Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
O o o o O: Name (Print)
Încărcat de
Azima TarannumDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
O o o o O: Name (Print)
Încărcat de
Azima TarannumDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NAME (PRINT):
Last/Surname
STUDENT #:
First IGiven Name
-----------------------
SIGNATURE:
----------------
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO MISSISSAUGA
DECEMBER 2013 FINAL EXAMINATION
PHY136H5F
Introductory Physics I
Wagih Ghobriel
Duration - 3 hours
Aids: Non-Programmable Calculators
The University of Toronto Mississauga and you, as a student, share a commitment to
academic integrity. You are reminded that you may be charged with an academic
offence for possessing any unauthorized aids c:Jur;ng the writing of an exam. Clear,
sealable, plastic bags have been provided for all electronic devices with . storage,
including but not limited to: cell phones, tablets, laptops, calculators, and MP3
players. Please turn off all devices, seal them in the bag provided, and place the bag
under your desk for the duration of the examination. You will not be able to touch the
bag or its contents until the exam is over.
If, during an exam, any of these items are found on your person or in the area of your
desk other than in the clear, sealable, plastic bag; you may be charged with an
academic offence. A typical penalty for an academic offence may cause you to fail
the course.
Please note, you CANNOT petition to re-write an examination once the exam has
begun.
Notes to students
o The exam consists of twenty (20) equally-valued multiple-choice problems.
o The total number of pages is 21, including the front page.
o The formula sheet will be handed out separately.
o Total mark of the exam equals 100.
o All the questions are multiple-choice questions to be answered on the scantron
o
o
o
sheet. The blank
space with each question is for your rough work and win not be marked.
Before each problem the mark and question number of that problem are written between square
brackets [... J and between round brackets ( ...), respectively.
Please fill in the scantron sheet very carefully including your name and ID number. The scantron
sheet will be the only paper that will be marked. Your answers on the problem book will not be
marked.
You are not allowed to bring your own prepared sheet of formulas or any other source of
information. You'll be provided with all the constants and formulas that you may need in this
exam.
continued on next page 2
PHY I 36H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 2 of 21
[5] (1) On September 8, 2004, the Genesis spacecraft crashed in the Utah desert because its parachute did not
open. The 210-kg capsule hit the ground at 311 kmJh and penetrated the soil to a depth of 81.0 cm.
(a) Assuming the acceleration during the crash to be constant, what force did the ground exert on the capsule
during the crash? Express the force in as a multiple of the capsule's weight. (b) For how long did this force last?
a. (471 W, 0.1782 s)
b. (471 W ,0.0187 s)
c. (236 W, 0.0187 s)
d. (198 W, 0.0235 s)
e. (236 W ,0.0374 s)
continued on next page 3
PHYl36H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 3 of 21
[5] (2) A 6.00-kg box sits on a ramp that is inclined at 37.0 above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic
friction between the box and the ramp is Pk = 0.30. What horizontal force is required to move the box up the
incline with a constant acceleration of 4.20 m1s2?
a. 121 N
b. 242 N
c. 363 N
d. 387 N
e. 408 N
continued on next page 4
PHY 136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 4 of 21
[5] (3) Two objects with masses 5.00 kg and 2.00 kg hang 0.600 m above the floor from
the ends of a cord 6.00 m long passing over a frictionless pulley. Both objects start from
rest. Find the maximum height reached by the 2.00-kg object above the floor.
[Ignore the weight of the cord]
a. 2.38 m
b. 2.15 m
c. 1.90 m
d. 1.46 m
e. 0.93 m
5.00 kg
Floor
continued on next page 5
PHY J 36H5F Dec 20] 3 Final Regular Exam
page 5 of 21
[5] (4) In Figure A, a sled is held on an inclined plane by a cord pulling directly up the plane. The sled is to be
on the verge of moving up the plane. In Figure B, the magnitude F required of the cord's force on the sled is
plotted versus a range of values for the coefficient of static friction f.1s between sled and plane: Fl = 2.0 N,
F2 = 5.0 N, and f.12 = 0.50. At what angle () is the plane inclined?
a.34.5
b. 29.6
c. 18.40
d. 10.70
e.8.4
Figure A
~------------------~------J1s
~2
Figure B
continued on next page 6
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 6 of 21
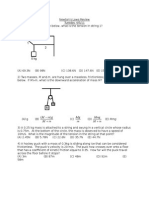
[5] (5) A "swing" ride at a carnival consists of chairs that are swung in a circle by
17.0-m cables attached to a vertical rotating pole, as the drawing shows. Suppose
the total mass of a chair and its occupant is 90.0 kg. Determine the tension in the
cable attached to the chair when its velocity is 38.0 mls. [Hint: You may need to
solve a quadratic equation to find
(a) 3361 N
(d) 6175 N
e.]
(b) 4934 N
(e) 7745 N
(c) 5457 N
--
continued on next page 7
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 7 of 21
[5] (6) If a car goes through a curve too fast, the car tends to slide out of the curve. For a banked curve with
friction, a frictional force acts on a fast car to oppose the tendency to slide out of the curve; the force is directed
do~n the bank (in the direction water would drain). Consider a circular curve of radius R = 200 m and bank
angle p, where the coefficient of static friction between tires and pavement is Jis. A car is driven around the
curve. For a bank angle of p= 10 fmd the ratio of the maximum car speed V max that puts the car on the verge of
sliding out for Jis = 0.60 (dry pavement) to that for Jis = 0.050 (wet or icy pavement). (Now you can see why
accidents occur in highway curves when icy conditions are not obvious to drivers, who tend to drive at normal
speeds.)
b. 1.60
c.1.95
d.2.83
e.3.15
a.1.47
,...",.
/'
-- ..... ------------.-...
continued on next page 8
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 FinaJ Regular Exam
page 8 of 21
[5] (7) In Figure, a 0.250 kg block of cheese lies on the floor of a 900 kg elevator cab that is
being pulled upward by a cable through distance d] = 2.40 m and then through distance
d 2 = 10.5 m. (a) Through d], if the normal force on the block from the floor has constant
magnitude FN = 3.00 N, how much work is done on the cab by the force from the cable?
(b) Tbrough d2 , if the work done on the cab by the (constant) force from the cable is 92.61
kJ, what is the magnitude qf F N?
a. (2.59 x 104 J , 1.28 N)
b. (3.19 x 104 J, 1.78 N)
c. (4.95 X 104 J ,2.45 N)
4
4
d. (3.40 X 10 J , 3.29 N)
e. (2.59 x 10 J , 2.45 N)
;;
..Ii.
-'!!
continued on next page 9
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 9 of 21
[5] (8) In Figure, a 2.0 kg package slides along a floor with speed VI = 4.0 rnls. It then runs into and compresses
a spring until the package momentarily stops. Its path to the initially relaxed spring is frictionless, but as it
compresses the spring, a kinetic frictional force from the floor, of magnitude 15 N, acts on the package. If
k = 10000 N/m, by what distance d is the spring compressed when the package stops?
a. 3.8 cm
b. 5.5 cm
c. 6.9 cm
d. 7.3 cm
e. 8.1 cm
Friction ---~) I(
(
Stop
Frictionless
First touch
continued on next page 10
PHYI36H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
[5] (9) A 700 g block is released from rest at height ho above a vertical spring
with spring constant k = 400 N/m and negligible mass. The block sticks to the
spring and momentarily stops after compressing the spring 19.0 cm.
(a) What is the value of ho? (b) If the block were released from height 2.00 ho
above the spring, what would be the maximum compression of the spring?
a. (0.86 m , 0.26 m)
b. (0.86 m , 0.38 m)
c. (0.57 m , 0.38 m)
d. (1.24 m, 0.21 m)
e. (0.86 m, 0.57 m)
page 10 of 21
T
ho
!T
d= 19 em
~
k=400N/m
'
..
continued on next page 11
PHY I36H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page II of 21
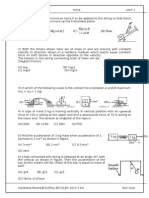
[5] (10) Tarzan, who weighs 688 N, swings from a cliff at the end of a vine 18 m
long (as shown in Figure). From the top of the cliff to the bottom of the swing, he
descends by 3.2 m. The vine will break if the force on it exceeds 950 N.
(a) Does the vine break? (b) \\'hat is the greatest force on it during the swing?
a (Does not break, 467 N)
b. (Breaks, 986 N)
c. (Breaks, 1025 N)
d. (Does not break, 933 N)
e. (Does not break, 624 N)
'---....--.....4______
continued on next page 12
PHY 136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 12 of 21
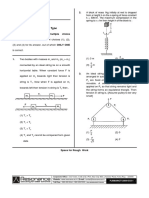
[5] (11) In Figure, a stationary block explodes into two pieces Land R that slide across a frictionless floor and
then into regions with friction, where they stop. Piece L, with a mass of 2.0 kg, encounters a coefficient of
kinetic friction J.1L = 0.40 and slides to a stop in distance dL = 0.15 m. Piece R encounters a coefficient of kinetic
friction J.1R = 0.50 and slides to a stop in distance dR = 0.25 m. What was the mass of the block?
a. 6.72 kg
b. 5.37 kg
c. 4.81 kg
d. 3.39 kg
e. 1.28 kg
(PL
~ dL ~
f.l=O
PR
1<
.:
dR
.1
mS
)1
continued on next page 13
PHY 136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 13 of 21
[51 (12) In Figure, block 1 of mass ml slides from rest along a frictionless ramp from height h = 2.50 m and then
collides with stationary block 2, which has mass m2 = 2.00 mi. After the collision, block 2 slides into a region
where the coefficient of kinetic friction Pk is 0.50 and comes to a stop in distance d within that region. What is
the value of distance difthe collision is (a) elastic and (b) completely inelastic?
a. (2.22 m, 0.556 m)
b. (1.86 m, 0.263 m)
c. (0.68 m, 0.185 m)
d. (3.12 m, 0.645 m)
e. (2.22 m, 0.142 m)
Frictionless
continued on next page 14
PHY l36H5F Dec 2013 FinaJ Regular Exam
page J4 of 21
[5] (13) In Figure, puck 1 of mass ml = 0.20 kg is sent sliding across a frictionless lab bench, to undergo a one
dimensional elastic collision with stationary puck 2. Puck 2 then slides off the bench and lands a distance
d from the base of the bench. Puck 1 rebounds from the collision and slides off the opposite edge of the bench,
landing a distance 2d from the base of the bench. What is the mass of puck 2? (Hint: Be careful with signs.)
a. 2.0 kg
b. 1.0 kg
c. 0.6 kg
d. 0.5 kg
e. 0.4 kg
1 .r I
2d-l
continued on next page 15
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 15 of 21
[5] (14) In Figure, a solid cylinder of radius 10 cm and mass 12 kg starts from
rest and rolls without slipping a distance L = 6.0 m down a roof that is inclined
../
at the angle e = 30. The roofs edge is at height H = 5.0 m. How far
\,J"""-""" ~
horizontally from the roof's edge does the cylinder hit the level ground? . /./~
a.6.0m
d. 3.1
b.5.4m
2.5
e. m
c.4.0m
\ ' ..........:
>..~ ~_--'r-'-8-:r-_~--'-"":"":"""":'_"':"";
continued on next page 16
PHY 136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 16 of 21
[5J (15) In Figure, a solid brass ball of mass 0.280 g will roll
smoothly along a loop-the-Ioop track when released from rest
along the straight section. The circular loop has radius
R = 14.0 cm, and the ball has radius r R.
(a) What is h if the ball is on the verge of leaving the track
when it reaches the top of the loop?
(b) If the ball is released at height h = 6.00 R, what is the
magnitude of the horizontal force component acting on the
ball at point OJ
a. (37.8 cm, 0.04 N)
c. (51.2 cm, 0.03 N)
e. (37.8 cm, 0.02 N)
b. (37.8 cm, 0.06 N)
d. (48.6 cm , 0.02 N)
continued on next page 17
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 17 of 21
[5] (16) A 12.0-kg box resting on a horizontal, frictionless surface is attached to a 5.00-kg weight by a thin,
light wire that passes over a frictionless pulley (as shown in Figure). The pulley has the shape of a uniform
solid disk of mass 2.00 kg and diameter 0.500 m. After the system is released, find the horizontal and vertical
components of the force that the axle exerts on the pulley. [Hint: You need to calculate the tension in the wire
on both sides of the pulley first.]
a. (32.6 N , 71.4 N)
c. (32.6 N , 55.0 N)
e. (56.2 N , 71.0 N)
b. (55.0 N , 55.0 N)
d. (49.1 N ,62.0 N)
12.0 kg
5.0kg
continued on next page 18
PHY I 36H5F Dec 20 I 3 Final Regular Exam
page 18 of 21
[5] (17) A block with mass M = 1.0 kg rests on a frictionless surface and is connected to a horizontal spring of
force constant k= 14.7 N/m, the other end of which is attached to a wall (as shown in Figure). A second block
with mass m = 0.5 kg rests on top of the first block. The coefficient of static friction between the blocks is
Jis = 0.3. Find the maximum amplitude of oscillation such that the top block will not slip on the bottom block.
a. 0.60 m
b. 0.52 m
c. 0048 m
d. 0040 m
e. 0.30 m
continued on next page 19
page 19 of 21
PHY 136H5F Dec 2013 Final """'F."U" Exam
[5] (18) On the planet Newtonia, a simple pendulum having a bob with a mass
1.25 kg and a
length 185.0 em
1
s, when
from rest, to swing through an angle of e 1
where it
has zero speed.
IS
to
51,400
planet
is the mass of
a. 2.14 x 1023
d. 9.08 X 1024 kg
8.03 x 1023 kg
e.3.15xl
kg
e. 9.17 x 1023
continued on next page 20
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 20 of 21
[5] (19) A tube, open at only one end, is cut into two shorter (non-equal) lengths. The piece that is open at both ends has a
fundamental frequency of 260 Hz, while the piece open only at one end has a fundamental frequency of 2670 Hz. What is
the fundamental frequency of the original tube?
(a) 124 Hz
(b) 195 Hz
(c) 248 Hz
(d) 310Hz
(e) 62 Hz
continued on next page 21
PHY136H5F Dec 2013 Final Regular Exam
page 21 of 21
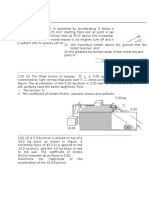
[5](20) A microphone is attached to a spring that is suspended from the ceiling, as
shown in figure. Directly below on the floor is a stationary 440-Hz source of sound.
The microphone vibrates up and down in simple harmonic motion with a period of
2.0 s. The difference between the maximum and minimum sound frequencies detected
by the microphone is 2.1 Hz. Ignoring any reflections of sound in the room and using
343 mls for the speed of sound, determine the amplitude of the simple harmonic
motion.
(a) 0.13 m
(b) 0.26 m
(c) 0.39 m
(d) 0.42 m
-'-=;;........_~_-.Y
(e) 0.65 m
&>~
""
s:;
CJ
Sound source
End of the PHY136HSF Final Exam Dec 2013. Total mark = 100
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- PC1431 Term Test 2012Document10 paginiPC1431 Term Test 2012MrshuaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument10 paginiMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAlejandro Torrico MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Old Exam With Solutions 051Document11 paginiPhysics Old Exam With Solutions 051poker100% (1)
- 102 Physics Answers-EK EditionDocument15 pagini102 Physics Answers-EK Editionadom09Încă nu există evaluări
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Evaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Psphystestju 02Document20 paginiPsphystestju 02STÎncă nu există evaluări
- PC1431 Term Test 2013Document8 paginiPC1431 Term Test 2013Ng Pei YaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 2 Newtons Laws ReviewDocument6 paginiDay 2 Newtons Laws Reviewnoel castilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP WpeDocument6 paginiDPP WpeMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phys 699Document25 paginiPhys 699joseftrihandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Document13 paginiWork and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Mansoor Al TunijiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Newton Laws of Motion DCET IIT JEEDocument11 paginiPhysics Newton Laws of Motion DCET IIT JEEprem19999Încă nu există evaluări
- Practice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Document9 paginiPractice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Hasan AlomariÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Should Be The Minimum Force P To Be Applied To The String So That Block of Mass M Just Begins To Move Up The Frictionless PlaneDocument6 paginiWhat Should Be The Minimum Force P To Be Applied To The String So That Block of Mass M Just Begins To Move Up The Frictionless Planeharshanauoc100% (1)
- ODocument11 paginiO2pwxanqt8aÎncă nu există evaluări
- JR Iit StarDocument18 paginiJR Iit Star2pwxanqt8aÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQs in Engineering Mathematics Part 10Document12 paginiMCQs in Engineering Mathematics Part 10Richster LofrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Int Mech Practice Exam 2Document9 paginiInt Mech Practice Exam 2Kevin ApodacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce2 Sample2Document5 paginiCe2 Sample2ParZiValÎncă nu există evaluări
- MECH Multiple Choice 2004Document7 paginiMECH Multiple Choice 2004clarencetan95Încă nu există evaluări
- Resonance Test SeriesDocument19 paginiResonance Test SeriesAman Shrivastava0% (1)
- AIIMS - Model Question Paper For Mbbs EntranceDocument24 paginiAIIMS - Model Question Paper For Mbbs EntrancerichuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resonance Test PaperDocument51 paginiResonance Test PaperSrijan Agrawal100% (1)
- Laws of Motion DPP For JEE Mains by Ajitlulla SirDocument16 paginiLaws of Motion DPP For JEE Mains by Ajitlulla SirVardhan AmanapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM 2014 Trial p1 Set 2 Q & ADocument17 paginiSTPM 2014 Trial p1 Set 2 Q & Achoichiang100% (1)
- 2018 June Test PrepquestionsDocument14 pagini2018 June Test PrepquestionsSiinozuko MasentseÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMK Tinggi Klang Trial Term 1 2014Document13 paginiSMK Tinggi Klang Trial Term 1 2014Souseiseki ChromeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy10 DiagnosticDocument96 paginiPhy10 DiagnosticMarc AlamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW05 - Energy ConservationDocument7 paginiHW05 - Energy ConservationBradley Nartowt0% (1)
- Lows of MotionDocument20 paginiLows of MotionSaswata Sundar LagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Final ExamDocument7 paginiPractice Final ExamChetanya SinglaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test 2Document7 paginiPractice Test 2Maria YurlovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 paginiChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test FinalDocument23 paginiPractice Test FinalAllison TielkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subjective Questions: FrictionDocument5 paginiSubjective Questions: FrictionwanderedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics-1 Recitation-3: 1) The Displacement of A 2 KG Particle Is Given by X atDocument15 paginiPhysics-1 Recitation-3: 1) The Displacement of A 2 KG Particle Is Given by X atRicard AltamirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Section - IDocument6 paginiPhysics Section - ISayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 2. Exam 2 AnswersDocument7 paginiPhysics 2. Exam 2 AnswersWino PazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsDocument57 paginiUnit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsLissa Hannah100% (1)
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument17 paginiRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument14 paginiRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêÎncă nu există evaluări
- SadfDocument6 paginiSadfKwammy BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP Nlm-IiDocument8 paginiDPP Nlm-IiMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheDocument7 paginiMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheRachel Du PreezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP S HW CH 4Document8 paginiCP S HW CH 4nurhasanahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immin111 6007Document4 paginiImmin111 6007Shreyas ShankerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYS1534 Exam 2018 MainDocument16 paginiPHYS1534 Exam 2018 MainGiftÎncă nu există evaluări
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Document19 paginiNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixADocument63 paginiIntro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixAGfour Maserati50% (2)
- End of Term 2 s.5 PhyDocument6 paginiEnd of Term 2 s.5 PhyMubiruIvanSnrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Final Exam 13SDocument8 paginiSample Final Exam 13SmarcÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP NLM and FrictionDocument3 paginiDPP NLM and FrictionMy Moto G2Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Question 2Document6 paginiSample Question 2charleswcoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExamDocument16 paginiExamnicolas dionisio ordonez barruetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCS120 Final ExamDocument10 paginiPCS120 Final ExamBetty WangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Test 2Document1 paginăTerm Test 2Azima TarannumÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHMoctober2004 MidtermDocument5 paginiCHMoctober2004 MidtermAzima TarannumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm October 2013Document5 paginiMidterm October 2013Azima TarannumÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY136/7 Lab Report Title Page: All Information Is RequiredDocument1 paginăPHY136/7 Lab Report Title Page: All Information Is RequiredAzima TarannumÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY136/7 Lab Report Title Page: All Information Is RequiredDocument1 paginăPHY136/7 Lab Report Title Page: All Information Is RequiredAzima TarannumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Algebra With ApplicationsDocument1.032 paginiLinear Algebra With ApplicationsAzima TarannumÎncă nu există evaluări
- SyllabusDocument6 paginiSyllabusAzima TarannumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unified Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 paginăUnified Mechanical Engineeringshalom_pklÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAPE Unit 1 Paper 2 2010 (PHYSICS)Document22 paginiCAPE Unit 1 Paper 2 2010 (PHYSICS)Christopher McCarthy100% (1)
- PBL Coaster 2018Document2 paginiPBL Coaster 2018api-325864985Încă nu există evaluări
- Prijslijst Eletta MarcolinDocument4 paginiPrijslijst Eletta MarcolinTenakhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1790@0@104911 WlaO4PLB96z Emailing Exercises - Work and EnergyDocument12 pagini1790@0@104911 WlaO4PLB96z Emailing Exercises - Work and Energyalirammal804Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample ProblemsDocument4 paginiSample ProblemsAnthropophobe NyctophileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Testing of M12 BoltsDocument72 paginiMaterial Testing of M12 BoltsdhaktodesatyajitÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 11Document55 paginiCH 11Mega LialitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-Flow RatesDocument8 paginiChapter 1-Flow RatesJeisther Timothy GalanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turbin99 IIDocument12 paginiTurbin99 IIKristijan HorvatÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World As A HologramDocument12 paginiThe World As A HologramsuccessmentorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moment Distribution MethodDocument13 paginiMoment Distribution MethodMD. SHUVO RAHMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of The Faraday and Kerr Effects in FerromagneticsDocument12 paginiTheory of The Faraday and Kerr Effects in FerromagneticsPeter RichterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Reading Bode PlotsDocument12 paginiUnderstanding Reading Bode PlotskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report TENSILEDocument13 paginiLab Report TENSILEshareen tanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 Gas FulDocument20 paginiLab 3 Gas FulMarouane AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energies 11 02687Document17 paginiEnergies 11 02687Lucas ErburuÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP 9 AC MainsDocument5 paginiEXP 9 AC MainsRude BøyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 - TENSION TEST OF MILD STEEL SPECIMENDocument10 paginiExperiment 1 - TENSION TEST OF MILD STEEL SPECIMENSamiha Maysoon Nooria100% (1)
- Assiment PDFDocument4 paginiAssiment PDFRedaEbidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial - Spur GearDocument2 paginiTutorial - Spur GearPrince KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eme Heat Transfer-1Document5 paginiEme Heat Transfer-1Syed AnsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument40 paginiElectromagnetic WaveFranchesco Jay C. LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce5610: Finite Element AnalysisDocument27 paginiCe5610: Finite Element AnalysisArjun RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Micro Project Report ON: Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, MumbaiDocument18 paginiA Micro Project Report ON: Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, MumbaiPrashant PoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Just Six NumbersDocument3 paginiJust Six Numbershotrdp5483Încă nu există evaluări
- Transverse Vibrations of A Rotating Uniform Cantilever Beam With Tip Mass As Predicted by Using Beam Characteristic Orthogonal Polynomials in The Rayleigh-Ritz MethodDocument12 paginiTransverse Vibrations of A Rotating Uniform Cantilever Beam With Tip Mass As Predicted by Using Beam Characteristic Orthogonal Polynomials in The Rayleigh-Ritz MethodHassanImranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum Equation.Document8 paginiMomentum Equation.Ayub Ali WehelieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hubbert and Willis, 1972 Mechanics of Hydr FracDocument19 paginiHubbert and Willis, 1972 Mechanics of Hydr Fracnic7522Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDe la EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDe la EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsDe la EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingDe la EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)De la EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Încă nu există evaluări
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorDe la EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.De la EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsDe la EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (9)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDe la EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- Transform Your 6-12 Math Class: Digital Age Tools to Spark LearningDe la EverandTransform Your 6-12 Math Class: Digital Age Tools to Spark LearningÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathDe la EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6De la EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)