Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ITC Lec06 Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode-I
Încărcat de
Anas AsifDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ITC Lec06 Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode-I
Încărcat de
Anas AsifDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lecture 06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
CS 101: Introduction to Computing
Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
Saima Jabeen
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Last time
Computer programming
Programming languages
Programming languages categorization
Algorithm
Today
Algorithms - Examples
Flowcharts
Expressing algorithms: Pseudocode
2
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Calculate and print the average grade
of 3 tests for the entire class
Input
output
3 test scores for each student
Average of 3 tests for each student
Process
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Get three scores
Add them together
Divide by three to get the average
Print the average
Repeat step 1 to 4 for next student
Stop if there are no more students
3
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Flow Charts
A flowchart is a visual
representation of an algorithm.
The flowchart employs a series of blocks and
arrows, each of which represents a particular
operation or step in the algorithm.
The arrows represent the sequence in which the
operations are implemented.
or
graphical
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Flowcharts Most Common Symbols
Function
Symbol Name
Terminal
Flow-line
Process
Represents the
of a program.
Represents the
flow of logic.
Represents calculations or data
manipulation.
Input/Output
Decision
beginning or end
Represents inputs or outputs
of data and information.
Represents a comparison,
question, or decision that
determines alternative paths to be
followed.
5
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
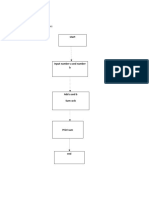
Flowcharts An Example
Find the solution of a quadratic equation
Ax2+Bx+C=0, given A, B and C.
START
INPUT
A, B, C
Calculate
R = SQRT(B2-4AC)
X1 = (-B+R)/(2A)
X2 = (-B-R)/(2A)
PRINT
A, B, C, X1, X2
END
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Comparison of Algorithm representations in Natural language, flowchart and
Pseudo-code
START
Step 1: Begin the calculations
INPUT
A, B
Step 2: Input two values A and B
Step 3: Add the values
Add A to B
and store in C
Step 4: Display the result
Step 5: End the calculation
BEGIN Adder
Input A and B
C=A+B
PRINT C
END Adder
OUTPUT
C
END
Natural language
Flowchart
Pseudo-code
7
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Algorithm Representation
(Natural Languages)
English or some other natural language.
Are not particularly good:
too verbose
Unstructured
too rich in interpretation (ambiguous)
imprecise
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Algorithm Representation
(Using Programming Language)
{
int I, m, Carry;
int a[100], b[100], c[100];
cin >> m;
for ( int j = 0 ; k <= m-1 ; j++ ) {
cin >> a[j];
cin >> b[j];
}
Carry = 0;
i = 0;
while ( i < m ) {
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Pseudo-code
Pseudo-code = English but looks like programming
Pseudocode is an artificial and informal language that helps
programmers develop algorithms.
Computer scientists use pseudo-code to express
algorithms:
English like constructs (or other natural language), but
modeled to look like statements in typical programming languages.
Good compromise
Simple, readable, no rules, don't worry about punctuation. Lets
you think at an abstract level about the problem.
Contains only instructions that have a well-defined structure and
resemble programming language
10
Lec06: Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode
S 101: Introduction to Computing
Pseudo-code Primitives
Three basic kind of operations:
Sequential
Computation ( Set )
Input/Output ( Get ... / Print ... )
Conditional
If Else
If
Iterative / looping
Repeat
While ...
11
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CNC Milling Machine - FYP Final Report - V1Document57 paginiCNC Milling Machine - FYP Final Report - V1Anas Asif64% (11)
- Introduction To Java Programming Brief Version 10th Edition Liang Test BankDocument19 paginiIntroduction To Java Programming Brief Version 10th Edition Liang Test Bankcharles100% (24)
- CAPE Computer Science Unit 1 Module 2 - Problem Solving With Computers January 7, 2022Document8 paginiCAPE Computer Science Unit 1 Module 2 - Problem Solving With Computers January 7, 2022Marcel ShieldsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect1 - Algorithms and FlowchartDocument29 paginiLect1 - Algorithms and FlowchartMM Ayehsa Allian Schück100% (2)
- 01 - Programming Problem-Solving PDFDocument114 pagini01 - Programming Problem-Solving PDFArkan RasyidÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITC Lect 06 (Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode-I)Document10 paginiITC Lect 06 (Algorithms Flowcharts Pseudocode-I)sayed Tamir janÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 PFDocument3 paginiLab 3 PFmaham sabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flowchart AlgorithmDocument13 paginiFlowchart AlgorithmSrija ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2 - Pseudo Code and FlowchartsDocument7 paginiLab 2 - Pseudo Code and Flowchartspioneer boysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python 4 - Variables - Strings and NumbersDocument15 paginiPython 4 - Variables - Strings and NumbersPeter CoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece126 Slide Notes - MZH - CH1&2 PDFDocument82 paginiEce126 Slide Notes - MZH - CH1&2 PDFgamerbÎncă nu există evaluări
- File 1697097709 GUSCSE202332294 Unit-IAlgorithmDocument14 paginiFile 1697097709 GUSCSE202332294 Unit-IAlgorithmpvatsala100Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To: Algorithms & FlowchartsDocument26 paginiIntroduction To: Algorithms & FlowchartsAfrah NasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compiler Design LabDocument15 paginiCompiler Design LabMosaddek Hossain100% (1)
- 4th Sem Bcom May 19Document10 pagini4th Sem Bcom May 19skÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSS 2 3RD Term Lesson NoteDocument22 paginiSSS 2 3RD Term Lesson NoteOyinade AdeoluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computing Technologies-ICTDocument30 paginiIntroduction To Computing Technologies-ICTPradyumna SAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Note: Week 1Document15 paginiLecture Note: Week 1Devesh GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programming Lab 6: - Example First Mid-Term Exam QuestionsDocument2 paginiProgramming Lab 6: - Example First Mid-Term Exam QuestionsŞemsettin karakuşÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logical Flow of A Program: Algorithms, Flowcharts, PseudocodeDocument20 paginiLogical Flow of A Program: Algorithms, Flowcharts, PseudocodeMuqadas HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Programming NotesDocument92 paginiPython Programming NotesSREEJITH S NAIRÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCSA1104 Unit 1Document25 paginiSCSA1104 Unit 1G.AkshayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design, Fifth EditionDocument48 paginiC++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design, Fifth Editionkyle_tosh3484Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter4 Python Programming SelectionDocument35 paginiChapter4 Python Programming SelectionMohamed MedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.algorithms and Flowcharts Continued PDFDocument46 pagini3.algorithms and Flowcharts Continued PDFBhumi VavadiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programming For Problem Solving: Assignment - I Answer KeyDocument4 paginiProgramming For Problem Solving: Assignment - I Answer KeyTAMMISETTY VIJAY KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Short Question AnswersDocument133 paginiPython Short Question AnswersBhaskar VeeraraghavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- C ManualDocument53 paginiC ManualChindiya BabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course: B.Tech 1 Year Manufacturing Engineering Subject: Programming For Problem SolvingDocument20 paginiCourse: B.Tech 1 Year Manufacturing Engineering Subject: Programming For Problem SolvingSuraj YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Prog Logic DevelopmentDocument8 paginiUnit 1 Prog Logic DevelopmentAtharv KhadatareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment PLC and Oop 2023Document12 paginiAssignment PLC and Oop 2023Hafsa ShykhÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Bcs Higher Education Qualifications BCS Level 4 Certificate in ITDocument6 paginiThe Bcs Higher Education Qualifications BCS Level 4 Certificate in ITJessica TiffanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.1 Types of Flowcharts: Saturday, 29 August 2020 1:13 PMDocument14 paginiB.1 Types of Flowcharts: Saturday, 29 August 2020 1:13 PMvj hernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- SE 100 Midterm 2 PDFDocument12 paginiSE 100 Midterm 2 PDFM.SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Introduction To Java Programming Comprehensive Version 9Th Edition Liang 97801329365 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiTest Bank For Introduction To Java Programming Comprehensive Version 9Th Edition Liang 97801329365 Full Chapter PDFjessica.talaga212100% (13)
- 3 G3 LAB Dec 02 2020Document9 pagini3 G3 LAB Dec 02 2020Muhammad Jawad IsmaeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: JR CSE Unit-I Introduction To Problem Solving TechniquesDocument11 paginiUnit 1: JR CSE Unit-I Introduction To Problem Solving TechniquesShanmuka SreenivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CD Record - 310618104006Document200 paginiCD Record - 310618104006Ajay BharadwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Basic 6.0 Lec1 To Lec3Document25 paginiVisual Basic 6.0 Lec1 To Lec3Hussein AlkafajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of A C Program: ObjectivesDocument79 paginiStructure of A C Program: ObjectivesAarti GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow ChartDocument60 paginiFlow Chartnavjotjyoti50% (2)
- C ProblemsDocument9 paginiC ProblemsggyuuouÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE101 - Lec 2 (Algorithm and Flowchart)Document33 paginiCSE101 - Lec 2 (Algorithm and Flowchart)Pawan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Programming: Iksan Bukhori, M.PhilDocument37 paginiEngineering Programming: Iksan Bukhori, M.PhilMuhammad Teguh IlhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Introduction To Java Programming Brief Version 10Th Edition Liang 0133592200 9780133592207 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiTest Bank For Introduction To Java Programming Brief Version 10Th Edition Liang 0133592200 9780133592207 Full Chapter PDFjessica.talaga212100% (14)
- McalabexperimentsDocument16 paginiMcalabexperimentsAntony SantoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit I - Part 2Document26 paginiUnit I - Part 2Danish JasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCD Lab Manual 2017Document46 paginiPCD Lab Manual 2017Shubhajit MallickÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02-CP Lab Manual PDFDocument71 pagini02-CP Lab Manual PDFAntriksh9Încă nu există evaluări
- CDSmanual New 10-11Document36 paginiCDSmanual New 10-11Ravi VarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 107 FlowchartsDocument3 pagini107 FlowchartsSyed Abdul HannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algo and FlowchartDocument32 paginiAlgo and FlowchartIshu AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithms and FlowchartsDocument12 paginiAlgorithms and FlowchartsRaj BrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- File 1665133050 GUSCSE202231895 Unit-IAlgorithmDocument14 paginiFile 1665133050 GUSCSE202231895 Unit-IAlgorithmAditya KDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daskom Daskom 55 Daskom Daskom 55: Flow Chart Flow Chart Flow Chart Flow ChartDocument14 paginiDaskom Daskom 55 Daskom Daskom 55: Flow Chart Flow Chart Flow Chart Flow ChartApÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ActivitiesDocument7 paginiLab ActivitiesBello, Romalaine Anne C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: Introduction To Programming Language ConceptsDocument20 paginiUnit 1: Introduction To Programming Language Conceptsडॉ. शुभेंदु शेखर शुक्लाÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIT C 1Document13 paginiBIT C 1Razza YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Program Logic FormulationDocument60 pagini1 - Program Logic FormulationHoney Girl100% (2)
- Introduction To Algorithms and FlowchartDocument48 paginiIntroduction To Algorithms and FlowchartAbdullah Al-suleimaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Computer Science Principles: Student-Crafted Practice Tests For ExcellenceDe la EverandAP Computer Science Principles: Student-Crafted Practice Tests For ExcellenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coding for beginners The basic syntax and structure of codingDe la EverandCoding for beginners The basic syntax and structure of codingÎncă nu există evaluări
- WochenstundenplΣne CS4DM WS20-21 Stand 27Okt20Document1 paginăWochenstundenplΣne CS4DM WS20-21 Stand 27Okt20Anas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Italy Masters ProgramsDocument3 paginiItaly Masters ProgramsAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- WochenstundenplΣne HCI WS20-21 Stand 27Okt20Document1 paginăWochenstundenplΣne HCI WS20-21 Stand 27Okt20Anas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphical SynthesisDocument58 paginiGraphical SynthesisAnas Asif100% (2)
- Stress Analysis (ME-416) 1Document47 paginiStress Analysis (ME-416) 1Anas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engg Masters ProgramsDocument37 paginiMechanical Engg Masters ProgramsAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Engine Types and OperationDocument57 pagini1 Engine Types and OperationAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importing A Catia File Into SolidWorks With AdobeDocument2 paginiImporting A Catia File Into SolidWorks With AdobeAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Assig PDFDocument15 paginiChapter 6 Assig PDFAnas Asif100% (1)
- Rules and Guidelines - GSD Musabaka 2017Document4 paginiRules and Guidelines - GSD Musabaka 2017Anas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Design Ch08 PG 1 of 2 SolmanDocument90 paginiEngineering Design Ch08 PG 1 of 2 Solmanbilly93Încă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of MaterialsDocument36 paginiMechanics of MaterialsAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITC Lec05 Computer Software and ProgrammingDocument11 paginiITC Lec05 Computer Software and ProgrammingAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITC Lec 08 C++Document18 paginiITC Lec 08 C++Anas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Components of Computer and Data Representation: Saima JabeenDocument18 paginiComponents of Computer and Data Representation: Saima JabeenAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Materials: Pure BendingDocument42 paginiMechanics of Materials: Pure BendingAnas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester Project C++Document4 paginiSemester Project C++Anas AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arena Users GuideDocument102 paginiArena Users Guidehenryieits0% (1)
- Automatic Sorting MachineDocument5 paginiAutomatic Sorting MachineJournal 4 ResearchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DateDocument35 paginiAssignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DateLinh Chôm chômÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus BCA - I ST YearDocument14 paginiSyllabus BCA - I ST YearTheRHKapadiaCollegeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Marketing Plan, Operasional Plan, Dan Human Capital PlanDocument15 paginiJurnal Marketing Plan, Operasional Plan, Dan Human Capital PlanyuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-1 Fundamentals of Problem Solving: Creating and Running ProgramsDocument13 paginiUNIT-1 Fundamentals of Problem Solving: Creating and Running ProgramsVimalesh RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Syllabus: Paper (1) IT Tools & Basics of NetworksDocument8 paginiO Level Syllabus: Paper (1) IT Tools & Basics of NetworksShishir Kant SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question BankDocument2 paginiQuestion BankAjmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document14 paginiLecture 1rohan65Încă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Skills in ItDocument5 paginiPresentation Skills in ItNolram LeuqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flowcharts Lesson With AnswersDocument18 paginiFlowcharts Lesson With AnswersAmos DakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opman TopicsDocument12 paginiOpman TopicsAnna Jane CatubagÎncă nu există evaluări
- BlueSYSTEM SIGMA - Eng05 PDFDocument115 paginiBlueSYSTEM SIGMA - Eng05 PDFEmmanuel HdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech - CSE Semester - I: Topic For The Class: Unit 1: Title: Date & TimeDocument31 paginiB.Tech - CSE Semester - I: Topic For The Class: Unit 1: Title: Date & TimemahindraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing: North South UniversityDocument14 paginiEngineering Drawing: North South UniversityMD. Zobayer Ahmed 1610766642Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 5 - Lecture in Algorithm and Flowcharting: Introduction To Programming LanguagesDocument46 paginiLesson 5 - Lecture in Algorithm and Flowcharting: Introduction To Programming LanguagesGucci Gutierrez0% (1)
- ECE Report Format PDFDocument11 paginiECE Report Format PDFRavi MuthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete NotesDocument112 paginiComplete NotesMalayalam moviesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Church Planting Proposal Guide 12.12Document5 paginiChurch Planting Proposal Guide 12.12Peter AdegoroyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programming Concepts PDFDocument20 paginiProgramming Concepts PDFDickerson Vallejos ManaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Senior Citizen SystemDocument32 paginiSenior Citizen SystemAdrian Nicolas Tanio100% (2)
- Programming Notes111updatedDocument56 paginiProgramming Notes111updatedliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Immersion E-PortfolioDocument25 paginiWork Immersion E-PortfolioJessica BernalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- OKRs How To GuideDocument12 paginiOKRs How To Guideアィィロゥ フランチÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 - Repetition - Iteration FlowchartDocument18 paginiModule 2 - Repetition - Iteration FlowchartNicole FolleroÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCA SyllabusDocument61 paginiBCA SyllabusAnurag Singh kushwahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Programming and FlowchartingDocument33 paginiChapter 1 - Introduction To Programming and FlowchartingRamachandran Nambissan TmÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 Tle-Ict-Template1 Unit Curriculum MapDocument3 pagini2022 Tle-Ict-Template1 Unit Curriculum MapNefarious MitsiukieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Flow ChartDocument10 paginiPractice Flow Chartthejahsree rajaridhuÎncă nu există evaluări