Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Function of The Simple Present Tense
Încărcat de
JoniTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The Function of The Simple Present Tense
Încărcat de
JoniDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
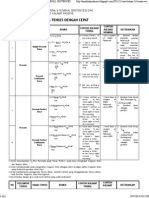
The function of the Simple Present Tense :
1.
To express habits, general truths, repeated actions or unchanging situations,
emotions, and wishes.
I smoke (habit).
I live in French (unchanging situations).
French is a mode city (general truth).
I hope I can go to French (wishes).
2.
To give instructions or directions.
Go down this road, and then the first right. Its on the right.
3.
To express fixed arrangements, presents or future.
Your course finishes at 5.00 p.m.
The formula of the Simple Present Tense :
a.
Without Verb :
(+) S + to be + Object / Compliment
(-) S + to be + not + Obj. / Comp.
(?) To be + S + Obj. / Comp. + ?
Example : (+) I am beautiful.
(-) I am not beautiful.
(?) Am I beautiful?
b.
With Verb :
(+) S + V1 + Compliment
(-) S + do/does + not + V1 + Compliment
(?) Do/does + S + V1 + Compliment + ?
J If the subject is third person singular (he, she, it, John, Mary, the book, etc.), the
verb uses the s/-es form.
Example : (+) I play computer.
>> He plays computer.
(-) I dont play computer.
>> He doesnt play computer.
(?) Do I play computer?
>> Does he play computer?
http://e-primboncha2.blogspot.com/2009/12/simple-present-tense.html
Riskys Daily Activity
Risky usually gets up at 4 oclock in the morning. Then, she cleans my room and
takes a bath. She puts on her clothes and prays. She helps her parents before she
has breakfast in the dinning room, and she never forgets to wash her hands before
having breakfast.
After breakfast at about 6 oclock, she goes to school. She goes to school by
motorcycle because her school is far from her house. She arrives at school at about
6.15. After school, she usually has lunch and takes a nap.
In the afternoon, she does her homework and sometimes watches TV. In the
evening, she stays at home with her parents and studies her lessons. Then, she
goes to bed at about 09.30 pm.
The paragraph above uses simple present to tell about Riskys activity. How do we
know that?
First of all we have to know the verb used in it, because tense is the changing of the
verb. Lets have a look the verb in that paragraph. All the verbs used in that
paragraph are simple verbs or V1 such as get, clean, take a bath, put and so on.
Those verbs are added with s/es because of the subject, the third singular subject
(she, he, it). To make it more clearly, look at the table below!
Verbal
Patterns
Example sentences
(+) I/You/They/We + V1
(- ) I/You/They/We + do not + V1
(?) Do + I/You/They/We + V1?
(+) She/He/It + V1(s/es)
(- ) She/He/It + does not + V1
(?) Does + She/He/It + V1?
They get up at 4 oclock every morning.
They do not get up at 4 oclock every morning.
Do they get up at 4 oclock every morning?
Yes, they do
No, they dont
He gets up at 4 oclock every morning.
He does not get up at 4 oclock every morning.
Does he get up at 4 oclock every morning?
Yes, he does
No, he doesnt
You see the different sentences above? They are similar in tense but different in
using the verbs. Look at the verb get in the table above! Seeing the table above,
we can conclude that if the subject she, he and it, the verb should be added by
s/es. However, when the subjects I, you, they and we, the verb should not be
added by s/es.
How to put s/es after the verb?
To put s/es in the verbs when the subject she, he and it, you should look at the end
of the verb. If the verb ends with ch, -sh, -ss, -x and -o, the verb should be added
by es. The other endings are just added by s. But remember it only happens when
the subjects she, he and it.
Example
watches TV before sleeping.
Push = pushes
Watch = watches
: She always
: He always pushes the door every time he wants to
enter the room.
Kiss = kisses
: My mother seldom kisses me
Box = boxes
: The boxer boxes another boxer hard.
Do = does
: He never does his homework himself instead of
cheating his friends.
The rule of putting -s/-es after the verb ending with y
The verb ending with y preceded by consonant, it is added by es.
Example:
Study = studies
: He studies his lessons everyday.
Fly = flies
: It often flies on my shoulders.
Cry = cries
: She seldom cries in the night.
Bury = buries
: He buries his cats death.
Modify = modifies : She often modifies her blog.
But when the verb ending with y preceded vocal, it is added just by s
Example:
Play = plays
: He plays badminton every night.
Buy = buys
: She buys a new book twice a week.
Enjoy = enjoys
: A cat enjoys eating a mouse.
Beside all of those rules above, the verbs are just added by s.
Example:
Open = opens
: She always opens her door early in the morning.
Close = closes
: He closes his door every time he wants to sleep.
Type = types
: She types her daily activity in her laptop.
See = sees
: Henry sees the mountain every other day.
Nominal
Patterns
Sentence examples
I am
You/ They/ We + are
She/ He/ It + is
I am a teacher.
You are students.
They are in the market.
We are diligent.
She is smart.
He is in Australia.
It is cute.
It is nominal rule. It uses to be (is/am/are) to relate between a subject and a
complement (ANA: Adjective, Noun and Adverb). The most important thing in this
part is that you should know the exact to be for the subjects. You may not put are
after subject I because every subject, I, you, they, we, she, he, it, has their own to
be.
Note:
You may note combine between VERBAL sentence and NOMINAL sentence.
Example:
I am study.
But
I study.
or
I am a student.
She is goes to market.
But
She goes to market. or
She is in the market.
Usage
This tense is used to express:
1.
Habitual action
To know whether the sentence is habitual action or not, we can look at the time in it.
For example, She always washes her clothes in the morning. Look at the adverb of
time always in that sentence. It is one of the adverbs of time that show the
sentence is simple present tense. Here are other adverbs of time that are used to
tell habitual action.
Often
Seldom
Always
Everyday
Every month
Every morning
Twice a week
Once a month
Never
Sometimes
Usually
Barely
Regularly
Frequently
Rarely
Ever (?)
2.
General Truth/ Permanent Statement
When you talk about the general truth or permanent statement that everybody will
know or it is always in that place, you should use simple present. You may not use
other tenses instead of simple present tense.
Example:
Fire is hot
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
A week has seven days.
A month has twelve months.
Everybody will admit the truth of the statement above. No one will say fire is cold
instead of a crazy man. Then, when you talk about the sun rises, it is a permanent
statement. It always rises in that place, in the east.
3.
Time table
When you talk about the schedule, we can use simple present.
Example:
The class starts at 7 p.m.
The bus leaves the station in the afternoon.
Although, it implies future time, you are still able to use simple present.
Check your understanding!
Change the verbs in the brackets based on the subjects and kinds of sentences
below!
1.
John ________(cook) in the kitchen every morning.
2.
Henry_______(go) to school everyday.
3.
Benny often________(give) me money.
4.
Ricky always________(wash) her dirty clothes.
5.
They_______(play) football every afternoon.
6.
Sandy and Salsa _______(be) students of SMKN 1 Rasau Jaya.
7.
They _________(be) handsome but cruel.
8.
I _________(speak) to foreigner everyday.
9.
We _________(not see) the mountain everyday.
Change the sentences below into negative and interrogative!
1.
She speaks English once a week.
2.
He always comes here on Sunday.
3.
They never play table tennis.
4.
We often jump like a frog.
5.
Everybody likes this blog.
http://hermansdata.blogspot.com/2010/07/simple-present-tense.html
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Simple Present TenseDocument15 paginiSimple Present TenseJoni100% (1)
- PAST FUTURE PERFECT TENSEDocument10 paginiPAST FUTURE PERFECT TENSEIndra FadhliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correlative-Conjunction-Exercises MyDocument8 paginiCorrelative-Conjunction-Exercises MyMinh Hanus100% (1)
- Answer Key Pertemuan 4Document5 paginiAnswer Key Pertemuan 4Melissa LissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obligation and Necessity (Modals)Document8 paginiObligation and Necessity (Modals)Muhammad Farhan100% (1)
- Passive VoiceDocument20 paginiPassive Voicesvitla0192% (13)
- Table For Change in Tense of Reported Speech For All TENSESDocument3 paginiTable For Change in Tense of Reported Speech For All TENSESlembda75% (8)
- Xercise Conditional Sentences Type 1,2,3Document9 paginiXercise Conditional Sentences Type 1,2,3FlashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduce Adverb Clause ExerciseDocument2 paginiReduce Adverb Clause ExerciseSitiKhodijah100% (2)
- 335.subject Verb Agreement Quiz 1 PDFDocument2 pagini335.subject Verb Agreement Quiz 1 PDFMaribie SA MetreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals ExerciseDocument5 paginiModals ExerciseJohanes BungaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE PRESENTED: AN OVERVIEWDocument12 paginiFUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE PRESENTED: AN OVERVIEWDatz leoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjective Clause Worksheet EslDocument4 paginiAdjective Clause Worksheet Eslmali Malek75% (4)
- Naskah Soal Intermediate English Regular CDocument2 paginiNaskah Soal Intermediate English Regular Ciqbal faris100% (1)
- Simple present tense fill in the blanksDocument2 paginiSimple present tense fill in the blanksThevasangiri Tanabalan75% (8)
- Here are the answers to the present perfect tense questions:1. a2. c 3. a4. a5. aDocument14 paginiHere are the answers to the present perfect tense questions:1. a2. c 3. a4. a5. aNaharulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Signal of TensesDocument3 paginiTime Signal of TensesAgni Ganesha Al-Karawi100% (1)
- Conditional Sentence and WishesDocument11 paginiConditional Sentence and WishesMelati Dubidu Bidam67% (9)
- Complex Sentences 1Document6 paginiComplex Sentences 1api-51553536650% (4)
- Contrasting ConjunctionsDocument2 paginiContrasting ConjunctionsStefania Popa100% (1)
- Making An AppointmentDocument2 paginiMaking An AppointmentFranÎncă nu există evaluări
- If Clause As Imperative and SuggestionDocument9 paginiIf Clause As Imperative and SuggestionPutri100% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris I: Toefl Preparation ModuleDocument82 paginiBahasa Inggris I: Toefl Preparation ModuleAfrida RahmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOAL Part of SpeechDocument3 paginiSOAL Part of SpeechNika Dinisa100% (1)
- Adjective ClausesDocument11 paginiAdjective ClausesChristine NadyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Structure UAP 2021-2022Document3 paginiAdvanced Structure UAP 2021-2022Melissa LissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suggest and Offer ExplanationDocument15 paginiSuggest and Offer ExplanationUlffah Ulffah MariaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjective ClauseDocument3 paginiAdjective ClausenicothalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal PronounDocument2 paginiPersonal PronounAirazzahra Pelangi67% (6)
- Chapter 2 - Past, Present, Future Perfect TenseDocument2 paginiChapter 2 - Past, Present, Future Perfect TenseRika Rahayu NingsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cara Belajar 16 Tenses (Verbal & Nominal Sentences) Dan Cara Membuat Kalimat Passive - Sayidin, S.PD (Bagaimana Belajar Bahasa Inggris Dengan Cepat DaDocument6 paginiCara Belajar 16 Tenses (Verbal & Nominal Sentences) Dan Cara Membuat Kalimat Passive - Sayidin, S.PD (Bagaimana Belajar Bahasa Inggris Dengan Cepat DaIrham SevenfoldismÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal UAP Dictation Gasal 2122 - Non RegulerDocument3 paginiSoal UAP Dictation Gasal 2122 - Non RegulerNining SagitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbal & Nominal SentencesDocument7 paginiVerbal & Nominal SentencesTengku Noprizal67% (3)
- How Culture Shapes ThinkingDocument5 paginiHow Culture Shapes ThinkingAnanda KayleenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Expansion 2 p. 348 (group of 3Document20 paginiGrammar Expansion 2 p. 348 (group of 314mandalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Simple Past and Present TenseDocument9 paginiModule 1 Simple Past and Present TenseQuennie86% (28)
- 6-07 Review of Gerund PhrasesDocument2 pagini6-07 Review of Gerund Phrasesbe hatemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relative Clauses - 1 - Multiple ChoiceDocument5 paginiRelative Clauses - 1 - Multiple ChoiceLocNguyen100% (1)
- Unit 1 Talking About Habits - TendenciesDocument2 paginiUnit 1 Talking About Habits - TendenciesValeria Bohorquez GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Habit - Used To/would/past SimpleDocument4 paginiPast Habit - Used To/would/past SimpleUna BeronjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adit Is 40 KG Dennis Is 55 KGDocument11 paginiAdit Is 40 KG Dennis Is 55 KGSandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use Direct and Indirect Speech AppropriatelyDocument2 paginiUse Direct and Indirect Speech AppropriatelyMarielle Villagonzalo100% (2)
- 20 Soal Latihan Gerund Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument1 pagină20 Soal Latihan Gerund Dalam Bahasa InggrisNurul HudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal Latihan Quantifiers A Few, Few, A Little, LittleDocument4 paginiSoal Latihan Quantifiers A Few, Few, A Little, LittleDewa YudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 Morphology and SyntaxDocument9 paginiWeek 1 Morphology and SyntaxAnnisa RahmadhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- TASK 1 BOTH AND. 21 - X.S3 - M Fazri Priya BDocument3 paginiTASK 1 BOTH AND. 21 - X.S3 - M Fazri Priya BWith NameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbal Nominal SentenceDocument1 paginăVerbal Nominal SentenceNuryani AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narrative TextDocument13 paginiNarrative TextMuliadi Shah Putra MangunsongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nominal and Verbal Sentences - Sem2 - Year1-1Document27 paginiNominal and Verbal Sentences - Sem2 - Year1-1Lelly NadyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjective clauses exercise guideDocument4 paginiAdjective clauses exercise guideAnjhielyn Dela Cruz CahiligÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elliptical SentenceDocument13 paginiElliptical SentencePutriAuliaRamadhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discussion Text Exercise 2Document2 paginiDiscussion Text Exercise 2Diki Roy Nirwansyah100% (7)
- Verbs and Tenses Helda Resky Ananda (4518111019)Document6 paginiVerbs and Tenses Helda Resky Ananda (4518111019)heldaresky100% (1)
- Worksheet 54 Reflexive PronounDocument2 paginiWorksheet 54 Reflexive PronounTharathep P100% (2)
- SImple Present TenseDocument15 paginiSImple Present TenseJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present Tense ExplainedDocument15 paginiSimple Present Tense ExplainedJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present: Repeated ActionDocument39 paginiSimple Present: Repeated ActionirmathesweetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4-7 of Oxford Practice GrammarDocument23 paginiUnit 4-7 of Oxford Practice GrammarHarjinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present TenseDocument11 paginiSimple Present Tenseabdul raufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present Tense Explained: Rules, Forms and ExamplesDocument9 paginiSimple Present Tense Explained: Rules, Forms and ExamplesEdi YuniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Resources & Volunteer Management Report Dec 2018Document32 paginiHuman Resources & Volunteer Management Report Dec 2018JoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volunteer HandbookDocument64 paginiVolunteer HandbookanandatimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxic Productivity: 4 Ways to Avoid BurnoutDocument10 paginiToxic Productivity: 4 Ways to Avoid BurnoutJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Meeting Agenda TemplateDocument4 paginiFirst Meeting Agenda TemplateJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- POLTEKKESSBY Studi 851 6.ABSTRAKDocument2 paginiPOLTEKKESSBY Studi 851 6.ABSTRAKJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Servomotor Gs 3630bbDocument1 paginăServomotor Gs 3630bbJohn CevallosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical MaintenanceDocument12 paginiMechanical MaintenanceJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hammering: M. Ilham Ramadhan (10) Wanda Pandu WiditirtoDocument14 paginiHammering: M. Ilham Ramadhan (10) Wanda Pandu WiditirtoJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of SWPDocument8 paginiDevelopment of SWPJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- x230 X230i Ug en IND PDFDocument191 paginix230 X230i Ug en IND PDFndomble_2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Aplikasi Flexiforce Pada Robot Pemindah Barang Otomatis Berbasis Mikrokontroler Avr Atmega 8Document7 paginiAplikasi Flexiforce Pada Robot Pemindah Barang Otomatis Berbasis Mikrokontroler Avr Atmega 8JoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aplikasi Flexiforce Pada Robot Pemindah Barang Otomatis Berbasis Mikrokontroler Avr Atmega 8Document7 paginiAplikasi Flexiforce Pada Robot Pemindah Barang Otomatis Berbasis Mikrokontroler Avr Atmega 8JoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitsubishi diesel forklifts 1.5-3.5 tonnesDocument2 paginiMitsubishi diesel forklifts 1.5-3.5 tonnesJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proximity Sensors: Inductiv e Capacitive Optical - Through-BeamDocument90 paginiProximity Sensors: Inductiv e Capacitive Optical - Through-BeamJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mifa BulkDocument2 paginiMifa BulkJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vibration SensorsDocument29 paginiVibration SensorsRajesh TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Continous TenseDocument12 paginiPast Continous TenseJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mifa Semen PalletDocument2 paginiMifa Semen PalletJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20110421184729Document12 pagini20110421184729Aleksandra KrstovskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Resistance Connections ExplainedDocument4 paginiElectrical Resistance Connections ExplainedJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hoppers: Packing SealsDocument2 paginiHoppers: Packing SealsJoni0% (1)
- Past Future Tense: Dimas Teguh Adi Prabowo Malik Abdul AjisDocument18 paginiPast Future Tense: Dimas Teguh Adi Prabowo Malik Abdul AjisJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument22 paginiActive and Passive VoiceJoni100% (1)
- Simple Present Tense ExplainedDocument15 paginiSimple Present Tense ExplainedJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Present Continuous Tense: Performed by Joni Wijayanto and Wanda Pandu WiditirtoDocument34 paginiThe Present Continuous Tense: Performed by Joni Wijayanto and Wanda Pandu WiditirtoJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Created By: Bagas Febryan Dwi Cahyo Pebri Ika Ndani EVE Batch 10Document20 paginiCreated By: Bagas Febryan Dwi Cahyo Pebri Ika Ndani EVE Batch 10JoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Created By: Bagas Febryan Dwi Cahyo Pebri Ika Ndani EVE Batch 10Document20 paginiCreated By: Bagas Febryan Dwi Cahyo Pebri Ika Ndani EVE Batch 10JoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Created By: Bagas Febryan Dwi Cahyo Pebri Ika Ndani EVE Batch 10Document20 paginiCreated By: Bagas Febryan Dwi Cahyo Pebri Ika Ndani EVE Batch 10JoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present Tense ExplainedDocument15 paginiSimple Present Tense ExplainedJoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Express U40 Adjectives and Adverbs 2Document4 paginiGrammar Express U40 Adjectives and Adverbs 2api-515535366Încă nu există evaluări
- Compound ConjunctionDocument10 paginiCompound ConjunctionMusliFatur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of VerbsDocument3 paginiList of VerbsWalter Cotrina Pandal50% (2)
- Ballad of A Mother's HeartDocument6 paginiBallad of A Mother's HeartRazel Resula100% (1)
- Mixed Conditional SentencesDocument15 paginiMixed Conditional SentencesOen Jan NelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mff1 - The Date, Age and Birthdays - Classroom ObjectsDocument5 paginiMff1 - The Date, Age and Birthdays - Classroom ObjectsGabriela MccawleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table of Specification 4thDocument1 paginăTable of Specification 4throdalyn ninofrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- THESISDocument27 paginiTHESISTutak SangkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- КТП 11 кл 2022-2023 HumanityDocument12 paginiКТП 11 кл 2022-2023 HumanityАйгерим КызайбайÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClassificationDocument2 paginiClassificationveronicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Target Cambridge English First - SB - Compressed PDFDocument178 paginiTarget Cambridge English First - SB - Compressed PDFЮліанна Мурдза75% (4)
- Basicsentencepatterns 140712215304 Phpapp01Document28 paginiBasicsentencepatterns 140712215304 Phpapp01Thiyagarajan CeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Perfect Vs Future ContinuousDocument3 paginiFuture Perfect Vs Future ContinuousMartha MaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- UPSR英文写作技巧Document7 paginiUPSR英文写作技巧Sok Feng Chan100% (1)
- Direct Speech and Reported (Indirect) Speech: Tell + Indirect Object + AboutDocument4 paginiDirect Speech and Reported (Indirect) Speech: Tell + Indirect Object + AboutchelovinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Tense Song LyricsDocument125 paginiPresent Tense Song Lyricsajay negi100% (1)
- Capitalization and Punctuation BASIC PDFDocument2 paginiCapitalization and Punctuation BASIC PDFAribella100% (1)
- Used To PDFDocument4 paginiUsed To PDFKatia LeliakhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objective IELTS Intermediate SBDocument144 paginiObjective IELTS Intermediate SBtritaaa86% (7)
- English 8 Q1 Summative Test Module 5Document5 paginiEnglish 8 Q1 Summative Test Module 5Tivorshio Macabodbod100% (1)
- Catch Up Friday TemplateDocument23 paginiCatch Up Friday TemplateMiriam RicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Speech - Task SheetsDocument10 paginiParts of Speech - Task SheetsNUR KAISAH KAMILIA BINTI MOHAMAD FAUZY IPG-PelajarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Word FormationDocument30 paginiModule 1 Word Formationmarco meduranda100% (3)
- Technical Writing Examples 01Document61 paginiTechnical Writing Examples 01asad qureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WORDREADY Academic English Guide 1.0.1.3Document10 paginiWORDREADY Academic English Guide 1.0.1.3jonMoat0% (1)
- Grammar Rubric #1Document1 paginăGrammar Rubric #1Nashwa RashedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerund and To InfinitiveDocument3 paginiGerund and To InfinitiveAZIZAH KHUSNUL HANIFAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Unit 47Document14 paginiGrammar Unit 47api-3826199Încă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1.1Document2 paginiHomework 1.1Alisson AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade K Ela Georgia Standards of ExcellenceDocument6 paginiGrade K Ela Georgia Standards of Excellenceapi-245879146Încă nu există evaluări