diameter. The cable is then connected to
the rigid bar ABC where it is pinned at B and a 60-kN force is applied at A. Assuming that the
cable and the rubber blocks deform elastically, determine the following:
ES 13: MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
2nd Sem AY 2015-16 | PROBSET 1
WFU1 [Junio]
Deadline: Feb. 15 (12 NN) | Pigeon Hole MH 102
a) stress in the steel cable (in
MPa)
b) deformation of the steel cable
(in mm)
c) shear stress on each of the
rubber blocks (in MPa)
d) shear strain in the block (in
rad) provided that the block
deforms into the shape shown
by the dashed lines
e) displacement of point D (in
mm)
f) displacement of point C (in
mm)
PROBLEM 5
Given the stressstrain diagram for a certain material, answer the following questions. The
coordinates of points in the diagram is also listed on the table.
a) What is the stress at the materials Proportional Limit?
b) What is the value of the materials Youngs Modulus?
c) What is the value of the materials modulus of resilience?
ES 13: MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
2nd Sem AY 2015-16 | PROBSET 1
WFU1 [Junio]
Deadline: Feb. 15 (12 NN) | Pigeon Hole MH 102
The specimen is loaded until it reached 400MPa. Answer the following questions based on this
new condition.
d) What is the permanent strain when the material is unloaded after reaching 400MPa of
stress?
e) What is the modulus of toughness of the material with permanent deformation according
to the new stress strain diagram (ie. after loading to 400 MPa and unloading)?
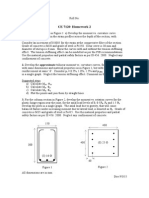
PROBLEM 6
The rigid member ABC is attached to steel members BD and CE as shown. When installed at
a temperature of 30 C and no load is applied, the members experienced no stress and have the
dimensions shown in the figure. The temperature changes to 20C and a 2000-N load was
applied. It is necessary to solve the forces in member BD and CE.
a)
Draw the necessary free
body diagram(s) and formulate the
necessary equilibrium equation(s).
b)
Find the relationship
between BD and CE.
c)
Determine the forces in
members BD and CE
d)
If the pin at B (single shear
connection) has a failure stress of
failure = 100 MPa, determine the
diameter of the pin necessary to
withstand the stresses. Use a factor
of safety of 1.5. If the pins are only
available in increments of 2 mm,
what
diameter
will
you
recommend?
PROBLEM 7
The structure shown below is subjected to a concentrated force P as shown and an increase in
temperature of 90 C. The material and section properties are provided in the table.
The steel and bronze rods are fixed at one end while the aluminum bar and the other end of the
steel bar is attached to a rigid plate. The aluminum and bronze bar is separated by a 0.2 mm
gap.
ES 13: MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
2nd Sem AY 2015-16 | PROBSET 1
WFU1 [Junio]
Deadline: Feb. 15 (12 NN) | Pigeon Hole MH 102
Determine the maximum allowable force P such that the allowable stresses will not
be exceeded.
500.2 mm
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 paginiEs 13 Prob Set 1Julian de LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Mechanics 2015 PaperDocument6 paginiStructural Mechanics 2015 PaperAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocument14 paginiLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech 260-Final ExamDocument3 paginiMech 260-Final ExamwerewaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument8 paginiDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 3 2003 ProblemsDocument9 paginiExam 3 2003 ProblemsNURI ONUR CATAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Es 13 Thr1 Prob Set 1Document6 paginiEs 13 Thr1 Prob Set 1Tim AcostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Quiz 2 May 19, 2020: CE 323/ BES 222Document2 paginiMechanics of Deformable Bodies Quiz 2 May 19, 2020: CE 323/ BES 222Nadlor Gasco Ozaus100% (1)
- ME 212 Solid Mechanics-I Tutorial 5 (5th October 2020Document2 paginiME 212 Solid Mechanics-I Tutorial 5 (5th October 2020Atul SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Document3 paginiEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment-3: Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar School of InfrastructureDocument2 paginiAssignment-3: Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar School of InfrastructureShipra RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 Assignment 3Document3 pagini2013 Assignment 3Sergey ShkapovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me HW For StudentsDocument8 paginiMe HW For StudentsLoyal NoobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final ExamSOMFinal 2016 FinalDocument11 paginiFinal ExamSOMFinal 2016 Finalkhalil alhatabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Design 1 EBME1021 January 2015 Semester Final ExaminationDocument8 paginiMechanical Engineering Design 1 EBME1021 January 2015 Semester Final ExaminationAnonymous 5YMOxVQÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Materials: Problem 1Document2 paginiMechanics of Materials: Problem 1Bretana joanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maravilla - Preliminary Examination-2Document7 paginiMaravilla - Preliminary Examination-2Jireh Van Kryzler MaravillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressDocument4 paginiENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressJoana Rosette TordecillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Reinforce Concrete Design Final PaperDocument7 paginiAdvance Reinforce Concrete Design Final PaperBryan ChooiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main Exam Paper Nov08, Smt211tDocument6 paginiMain Exam Paper Nov08, Smt211tPortia ShilengeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correl DesignDocument14 paginiCorrel DesignClashing CouchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Objective Type Paper - IDocument23 paginiCivil Engineering Objective Type Paper - IVishal RanganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- M 004 ExercisesDocument33 paginiM 004 ExercisesKannan MuthusamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial QuestionsDocument7 paginiMEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial Questionsha haÎncă nu există evaluări
- R5 210304 Mechanics of SolidsDocument2 paginiR5 210304 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Design Model PaperDocument2 paginiMachine Design Model PaperVinay Karanam100% (1)
- HW05Document4 paginiHW05Potatoes123Încă nu există evaluări
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)Document2 paginiAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)nvnrevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DDocument7 paginiCe-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DAshutosh AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- r13 Mos Old Q PapersDocument21 paginir13 Mos Old Q PapersSrinu ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guided Tour: Chapter IntroductionDocument3 paginiGuided Tour: Chapter IntroductionJenny PriceÎncă nu există evaluări
- A1 Mechanics of Materials I FA18Document2 paginiA1 Mechanics of Materials I FA18Muhammad Shahan AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech 260-Final ExamDocument3 paginiMech 260-Final ExamwerewaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce 203: Structural Mechanics I: Civil & Environmental Engineering DepartmentDocument2 paginiCe 203: Structural Mechanics I: Civil & Environmental Engineering DepartmentjacobllÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsDocument6 pagini2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsMartin MugoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Sheet - 2 Topic: Stress Submission Date: 27/08/2019Document3 paginiProblem Sheet - 2 Topic: Stress Submission Date: 27/08/2019Beesam Ramesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMCV312 Final Exam Paper - 2022Document7 paginiMMCV312 Final Exam Paper - 2022Praveet ChandÎncă nu există evaluări
- QLM of SOMDocument4 paginiQLM of SOMatulkumargaur26Încă nu există evaluări
- Design 1qsy1718 QuestionsDocument9 paginiDesign 1qsy1718 QuestionsRachel Delos ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW5Document4 paginiHW5Wesley MoranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-3 Simple Stresses 1-3-1 Axial StressDocument32 pagini1-3 Simple Stresses 1-3-1 Axial StressHazim KhalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Material ExerciseDocument4 paginiMechanics of Material ExerciseFaiz Fauzi0% (1)
- ES 13 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Second Departmental Examination Samplex September 28, 2017 (6:00-8:00 PM) First Semester 2017-2018Document3 paginiES 13 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Second Departmental Examination Samplex September 28, 2017 (6:00-8:00 PM) First Semester 2017-2018Carl Justin AzucenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument8 paginiDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Document4 paginiProblemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Gerardo BocanegraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeDocument15 paginiDE5302 Strength of Materials. Semester 1, 2018 Exam and FormulaeGopal KrishanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th SamplExDocument3 pagini4th SamplExhannah30Încă nu există evaluări
- Mec 323 FinalDocument7 paginiMec 323 FinalJihadHejaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 paginiStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 404/504 Homework 5 - Finite element applications in EngineeringDocument2 paginiME 404/504 Homework 5 - Finite element applications in EngineeringSeyfullahYıldızÎncă nu există evaluări
- MM312 Final Exam Paper - 2020Document6 paginiMM312 Final Exam Paper - 2020Praveet ChandÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Document5 paginiCVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Avinash SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer ALL Questions.: Solid Mechanics (NMB21104)Document2 paginiAnswer ALL Questions.: Solid Mechanics (NMB21104)aimranÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEE322 Final Exam S20Document5 paginiMEE322 Final Exam S20Nabil SweidanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 paginiAssignment For IPEAbirHasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions On Advanced ConcreteDocument1 paginăQuestions On Advanced ConcreteRatna Sai100% (1)
- American University of Beirut: Mechanics of Materials (Mech320) QUIZ 2 - (Spring 2011) - 2HDocument10 paginiAmerican University of Beirut: Mechanics of Materials (Mech320) QUIZ 2 - (Spring 2011) - 2HChanjoh RexsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Thermo Notes MRIIDocument24 paginiThermo Notes MRIIReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013, N.M.Document26 pagini2013, N.M.Reynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- JakcbkjbcsajkDocument13 paginiJakcbkjbcsajkReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 1 and 2 - Revised2Document5 paginiExercise 1 and 2 - Revised2Vivekka Olivia JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- PFD ExerciseDocument1 paginăPFD ExerciseReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock TestDocument2 paginiMock TestReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Pids v1.2 ActivityDocument1 pagină02 Pids v1.2 ActivityReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mercaptan Removal Cyclic AdsorptionDocument12 paginiMercaptan Removal Cyclic AdsorptionReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 BSChE ProgramDocument1 pagină2013 BSChE ProgramJohnBrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Area Perimeter Figs PDFDocument2 paginiMS Area Perimeter Figs PDFReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA Technology - To EmailDocument42 paginiBasic Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA Technology - To EmailReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Language and PeopleDocument1 paginăLanguage and PeopleReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samplex 2Document3 paginiSamplex 2Reynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batch MeltingDocument1 paginăBatch MeltingReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Acid Dissociation Constant of Methyl RedDocument1 paginăSpectrophotometric Determination of The Acid Dissociation Constant of Methyl RedReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document1 pagină1Reynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- BerlinDocument2 paginiBerlinReynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document1 pagină1Reynald DaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broadband Metamaterials in ElectromagneticsDocument399 paginiBroadband Metamaterials in ElectromagneticsFarhad AzadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Device G FdsDocument2 paginiDevice G FdsvijayakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marine HVAC SystemsDocument58 paginiMarine HVAC SystemsSiti Aishah Hussien100% (3)
- Best Practices in Adhesive Bonding - Max DavisDocument43 paginiBest Practices in Adhesive Bonding - Max DavisAndrea SantoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling Fluids PDFDocument12 paginiDrilling Fluids PDFnikhil_barshettiwat95% (20)
- Thermodynamic Relation IntroDocument4 paginiThermodynamic Relation IntromahendranÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESR and NMRDocument20 paginiESR and NMRUmang SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Lecture 11 Manufacturing State of The Art 2015Document21 pagini2015 Lecture 11 Manufacturing State of The Art 2015Raphael RosadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARTIS - TCR MaterialDocument24 paginiARTIS - TCR MaterialMMPAPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metallographic Preparation Technique For HDG PDFDocument8 paginiMetallographic Preparation Technique For HDG PDFAon Hemmatad100% (1)
- Crystal Growth TechniquesDocument46 paginiCrystal Growth Techniquesxyzabacus123Încă nu există evaluări
- Polymer EmulsionDocument1 paginăPolymer EmulsionSudhir Mahajan33% (3)
- Shear Capacity of Steel Plate Girders With Large Web OpeningsDocument3 paginiShear Capacity of Steel Plate Girders With Large Web OpeningsPauloAndresSepulvedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Three Types of Magnets Used in MRI ScannersDocument5 paginiThe Three Types of Magnets Used in MRI ScannersBenjámin KoltaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MetallurgyDocument9 paginiMetallurgyRj SakthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- By:Shounak Rajat Mukesh Project Supervisor:KV SAI SRINADHDocument9 paginiBy:Shounak Rajat Mukesh Project Supervisor:KV SAI SRINADHShounak KossambeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 - Foundation in RockDocument52 paginiChapter 6 - Foundation in RockKoh Jia Jie100% (1)
- Densolen - System AS39P / R20HT: Product InformationDocument2 paginiDensolen - System AS39P / R20HT: Product InformationCarlos PazÎncă nu există evaluări
- M (Length of Foundation) / (Width of Foundation) : Soil TypeDocument2 paginiM (Length of Foundation) / (Width of Foundation) : Soil TypeSashi BooshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACTIVITY#2 Group Activity PDFDocument5 paginiACTIVITY#2 Group Activity PDFAlfaro, Jeff SimonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MC-306 enDocument2 paginiMC-306 enminhhieuhanam93Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Physics: Solid ExpansionDocument3 paginiThermal Physics: Solid ExpansionBilly BlattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Microestructure Degradation of Creep Exposed Boiler SteelsDocument4 paginiAssessment of Microestructure Degradation of Creep Exposed Boiler SteelsdantegimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMT 405 - Distillation PDFDocument72 paginiCMT 405 - Distillation PDFMuhammad Azri HaziqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid PropertiesnumericalsDocument10 paginiFluid PropertiesnumericalsMishell Rubio100% (1)
- 2 D MaterialsDocument16 pagini2 D Materialsisimone7Încă nu există evaluări
- Congress ProgrammeDocument144 paginiCongress ProgrammeImelda Dewi AgustiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sif02 PDFDocument436 paginiSif02 PDFprajjwal patidarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials: Experimental and Numerical Investigations of High-Speed Projectile Impacts On 7075-T651 Aluminum PlatesDocument15 paginiMaterials: Experimental and Numerical Investigations of High-Speed Projectile Impacts On 7075-T651 Aluminum PlatesYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Design Guide For Forging PDFDocument31 paginiProduct Design Guide For Forging PDFmelvin ekboteÎncă nu există evaluări