Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cap 8 Apendice de Unidades y Conversiones PDF
Încărcat de
Angel AriasTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cap 8 Apendice de Unidades y Conversiones PDF
Încărcat de
Angel AriasDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Appendix: Units,
Dimensions and
Conversion Factors
APPENDIX
The system of dimensions and units used in mechanics and
related engineering disciplines are based on Newton's second law of motion, which is force equals mass multiplied by
acceleration, or
F = ma
[A-1]
The above equation can be used with any consistent systems
of units.
Over the past four decades there has been a great deal of
effort to try to make the English unit system have a methodology of practical use that works like the methodology of
practical use of the International System of Units (or SI metric). This involved the creation of "new" artificial terms like
lbf and lbm (and even Nf and Nm) together with g and gc
to adjust equations to one or the other system of units. The
objective ofthis exercise was make the two unit systems "easier" to use. This did not happen. In fact, the exercise allowed
scientists and engineers to avoid learning the two systems
of units properly. In essence, the exercise that created these
artificial units and their associated terms was unnecessary.
To properly understand how to use the two systems of units
it is only necessary to practice the two systems of units side
by side with a simple dynamics problem. The two systems
of units are used in exactly the same manner.
In the English unit system, scientists and engineers define
a pound of force as the force required to accelerate one slug
of mass at the rate of one foot per second per second. One
slug of mass has a weight of approximately 32.2 lb when
acted upon by the acceleration of gravity present at the surface of the earth. Thus, using Equation A-1 in the English
units is
1 lb -- (1 slug)(1
ft./S 2)
Using the above it can be found that
1 slug = 1 l b - s 2
ft.
In SI metric, engineers define a Newton of force as the
force required to accelerate on kilogram of mass at the rate
of one meter per second per second. Thus, Equation A-1 in
the SI metric is
1 N = (1 kg)(1 m / s 2)
English unit system, we simply need to divide the weight by
the acceleration of gravity to determine the object mass. To
determine the weight of an object in the SI metric system
we simply need to multiply the mass by the acceleration of
gravity.
The two systems can be used in all science and engineering calculations. However, often one system is preferred over
another in most problem types (e.g., the SI metric system is
usually preferred for dynamics problems and the English
system of units is usually preferred for strength of materials
problems).
This handbook avoids the use of these artificial terms and
uses these two systems of units in a consistent manner as
described below.
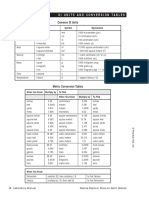
Table A-1 Basic Definitions of the English Unit System
Force
1 lb = 1 slug-ft./s e
Area
1 acre = 43,560 ft.2
Energy
1 Btu = 778 ft.-lb
Flowrate
1 cfs = 448.83 gpm
Length
l f t . = 12in.
lyd =3ft.
1 statute mile -- 5280 ft.
1 nautical mile = 6000 ft.
Mass
I slug = 1 lb-s2/ft.
Power
i hp = 550 ft.-lb/s = 0.708 Btu/sec
Velocity
I mph = 1.467 ft./s
I knot - 1.689 ft./s = 1.152 mph
Volume
i ft. 3 = 7.48 U.S. gal
1 U.S. gal = 231 in. 3 = 0.1337 ft. 3
(8.34 lb of water)
1 British imperial gal = 1.2 U. S. gal
(10 lb of water)
Weight
1 U.S. (short) ton -- 2000 lb
1 British (long) ton = 2240 lb
Using the above, it can be found that
N - sec 2
l k g = l ~
m
The mass units in both systems are made up of force,
length, and time units. The mass unit of either system cannot
be measured directly. On the surface of the earth it is necessary to measure the mutual attraction force between the
mass and the mass of the earth (this force is called weight).
Then knowing the acceleration of gravity on earth, that force
can be converted to the mass unit. The mass units in both
systems are not independent units. They are made up of
pounds, feet, and seconds in the English unit system and N,
m, and sec in the SI metric system.
The English system ofunits is called agravitationalsystem
since it denotes any mass by its weight (i.e., lb). Weight is
a specially named force that is the mutual attraction force
between an object mass and the mass of the earth. The SI
metric system is called an absolute system since it denotes
any mass by its mass unit (i.e., kg). Except for this distinction
between the weight of an object and the mass of an object,
the two systems are used in exactly the same manner in making practical calculations. Both require the measurement of
the weight before the mass unit can be determined. We list
mass in the SI metric system to define an object and we list
weight in the English unit system to define an object. In the
Table A-2 Basic Definitions of the SI Metric System
Force
1 N = 1 kg-m/s 2
Area
1 Hectare (ha) = 104 m 2 = 100 m square
Energy (or work)
1 Joule 0) = 1 N-m
Flowrate
m 3/s - 60,0001 pm
Length
i cm - 10 mm
i m - 100 cm
i km = 1000 m
Mass
I kg = 1000 g
I metric ton = 1000 kg
Power
1 Watt - 1 N-m/s
Velocity
i kph = 1000 m / h r = 0.277 m / s
Volume
i m 3 - 1000 L
1 L - 103 cm
APPENDIX
Table .4-3 Basic quantities in English and SI Metric
English Unit
SI Unit
Acceleration of gravity
32.2 ft./s 2
Density of water (at 39.4~ or 4~
Specific weight of fresh water
Standard sea level atmospheric pressure
API (at 60~
ASME (at 68~
UK (at 60~
Continental Europe (at 15 ~C)
1.94 slug/ft. 3
9.81 m / s 2
1000 k g / m 3
62.4 lb/ft. 3
9810 N / m 3
14.696 psia
14.7 pisa
30.00 in. of Hg
750 m m of Hg
Table .4-4 Other important English and SI Metric Conversions
Engineering gas constant R
English
Metric
Energy
English
Metric
Heat
English
Metric
Temperature
English
Metric
Pressure
English
Metric
Power
English
Metric
Absolute viscosity
English
Metric
Kinematic viscosity
English
Metric
R = 53.36 ft.-lb/lb -~R
R = 29.28 N-m/N-K
1 ft.-lb = 1 lb-ft.
1 N-m = 1 joule (J)
1 Btu = 252 cal (heat required to raise 1.0 lb of water 1.0~
1 cal = 4.187 J(heat required to raise 1.0 g of water 1.0 K)
oR = 459.67 ~ + ~
K = 273.15 + ~
1 lb/ft. 2 = 144 psi
1 Pascal (Pa) = N / m 2
1 horsepower = 550 ft.-lb/s
i watt (W) = 1 J / s (or 1 N-m/sec)
1 lb-s/ft. 2 = 47.88 N - s / m 2
1 Poise (P) = 10 -1 N-s/N 2
I ft. 2/s = 0.0929 m z/s
1 Stroke (St) = 10 -4 mZ/s
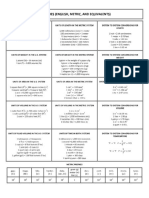
Table A-5 Commonly Used Prefixes for SI Metric Units
Factor by which
unit is multiplied
Prefix
Symbol
1012
109
10 a
103
102
10
10 -1
10 .2
10 .3
10 -a
10 .9
tera
giga
mega
kilo
hecto
deka
deci
centi
milli
micro
nano
T
G
M
k
h
da
d
c
m
g
n
APPENDIX
Table A-6 Alphabetical List of Units (symbols of SI units given in parentheses)
To Convert From
To
Multiply By
abampere
abcoulomb
abfarad
abhenry
abmho
ampere (A)
coulomb (C)
farad (F)
henry (H)
siemens (S)
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
E+01
E+01
E +09
E - 09
E +09
abohm
abvolt
acre-foot (U.S. survey) (1)
acre (U.S. survey) (1)
ampere hour
ohm (~)
volt (V)
meter3 (m3)
meter 2 (m2)
coulomb (C)
1.0
1.0
1.233 489
4.046 873
3.6
E - 09
E - 08
E+03
E+03
E+03
are
angstrom
astronomical unit
atmosphere (standard)
atmosphere (technical = 1 kgf/cm 2)
meter 2 (m2)
meter (m)
meter (m)
pascal (Pa)
pascal (Pa)
1.0
1.0
1.495 979
1.013 250
9.806 650
E+02
E-10
E+11
E+05
E +O4
bar
barn
barrel (for petroleum, 42 gal)
board foot
pascal (Pa)
meter 2 (m2)
meter 3 (m3)
meter 3 (m3)
1.0
1.0
1.589 873
2.359 737
E+05
E - 28
E-01
E - 03
British thermal
British thermal
British thermal
British thermal
British thermal
British thermal
joule
joule
joule
joule
joule
joule
1.055 056
1.055 87
1.054 350
1.059 67
1.054 80
1.054 68
E+03
E+03
E+03
E+03
E+03
E+03
unit
unit
unit
unit
unit
unit
(International Table) (2)
(mean)
(thermochemical)
(39~
(59~
(60~
0)
(J)
(J)
(J)
(J)
(J)
Btu (International Table)-ft./(hr-ft.2-~
(thermal conductivity)
Btu (thermochemical)-ft./(hr-ft.2-~
(thermal conductivity)
Btu (International Table)-in./(hr-ft.2-~
(thermal conductivity)
Btu (thermochemical)-in./(hr-ft.2-~
(thermal conductivity)
Btu (International Table)-in./(s-ft.2-~
(thermal conductivity)
Btu (thermochemical)-in./(s-ft.2-~
(thermal conductivity)
watt per meter kelvin [W/(m.k) ]
1.730 735
E +00
watt per meter kelvin [W/(m.k)]
1.729 577
E +00
watt per meter kelvin [W/(m.k) ]
1.442 279
E-01
watt per meter kelvin [W/(m.k) ]
1.441314
E-01
watt per meter kelvin [W/(m.k) ]
5.192 204
E+02
watt per meter kelvin [W/(m.k) ]
55.188 732
E+02
Btu
Btu
Btu
Btu
(International Table)/hr
(thermochemical)/hr
(thermochemical)/min
(thermochemical)/s
watt
watt
watt
watt
2.930 711
2.928 751
1.757 250
1.054 350
E-01
E-01
E+01
E +03
Btu
Btu
Btu
Btu
Btu
(International Table)/ft. 2
(thermochemical)/ft. 2
(thermochemical) / (ft.2-hr)
(thermochemical) / (ft.2-min)
(thermochemical) / (ft.2-s)
joule per meter 2 (J/m 2)
joule per meter 2 (J/m 2)
watt per meter 2 (W/m 2)
watt per meter 2 (W/m 2)
watt per meter 2 (W/m 2)
1.135 653
1.134 893
3.152 481
1.891489
1.134 893
E+04
E +04
E +00
E+02
E+04
Btu (thermochemical) / (in.2-s)
Btu (International Table) / (hr-ft.2-~
(thermal conductance)
Btu (thermochemical)/(hr-ft.2-~
(thermal conductance)
Btu (International Table) / (s-ft.2-~
Btu (thermochemical) / (s-ff.2-~
watt per meter 2 (W/m 2)
watt per meter 2 kelvin [W/(m2.k) ]
1.634 246
5.678 263
E +06
E +00
watt per meter 2 kelvin [W/(m2.k) ]
5.674466
E +00
watt per meter 2 kelvin [W/(m2.k) ]
watt per meter 2 kelvin [W/(m2.k) ]
2.044175
2.042 808
E +04
E+04
Btu (International Table)/lbm
Btu (thermochemical)/lbm
Btu (International Table)/(lbm-~
(heat capacity)
Btu (thermochemical)/(lbm-~
(heat capacity)
joule per kilogram (J/kg)
joule per kilogram (J/kg)
joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg.K)]
2.326
2.324 444
4.1868
E+03
E+03
E+03
joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg.K) ]
4.184000
E +03
(W)
(W)
(W)
(W)
(continued)
APPENDIX
Table A-6 Alphabetical List of Units (symbols of SI units given in parentheses) (continued)
To Convert From
To
Multiply By
bushel
caliber
calorie
calorie
calorie
(U.S.)
(inch)
(International Table)
(mean)
(thermochemical)
meter 3 (m 3)
meter (m)
joule (J)
joule 0)
joule (J)
3.523 907
2.54
4.186 8
4.190 02
4.184
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
02
02
00
00
00
calorie
calorie
calorie
calorie
calorie
(15~C)
(20~
(kilogram, International Table)
(kilogram, mean)
(kilogram, thermochemical)
joule
joule
joule
joule
joule
4.185 80
4.18190
4.186 8
4.190 02
4.184
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
+
00
00
03
03
03
joule per meter 2 (J/m 2)
joule per kilogram (J/kg)
joule per kilogram (J/kg)
joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg. K) ]
joule per kilogram kelvin [J/(kg. K) ]
4.184
4.186
4.184
4.1868
4.184
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
+
04
03
03
03
03
cal (thermochemical)/min
cal (thermochemical)/s
cal (thermochemical) / (cmZ.min)
cal (thermochemical) / (cruZ.s)
cal (thermochemical) / (cm. s. ~
capture unit (c.u. = 10-3 cm -1)
watt (W)
watt (W)
watt per meter 2 @V/m2)
watt per meter 2 @V/m2)
watt per meter kelvin [W/(m.K)]
per meter (m-l)
6.973 333
4.184
6.973 333
4.184
4.184
1.0
E - 02
E + 00
E + 02
E + 04
E + 02
E-01
carat (metric)
centimeter of mercury (0~
centimeter of water (4~
cenfipoise
cenfistokes
(kg)
pascal (Pa)
pascal (Pa)
pascal second (Pa.s)
meter 2 per second (m2/s)
2.0
1.333 22
9.806 38
1.0
1.0
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
-
circular mil
clo
cup
curie
cycle per second
meter 2 (m 2)
kelvin meter 2 per watt [ (K.m 2)/W]
meter a (m a)
becquerel (Bq)
hertz (Hz)
5.067 075
2.003 712
2.365 882
3.7
1.0
E
E
E
E
E
- 10
- 01
- 04
+ 10
+00
day (mean solar)
day (sidereal)
degree (angle)
second (s)
second (s)
radian (rad)
8.640 000
8.616 409
1.745 329
E + 04
E + 04
E - 02
degree
degree
degree
degree
degree
kelvin (K)
TK = Toc + 273.15
degree Celsius
kelvin (K)
kelvin (K)
Toc = (Toy - 32)/1.8
TK = (ToF + 459.67)/1.8
TK = TOR/1.8
kelvin meter 2 per watt [ (K.m 2)/W]
1.781102
E - 01
cal
cal
cal
cal
cal
(thermochemical)/cm 2
(International Table)/g
(thermochemical)/g
(International Table) / (g.~
(thermochemical) / (g.~
Celsius
centigrade (see degree Celsius)
Fahrenheit
Fahrenheit
Rankine
(J)
(J)
(J)
(J)
(J)
04
03
01
03
06
~F-hr-ft. 2/Btu (International Table)
(thermal resistance)
~
2/Btu (thermochemical)
(thermal resistance)
denier
dyne
dyne-cm
dyne/cm 2
electronvolt
kelvin meter 2 per watt [ (K.m 2)/W]
1.762 250
E - 01
kilogram per meter (kg/m)
newton (N)
newton meter (N.m)
pascal (Pa)
joule 0)
1.111111
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.602 19
E - 07
E - O5
E - O7
E-01
E - 19
EMU
EMU
EMU
EMU
EMU
farad (F)
ampere (A)
volt (V)
henry (H)
ohm (f~)
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
E
E
E
E
E
farad (F)
ampere (A)
volt (V)
henry (H)
ohm (~)
1.112 650
3.335 6
2.997 9
8.987 554
8.987 554
EEE+
E+
E+
ESU
ESU
ESU
ESU
ESU
of capacitance
of current
of electric potential
of inductance
of resistance
of capacitance
of current
of electric potential
of inductance
of resistance
+O9
+ 01
- O8
- O9
- 09
12
10
02
11
11
(continued)
APPENDIX
Table .4-6 Alphabetical List of Units (symbols of SI units given in parentheses) (continued)
To Convert From
To
Multiply By
erg
erg/cm2.s
erg/s
faraday (based on carbon-12)
faraday (chemical)
faraday (physical)
fathom
fermi (femtometer)
fluid ounce (U.S.)
joule (J)
watt per meter 2 (W/m 2)
watt (W)
coulomb (C)
coulomb (C)
coulomb (C)
meter (m)
meter (m)
meter 3 (m 3)
1.0
1.0
1.0
9.648 70
9.649 57
9.65219
1.828 8
1.0
2.957 353
E - 07
E - 03
E - 07
E +04
E+04
E +04
E +00
E-15
E -05
foot
foot (U.S. survey) ~1)
foot of water (39.2 ~
sq ft.
ft.2/hr (thermal diffusivity)
ft.2/s
meter (m)
meter (m)
pascal (Pa)
meter 2 (m 2)
meter 2 per second (m 2/s)
meter 2 per second (m 2/s)
3.048
3.048 006
2.988 98
9.290 304
2.580 640
9.290 304
E-01
E-01
E+03
E - 02
E - 05
E - 02
cu ft. (volume; section modulus)
ft.3/min
ft.3/s
ft.4 (moment of section) (3)
meter 3 (m 3)
m e t e r 3 per second (m3/s)
meter 3 per second (m3/s)
meter 4 (m 4)
2.831685
4.719 474
2.831685
8.630 975
E
E
E
E
ft./hr
ft./min
ft./s
footcandle
footlambert
meter per second (m/s)
meter per second (m/s)
meter per second (m/s)
meter per second 2 ( m / s 2)
lux (lx)
candela per meter 2 (cd/m 2)
8.466 667
5.080
3.048
3.048
1.076 391
3.426 259
E -05
E - 03
E-01
E-01
E+01
E +00
ft.-lb
ft.-lb/hr
ft.-lb/min
ft.-lb/s
free fall, standard (g)
joule (J)
watt (W)
watt (W)
watt (W)
meter per second 2 (m/s 2)
1.355 818
3.766161
2.259 697
1.355 818
9.806 650
E
E
E
E
E
+00
- 04
- 02
+00
+00
cm/s 2
gallon (Canadian liquid)
gallon (U.IC liquid)
gallon (U.S. dry)
gallon (U.S. liquid)
gal (U.S. liquid)/day
gal (U.S. liquid)/min
gal (U.S. liquid)/hp-hr (SFC, specific fuel
consumption)
meter per second 2 (m/s 2)
meter 3 (m 3)
m e t e r 3 (m 3)
m e t e r ~ (m 3)
m e t e r 3 (m 3)
meter 3 per second (m 3/s)
m e t e r ~ per second (m 3/s)
m e t e r 3 per joule (m3/j)
1.0
4.546 090
4.546 092
4.404 884
3.785 412
4.381264
6.309 020
1.410089
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
gamma (magnetic field strength)
gamma (magnetic flux density)
gauss
gilbert
gill (U.K.)
gill (U.S.)
ampere per meter (A/m)
tesla (T)
tesla (T)
ampere (A)
meter 3 (m 3)
meter 3 (m 3)
7.957 747
1.0
1.0
7.957 747
1.420 654
1.182 941
E - 04
E - 09
E - 04
E-01
E - 04
E - 04
grad
grad
grain (1/7000 lbm avoirdupois)
grain (lbm avoirduposis/7000)/gal
(U.S. liquid)
degree (angular)
radian (rad)
kilogram (kg)
kilogram per meter 3 ( k g / m 3)
9.0
1.570 796
6.479 891
1.711806
E-01
E - 02
E - 05
E - 02
gram
g/cm 3
gram-force/cm 2
hectare
horsepower (550 ft.-lbf/s)
kilogram (kg)
kilogram per meter 3 ( k g / m 3)
pascal (Pa)
meter z (m z)
watt (W)
1.0
1.0
9.806 650
1.0
7.456 999
E
E
E
E
E
horsepower (boiler)
horsepower (electric)
horsepower (metric)
watt (W)
watt (W)
watt (W)
9.809 50
7.460
7.354 99
E + 03
E + 02
E + 02
ft./s 2
+
+
+
+
02
04
02
03
02
03
03
03
03
08
05
09
03
03
01
04
02
(continued)
APPENDIX
Table A-6 Alphabetical List of Units (symbols of SI units given in parentheses) (continued)
To Convert From
To
Multiply By
horsepower (water)
horsepower (U.K.)
watt (W)
watt (W)
7.460 43
7.457 0
E + 02
E + 02
hour (mean solar)
hour (sidereal)
hundredweight (long)
hundredweight (short)
second (s)
second (s)
kilogram (kg)
kilogram (kg)
3.600 000
3.590170
5.080 235
4.535 924
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
03
03
01
01
inch
inch
inch
inch
inch
meter (m)
pascal (Pa)
pascal (Pa)
pascal (Pa)
pascal (Pa)
2.54
3.386 38
3.376 85
2.490 82
2.488 4
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
02
03
03
02
02
sq in.
cu in. (volume; section modulus) (4)
in. 3/rain
in. 4 (moment of section) (3)
meter 2 (m 2)
meter~ (m3)
mete~ per second (m 3/s)
meter 4 (m 4)
6.4516
1.638 706
2.731177
4.162314
E - 04
E - 05
E - 07
E-07
in./s
in./s 2
kayser
kelvin
meter per second (m/s)
meter per second 2 (m/s 2)
I per meter (l/m)
degree Celsius
2.54
E - 02
2.54
E - 02
1.0
E + 02
Toc = TK - 273.15
joule (J)
joule (J)
joule (J)
watt (W)
watt (W)
4.186 8
4.190 02
4.184
6.973 333
4.184
E
E
E
E
E
km/h
kilopond
kilowatthour (kW-hr)
kip (1000 lbf)
kip/in. 2 (ksi)
knot (international)
meter per second (m/s)
newton (N)
joule (J)
newton (N)
pascal (Pa)
meter per second (m/s)
2.777 778
9.806 65
3.6
4.448 222
6.894 757
5.144444
E - 01
E + 00
E + 06
E + 03
E + 06
E-01
lambert
lambert
langley
league
light year
liter
candela per meter 2 (cd/m 2)
candela per meter 2 (cd/m 2)
joule per meter 2 (J/m 2)
meter (m)
meter (m)
meter 3 (m 3)
1/x
E+
3.183 099
E+
4.184
E+
(see Footnote 1)
9.46055
E+
1.0 9
E-
maxwell
mho
microinch
microsecond/foot (~s/ft.)
micron
rail
weber (Wb)
siemens (S)
meter (m)
microsecond/meter (~s/m)
meter (m)
meter (m)
1.0
1.0
2.54
3.280 840
1.0
2.54
E
E
E
E
E
E
- 08
+00
- 08
+ 00
- 06
- 05
mile
mile
mile
mile
mile
mile
meter
meter
meter
meter
meter
meter
1.609 344
1.609 3
1.609 347
1.852
1.853184
1.852
E
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
+
+
of mercury (32~
of mercury (60~
of water (39.2~
of water (60~
kilocalorie
kilocalorie
kilocalorie
kilocalorie
kilocalorie
(International Table)
(mean)
(thermochemical)
(thermochemical)/rain
(thermochemical)/s
(international)
(statute)
(U.S. survey) (1)
(international nautical)
(U.K. nautical)
(U.S. nautical)
(m)
(m)
(m)
(m)
(m)
(m)
+
+
+
+
+
03
03
03
01
03
04
03
04
15
03
03
03
03
03
03
03
sq mile (international)
sq mile (U.S. survey) r
mile/hr (international)
mile/hr (international)
mile/rain (international)
mile/s (international)
meter 2 (m 2)
meter 2 (m 2)
meter per second (m/s)
kilometer per hour (kin/h)
meter per second (m/s)
meter per second (m/s)
2.589 988
2.589 998
4.4704
1.609 344
2.682 24
1.609 344
E + 06
E + 06
E-01
E + 00
E + 01
E + 03
millibar
millimeter of mercury (0~
minute (angle)
minute (mean solar)
pascal (Pa)
pascal (Pa)
radian (rad)
second (s)
1.0
1.333 22
2.908 882
6.0
E
E
E
E
+ 02
+ 02
- 04
+01
(continued)
APPENDIX
Table .4-6 Alphabetical List of Units (symbols of SI units given in parentheses) (continued)
To Convert From
To
Multiply By
minute (sidereal)
month (mean calendar)
second (s)
second (s)
5.983617
2.628 000
E + 01
E + 06
oersted
ohm centimeter
ohm circular-rail per ft.
7.957 747
1.0
1.662 426
E + 01
E - 02
E - 03
ounce (avoirdupois)
ounce (troy or apothecary)
ounce (U.K. fluid)
ounce (U.S. fluid)
ounce-force
ozf-in,
ampere per meter (A/m)
ohm meter (tl-m)
ohm millimeter 2 per meter
[(tl-mm2)m]
kilogram (kg)
kilogram (kg)
meter 3 (m 3)
m e t e r ~ (m 3)
newton (N)
newton meter (N.m)
2.834 952
3.110 348
2.841307
2.957 353
2.780139
7.061552
E
E
E
E
E
E
02
02
05
05
01
03
oz (avoirdupois)/gal (U.K. liquid)
oz (avoirdupois)/gal (U.S. liquid)
oz (avoirdupois)/in. 3
oz (avoirdupois)/ft. 2
oz (avoirdupois)/yd 2
parsec
peck (U.S.)
kiligram per
kiligram per
kiligram per
kiligram per
kiligram per
meter (m)
meter ~ (m 3)
6.236 021
7.489152
1.729 994
3.051517
3.390 575
3.085 678
8.809 768
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
-
00
00
03
01
02
16
03
pennyweight
perm (~ (5)
kilogram (kg)
kilogram per pascal
[kg/(Pa. s.m 2) ]
kilogram per pascal
[kg/(Pa. s.m z) ]
kilogram per pascal
[kg/(Pa.s.m) ]
kilogram per pascal
[kg/(Pa. s.m) ]
second meter 2
1.555174
5.72135
E - 03
E - 11
second meter z
5.745 25
E - 11
second meter
1.453 22
E - 12
second meter
1.459 29
E - 12
perm (23~
(5)
perm-in. (0~
perm-in. (23~
(6)
(6)
meter ~ ( k g / m 3)
meter 3 ( k g / m 3)
m e t e r ~ ( k g / m 3)
meter 2 ( k g / m 2)
meter z ( k g / m 2)
phot
pica (printer's)
pint (U.S. dry)
pint (U.S. liquid)
point (printer's)
poise (absolute viscosity)
pound fib)
lumen per meter 2 (lm/m 2)
meter (m)
m e t e r 3 (m 3)
m e t e r ~ (m 3)
meter (m)
pascal second (Pa.s)
newton (N)
1.0
4.217 518
5.506105
4.731765
3.514 598
1.0
4.448 222
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
04
03
04
04
04
01
00
lb/in, z
lb-ft,
lb-ft./in,
lb-in,
lb-in./in,
lb-s/ft, z
lb-ft,
lb-ft. 2
lb-in,
lb-in, z (psi)
pascal (Pa)
newton meter (N.m)
newton meter per meter [ (N.m)/m) ]
newton meter (N.m)
newton meter per meter [ (N.m)/m]
pascal second (Pa.s)
newton per meter (N/m)
pascal (Pa)
newton per meter (N/m)
pascal (Pa)
6.895
1.355 818
5.337 866
1.129 848
4.448 222
4.788 026
1.459 390
4.788026
1.751268
6.894 757
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
00
00
01
01
00
01
01
01
02
03
quart (U.S. dry)
quart (U.S. liquid)
rad (radiation dose absorbed)
rhe
rod
roentgen
meter ~ (m 3)
meter 3 (m 3)
gray (Gy)
1 per pascal second [ 1/(Pa.s) ]
meter (m)
coulomb per kilogram (C/kg)
1.101221
E 9.463 529
E 1.0
E 1.0
E+
(see Footnote 1)
2.58
E -
03
04
02
01
second (angle)
second (sidereal)
section
shake
radian (rad)
second (s)
meter 2 (m 2)
second (s)
4.848137
E - 06
9.972696
E - 01
(see Footnote 1)
1.000 000
E - 08
slug
slug/(ft.-s)
slug/ft. 3
kilogram (kg)
pascal second (Pa. s)
kilogram per meter 3 ( k g / m 3)
1.459 390
4.788 026
5.153 788
E + 01
E + 01
E + 02
statampere
statcoulomb
ampere (A)
coulomb (C)
3.335 640
3.335640
EE-
04
10
10
(continued)
APPENDIX
Table .4-6 Alphabetical List of Units (symbols of SI units given in parentheses) (continued)
To Convert F r o m
To
Multiply By
staffarad
stathenry
statmho
farad (F)
h e n r y (H)
siemens (S)
1.112 650
8.987 554
1.112 650
E - 12
E + 11
E - 12
statohm
statvolt
stere
stilb
stokes (kinematic viscosity)
ohm (f~)
volt (V)
meter 3 (m 3)
candela per meter 2 ( c d / m 2)
meter 2 per second (m 2/s)
8.987 554
2.997 925
1.0
1.0
1.0
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
-
11
02
00
04
04
tablespoon
teaspoon
rex
therm
meter 3 (m 3)
meter 3 (m 3)
kilogram per meter (kg/m)
joule (J)
1.478 676
4.928 922
1.0
1.055 056
E
E
E
E
05
06
06
08
ton
ton
ton
ton
ton
ton
kilogram (kg)
kilogram (kg)
kilogram (kg)
joule 0)
watt (W)
meter 3 (m 3)
2.916667
1.016047
1.0
4.184
3.516 800
2.831685
EE +
E +
E +
E +
E +
02
03
03
09 (12)
03
00
ton (short, 2000 lb)
ton (long)/yd 3
ton ( s h o r t ) / h r
ton-force (2000 lb)
tonne
kilogram (kg)
kilogram per meter 3 ( k g / m 3)
kilogram per second (kg/s)
newton (N)
kilogram (kg)
9.071847
1.328 939
2.519958
8.896 444
1.0
E
E
E
E
E
+
+
+
+
02
03
01
03
03
torr (ram Hg, 0~
township
unit pole
watthour (W-hr)
W.s
W/cm 2
W/in. 2
pascal (Pa)
meter 2 (m 2)
weber (Wb)
joule (J)
joule (J)
watt per meter 2 ( W / m 2)
watt per meter 2 ( W / m 2)
1.333 22
E +
(see Footnote 1)
1.256 637
E 3.60
E+
1.0
E +
1.0
E +
1.550 003
E +
02
07
03
00
04
03
yard
yd 2
yd 3
yd3/min
meter (m)
meter 2 (m 2)
meter ~ (m 3)
meter 3 per second (m3/s)
9.144
8.361274
7.645 549
1.274 258
E
E
E
E
01
01
01
02
year (calender)
year (sidereal)
year (tropical)
second (s)
second (s)
second (s)
3.153600
3.155 815
3.155693
E + 07
E + 07
E + 07
(assay)
(long, 2240 lb)
(metric)
(nuclear equivalent of TNT)
(refrigeration)
(register)
(1) Since 1893 the U.S. basis of length measurement has been derived from metric standards. In 1959 a small refinement was made in the
definition of the yard to resolve discrepancies both in this country and abroad, which changed its length from 3600/3937 m to 0.9144 m
exactly. This resulted in the new value being shorter by two parts in a million. At the same time it was decided that any data in feet derived
from and published as a result of geodetic surveys within the U.S. would remain with the old standard (1 ft. = 1200/3937 m) until further
decision. This foot is named the U.S. survey foot. As a result, all U.S. land measurements in U.S. customary units will relate to the meter by
the old standard. All the conversion factors in these tables for units referenced to this footnote are based on the U.S. survey foot, rather than
the international foot. Conversion factors for the land measure given below may be determined from the following relationships:
I league
1 rod
I chain
I section
I township
=
=
=
=
3 miles (exactly)
161/2 ft. (exactly)
66 ft. (exactly)
1 sq mile
36 sq miles
(2) This value was adopted in 1956. Some of the older International Tables use the value 1.055 04 E + 03. The exact conversion factor is
1.055 055 852 62* E + 03.
(3) This sometimes is called the moment of inertia of a plane section about a specified axis.
(4) The exact conversion factor is 1.638 706 4*E - 05.
(5) Not the same as reservoir "perm."
(6) Not the same dimensions as "millidarcy-foot."
10
APPENDIX
Table .4-7 Conversion Factors for the Vara*
Location
Argentina, Paraguay
Cadiz, Chile, Peru
California, except San Francisco
San Francisco
Central America
Colombia
Honduras
Mexico
Portugal, Brazil
Spain, Cuba, Venezuela, Philippine Islands
Texas
Jan. 26, 1801, to Jan. 27, 1838
Jan. 27, 1838 to June 17, 1919, for surveys of state
land made for Land Office
Jan. 27, 1838 to June 17, 1919, on private surveys
(unless changed to 33-1/3 in. by custom arising to
dignity of law and overcoming former law)
June 17, 1919, to present
Value of Vara
in Inches
34.12
33.37
33.3720
33.0
33.87
31.5
33.0
Conversion Factor,
Varas to Meters
43.0
33.38**
8.666
8.476
8.47649
8.38
8.603
8.00
8.38
8.38O
1.09
8.479
E-01
E-01
E -01
E-01
E-01
E-01
E-01
E-01
E +00
E-01
32.8748
33-1/3
8.350 20
8.466667
E-O1
E-O1
32.8748
8.350 20
E - 01
33-1/3
8.466 667
E - 01
*McElwee, P. G., The Texas Vara, available from commissioner, General Land Office, State of Texas, Austin, Texas (April30, 1940).
Courtesy of Society of Petroleum Engineers.
APPENDIX
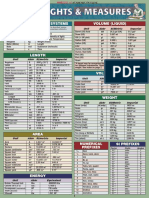
Table A-8 "MemoryJogger"-- Metric Units
"BallPark" Metric Values;
(Do Not Use As
Conversion Factors)
Customary Unit
acre
barrel
British thermal unit
British thermal unit per pound-mass
calorie
cenfipoise
centistokes
darcy
degree Fahrenheit (temperature difference)
dyne per centimeter
foot
cubic foot (cuft)
cubic foot per pound-mass (ff.3/lbm)
square foot (sq ft)
foot per minute
foot-pound-force
foot-pound-force per minute
foot-pound-force per second
horsepower
horsepower, boiler
inch
kilowatthour
mile
ounce (avoirdupois)
ounce (fluid)
pound-force
pound-force per square inch (pressure, psi)
pound-mass
pound-mass per cubic foot
section
ton, long (2240 pounds-mass)
ton, metric (tonne)
ton, short
*Exact equivalents
Courtesy of Society of Petroleum Engineers
4000
0.4
0.16
1000
2300
2.3
4
1"
1"
1
0.5
1"
{ 3o
0.3
0.03
0.06
0.1
0.3
5
1.4
0.02
1.4
75O
10
2.5
3.6*
1.6
28
3O
4.5
7
0.5
16
260
2.6
2.6
1000
1000"
900
square meters
hectare
cubic meter
joules
joules per kilogram
kilojoules per kilogram
joules
millipascal-second
square millimeter per second
square micrometer
kelvin
millinewton per meter
centimeters
meter
cubic meter
cubic meter per kilogram
square meter
meter per minute
millimeters per second
joules
watt
watts
watts (3 kilowatt)
kilowatts
centimeters
megajoules
kilometers
grams
cubic centimeters
newtons
kilopascals
kilogram
kilograms per cubic meter
hectares
million square meters
square kilometers
kilograms
kilograms
kilograms
11
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- SI ConversionsDocument1 paginăSI ConversionskiteflyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Study Weights & Measures PDFDocument4 paginiQuick Study Weights & Measures PDFheysemberg100% (6)
- Guidelines For Operation Assembly Repair Inspection of HM Cargo Tanks June 09 508Document105 paginiGuidelines For Operation Assembly Repair Inspection of HM Cargo Tanks June 09 508paulon9271Încă nu există evaluări
- Farm Calculator PDFDocument3 paginiFarm Calculator PDFJeny SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge Welding Reference Manual FHWA 2019Document346 paginiBridge Welding Reference Manual FHWA 2019Daniel Fernando Atehortua LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Rise of CB WeaponsDocument393 paginiThe Rise of CB Weaponsgraphicimages100% (1)
- Volvo EC55B Compact Excavator Service Repair Manual PDFDocument20 paginiVolvo EC55B Compact Excavator Service Repair Manual PDFjkdmsmemmd75% (4)
- tm35100 A4 PDFDocument3 paginitm35100 A4 PDFaloknayak123100% (1)
- Chicxulub: The Impact and TsunamiDocument146 paginiChicxulub: The Impact and TsunamiArturo KrasniyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Word - Measures - English, Metric, and EquivalentsDocument1 paginăMicrosoft Word - Measures - English, Metric, and EquivalentsLen HebronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Report Los Filos PDFDocument513 paginiTechnical Report Los Filos PDFdavidgaro12Încă nu există evaluări
- Dowel Bar Calculation-06106Document164 paginiDowel Bar Calculation-06106Nguyễn Văn Ban100% (2)
- Testing and Recommended Practices To Improve Nurse Tank Safety, Phase IDocument128 paginiTesting and Recommended Practices To Improve Nurse Tank Safety, Phase IReven JanardharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE DigitalFlow GF868Document163 paginiGE DigitalFlow GF868smab2162094Încă nu există evaluări
- Fssai Form d2Document6 paginiFssai Form d2Sarthak SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 452Document365 pagini452Lincoln RibeiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM Tables ConvertersDocument314 paginiASTM Tables ConvertersVasileios PantouvakisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimation QuestionDocument66 paginiEstimation Questionnikesh25Încă nu există evaluări
- Metric Conversion Guide PDFDocument6 paginiMetric Conversion Guide PDFGuthrie WardÎncă nu există evaluări
- MN PDFDocument78 paginiMN PDFRoberto DominguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 5 MeasurementDocument62 paginiCH 5 MeasurementHarry White100% (1)
- Astm Si 10-2002 PDFDocument69 paginiAstm Si 10-2002 PDFdavidlopesdeoliveira100% (1)
- Engineering Unit Conversion FileDocument27 paginiEngineering Unit Conversion Filevellore2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 301 PDFDocument32 pagini3 301 PDFJusto Paniagua ChampaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measures-English, Metric, and Equivalents PDFDocument1 paginăMeasures-English, Metric, and Equivalents PDFMater DiwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baltic Exchange Dry Cargo ROUTESDocument4 paginiBaltic Exchange Dry Cargo ROUTESVarun Ganesh50% (4)
- PSA Sical Terminal TariffDocument16 paginiPSA Sical Terminal TariffMaharyasa ArdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard CostingDocument24 paginiStandard Costingharsh100% (1)
- Oilfield Units Conversion FactorsDocument11 paginiOilfield Units Conversion FactorsGuru Prasanna VÎncă nu există evaluări
- PP Nomor 35 Tahun 2019Document1.602 paginiPP Nomor 35 Tahun 2019Chandra Ramadhani100% (1)