Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Environmental Theory
Încărcat de
Ara Gayares GalloDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Environmental Theory
Încărcat de
Ara Gayares GalloDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ENVIRONMENTAL THEORY
Florence Nightingale (1820-1910)
Founder of Modern Nursing
The first nursing theorist
Also known as The Lady with the Lamp
She was the first to propose nursing
required specific education and training
Origins of the Theory
Nightingale developed her Environmental
Model in 1859 and titled it Notes on
Nursing: What It Is and What It Is Not,
based
on
her
observations
and
experiences while treating the soldiers
during the war.
She used inductive reasoning from her
experiences and observation, addressed
with logical thinking and philosophy.
MAJOR CONCEPTS
"Environment could be altered to improve
conditions so that the natural laws would
allow healing to occur."
Health
The goal of all nursing activities should
be client health
Nursing should provide care to the
healthy as well as the ill
Disease is considered as dys-ease or
the absence of comfort.
Nursing as the act of utilizing the environment
of the patient to assist him in his recovery.
SUBCONCEPTS
Nursing
Health of Houses
Badly constructed houses do for the healthy
what badly constructed hospitals do for the sick.
Nursing is the "activities that promote
health which occur in any caregiving
situation. They can be done by anyone."
It signifies the proper use of fresh air,
light, warmth, cleanliness, quiet, and the
proper selection and administration of
diet.
Ventilation and Warming
Keep the air he breathes as pure as the
external
air,
without
chilling
him.
Human Beings
People are multidimensional, composed
of biological, psychological, social and
spiritual components.
Light
Second to fresh air, the sick need light. Direct
sunlight was what patients wanted.
Environment
Poor or difficult environment led to poor
health and disease
Noise
Patients should never be waken intentionally or
accidentally during the first part of sleep.
Whispered or long conversations about patients
Nightingale was very concerned about noxious
air or effluvia or foul odors that came from
excrement and fumigations.
are thoughtless and cruel. Unnecessary noise,
including noise from female dress, as cruel and
irritating to the patient.
Variety
The need for changes in color and form,
including bringing the patient brightly colored
flowers or plants. Nightingale also advocated
reading, needlework, writing, and cleaning as
activities to relieve the sick of boredom.
Bed and Bedding
Adult in health exhales about three pints of
moisture through the lungs and skin in 24-hours.
Bed should be placed in the lightest part of the
room and placed so the patient could see out of
a window. Caregiver should not lean against, sit
upon, or unnecessarily shake the bed.
Personal Cleanliness
it is necessary to keep pores of the skin free
from all obstructing excretions.
Every nurse ought to wash her hands very
frequently during the day.
Nutrition and Taking Food
Individuals desire different foods at different
times of the day and that frequent small servings
may be more beneficial to the patient than a
large breakfast or dinner.
Chattering Hopes and Advices
To falsely cheer the sick by making light of their
illness and its danger is not helpful.
The nurse should heed what is being said by
visitors, believing that sick persons should hear
good news that would assist them in becoming
healthier.
Social Considerations
The importance of looking beyond the individual
to the social environment in which he or she
lived.
OVERALL EVALUATION
The Environmental Theory of Nursing is a
patient-care theory. It focuses in the alteration of
the patients environment in order to affect
change in his or her health. Caring for the
patient is of more importance rather than the
nursing process, the relationship between
patient and nurse, or the individual nurse.
The environmental factors affect different
patients unique to their situations and illnesses,
and the nurse must address these factors on a
case-by-case basis in order to make sure the
factors are altered in a way that best cares for
an individual patient and his or her needs.
Strengths:
Nightingales theory has broad applicability to
the practitioner. Her model can be applied in
most
complex
hospital
intensive
care
environment, the home, a work site, or the
community at large.
Weaknesses:
The application of her concepts in the twentieth
century is in question.
The environmental conditions that is progressing
along with the technologys advancement out
the theorys applicability in question. The
components of the theory can only be reached
in a very ideal scenario.
USEFULNESS
Environmental adaptation remains
basis of holistic nursing care.
Patients are to be put in the best condition
for nature to act on them, it is the
responsibility of nurses to reduce noise, to
relieve patients anxieties, and to promote
patients wellbeing by making sure all
components of the environment has been
properly set up.
Reading her work raises a consciousness in the
nurse about how the environment influences
client outcomes.
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
1. Pure fresh air
2. Pure water
3. Effective drainage
4. Cleanliness
5. Light (especially direct sunlight)
the
It is true that a healthy environment heals as
what Nightingale stated but the question now is
how our environment would remain health
amidst the negative effects of the progress of
technology and industrialization.
Research Based on Nightingales theory
The Legacy of Florence Nightingales
Environmental Theory: Nursing Research
Focusing on the Impact of Healthcare
Environments: Descriptive statistics reveal that
topics and settings most frequently cited are in
keeping with the current healthcare foci of
patient care quality and safety in acute and
intensive care environments
Nightingale theory and intentional comfort touch
in management of tinea pedis in vulnerable
populations: This describes methods for
mitigating the severity of fungal growth,
decreasing the risk of secondary infections, and
improving skin integrity by manipulating the
micro-environment of the patients' feet.
Incorporating Florence Nightingale's theory of
nursing into teaching a group of preadolescent
children about negative peer pressure: This
clinical practicum project successfully used
Nightingale's primary tenets, such as building
trust, self-assessment, and group leadership, as
a theoretical framework in a nursing practice
group for the purpose of teaching a group of
preadolescent children about negative peer
pressure. The children and their parents
reported positive outcomes from the nurse-led
group sessions.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nightingale TheoryDocument19 paginiNightingale TheoryRohini Rai100% (5)
- Martha RogerDocument10 paginiMartha RogerprashanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ernestine WiedenbachDocument5 paginiErnestine Wiedenbachashidadingshady100% (7)
- Human Becoming TheoryDocument2 paginiHuman Becoming TheoryJane Febe Cabatingan50% (2)
- Abdellah's TheoryDocument15 paginiAbdellah's TheoryGayatri Mudliyar100% (2)
- Evolution of Nursing TheoriesDocument79 paginiEvolution of Nursing TheoriesSundaraBharathi75% (20)
- TFN Concept AsnwesxrationalesDocument34 paginiTFN Concept Asnwesxrationalestflorenz100% (2)
- Virginia Henderson 14 Basic Human NeedsDocument34 paginiVirginia Henderson 14 Basic Human NeedsJi GozelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kings TheoryDocument15 paginiKings TheoryRana VandanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 18 Application Theory in Nursing PracticeDocument27 paginiCHAPTER 18 Application Theory in Nursing PracticeRong Yu100% (2)
- Orlando's TheoryDocument52 paginiOrlando's TheorySimran Josan100% (1)
- Abraham Flexner Six Criteria of A ProfessionDocument1 paginăAbraham Flexner Six Criteria of A ProfessionSonya Robb100% (4)
- Theory ApplicationDocument38 paginiTheory ApplicationAnusha VergheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Nursing Theory of Dorothea Orem WRDDocument26 paginiApplication of Nursing Theory of Dorothea Orem WRDLIDIYA MOL P V100% (5)
- The Helping Art of Clinical Nursing by Ernestine WeidenbachDocument16 paginiThe Helping Art of Clinical Nursing by Ernestine Weidenbachhasan rashid100% (1)
- Nursing as Caring A Model for Transforming PracticeDe la EverandNursing as Caring A Model for Transforming PracticeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSC Form 6 (Leave Form-New)Document4 paginiCSC Form 6 (Leave Form-New)Ara Gayares Gallo63% (8)
- Blueprints Obstetrics and Gynecology 5th Edition MCQDocument30 paginiBlueprints Obstetrics and Gynecology 5th Edition MCQsinglez100% (1)
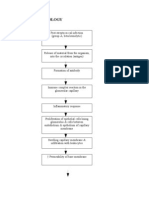
- Pathophysiology of Acute GlumerulonephritisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Acute GlumerulonephritisMASII75% (12)
- NIGHTINGALEDocument7 paginiNIGHTINGALEvikas tak100% (1)
- Florence Nightingales Environmental TheoryDocument5 paginiFlorence Nightingales Environmental TheoryRoshin Tejero100% (1)
- Introduction:-: Background of Theorist (Dorothea Orem 1914-2007)Document27 paginiIntroduction:-: Background of Theorist (Dorothea Orem 1914-2007)Pragnya BhattacharjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virginia HendersonDocument21 paginiVirginia HendersonBabita Dhruw100% (2)
- Abdellah TheoryDocument12 paginiAbdellah TheorygopscharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHN TheoriesDocument89 paginiCHN TheoriesNeethu Vincent100% (1)
- Lydia E Hall's Theory (Nov 06)Document42 paginiLydia E Hall's Theory (Nov 06)soniya naik100% (2)
- Introduction To Nursing TheoriesDocument7 paginiIntroduction To Nursing TheoriesMabes100% (2)
- Nursing TheoriesDocument20 paginiNursing TheoriesMaria Poly100% (1)
- Virginia Henderson's Need TheoryDocument5 paginiVirginia Henderson's Need TheoryNisrin Saud50% (2)
- Peplau's Nursing Theory (Theory of Interpersonal Relation)Document11 paginiPeplau's Nursing Theory (Theory of Interpersonal Relation)Gayatri Mudliyar100% (1)
- Abdellah's 21 Nursing Problems TheoryDocument9 paginiAbdellah's 21 Nursing Problems TheoryAlex AlegreÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Icn Code of Ethics For NursesDocument17 paginiThe Icn Code of Ethics For NursesSanjay Kumar Sanju100% (1)
- Abdellah's TheoryDocument6 paginiAbdellah's TheoryBaldeep GrewalÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Handerson TheoryDocument26 paginiOn Handerson Theoryvikas tak100% (1)
- Orems TheoryDocument37 paginiOrems TheoryGiri Siva100% (2)
- Principles and Techniques of CounsellingDocument22 paginiPrinciples and Techniques of Counsellingchetankumarbhumireddy100% (1)
- Health Promotion ModelDocument9 paginiHealth Promotion ModelSneha100% (1)
- Nursing Seminar Sas 1Document7 paginiNursing Seminar Sas 1Agnes Jeane Enriquez100% (1)
- Nursing TheoriesDocument78 paginiNursing TheoriesElaine Malzan De Guzman100% (7)
- Patricia Benner R.N., PH.D., F.A.A.N., F.R.C.N.: PurposeDocument6 paginiPatricia Benner R.N., PH.D., F.A.A.N., F.R.C.N.: PurposeKhieryl MaranionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joyce TravelbeeDocument15 paginiJoyce TravelbeeGiorgette100% (1)
- Wiedenbach's TheoryDocument41 paginiWiedenbach's TheoryAnnaya KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Nursing Theories and TheoristsDocument4 paginiList of Nursing Theories and Theoristscecedrake100% (2)
- Roy Adaptation TheoryDocument53 paginiRoy Adaptation Theoryrittika das50% (2)
- Application of Orem TheoryDocument17 paginiApplication of Orem TheoryKit LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Imogene KingDocument9 paginiApplication of Imogene KingAnnapurna Dangeti100% (3)
- Classification - of - Nursing - TheoriesDocument20 paginiClassification - of - Nursing - Theoriesako at ang exoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research ProjectDocument15 paginiResearch ProjectPravalika NatarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing TheoriesDocument27 paginiNursing TheoriesKeren Happuch Espiritu100% (1)
- Self-Care Deficit Theory of Nursing: Dorothea E. OremDocument30 paginiSelf-Care Deficit Theory of Nursing: Dorothea E. OremNayzila Briedke UtamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Theories and ApplicationDocument80 paginiNursing Theories and ApplicationJed Ray Gengoba Montayre100% (3)
- Humanistic Nursing TheoryDocument4 paginiHumanistic Nursing Theorymed ward0% (1)
- Pediatric Nursing and Nursing theory-YADocument31 paginiPediatric Nursing and Nursing theory-YALuthi PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis - and - Evaluation - of - Theoretical - Knowledge - in - NursingDocument9 paginiAnalysis - and - Evaluation - of - Theoretical - Knowledge - in - Nursingako at ang exo100% (1)
- Roles and Functions of A NurseDocument3 paginiRoles and Functions of A Nursejhing_tajulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orem's TheoryDocument54 paginiOrem's TheoryGiri SivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orem's TheoryDocument26 paginiOrem's TheorySathish Rajamani100% (2)
- Assignment On Historcal Evolution of Research in NursingDocument35 paginiAssignment On Historcal Evolution of Research in NursingPoonam Dhatwalia100% (1)
- Roger's TheoryDocument57 paginiRoger's TheorySimon Josan100% (1)
- Nurse TheoristsDocument27 paginiNurse TheoristsTami GemarinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing TheoriesDocument5 paginiNursing Theoriesavinash dhameriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Florence Nightingale: Environmental TheoryDocument25 paginiFlorence Nightingale: Environmental TheoryJAMES TONNY OKINYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Florence NightingaleeDocument40 paginiFlorence NightingaleeFiraol NigussieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vanilla OREO Surprise Cupcakes With Marshmallow FrostingDocument3 paginiVanilla OREO Surprise Cupcakes With Marshmallow FrostingAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book 4 The Void of Mist and ThunderDocument215 paginiBook 4 The Void of Mist and ThunderAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Book For The Christian Basics Comprehension TestDocument29 paginiStudy Book For The Christian Basics Comprehension TestAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Tale of Two Prophets - Elijah and ElishaDocument31 paginiA Tale of Two Prophets - Elijah and ElishaAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book 1 The Journal of Curious LettersDocument297 paginiBook 1 The Journal of Curious LettersAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amazing GRaceDocument6 paginiAmazing GRaceAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Jeremiah-The Gloomy PatriotDocument7 pagini10 Jeremiah-The Gloomy PatriotAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flute SongsDocument12 paginiFlute SongsAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glance Hobble Incorrigible Keen Likewise Mirage Orator Nonesense Prime RuffleDocument2 paginiGlance Hobble Incorrigible Keen Likewise Mirage Orator Nonesense Prime RuffleAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Interpersonal RelationsDocument2 paginiTheory of Interpersonal RelationsAra Gayares Gallo100% (1)
- Hildegard Peplau PaperDocument15 paginiHildegard Peplau PaperAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBM Service Vehicle CircularDocument5 paginiDBM Service Vehicle CircularAra Gayares GalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- EmceeDocument3 paginiEmceeAra Gayares Gallo100% (1)
- GBS Review2Document64 paginiGBS Review2Vladimir BasurtoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.respiratory Distress Dental LectureDocument40 pagini5.respiratory Distress Dental LecturehaneeneeÎncă nu există evaluări
- G4 - SCI Summative Test in Science IV (Chapters 14 - 19)Document4 paginiG4 - SCI Summative Test in Science IV (Chapters 14 - 19)Ador Isip100% (2)
- Severe Sepsis Is Sepsis CausingDocument6 paginiSevere Sepsis Is Sepsis CausingHerryanto AgustriadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roleplay FastfoodDocument9 paginiRoleplay FastfoodIndra DarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Residential Treatment Fee Agreement - FarmDocument1 paginăResidential Treatment Fee Agreement - FarmDawn FarmÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCMA113 FUNDA SKILL 1 Performing Medical HandwashingDocument3 paginiNCMA113 FUNDA SKILL 1 Performing Medical HandwashingJessoliver GalvezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatherapy Associates DejnuyoDocument5 paginiAromatherapy Associates Dejnuyobaroqueclothing4269Încă nu există evaluări
- Ichroma II Test Panels 210331 104829Document2 paginiIchroma II Test Panels 210331 104829Sinergy DiagnosticÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV Doctor RahulDocument6 paginiCV Doctor RahulRahul PoddarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Uleration: Thilanka Umesh SugathadasaDocument37 paginiOral Uleration: Thilanka Umesh SugathadasaJuhiJahan AmanullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Express Mini Wall ChartDocument1 paginăExpress Mini Wall ChartchusetapÎncă nu există evaluări
- ManilaDocument17 paginiManilaSarah Jean TraballoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salk Vaccine Cover-Up Resonates TodayDocument2 paginiSalk Vaccine Cover-Up Resonates TodayCTSoldier100% (1)
- Breast Self Examination 1Document36 paginiBreast Self Examination 1zehan iraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 WHO Global Tuberculosis ReportDocument232 pagini2020 WHO Global Tuberculosis Reportsana shakeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- SixthEditionSyllabus2008 01 23Document44 paginiSixthEditionSyllabus2008 01 23kresennnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torn Meniscus A Sports InjuryDocument35 paginiTorn Meniscus A Sports InjuryPradeep RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof Norhayati RMC KPJUCDocument18 paginiProf Norhayati RMC KPJUCtheskywlkrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dapus SkripsiDocument3 paginiDapus SkripsiGaluh MahardikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Thyroxine and Treatment of Hypothyroidism - 2019Document8 pagini2 - Thyroxine and Treatment of Hypothyroidism - 2019Johanna Bustos NutricionistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- White FungusDocument279 paginiWhite FungusDjsjsbÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Risk Prenatal Client - Hiv - AidsDocument20 paginiHigh-Risk Prenatal Client - Hiv - AidsMichael Angelo SeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teratogens and Their EffectsDocument8 paginiTeratogens and Their EffectsrayaimÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCR Testing Centers in The PhilippinesDocument36 paginiPCR Testing Centers in The Philippineskhrayzie bhoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- FFMedicalDevicesRules2017Notifiedon16 01 2018Document93 paginiFFMedicalDevicesRules2017Notifiedon16 01 2018Anonymous dukfCrCBdnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Issu in Midwifery ICM PDFDocument9 paginiQuality Issu in Midwifery ICM PDFFarhatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomedical Acupuncture For Sports and Trauma Rehabilitation: Dry Needling TechniquesDocument6 paginiBiomedical Acupuncture For Sports and Trauma Rehabilitation: Dry Needling Techniquesbysinuti0% (2)