Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Jantar Mantar Facts
Încărcat de
Sanjana Sujith0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
82 vizualizări19 paginiJantar Mantar Facts, jaipur
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentJantar Mantar Facts, jaipur
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
82 vizualizări19 paginiJantar Mantar Facts
Încărcat de
Sanjana SujithJantar Mantar Facts, jaipur
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 19
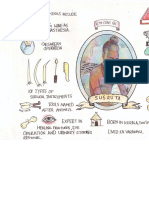
JANTAR MANTAR
Jantar Mantar is a collection
of architectural astronomical
instruments, built by Sawai Jai
Singh in the early 18th century.
Jantar Mantar is combination of
Religion, Science and Art. The
name Jantar Mantar is derived
from Sanskrit Term Yantra
(Instruments) and Mantras
( Formula in this Context
Calculation) Yantra further
changed to Jantar . So Jantar
Mantar translated as Magical
Calculations. Jantar Mantar of
Jaipur was Part of five
Observatories built in New Delhi,
Ujjain, Varanasi, Matura and
Jaipur. The Jantar Mantar of
jaipur is biggest.
The Observatory Consists of
many Giant geometric devices
for measuring time, predicting
eclipses, tracking stars and so
on. . . At old time local
astronomers use it to predict the
weather for farmers, announcing
eclipses and the arrival of
monsoons. The Instruments here
can tell the time with the
accuracy of 2 seconds..
1. Laghu Samrat Yantra (small
sun-dial)
used for time calculation. From
one side wall is inclined at an
angle of 27 which is equivalent
to latitude of jaipur. The left for
time in the morning and right for
afternoon. Both the quadrants
are divided by 6 hrs., 60 min.
and each minute by 60 seconds.
With the help of the shadow of
the gnomon which falls on one
of the quadrants , we find out
the time of jaipur.
Ram Yantra Altitude
instrument
This is an instrument which
helps astronomers to find out
the zenith distance and the
altitude of the sun. It gives us
direct readings. Consists of two
circular stone building. If we
unite them together, it becomes
one instrument. A prependicular
rod is fixed at center of building.
Twelve stone triangles are fixed
above the ground. These
triangular stone slabs are
graduated from 90 degree to 45
degree, while 45 to 0 degree the
graduations are on the circular
wall. This is an instrument by
which we come to know the
movement of stars.
Nadivalaya Yantra Dakshin
Gola (equatorial instrument
southern hemisphere)
21st March and 22nd Sept are
days when sun reaches an
equinox(directly above equator),
21st march-23rd of sept. the Sun
is in northern hemisphere and
23rd sept. - 21st March, the sun
is in southern hemispehere. The
position of sun is calculated by
Narivalya Yantra.
The IST can also be calculated
by this yantra. Local solar time
is read off from the angular
position of the gnomon's shadow
on the dial. From the faint
shadow of the gnomon the local
time is about 11:00.
There are two paired
instruments, one for use in
winter and the other for use in
summer.
Rashivalaya Yantra (zodiac
sign instrument)
Their purpose is to calculate
constellation time rather than
solar time. The advantage of
using sidereal coordinates is that
they depend only on the annual
orbit of the earth around the
sun, not on the earth's daily
rotation.
Sidereal time is measured
relative to the path of earth's
orbit across the heavens. The
path is divided into 12 parts,
each part named after a
constellation that is located
there. The 12 constellations are
called the "Zodiac.
In the Rashivalaya Yantras, each
of the 12 instruments is
associated with one of the 12
signs of the zodiac.
For any given instrument, say
"Pisces", the curved scale of that
instrument lines up with the
(1/12) part of the earths path
that contains the constellation
Pisces. The twelve instruments
actually act as a single
instrument that covers the
entire earths path.
To make an observation, first
choose the instrument that
covers the constellation
currently occupied by the sun
(the Jai Prakash yantra will tell
you). Then, the position of the
gnomon's shadow on the scale
gives the sidereal time - that is,
the celestial longitude of the sun
in sidereal coordinates.
Jai Praksh Yantra
A map of the visible heavens is
inscribed on the inner surface of
the bowls. The shadow of a
small ring, suspended from cross
wires, projects the position of
the sun onto the inscribed
celestial map.
The ring is visible (barely) in this
photograph.
The instrument is made more
useful by cutting out sections in
alternation (like the Ram Yantra),
to allow an observer to make
measurements from the inside.
At night, an observer could sight
through the ring to discover the
position of any star or planet of
interest.
Chakra Yantra (circle
instrument)
Two circular instruments framed
on stone pillars, made of seven
alloys, so that seasons do not
affect the readings, and have
graduated scales from 0 to 360
degree. A hole in the middle to
place another instrument for
observations. The metallic
instruments are free to revolve
paralel to earth's axis, and
points towards the pole.
To find the Meridian Pass Time
and declinition of a particular
planet, a metallic tube whose
extremes are touching the
graduated circle, is placed in the
middle hole of the instrument.
Through this tube we see the
particular celestial object , and
the position on the southern disc
will be indicating Meridian Pass
Time.
Brihat Samrat Yantra (large
sun-dial). In this sun-dial, local
time can be known accurately
upto 2 seconds. The reason they
didnt think of constructing one
where the time could be
accurately calculated upto 1
second is because human eye
cannot see such minor change.
Hence, it would be useless to do
so. This is the largest sun-dial.
The gnomon is 90 feet high and
has recess to wall to protect
from. The gnomon is right
angled wall and the hypotenuse
has steps to climb up. The
hypotenuse has also a scale to
find out the altitude of the sun.
The hypotenuse points towards
the pole On either side of the
pole is masonary quadrant. the
centres of which lie on the edge
of gnomon. The edge of
quadrants are graduated in
hours, minutes and seconds. In
this scale one minute has been
divided to the extent of 30 parts,
this way it is accurate upto 2
seconds.
Yantra Raj (the astrolabe)
It is a circular masonry disc of 7
alloys, so that it remains the
same size. The hole in the
center is the position of Pole
Star. The latitude of Jaipur is 27
degree. The outer circle is
graduated in 24 hours of 6
fractions each. The inner circle
has 360 degrees, each of 6 subdivisions. The most important
planets are marked in outer
circle at their corresponding
position in the sky.
By placing a separate disc in the
hole(which is graduated from 0
degree to 180 degree), of
instrument, we can calculate the
positions of various planets and
dividing by time interval, the
speed of rotation of a particular
planet is calculated .
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Jantar Mantar, JaipurDocument5 paginiJantar Mantar, JaipurAparna Kulshrestha100% (1)
- OlmecDocument190 paginiOlmecdanym9899Încă nu există evaluări
- EscherDocument33 paginiEscherAmva Valle de Aragón100% (1)
- 132 Sanmiguel - Very Long SilenceDocument17 pagini132 Sanmiguel - Very Long SilenceJuariDocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Comparative Literature and Aesthetics, Vol. XXIII, Nos. 1-2, 2000Document179 paginiJournal of Comparative Literature and Aesthetics, Vol. XXIII, Nos. 1-2, 2000Viraj ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Levy, D A - "To Be A Discrepancy in Cleveland"Document25 paginiLevy, D A - "To Be A Discrepancy in Cleveland"Julian West100% (1)
- The Complete Ourang-Outang by de Villo SloanDocument127 paginiThe Complete Ourang-Outang by de Villo SloanMinXusLynxusÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Revolution of 1910 and Its Aftermath: La Muerte de Artemio CruzDocument14 paginiThe Revolution of 1910 and Its Aftermath: La Muerte de Artemio CruzfeskerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surrealist Persona - Max Ernst and LoplopDocument11 paginiSurrealist Persona - Max Ernst and LoplopJeffrey Alester TehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sans Soleil and The Lyotardian Sublime - Sarah FrenchDocument18 paginiSans Soleil and The Lyotardian Sublime - Sarah FrenchRachel Angharad BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- London Bulletin 18-20-1940Document56 paginiLondon Bulletin 18-20-1940juliomcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactives - Exhibitiions - 2006 - America FantasticaDocument7 paginiInteractives - Exhibitiions - 2006 - America FantasticammbasquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Victims of Che Guevara in CubaDocument2 paginiVictims of Che Guevara in CubaIn Linie Dreapta50% (2)
- Chicago Review 47 (4) - 48 (1) 2001-2 Stan Brakhage CorrespondencesDocument211 paginiChicago Review 47 (4) - 48 (1) 2001-2 Stan Brakhage CorrespondencesTomásVonDerOstenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Filliou SamplerDocument19 paginiFilliou SamplerCorpo EditorialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broom Magazine - 1923-Includes A Vitrac Play Among Other ThingsDocument52 paginiBroom Magazine - 1923-Includes A Vitrac Play Among Other ThingsthephantomoflibertyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Meaning of ShapesDocument3 paginiThe Meaning of Shapesapi-235022204Încă nu există evaluări
- The Guarantor of Chance-Surrealism's Ludic Practices by Susan LaxtonDocument17 paginiThe Guarantor of Chance-Surrealism's Ludic Practices by Susan LaxtonArkava DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brion, Rofel - English Lessons Towards The Aesthetics of The Contemporary Filipino Novel in EngliDocument16 paginiBrion, Rofel - English Lessons Towards The Aesthetics of The Contemporary Filipino Novel in EngliIan Rosales Casocot100% (1)
- A Private Revolution Alejandra Pizarniks PDFDocument19 paginiA Private Revolution Alejandra Pizarniks PDFCarlos MascioniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haveth Childers EverywhereDocument42 paginiHaveth Childers EverywhereccapersÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lonely Voice2Document11 paginiThe Lonely Voice2Bruna CarmelinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Martin CarterDocument3 paginiMartin CarterroughisleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lionel Ziprin - FriezeDocument6 paginiLionel Ziprin - FriezeScott MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impressions Africa PDFDocument26 paginiImpressions Africa PDFNicholas Jeffries0% (1)
- The Flame Is OursDocument333 paginiThe Flame Is OursRyan MurrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dechirures, Joyce MansourDocument1 paginăDechirures, Joyce MansourpossesstrimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anoedipal Fiction - Schizo Analysis and The Black DahliaDocument43 paginiAnoedipal Fiction - Schizo Analysis and The Black DahliaAline SanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meek'S Cutoff: Official SelectionDocument21 paginiMeek'S Cutoff: Official SelectionJorge RicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CGH MexManuscripts. OCRDocument23 paginiCGH MexManuscripts. OCRDiosEolo100% (1)
- Dealing With Concerns About Library ResourcesDocument4 paginiDealing With Concerns About Library ResourcesMichael BrocatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jack The Ripper ManualDocument51 paginiJack The Ripper ManualNewMaxx0% (1)
- Readings of Jakob Von Uexküll and Juri LotmanDocument7 paginiReadings of Jakob Von Uexküll and Juri LotmanDavid Terrazas TelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Camera Graeca Photographs Narratives Materialities 2015Document396 paginiCamera Graeca Photographs Narratives Materialities 2015Renan Falcheti PeixotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crypt of Cthulhu #57Document29 paginiCrypt of Cthulhu #57arnaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1945 - A Break With The PastDocument317 pagini1945 - A Break With The PastSlovenianStudyReferences100% (11)
- The North American Book of the Dead Part IIDocument11 paginiThe North American Book of the Dead Part IIDean InksterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waiata 119Document2 paginiWaiata 119alexanderbisleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- W. Dennison - Ch. R. Morey, Studies in East Christian and Roman Art, New York - London 1918Document350 paginiW. Dennison - Ch. R. Morey, Studies in East Christian and Roman Art, New York - London 1918diadass100% (1)
- Monk Ambrosio On Freud's SofaDocument14 paginiMonk Ambrosio On Freud's Sofaantónio_gomes_47Încă nu există evaluări
- Jacques Lizot - Tales of The YanomamiDocument215 paginiJacques Lizot - Tales of The Yanomamialexandra50% (2)
- Chicago Trial Transcript, People v. Lenny BruceDocument418 paginiChicago Trial Transcript, People v. Lenny BruceMeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manuel Maples Arce Salvador Novo and The Origin of Mexican Vanguard AutobiographiesDocument19 paginiManuel Maples Arce Salvador Novo and The Origin of Mexican Vanguard AutobiographiesLaura R QcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sun Also Critical InsightsDocument13 paginiSun Also Critical InsightsRebecca RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Town History: HISTORY OF KUTNÁ HORADocument6 paginiTown History: HISTORY OF KUTNÁ HORAACBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samuel Delany, Samuel R. Delany-Times Square Red, Times Square Blue (2001)Document223 paginiSamuel Delany, Samuel R. Delany-Times Square Red, Times Square Blue (2001)Ribamar OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Borges y Los JudíosDocument43 paginiBorges y Los JudíosEnrique Martínez Ruiz100% (1)
- Across The Wounded Galaxies - Interviews With Contemporary American Science Fiction Writers (1990)Document277 paginiAcross The Wounded Galaxies - Interviews With Contemporary American Science Fiction Writers (1990)Jim Jones100% (4)
- Rose Corral - Ficciones Limítrofes: Seis Estudios Sobre Narrativa Hispanoamericana de VanguardiaDocument13 paginiRose Corral - Ficciones Limítrofes: Seis Estudios Sobre Narrativa Hispanoamericana de VanguardiaAndrea Abarca OrozcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MacDiarmid & PoundDocument15 paginiMacDiarmid & PoundGordon LoganÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Charles Eliot Norton Lectures, 45) Umberto Eco - Six Walks in The Fictional Woods-Harvard University Press (1995)Document161 pagini(Charles Eliot Norton Lectures, 45) Umberto Eco - Six Walks in The Fictional Woods-Harvard University Press (1995)demestradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Against the Current: The Story of the Surrealist Group of CzechoslovakiaDocument10 paginiAgainst the Current: The Story of the Surrealist Group of CzechoslovakiaSarah Andrews McNeilÎncă nu există evaluări
- GREEK CLUB OF ADDIS ABABA "Olympiakos"Document19 paginiGREEK CLUB OF ADDIS ABABA "Olympiakos"papadopoulos sarantisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pike - The City PDFDocument9 paginiPike - The City PDFEunice Garcia GÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 An Interview With Manuel PuigDocument8 pagini4 An Interview With Manuel Puigapi-26422813Încă nu există evaluări
- Vol52 2 2017 Art13Document3 paginiVol52 2 2017 Art13gaurnityanandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jantar Mantar Perlus AddendumDocument9 paginiJantar Mantar Perlus AddendummaripakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE Assignment ON Jantar Mantar: Arya College of Engineering and I.T. JaipurDocument15 paginiTHE Assignment ON Jantar Mantar: Arya College of Engineering and I.T. JaipurharshabidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jantar Mantar Location of Jantar MantarDocument9 paginiJantar Mantar Location of Jantar MantarShobhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Horse Leg AnatomyDocument1 paginăHorse Leg AnatomySanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Profit To EarningsDocument7 paginiProfit To EarningsSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhopal FactsDocument6 paginiBhopal FactsSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mandu FactsDocument4 paginiMandu FactsSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Susruta A Brief SummaryDocument1 paginăSusruta A Brief SummarySanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- History: Vidyadhara(s) Literally "WisdomDocument6 paginiHistory: Vidyadhara(s) Literally "WisdomSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Project RocketDocument1 paginăSchool Project RocketSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gwalior Facts: Kachhwaha Clan of The EighthDocument7 paginiGwalior Facts: Kachhwaha Clan of The EighthSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bijapur Facts History Barah KamanDocument3 paginiBijapur Facts History Barah KamanSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP - Unkown Tourist PlacesDocument53 paginiMP - Unkown Tourist PlacesSanjana Sujith0% (1)
- Junagarh FactsDocument14 paginiJunagarh FactsSanjana Sujith100% (1)
- Agra FactsDocument7 paginiAgra FactsSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nahargarh FactsDocument15 paginiNahargarh FactsSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hawa Mahal FactsDocument6 paginiHawa Mahal FactsSanjana SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moto E User Manual English US InternationalDocument68 paginiMoto E User Manual English US InternationalAtul GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ups Apc Bx600ci User ManualDocument10 paginiUps Apc Bx600ci User ManualSindhu SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nature of The UniverseDocument15 paginiNature of The Universeafifah_rabbaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 Physics Assignment 2 Gravitational Fields and Satellite MotionDocument6 paginiA2 Physics Assignment 2 Gravitational Fields and Satellite MotionJonny Muljadi100% (1)
- Lesson AstronomyDocument3 paginiLesson AstronomyPepito ManlolokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquarian AgeDocument11 paginiAquarian AgeAnna Nagy100% (2)
- T G 1664208053 Latitude and Longitude Crossword Ver 4Document2 paginiT G 1664208053 Latitude and Longitude Crossword Ver 4rosinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCN C e PDFDocument121 paginiHCN C e PDFkalim mahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 000 Equinox and Solstice in UT + T PDFDocument80 pagini000 Equinox and Solstice in UT + T PDFAnonymous r57d0G100% (1)
- M002-Cartesian State Vectors To Keplerian Orbit ElementsDocument2 paginiM002-Cartesian State Vectors To Keplerian Orbit ElementsFaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zodiac: EclipticDocument5 paginiZodiac: EclipticsicavelicuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eclipses: "Hot Spot"Document6 paginiEclipses: "Hot Spot"Aycan ÖzenbaşÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celestial Mechanics With MatlabDocument151 paginiCelestial Mechanics With MatlabEyjay Samson100% (2)
- NOAA Solar Calculations YearDocument36 paginiNOAA Solar Calculations YearAnonymous ycf68kf2x8Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy Assignment 2Document4 paginiPhy Assignment 2Amanjot KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lunar Eclipses and Solar Eclipses: What Is An Eclipse?Document3 paginiLunar Eclipses and Solar Eclipses: What Is An Eclipse?Amman AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- SwephprgDocument94 paginiSwephprgAbhisekAcharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JpsDocument4 paginiJpsIshanSaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions For The BOAA Competition Paper April 2015 Revised PDFDocument4 paginiSolutions For The BOAA Competition Paper April 2015 Revised PDFAvik DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celestial Sphere and Equinoctial System of CoordinatesDocument9 paginiCelestial Sphere and Equinoctial System of CoordinatesVibhav KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Which Way Does The Earth Spin Clockwise or AnticlockwiseDocument3 paginiWhich Way Does The Earth Spin Clockwise or Anticlockwiseklatifdg100% (1)
- Ayanaamsa by HariprasadDocument11 paginiAyanaamsa by HariprasadGarga100% (1)
- SETS DO-01A Plan and Conduct A Passage - Celestial NavigationDocument40 paginiSETS DO-01A Plan and Conduct A Passage - Celestial NavigationOsmar Lerma100% (1)
- 1a-Orbital ParametersDocument19 pagini1a-Orbital ParametersMehaboob MujawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2 Exploring The Celestial GlobeDocument4 paginiLab 2 Exploring The Celestial GlobeKIPNGENO EMMANUEL100% (2)
- Rotation and RevolutionDocument9 paginiRotation and Revolutionaditya senÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Undergraduate Lecture Notes in Physics) Giulio Magli (Auth.) - Archaeoastronomy - Introduction To The Science of Stars and Stones-Springer International Publishing (2016)Document253 pagini(Undergraduate Lecture Notes in Physics) Giulio Magli (Auth.) - Archaeoastronomy - Introduction To The Science of Stars and Stones-Springer International Publishing (2016)Edwin Rolando Asmat Vasquez100% (1)
- Kepler's Laws of Planetary MotionDocument4 paginiKepler's Laws of Planetary MotionWorldWideMirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scale of the Solar System AssignmentDocument1 paginăScale of the Solar System AssignmentYang Woo SeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- AstronomyDocument158 paginiAstronomyBeyondlessÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Solar EclipseDocument1 paginăA Solar EclipseMia Farah KamilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Eclipses and Earth RotationDocument574 paginiHistorical Eclipses and Earth Rotationpecinta dakwah IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1104)
- Mercury in Retrograde: And Other Ways the Stars Can Teach You to Live Your Truth, Find Your Power, and Hear the Call of the UniverseDe la EverandMercury in Retrograde: And Other Ways the Stars Can Teach You to Live Your Truth, Find Your Power, and Hear the Call of the UniverseEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- The Accelerating Universe: Infinite Expansion, the Cosmological Constant, and the Beauty of the CosmosDe la EverandThe Accelerating Universe: Infinite Expansion, the Cosmological Constant, and the Beauty of the CosmosEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (25)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDe la EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityÎncă nu există evaluări
- When the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyDe la EverandWhen the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (7)
- Believing Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithDe la EverandBelieving Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (32)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDe la EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2193)
- Across the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsDe la EverandAcross the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginning and the End of Everything: From the Big Bang to the End of the UniverseDe la EverandBeginning and the End of Everything: From the Big Bang to the End of the UniverseEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (61)
- The Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodDe la EverandThe Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Under Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseDe la EverandUnder Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (16)
- The Varieties of Scientific Experience: A Personal View of the Search for GodDe la EverandThe Varieties of Scientific Experience: A Personal View of the Search for GodEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (272)
- You Are Here: A Portable History of the UniverseDe la EverandYou Are Here: A Portable History of the UniverseEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (30)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)De la EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (155)
- The Astrology Dictionary: Cosmic Knowledge from A to ZDe la EverandThe Astrology Dictionary: Cosmic Knowledge from A to ZEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- The Extraterrestrial Species Almanac: The Ultimate Guide to Greys, Reptilians, Hybrids, and NordicsDe la EverandThe Extraterrestrial Species Almanac: The Ultimate Guide to Greys, Reptilians, Hybrids, and NordicsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (37)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDe la EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (75)
- The Book of the Moon: A Guide to Our Closest NeighborDe la EverandThe Book of the Moon: A Guide to Our Closest NeighborEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (11)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDe la EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)
- An Astrological Study Of Psychological ComplexesDe la EverandAn Astrological Study Of Psychological ComplexesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (12)