Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Organelle Structure and Function
Încărcat de
Melou Jane Depositario SultonesDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Organelle Structure and Function
Încărcat de
Melou Jane Depositario SultonesDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Organelle Structure and Function
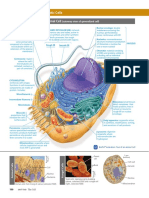
Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures
within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are
called Organelles. The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by
an electron microscope) is called the cell's ultrastructure. Organelles
perform different functions within a cell, and this is called theDivision of
Labour.
Membrane Bound Organelles
The Nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell. It contains a dense structure
called the Nucleolus and is surrounded by the Nuclear Envelope, a structure
composed of two membranes, seperated by fluid, which contain a number of
nuclear pores that can allow relatively large molecules through. The nucleus
contains nearly all of the cell's genetic material.
The Nucleolus creates Ribonucleic Acid and Ribosomes, which then travel
out of the nucleus, through the nuclear pores, to the cytoplasm where they are
involced in Protein Synthesis.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is found near the Nucleas and is made
up of a number of flattened sacs called Cisternae, which are continuous with
the Nuclear Envelope. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is called so
because it has a lot of Ribosomes on its outer surface. The Smooth
Endoplasmic Reticulum however, does not have Ribosomes. The
Roughtransports proteins that are synthesised in the Ribosomes, and
the Smooth synthesises Lipids.
The Golgi Apparatus is a stack of membrane bound flattened sacs,
and are responsible for the modification of proteins received from the ER.
These proteins are then transported in vesicles around the cell.
Lysosomes are membrane bound spherical sacs which
contain digestive enzymes used to break down materials, such as nonself microorganisms engulfed by Phagocytes.
Mitochondria are round double membrane bound
organellesresponsible for Aerobic Respiration. Their inner membrane is
foldedinside to form Cristae, which are folded in the Matrix - the central part
of a Mitochondrion. During Aerobic Respiration, ATP is produced in the
Mitochondria.
Found only in plants and some protoctists, Chloroplasts are responsible
for Photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain two fluid separated
membranes and the inner membrane is folded into a network
offlattened sacs called Thylakoids that are stacked into Grana (one
Granum, two Grana). The Thylakoids contain Chlorophyll in which the
process of Photosynthesis occurs.
Vesicles are membrane bound sacs that are used to store or transport
substances around the cell. Lysosomes are actually Vesicles.
Vacuoles are essentially larger Vesicles, and they are formed by
thejoining together of many Vesicles. They are membrane bound
organelles that have no specific shape and contain water with a number
of different compounds within it. Their function varies greatly
depending on the type of cell they are part of. In plant cells they are
important in maintaining Turgor Pressure.
Non Membrane Bound Organelles
Ribosomes are small spherical organelles, composed of two subunits,
which can be found on the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (and also in the
cytoplasm and in mitochondria, and other places). Ribosomestranslate
genetic information in the form of mRNA into proteins.
Centrioles are microtubules found next to the nucleus of animal cells
and some protoctists. They move Chromosomes around by
formingfibres called Spindle, during cell division.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 6 Cell OrganellesDocument4 pagini6 Cell OrganellesAnna Mae Dollente100% (1)
- Assigment HistologyDocument40 paginiAssigment Histologynurul fatinajihahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 Exocytosis and EndocytosisDocument6 pagini09 Exocytosis and Endocytosisdrhendyjunior100% (1)
- The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument50 paginiThe Cellular Basis of LifeSteve EstebanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFDocument43 paginiDJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFNick_989893Încă nu există evaluări
- Biological ScienceDocument13 paginiBiological Sciencenhoj eca yabujÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicrotubulesDocument39 paginiMicrotubulesAdnan QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pig Heart Dissection Lab - Final PDFDocument15 paginiPig Heart Dissection Lab - Final PDFapi-1127245210% (1)
- Plant CellDocument112 paginiPlant CellAlfonso PlantillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CELL PARTS and PROKARYOTESDocument6 paginiCELL PARTS and PROKARYOTESHarry ParconÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 paginiExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Endosymbiotic TheoryDocument4 paginiEndosymbiotic TheoryJoshi MaitreyeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structures and Functions 02Document22 paginiCell Structures and Functions 02YASMEROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Biology NotesDocument6 paginiCell Biology Notessaadc786100% (1)
- Exocytosis Transport: Diana Nicole Bonilla BarriosDocument6 paginiExocytosis Transport: Diana Nicole Bonilla BarriosclaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant CellDocument19 paginiPlant CellIdasari DewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cilia and Flagella: Structure and Function in EukaryotesDocument10 paginiCilia and Flagella: Structure and Function in EukaryotesEr Purushottam PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument1 paginăCell Membrane and Transport MechanismsAldemer Laron BoretaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions Lesson 1Document33 paginiContemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions Lesson 1shella congeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Globalization: Research QuestionDocument16 paginiGlobalization: Research QuestionFelix, Rysell De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To EcosystemDocument18 paginiIntroduction To EcosystemrizaabduljaleelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant and Animal CellDocument7 paginiPlant and Animal CellHera Lopez100% (1)
- History of ZoologyDocument4 paginiHistory of ZoologyBen Gabriel MaghuyopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Biology Practical 3 PDFDocument11 paginiCell Biology Practical 3 PDFEswaran Singam100% (1)
- Membrane TransportDocument4 paginiMembrane TransportNiharika GhoshalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eukaryotic Cell OrganellesDocument7 paginiEukaryotic Cell OrganellesMary100% (2)
- Life and Works of RizalDocument5 paginiLife and Works of RizalGabrielle Beatrice TroncoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio111 - Mitosis-Mieosis SRDocument11 paginiBio111 - Mitosis-Mieosis SRapi-3009338780% (1)
- Gen Biology Module Lesson 2&3Document13 paginiGen Biology Module Lesson 2&3Albert Jade Pontimayor LegariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.2 Domain Bacteria and Archaea PDFDocument41 pagini11.2 Domain Bacteria and Archaea PDFMazlisya NadhirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 Chemistry of LifeDocument31 paginiTopic 1 Chemistry of LifeHapsah Muhammad100% (1)
- Problem Solving-How To Protect Endangerd SpeciesDocument2 paginiProblem Solving-How To Protect Endangerd Specieshong1988100% (4)
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 paginiProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Cagayan State UniversityDocument4 paginiCagayan State UniversityRexson TagubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument10 paginiDifferences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastAsma Adawiyah Idris100% (1)
- Cytoplasm - Filling Fluid: Cytoplasm Is The Fluid That Fills A Cell. Scientists Used To Call TheDocument5 paginiCytoplasm - Filling Fluid: Cytoplasm Is The Fluid That Fills A Cell. Scientists Used To Call TheSiti Nur ShafiqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsDocument13 pagini8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsEnmuskÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organelle, Descrpition and FunctionDocument2 paginiOrganelle, Descrpition and Functionjahajaha_svensson609Încă nu există evaluări
- Tissue and Tissue Systems - STD 9Document14 paginiTissue and Tissue Systems - STD 9Syamala Natarajan100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function: BiologyDocument69 paginiCell Structure and Function: BiologyAsif Ali100% (1)
- Plant TissuesDocument24 paginiPlant TissuesKen Torres Paycana100% (1)
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument7 paginiCell Organelles WorksheetKenneth ParungaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phylum Porifera, Characteristics and Class ExamplesDocument4 paginiPhylum Porifera, Characteristics and Class ExamplesRobert BarrettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agr122 Lab Report 2Document11 paginiAgr122 Lab Report 2Nur AthirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Federis-3a-Act 1 Ra 1425Document5 paginiFederis-3a-Act 1 Ra 1425Faye Domini FederisÎncă nu există evaluări
- CellDocument32 paginiCellSrinivas Nakka100% (1)
- Phylum Porifera: / P Ɒ R Ɪ F ƏR ƏDocument4 paginiPhylum Porifera: / P Ɒ R Ɪ F ƏR ƏPeterjohn QuimingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesDocument12 paginiAlkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesS JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devl Biol-SpermatogenesisDocument9 paginiDevl Biol-SpermatogenesisSuresh DavuluriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mammalian Histology AssignmentDocument9 paginiMammalian Histology AssignmentSana Sultana100% (1)
- Chloroplast Photosynthesis-FileDocument17 paginiChloroplast Photosynthesis-Filesiguro hwahahahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanism of Loss of Water by PlantsDocument24 paginiMechanism of Loss of Water by PlantsarenaierÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.2 Domain Bacteria and ArchaeaDocument39 pagini11.2 Domain Bacteria and ArchaeaZkdlin SpaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocytosis - Exocytosis16engDocument47 paginiEndocytosis - Exocytosis16engnicole bÎncă nu există evaluări
- CELLSDocument6 paginiCELLSFenny May SebonÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument4 paginiUntitledAbby Joy SeniningÎncă nu există evaluări
- CellDocument5 paginiCellapi-267979304Încă nu există evaluări
- General BiologyDocument14 paginiGeneral BiologybonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making War in The HeavenliesDocument2 paginiMaking War in The HeavenliesMelou Jane Depositario SultonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- In The Presence of AngelsDocument3 paginiIn The Presence of AngelsMelou Jane Depositario SultonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title/name of Instrument: Modified Looping TrackDocument33 paginiTitle/name of Instrument: Modified Looping TrackMelou Jane Depositario SultonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 - ResultDocument4 pagini5 - ResultMelou Jane Depositario SultonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles ReviewDocument19 paginiCell Organelles ReviewJelin VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Bio 6.4-6.6 OutlineDocument5 paginiAP Bio 6.4-6.6 OutlineShivali PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Exam #2Document14 paginiBiology - Exam #2Juliana RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout - Grade 6 Cell - Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument4 paginiHandout - Grade 6 Cell - Fundamental Unit of Lifesuhasacharya117Încă nu există evaluări
- Zoo Lab ActivityDocument1 paginăZoo Lab ActivityHarold DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ukp - Flagella UltrastructureDocument13 paginiUkp - Flagella UltrastructureujjalkrpatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure and Functions ppt-3Document16 paginiCell Structure and Functions ppt-3rajesh duaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Principles of ZoologyDocument41 paginiIntegrated Principles of ZoologyEstherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Comparison ChartDocument3 paginiCell Comparison ChartJake BryantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Act 1 - The CellDocument3 paginiAct 1 - The CellFaith Ann CortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocument3 paginiRajeem Outlaw Wright - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetRajeem Outlaw WrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 paginiCell Organelles Worksheet537777333% (3)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument51 paginiCell Structure and FunctionRaufur Rahman AkandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument21 paginiCell Parts and Their FunctionsJeff Poi50% (2)
- Bio, Plant & Animal CellsDocument6 paginiBio, Plant & Animal CellssparklyhinataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument57 paginiLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam Arya100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function Matching KEYDocument3 paginiCell Structure and Function Matching KEYJustin Lin100% (1)
- Golgi Apparatus - WikipediaDocument17 paginiGolgi Apparatus - WikipediaPrakashananda ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 paginiAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biologia A ColorDocument2 paginiBiologia A ColorJorge Andres Vasquez Avila100% (1)
- Lab 2Document22 paginiLab 2fgnjdgnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science For Grade 7Document6 paginiFinal A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science For Grade 7Kresha LluismaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Golgi Body, Rer & SerDocument8 paginiGolgi Body, Rer & SerZainab ZahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6th Science PDE Worksheet 2018 1 TermDocument5 pagini6th Science PDE Worksheet 2018 1 TermJUAN CARLOS0% (1)
- The Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesDocument1 paginăThe Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesEnrique the ThirdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETDocument18 paginiCell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETsanjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Parts Practice QuizDocument3 paginiCell Parts Practice QuizAnonymous yFS1ZfmBpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neet Pyq Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument4 paginiNeet Pyq Cell - The Unit of LifeAyush DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbio LEC SAS 3Document3 paginiMicrobio LEC SAS 3spooderm4nÎncă nu există evaluări