Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Duhamel's Integral
Încărcat de
ponjoveDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Duhamel's Integral
Încărcat de
ponjoveDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Duhamel's integral - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Page 1 of 3
Duhamel's integral
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In theory of vibrations, Duhamel's integral is a way of calculating the response of linear systems and
structures to arbitrary time-varying external excitations.
Contents
1 Introduction
1.1 Background
1.2 Conclusion
2 See also
3 References
4 External links
Introduction
Background
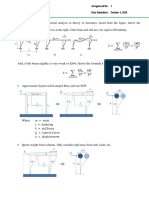
The response of a linear, viscously damped single-degree of freedom (SDF) system to a time-varying
mechanical excitation p(t) is given by the following second-order ordinary differential equation
where m is the (equivalent) mass, x stands for the amplitude of vibration, t for time, c for the viscous
damping coefficient, and k for the stiffness of the system or structure.
If a system is initially rest at its equilibrium position, from where it is acted upon by a unit-impulse at
the instance t=0, i.e., p(t) in the equation above is a delta function (t),
, then by
solving the differential equation one can get a fundamental solution (known as a unit-impulse response
function)
where
is called the damping ratio of the system, n is the natural circular frequency of the
undamped system (when c=0) and
is the circular frequency when damping effect is
taken into account (when
). If the impulse happens at t= instead of t=0, i.e. p(t) = (t ), the
impulse response is
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duhamel's_integral
11/14/2007
Duhamel's integral - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Page 2 of 3
Conclusion
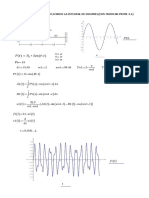
Regarding the arbitrarily varying excitation p(t) as a superposition of a series of impulses:
then it is known from the linearity of system that the overall response can also be broken down into the
superposition of a series of impulse-responses:
Letting
, and replacing the summation by integration, the above equation is strictly valid
Substituting the expression of h(t-) into the above equation leads to the general expression of
Duhamel's integral
See also
Duhamel's principle
References
Ni Zhenhua, Mechanics of Vibrations, Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, Xi'an, 1990 (in Chinese)
R. W. Clough, J. Penzien, Dynamics of Structures, Mc-Graw Hill Inc., New York, 1975.
Anil K. Chopra, Dynamics of Structures - Theory and applications to Earthquake Engineering,
Pearson Education Asia Limited and Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, 2001
Leonard Meirovitch, Elements of Vibration Analysis, Mc-Graw Hill Inc., Singapore, 1986
External links
Duhamel's formula (http://tosio.math.toronto.edu/wiki/index.php/Duhamel's_formula) at
"Dispersive Wiki".
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duhamel%27s_integral"
Categories: Mechanics | Structural analysis | Integrals
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duhamel's_integral
11/14/2007
Duhamel's integral - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Page 3 of 3
This page was last modified 23:02, 18 October 2007.
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free
Documentation License. (See Copyrights for details.)
Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia
Foundation, Inc., a U.S. registered 501(c)(3) tax-deductible
nonprofit charity.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duhamel's_integral
11/14/2007
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Algebraic Methods in Statistical Mechanics and Quantum Field TheoryDe la EverandAlgebraic Methods in Statistical Mechanics and Quantum Field TheoryÎncă nu există evaluări
- EBB 01 FrontCover 30May2013.Doc - Earthquakebehaviour06172017025353283Document69 paginiEBB 01 FrontCover 30May2013.Doc - Earthquakebehaviour06172017025353283МембранингСтудиоÎncă nu există evaluări
- ModesDocument6 paginiModesPuneet Sharma100% (1)
- H2.4.10-Response To Step and Ramp ForcesDocument4 paginiH2.4.10-Response To Step and Ramp ForcesMD NayeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampleproblems FEDocument6 paginiSampleproblems FEnial69100% (1)
- Exercises 1 Continuum MechanicsDocument2 paginiExercises 1 Continuum MechanicsankurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Vibration of SDF SystemsDocument14 paginiFree Vibration of SDF Systemspattrapong pongpattraÎncă nu există evaluări
- IL For Indeterminate Structures7-37Document37 paginiIL For Indeterminate Structures7-37Nirjhor KabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- StodolaDocument3 paginiStodolaGlenda HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duhamel's IntegralDocument5 paginiDuhamel's IntegralMichael Bautista Baylon0% (1)
- Structural Dynamics - Mock ExamDocument4 paginiStructural Dynamics - Mock Examgen ridanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Response of Structures To DynaDocument61 paginiChapter 3 Response of Structures To DynaSayyadh Rahamath BabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework On Dynamics of StrucutresDocument2 paginiHomework On Dynamics of StrucutresShahidul Islam ShahariarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 33Document13 paginiLec 33sknlndsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCE2010Document500 paginiCCE2010stefancuandreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effect of Shear Deformations On The Elastic Critical Column LoadDocument5 paginiThe Effect of Shear Deformations On The Elastic Critical Column Loadashok paul100% (1)
- Energy Based Seismic - Design Methodlogy For RCC StructuresDocument4 paginiEnergy Based Seismic - Design Methodlogy For RCC StructuresBijay banÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Response To Harmonic & Impulsive LoadingDocument14 pagini02 Response To Harmonic & Impulsive LoadingMar MartillanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- And, If The Beam Rigidity Is Very Weak or EI 0, Derive The FormulaDocument6 paginiAnd, If The Beam Rigidity Is Very Weak or EI 0, Derive The FormulaFely TambeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2005 Ibarra, Medina y Krawinkler PDFDocument23 pagini2005 Ibarra, Medina y Krawinkler PDFLuis Gibran Urenda JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cdnj04820enc 001Document362 paginiCdnj04820enc 001Oscar CcamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics of Rotating Machines: Solution ManualDocument116 paginiDynamics of Rotating Machines: Solution ManualHassen M OuakkadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strain Energy Density FunctionDocument35 paginiStrain Energy Density Functionsamir_ssh7151Încă nu există evaluări
- A.MAULANA MALIK MH Dinamika Struktur c10Document6 paginiA.MAULANA MALIK MH Dinamika Struktur c10Maulana MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Dynamics & Earthquake EngineeringDocument34 paginiStructural Dynamics & Earthquake EngineeringHema Chandra Reddy Karimireddy100% (1)
- DSLL1Document53 paginiDSLL1simon maaaklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework4 PDFDocument2 paginiHomework4 PDFRodolfo Angel Carrillo VelasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systems With Distributed Mass and ElasticityDocument59 paginiSystems With Distributed Mass and ElasticityAhmet TükenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Damy J Soil Stresses Under A Polygonal Area Uniformly Loaded PDFDocument3 paginiDamy J Soil Stresses Under A Polygonal Area Uniformly Loaded PDFMartin CgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preliminary Report Mexico2017 v9Document20 paginiPreliminary Report Mexico2017 v9Ghiff FaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automated Solar Powered Pumping Systems For IrrigationDocument10 paginiAutomated Solar Powered Pumping Systems For IrrigationfarizalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorials 7635839 002824 27531Document1 paginăTutorials 7635839 002824 27531zentex2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Presentacion Dos ANIL K CHOPRADocument35 paginiPresentacion Dos ANIL K CHOPRARafhael Andres Luna TeznaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear Wall - CouplingDocument6 paginiShear Wall - CouplingZack JspÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plate Theory Slides From WEB PDFDocument20 paginiPlate Theory Slides From WEB PDFHarish ShridharamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bending of Plates - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 paginiBending of Plates - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadidodido_67Încă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Performance of A 3D Full Scale HDocument27 paginiSeismic Performance of A 3D Full Scale HPravasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Galerkin MethodsDocument7 paginiGalerkin MethodsM sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document109 paginiChapter 2Muaz HararÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 2Document7 paginiHomework 2Chinny LyheangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework2 PDFDocument2 paginiHomework2 PDFRobin Robertson100% (1)
- Solucion de La Integral de Duhamel Con MathcadDocument3 paginiSolucion de La Integral de Duhamel Con MathcadLuis Ciriaco Molina100% (1)
- ST1 Manuel en Version 23Document327 paginiST1 Manuel en Version 23Ashutosh Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poutres Continues CaquotDocument30 paginiPoutres Continues CaquotKadourSelloumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Exam 1 - QuestionsDocument8 paginiTerm Exam 1 - Questionsamadeus135Încă nu există evaluări
- 08 Plasticity 03 Yield CriteriaDocument21 pagini08 Plasticity 03 Yield Criteria한종훈100% (1)
- 2019 - (Salem Et Al) - Seismic Loading On Cantilever Retaining Walls Full-Scale Dynamic AnalysisDocument20 pagini2019 - (Salem Et Al) - Seismic Loading On Cantilever Retaining Walls Full-Scale Dynamic AnalysisHarsha TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil GeomechanicsAndStructuresDocument64 paginiCivil GeomechanicsAndStructuresJOE G PHILIP CEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Chopra4Document1 paginăDynamic Chopra4Mehdi Rahmati0% (1)
- KH4434-Kuliah 003 - 1718 OmbakDocument27 paginiKH4434-Kuliah 003 - 1718 OmbakAmira SyazanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Lecture - 2 - Updated) Dynamics of Structures Chapter 2 PDFDocument37 pagini(Lecture - 2 - Updated) Dynamics of Structures Chapter 2 PDFMasood AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stability Coefficients For Earth SlopesDocument25 paginiStability Coefficients For Earth SlopesDaniel Felipe Rodriguez RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- M17 - CHOPRA - Dinamica - Systems With Distributed Mass and ElasticityDocument32 paginiM17 - CHOPRA - Dinamica - Systems With Distributed Mass and ElasticityRocío Alvarez Jiménez100% (1)
- 9A21702 Vibrations and Structural DynamicsDocument4 pagini9A21702 Vibrations and Structural DynamicssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Aspects of Dam Design PDFDocument12 paginiSeismic Aspects of Dam Design PDFAlokÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH2Document4 paginiMATH2Rondio LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vibration Under General Forcing ConditionsDocument23 paginiVibration Under General Forcing ConditionsJuan Paulo Mayor0% (1)
- Unit I PDFDocument15 paginiUnit I PDFarunachelamÎncă nu există evaluări
- NPTEL - Mechanical Engineering - Vibration ControlDocument10 paginiNPTEL - Mechanical Engineering - Vibration Control8104772799Încă nu există evaluări
- Questions For InvestmentDocument113 paginiQuestions For InvestmentElfin AntoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flat Plate System s0733-9445 (2009)Document2 paginiFlat Plate System s0733-9445 (2009)ponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erudrna PaperDocument15 paginiErudrna PaperponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cover 3Document1 paginăCover 3ponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 California Code of Regulations, TitleDocument1 pagină5 California Code of Regulations, TitleponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope and Administration - . - . - 3: CHAPTER 2 DEFINITIONS - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . 35Document4 paginiScope and Administration - . - . - 3: CHAPTER 2 DEFINITIONS - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . 35ponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memorandum: From: TJC and Associates, Inc. Date: March, 2014 Subject: Seismic Anchorage Submittals ChecklistDocument2 paginiMemorandum: From: TJC and Associates, Inc. Date: March, 2014 Subject: Seismic Anchorage Submittals ChecklistponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tek 12-03CDocument16 paginiTek 12-03CponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Upgrade of Fault Crossing Water Pipelines Using Large Diameter Earthquake Resistant Ductile Iron PipeDocument12 paginiSeismic Upgrade of Fault Crossing Water Pipelines Using Large Diameter Earthquake Resistant Ductile Iron PipeponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Viscous Damper Based Seismic RetroDocument18 paginiFluid Viscous Damper Based Seismic RetroponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applsci 10 06883Document19 paginiApplsci 10 06883ponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- A07 UsersTroubleDocument4 paginiA07 UsersTroubleponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opensees Command Language Manual: Open System For Earthquake Engineering Simulation (Opensees)Document465 paginiOpensees Command Language Manual: Open System For Earthquake Engineering Simulation (Opensees)bobyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A5 StructModeling 2010Document39 paginiA5 StructModeling 2010ponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remember Opensees Is A Software Framework?: Getting Started With OpenseesDocument12 paginiRemember Opensees Is A Software Framework?: Getting Started With OpenseesponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation GuideDocument1 paginăInstallation GuideponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Sees Command Language ManualDocument451 paginiOpen Sees Command Language ManualSelene Cárdenas RodríguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reliability and Sensitivity Analysis in OpenseesDocument15 paginiReliability and Sensitivity Analysis in OpenseesponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peer / Nees Opensees Days 2010: Simulation in Earthquake EngineeringDocument12 paginiPeer / Nees Opensees Days 2010: Simulation in Earthquake EngineeringponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opensees Workshop Sept 2 and 3, 2010Document14 paginiOpensees Workshop Sept 2 and 3, 2010ponjoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Four Quartets: T.S. EliotDocument32 paginiFour Quartets: T.S. Eliotschwarzgerat00000100% (1)
- Ocular Trauma - BantaDocument211 paginiOcular Trauma - BantaLuisa Fernanda Arboleda100% (1)
- 01 Childrenswear Safety Manual 2009 - ClothingDocument57 pagini01 Childrenswear Safety Manual 2009 - Clothingmorshed_mahamud705538% (8)
- AEC 34 - ACB Assignment: Module 1: Problem 1-1.TRUE OR FALSEDocument5 paginiAEC 34 - ACB Assignment: Module 1: Problem 1-1.TRUE OR FALSEDrew BanlutaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phyto Pharmacy: Current Concepts and GMP NormsDocument22 paginiPhyto Pharmacy: Current Concepts and GMP NormsSunitha Katta100% (1)
- Ingles - 1 - Bach - Modulo - 2 (20 - 21)Document32 paginiIngles - 1 - Bach - Modulo - 2 (20 - 21)John Alex Almeida50% (2)
- 08 BQ - PADSB - Elect - P2 - R2 (Subcon Empty BQ)Document89 pagini08 BQ - PADSB - Elect - P2 - R2 (Subcon Empty BQ)Middle EastÎncă nu există evaluări
- E. What Was The Chinese POW Death Rate in WW2 and The Second Sino-Japanese WarDocument3 paginiE. What Was The Chinese POW Death Rate in WW2 and The Second Sino-Japanese WarPamela SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4612 4621 Vitamin D Supplementation For Osteoporosis in Older AdultsDocument10 pagini4612 4621 Vitamin D Supplementation For Osteoporosis in Older AdultsMohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular System NotesDocument6 paginiMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Management Software Director in Austin TX Resume Chad ThreetDocument2 paginiProduct Management Software Director in Austin TX Resume Chad ThreetChad ThreetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis MaltaDocument6 paginiThesis Maltaaprilwbndsouthbend100% (2)
- Entrance 2021: Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Uran AkademiDocument2 paginiEntrance 2021: Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Uran Akademird meshramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alma Matter SpeechDocument1 paginăAlma Matter Speechlariza gallegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentialequations, Dynamicalsystemsandlinearalgebra Hirsch, Smale2Document186 paginiDifferentialequations, Dynamicalsystemsandlinearalgebra Hirsch, Smale2integrationbyparths671Încă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 Mock 1Document11 paginiGrade 8 Mock 1yutika GhuwalewalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- World War 1 NotesDocument2 paginiWorld War 1 NotesSoarSZNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anilkumar Surendran 3-AdDocument4 paginiAnilkumar Surendran 3-AdAnil AmbalapuzhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics For EconomicsDocument58 paginiStatistics For EconomicsKintu GeraldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prayer For Protection PDFDocument3 paginiPrayer For Protection PDFtim100% (1)
- Opening StrategyDocument6 paginiOpening StrategyashrafsekalyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viva Questions For Even SemestersDocument22 paginiViva Questions For Even SemestersSiddhanta DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TTD Accommodation ReceiptDocument2 paginiTTD Accommodation ReceiptDharani KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2Document31 paginiDrinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2josephsedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock MeetingDocument2 paginiMock MeetingZain ZulfiqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GMN RodamientosDocument51 paginiGMN RodamientosJayÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCU II Open Protocol Communication Manual FV 9 10 31 08 PDFDocument17 paginiRCU II Open Protocol Communication Manual FV 9 10 31 08 PDFAndrés ColmenaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Income Tax - MidtermDocument9 paginiIncome Tax - MidtermThe Second OneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft 365 LicensingDocument18 paginiMicrosoft 365 Licensingwendy yohanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study - Id23039 - Travel and Tourism in India Statista Dossier PDFDocument60 paginiStudy - Id23039 - Travel and Tourism in India Statista Dossier PDFaashmeen25Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EDe la EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (6)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersDe la EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemDe la EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesDe la EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisDe la EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesDe la EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityDe la EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsDe la EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDe la EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesDe la EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (14)
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesDe la EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersDe la EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (12)
- Benchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementDe la EverandBenchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersDe la EverandFundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyDe la EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (2)
- Culture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsDe la EverandCulture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignDe la EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)
- What Went Wrong?: Case Histories of Process Plant Disasters and How They Could Have Been AvoidedDe la EverandWhat Went Wrong?: Case Histories of Process Plant Disasters and How They Could Have Been AvoidedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeDe la EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (21)
- Tensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesDe la EverandTensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesDe la EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)