Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit Calendar With Objectives
Încărcat de
api-263241074Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit Calendar With Objectives
Încărcat de
api-263241074Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
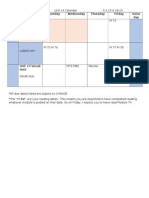
Day
Objective
-To compete vocabulary for
Unit 4
Activities
Questions
Vocab
-Students will work on Unit 4
Vocabulary
-Textbook Check
-Reading Quiz
-Students will take notes over
the Introduction to Sensation
and Perception
n/a
n/a
-How does our attention limit
or expand what we
experience?
-How do evolutionary
processes influence our
sensation and perception?
-How do our expectations,
contexts, emotions and
motivations impact our
perceptions?
-Describe sensory processes
(e.g., hearing, vision, touch,
taste, smell, vestibular,
kinesthesis, pain), including
the specific nature of energy
transduction, relevant
anatomical structures, and
specialized pathways in the
brain for each of the
senses.
-Identify the major historical
figures in sensation and
perception (e.g., Gustav
Fechner, David Hubel, Ernst
Weber, Torsten Wiesel).
-Students will take notes over
the Visual system (based on
light and the eye)
-Students will work on
labeling a diagram of the eye
-how do they eye and the brain
process visual information?
-sensation
-perception
-bottom-up processing
-top-down processing
-selective attention
-inattentional blindness
-change blindness
Transduction
-psychophysics
-absolute threshold
-signal detection theory
-subliminal
-priming
-difference threshold
-Webers Law
-sensory adaption
-wavelength
-hue
-intensity
-pupil
-iris
-lens
-retina
-accommodation
-rods
-cones
-optic nerve
-blind spot
-fovea
-feature detectors
-parallel processing
-Describe sensory processes
(e.g., hearing, vision, touch,
-Students will review the
process of color vision with a
--how do the theories of color
vision work together to explain
-Discuss basic principles of
sensory transduction,
including absolute threshold,
difference threshold, signal
detection, and sensory
adaptation.
-Discuss the role of attention
in behavior
-Identify the major historical
figures in sensation and
perception (e.g., Gustav
Fechner, David Hubel, Ernst
Weber, Torsten Wiesel).
-Young-Helmholtz
Trichromatic Color
taste, smell, vestibular,
kinesthesis, pain), including
the specific nature of energy
transduction, relevant
anatomical structures, and
specialized pathways in the
brain for each of the
senses.
-Explain common sensory
disorders (e.g., visual and
hearing impairments).
-Describe general principles of
organizing and integrating
sensation to promote
stable awareness of the
external world (e.g., Gestalt
principles, depth
perception).
-Discuss how experience and
culture can influence
perceptual processes (e.g.,
perceptual set, context
effects).
-Explain the role of top-down
processing in producing
vulnerability to illusion
-Identify the major historical
figures in sensation and
perception (e.g., Gustav
Fechner, David Hubel, Ernst
Weber, Torsten Wiesel).
-Describe sensory processes
(e.g., hearing, vision, touch,
taste, smell, vestibular,
kinesthesis, pain), including
the specific nature of energy
transduction, relevant
anatomical structures, and
specialized pathways in the
pen demonstration
-Review Color Blindness
-Students will view clips from
the Myth Busters Pirate
themed episode over rods &
cones and the pirate eye
patch
-Students will begin to review
perceptual cues
how we see color?
-how do perceptual constancies
help us organize our sensations
into meaningful perceptions?
Theory
-opponent process
theory
-Students will finish a review
of perceptual cues
-Students will work in a group
to complete an evaluation of
works from MC Escher
-Students will create a picture
using colors to demonstrate
their understanding of
perceptual cues (HMWK)
-how do perceptual constancies
help us organize our sensations
into meaningful perceptions?
-gestalt
-figure-ground
-grouping
-depth perception
-visual cliff
-retinal disparity
-monocular cues
-phi phenomenon
-perceptual constancy
-color constancy
-perceptual adaptation
-Students will take notes over
the auditory system and will
fill out a diagram of the ear
-Students will review Place
Theory and Frequency Theory
-Students will review the
different types of deafness
and learn about cochlear
-How do we locate sounds?
-How we understand pitch?
-audition
-frequency
-pitch
-middle ear
-cochlea
-inner ear
-Sensorineural hearing
loss
brain for each of the
senses.
-Explain common sensory
disorders (e.g., visual and
hearing impairments).
Assessment
-Describe sensory processes
(e.g., hearing, vision, touch,
taste, smell, vestibular,
kinesthesis, pain), including
the specific nature of energy
transduction, relevant
anatomical structures, and
specialized pathways in the
brain for each of the
senses.
Review
Review
Assessment
implants
-conduction hearing
loss
-Cochlear implant
-Place theory
-frequency theory
n/a
-Vocabulary Due
-Kahoot! Vocabulary review
quiz
-Vocabulary Quiz
-Students will review the
other senses (taste, smell,
touch) & pain
-Students will create review
sheets that will be copied by
other members of the class
n/a
-How do we sense touch, taste,
and smell?
-How do all of our senses
interact?
-gate control theory
-kinesthesia
-Vestibular sense
-sensory interaction
-embodied cognition
-Highlights & class discussion
review
-Sensation and Perception lab
activities
-Crash Course videos
-Kahoot! Review (pairs)
-review of application style
questions
-Unit 4 Exam
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
IV. Sensation and Perception (68%)
Everything that organisms know about the world is first encountered when stimuli inthe environment activate sensory organs,
initiating awareness of the external world.Perception involves the interpretation of the sensory inputs as a cognitive process.
AP students in psychology should be able to do the following:
Discuss basic principles of sensory transduction, including absolute threshold, difference threshold, signal detection, and
sensory adaptation.
Describe sensory processes (e.g., hearing, vision, touch, taste, smell, vestibular, kinesthesis, pain), including the specific nature
of energy transduction, relevant
anatomical structures, and specialized pathways in the brain for each of the senses.
Explain common sensory disorders (e.g., visual and hearing impairments).
Describe general principles of organizing and integrating sensation to promote stable awareness of the external world (e.g.,
Gestalt principles, depth
perception).
Discuss how experience and culture can influence perceptual processes (e.g., perceptual set, context effects).
Explain the role of top-down processing in producing vulnerability to illusion.
Discuss the role of attention in behavior.
Challenge common beliefs in parapsychological phenomena.
Identify the major historical figures in sensation and perception (e.g., Gustav Fechner, David Hubel, Ernst Weber, Torsten
Wiesel).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Understanding Sensation and PerceptionDocument55 paginiUnderstanding Sensation and PerceptionValerie Ah-YenÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP PSYCH SENSATION PERCEPTIONDocument7 paginiAP PSYCH SENSATION PERCEPTIONjohnz395Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Cheat SheetsDocument4 paginiFinal Cheat SheetsSalsa MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap Psychology Unit 7 Overview Revised 2015Document5 paginiAp Psychology Unit 7 Overview Revised 2015api-262090199Încă nu există evaluări
- Perseptual MotorDocument32 paginiPerseptual MotorDyas Laksmita UtamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSYBIODocument44 paginiPSYBIOMaria HazelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Senses Unit PlanDocument8 pagini5 Senses Unit Planapi-482110307Încă nu există evaluări
- RPH Sains T2Document11 paginiRPH Sains T2anon_438795505Încă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan Science f2Document26 paginiYearly Plan Science f2lccjane8504Încă nu există evaluări
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Experimental and Behavioral PsychologyDe la EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Experimental and Behavioral PsychologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensory Science Lesson Plan for Form 2 StudentsDocument26 paginiSensory Science Lesson Plan for Form 2 StudentsAldrich Malaga Gregory MÎncă nu există evaluări
- SensationDocument3 paginiSensationtaunkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Senses: Microscopic StructureDocument2 paginiSpecial Senses: Microscopic StructureAtiqah YeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epistemology S3 PhenomenologyDocument60 paginiEpistemology S3 PhenomenologyEko PrasetyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sense Experience The Role of Senses in The Experience of ArtDocument36 paginiSense Experience The Role of Senses in The Experience of ArtJomar OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories of Speech PerceptionDocument5 paginiTheories of Speech PerceptionZaid Al-Dabbagh100% (1)
- cog psych all modulesDocument67 paginicog psych all modulesMansi AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 5Document23 paginiCH 5Body ShamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kepy 105Document28 paginiKepy 105AWSAF AHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych 3260 NotesDocument45 paginiPsych 3260 NotesKinzaIqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - PSYC226 PDFDocument5 paginiChapter 1 - PSYC226 PDFWomens Program AssosciationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Lecture 6 & 7Document74 paginiChapter 4: Sensation and Perception Lecture 6 & 7DrGasnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes ch-5 Class-11Document8 paginiNotes ch-5 Class-11Bhumika ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Memories Can BringDocument4 paginiWhat Memories Can BringopocinschilorenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 Presentation PiagetDocument61 paginiWeek 3 Presentation Piagetapi-286676490Încă nu există evaluări
- Sensory Integration TherapyDocument97 paginiSensory Integration TherapyLakshmi Prasanna100% (2)
- The Nature of Experience: Thoughts on the Reality of ConsciousnessDe la EverandThe Nature of Experience: Thoughts on the Reality of ConsciousnessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych 101 NotesDocument15 paginiPsych 101 NotesJe-anne Alodia PresadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affective Neuroscience IntroDocument80 paginiAffective Neuroscience IntromuramadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan CH 5 Body MovementDocument11 paginiLesson Plan CH 5 Body MovementHIRAL SOLANKIÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5e Lesson Planning Template Spring 2021 4 4Document3 pagini5e Lesson Planning Template Spring 2021 4 4api-556980017Încă nu există evaluări
- AP Psychology Chapter 1 NotesDocument8 paginiAP Psychology Chapter 1 NoteshannabbiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art TherapyDocument7 paginiArt TherapyElizalde HusbandÎncă nu există evaluări
- clil_unit_planDocument22 paginiclil_unit_planmuñoz CinthiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obcl 1 Week 16 Perception and CoordinationDocument20 paginiObcl 1 Week 16 Perception and CoordinationMichelle Mallare100% (1)
- Major Schools of Psychology: Wundt's StructuralismDocument13 paginiMajor Schools of Psychology: Wundt's StructuralismTANAY KIKLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Psychological - Kevin ThompsonDocument32 paginiChapter 4 - Psychological - Kevin ThompsonAive Marist ObsiomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview - "Listen Up!" - Grade 1: TimbreDocument5 paginiOverview - "Listen Up!" - Grade 1: TimbreBAFICA'S PhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 1 Science Senses: Unit Plan January-February 2016 Miss PrattDocument7 paginiGrade 1 Science Senses: Unit Plan January-February 2016 Miss Prattapi-299674646Încă nu există evaluări
- Brain TypingDocument12 paginiBrain TypingAylwin Y100% (1)
- Learn About the Five SensesDocument6 paginiLearn About the Five SensesWaleed AfrÎncă nu există evaluări
- SH and CH SoundsDocument3 paginiSH and CH Soundsapi-347880027Încă nu există evaluări
- Light - Sound 2017-18Document5 paginiLight - Sound 2017-18Gerald HinkleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurocognitive DanceDocument12 paginiNeurocognitive DanceKristina KljucaricÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manish_Jadhav-HSS1Document12 paginiManish_Jadhav-HSS1IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan 8Document7 paginiLesson Plan 8api-338337678Încă nu există evaluări
- SampleDocument17 paginiSampleJasper muiruriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensation & Perception: How We Process StimuliDocument2 paginiSensation & Perception: How We Process StimulitekleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiLesson PlanFarimah TanggoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antinro LessoncycleDocument1 paginăAntinro Lessoncycleapi-317370288Încă nu există evaluări
- Engleski VjezbeDocument6 paginiEngleski VjezbeEmina ŠabanovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Does The Brain Learn Through MusicDocument43 paginiHow Does The Brain Learn Through MusicShubham RankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KJHKNLMDocument25 paginiKJHKNLMmtfb29Încă nu există evaluări
- Sensation and Perception Lesson PlanDocument13 paginiSensation and Perception Lesson PlanBrylle DeeiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE PEDAGOGY of LearningDocument47 paginiTHE PEDAGOGY of LearningCaliso, AbigailÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpenStax Psychology2e LN05Document6 paginiOpenStax Psychology2e LN05Whitney CartwrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emotional Aspects of Music VideoDocument10 paginiEmotional Aspects of Music VideoJuan Carlos ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of TeachingDocument219 paginiPrinciples of TeachingShiela BayunganÎncă nu există evaluări
- PERCEPTION Presentation (GROUP 1)Document43 paginiPERCEPTION Presentation (GROUP 1)Sawera KhadimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 ScheduleDocument2 paginiUnit 5 Scheduleapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Plan Civil War and ReconstructionDocument5 paginiUnit Plan Civil War and Reconstructionapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Guide Unit 3Document3 paginiUnit Guide Unit 3api-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Calendar and Activities 16Document2 paginiCalendar and Activities 16api-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Day Objective Activities Higher Order Questions VocabDocument4 paginiDay Objective Activities Higher Order Questions Vocabapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit PlanDocument2 paginiUnit Planapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 6 Plan 2016Document1 paginăUnit 6 Plan 2016api-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 PlanDocument4 paginiUnit 1 Planapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- US History Unit 2: The American Revolution and Constitution: Day Activity GoalDocument3 paginiUS History Unit 2: The American Revolution and Constitution: Day Activity Goalapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- AP Psychology 2016-2017 Unit Schedule Unit: 14 Social PsychologyDocument5 paginiAP Psychology 2016-2017 Unit Schedule Unit: 14 Social Psychologyapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit VII CalendarDocument1 paginăUnit VII Calendarapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap Review CalendarDocument1 paginăAp Review Calendarapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Calendar and ActivitiesDocument1 paginăCalendar and Activitiesapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- CalendarDocument1 paginăCalendarapi-263241074Încă nu există evaluări
- Cultural Aspects of International Business NegotiationsDocument13 paginiCultural Aspects of International Business NegotiationsYefryParedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretest PhilosophyDocument2 paginiPretest PhilosophyMark Nel Venus100% (2)
- Vygotskys Socio Cultural Theory New LastDocument58 paginiVygotskys Socio Cultural Theory New LastBahay LangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casement The Interiorizing Movement of Logical Life Reflections On Wolfgang GiegerichDocument18 paginiCasement The Interiorizing Movement of Logical Life Reflections On Wolfgang GiegerichLuiz Filipi Marques100% (1)
- Farias 2011 The Politics of Urban Assemblages. SubmissionDocument11 paginiFarias 2011 The Politics of Urban Assemblages. SubmissionJohn_Doe_21Încă nu există evaluări
- Literacy Toolkit GuideDocument26 paginiLiteracy Toolkit GuideDevaki Kirupaharan100% (1)
- Effective Instructional StrategiesDocument19 paginiEffective Instructional StrategiesSheryl Ann Tumacder DionicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Skills and Leadership Performance Nine Critical SkillsDocument16 paginiCognitive Skills and Leadership Performance Nine Critical SkillsSarvesh Deepak KoyandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BLOOM's TaksonomyDocument3 paginiBLOOM's TaksonomyDeky SusantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Tips: How To Use CLIL in The ClassroomDocument2 paginiTeaching Tips: How To Use CLIL in The Classroomalejandra_fares7281100% (1)
- Apollo 13Document6 paginiApollo 13Chitrini ChalmelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inquiry 5e Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 paginiInquiry 5e Lesson Plan Templateapi-488024167100% (1)
- Principles of Teaching 1: A Course Module ForDocument41 paginiPrinciples of Teaching 1: A Course Module ForMark Dave Joven Lamasan AlentonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspects of Scientific Facts HempelDocument86 paginiAspects of Scientific Facts HempelAnonymous LOcT0gjqdSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classroom ManagementDocument91 paginiClassroom ManagementSheila G. DolipasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn or Die Hess en 23264Document5 paginiLearn or Die Hess en 23264albertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phil of Education Matrix PDFDocument2 paginiPhil of Education Matrix PDFmarichu apilado100% (2)
- Wallace SamathaDocument14 paginiWallace SamathaMartin SeidenstickerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bloom Taxonomy LevelsDocument2 paginiBloom Taxonomy LevelsEvelyn TingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why We Must Study EthicsDocument12 paginiWhy We Must Study EthicsStevenzel EstellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypothesisDocument4 paginiHypothesisM Aziz KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindset Elevation BlueprintDocument26 paginiMindset Elevation BlueprintJobsue Camacho100% (1)
- HOTS in Vocational Education - ERIC-Sandra KerkaDocument97 paginiHOTS in Vocational Education - ERIC-Sandra KerkaYessica Mega ApritaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TFTF Team Leaders Bv2-1bDocument24 paginiTFTF Team Leaders Bv2-1bAnonymous GzyRIHiBkN67% (3)
- Exam in Educational TechnologyDocument2 paginiExam in Educational TechnologyMaRvz Nonat MontelibanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra Credit QuestionsDocument5 paginiExtra Credit QuestionsRaahil MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Public Speaking and DebateDocument3 paginiLesson Plan in Public Speaking and Debatejehlo12333% (3)
- Roxburgh, Shelagh - Witchcraft, Violence and Mediation in Africa - A Comparative Study of Ghana and Cameroon (2014)Document256 paginiRoxburgh, Shelagh - Witchcraft, Violence and Mediation in Africa - A Comparative Study of Ghana and Cameroon (2014)Pedro SoaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecp0803334.pdf0t SDocument11 paginiEcp0803334.pdf0t SkotakmeghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 Chapter 2Document35 pagini06 Chapter 2Sagarika DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări