Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems - GATE Study Material in PDF
Încărcat de
Praveen AgrawalDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems - GATE Study Material in PDF
Încărcat de
Praveen AgrawalDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
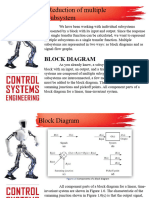
Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems GATE Study Material in PDF
If you are preparing Control Systems for GATE 2017 examination, you will need to learn
the most common form for representing a control system - the Block Diagram. To start
off, you need to understand Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems to help you better
navigate the topic of Signal Flow Graphs and Block Diagrams in Control Systems.
These block diagrams are used to graphically show the system components and flow of
signals while containing the information about dynamic behavior of the system. It uses
functional blocks to link the system variable.
In these free GATE notes, you can learn all about Block Diagram Reduction Techniques.
You can even download this GATE Study Material in PDF so that you can revise at your
convenience. This GATE Study Material is also useful for other exams like IES, BSNL,
DRDO, BARC etc.
Recommended Reading before you begin with Block Diagram Algebra in Control
Systems
Sensitivity & Its Effects on Parameters in Open & Closed Loop Systems
Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems
Block represents the mathematical operation on the incoming signal. Arrows are used
to indicate the direction of signal flow. Also, a system can be represented by more than
one type of block diagram. Once represented, systems can be analyzed further for
various parameters like stability, system gain, etc. It is the basic tool used for the
mathematical modeling of the systems. The various points for analyzing and reduction
of these units are explained below.
1|Page
Basic Blocks in a Control System
The elements used for the connectivity in a block diagram are given as follows.
Summing point: It refers to the summing operation on the incoming signals.
Summing Point Representation in a Block Diagram:
It should be noted that the dimensions of the incoming signals on which the summing
operation is performed, must be same.
Branch point: It is the point from where the signal goes concurrently to the other place
in block diagram.
Branch Point Representation in a Block Diagram:
Block Diagram of a Closed Loop Transfer Function:
The output C(s) of the system is fed back to the input through H(s). Before comparing
the output to the input, the form of output has to be changed and made alike input, for
this purpose H(s) is used.
2|Page
Block Diagram Algebra
When a number of blocks are connected in block diagram then overall transfer
function can be obtained by block diagram reduction technique.
Rules for Block Diagram Reduction
(1) Blocks in Cascade Reduction:
We can calculate:
C(s) C(s) T(s)
=
.
= G1 (s). G2 (s)
R(s) T(s) R(s)
(2) Blocks in Parallel Reduction:
(3) Moving a Take-off Point After the Block:
While transforming the block diagram we have to keep in mind that the signals at points
must not change. As we can see that signal at (1) is R(s) and signal at (3) is again
1
R(s) . G(s) .
= R(s).
G(s)
3|Page
(4) Moving a Take-off Point Before the Block:
(5) Moving a Summing Point Before the Block:
(6) Moving a Summing Point After the Block:
(7) Interchanging Two Summing Points:
4|Page
(8) Moving a Take-Off Point Before a Summing Point:
(9) Moving a Take-Off Point After a Summing Point:
(10) Eliminating Feedback Loop:
Liked this article on Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems? Let us know in the
comments! Here are more articles that you may like
Laplace Transforms - Concepts & Formula Sheet
5|Page
Basic Network Theory Concepts
Eigen Values & Eigen Vectors
Opportunities through GATE 2017
6|Page
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Analog Automation and Digital Feedback Control TechniquesDe la EverandAnalog Automation and Digital Feedback Control TechniquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDocument29 paginiBlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDienies TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlDe la EverandNonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transfer FunctionDocument11 paginiTransfer FunctionNagmani KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signal Flow Graph and Block DiagramDocument23 paginiSignal Flow Graph and Block DiagramSolayao, Jan Marvin J.Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15De la EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15Încă nu există evaluări
- Controls Finals ResearchDocument15 paginiControls Finals ResearchRenz Xynor Liotib CadizÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSD2Document47 paginiMSD2moeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson #2 Lecture #2 Block Diagram RepresentationDocument32 paginiLesson #2 Lecture #2 Block Diagram RepresentationShazidÎncă nu există evaluări
- C.S Unit - 2Document22 paginiC.S Unit - 2Rajendar PonagantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofDocument10 paginiStudy, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofTana AzeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Block DiagramDocument47 paginiIntroduction To Block DiagramAini SalwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALL5 Block DiagramDocument8 paginiALL5 Block Diagramstudents answerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zahra AbdulHameed ShukrDocument11 paginiZahra AbdulHameed ShukrTana AzeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Document45 paginiControl Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Ayub Abd RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document14 paginiLecture 2Abdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagrams EnotesDocument7 paginiBlock Diagrams Enotespatel_vicky87Încă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Document45 paginiControl Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Akula VeerrajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- FME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsDocument47 paginiFME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsJesse Jon FerolinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Perform A Block Diagram Reduction Using MATLAB - Matlab ExamplesDocument5 paginiTo Perform A Block Diagram Reduction Using MATLAB - Matlab Examplesdanycg85Încă nu există evaluări
- Block DiagramDocument12 paginiBlock DiagramJohn Cedrik RetardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 02: 1 What Is Meant by Mathematical Modelling of A Control SystemDocument2 paginiAssignment 02: 1 What Is Meant by Mathematical Modelling of A Control SystemSyed AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5-Feedback ControlDocument12 paginiLecture 5-Feedback ControlKAILA FUNTANILLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wala Pa NahumanDocument3 paginiWala Pa NahumanJohnCarloTigueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture-Block Diagram Reduction (Compatibility Mode)Document21 paginiLecture-Block Diagram Reduction (Compatibility Mode)Miera SmaelzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems Theory: Introduction To Block DiagramDocument47 paginiControl Systems Theory: Introduction To Block DiagramFadly ShafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON2 ControlSystemBlockDiagramDocument20 paginiLESSON2 ControlSystemBlockDiagramalexancog456Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10Document93 paginiChapter 10Carraan Dandeettirra Caala Altakkatakka100% (1)
- Signals Flow GraphsDocument14 paginiSignals Flow GraphsMAFOQ UL HASSANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Mathematical Modeling - 2Document15 paginiChapter 2 - Mathematical Modeling - 2Qadeer AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagrams and Signal Flow Graphs: Lesson PlanDocument23 paginiBlock Diagrams and Signal Flow Graphs: Lesson PlanVARUN B MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control SystemsDocument32 paginiControl Systemsselvi0412100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic SystemDocument56 paginiChapter 2 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic SystemAmanuel AsfawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Control SystemDocument72 paginiModern Control SystemBewnet GetachewÎncă nu există evaluări
- L - Block Diagrams of A Control System PDFDocument22 paginiL - Block Diagrams of A Control System PDFKunal NarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slides 3: Reduction of Multiple SystemsDocument25 paginiSlides 3: Reduction of Multiple SystemsAhmad AbunassarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEXP2Document15 paginiCSEXP2Kavita DhamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagram Representation2Document74 paginiBlock Diagram Representation2Chernet TugeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System LP 3Document13 paginiControl System LP 3Neans PlanterasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 003 ME31002 - Block Diagram-2021febDocument54 pagini003 ME31002 - Block Diagram-2021febShek Yu LaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feedback and Control System Module - 19Document28 paginiFeedback and Control System Module - 19AkiHiro San CarcedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transfer Functions Block Diagrams Signal Flow Graph Mason's Gain FormulaDocument28 paginiTransfer Functions Block Diagrams Signal Flow Graph Mason's Gain FormulaMesut OzilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detect Abrupt System Changes Using Identification TechniquesDocument6 paginiDetect Abrupt System Changes Using Identification TechniquesPierpaolo VergatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objectives : Transfer Function +Document5 paginiObjectives : Transfer Function +Ehab SagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 45Document73 paginiLec 45api-247714257Încă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Mechatronic Systems ContentsDocument8 paginiOverview of Mechatronic Systems Contentsjerry4dÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagrams - Lecture NotesDocument8 paginiBlock Diagrams - Lecture NotesMichael HsiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block DiagramDocument20 paginiBlock DiagramabcdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagram and Signal FlowDocument23 paginiBlock Diagram and Signal Floweltn s.Încă nu există evaluări
- Transfer Functions, Block Diagram and Signal Flow Graph (Week 2 & 3)Document17 paginiTransfer Functions, Block Diagram and Signal Flow Graph (Week 2 & 3)Wan TingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab # 8 SolvedDocument10 paginiLab # 8 SolvedZabeehullahmiakhailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment 1 (B)Document15 paginiLab Experiment 1 (B)Laiba MaryamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab # 8 Control SystemDocument10 paginiLab # 8 Control SystemZabeehullahmiakhailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 4 - Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsDocument28 paginiLect 4 - Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsMahatma Pandima Putra100% (1)
- Lab 04 - Husnain ZDocument10 paginiLab 04 - Husnain ZMuhammad MohsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1Document13 paginiExperiment 1Mike QuinteroÎncă nu există evaluări
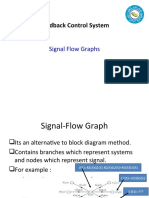
- Signal Flow Graph - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument5 paginiSignal Flow Graph - GATE Study Material in PDFAtul ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Engineering MT-353: Signal Flow GraphsDocument21 paginiControl Engineering MT-353: Signal Flow GraphsTahaKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coverage Analysis For Model Based Design Tools: William Aldrich The Mathworks, Inc. 3 Apple Hill Dr. Natick, Ma 02478Document17 paginiCoverage Analysis For Model Based Design Tools: William Aldrich The Mathworks, Inc. 3 Apple Hill Dr. Natick, Ma 02478Lindung SiswantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read Chapter 4 Minicase: Fondren Publishing, Inc. From The Sales Force Management Textbook by Mark W. Johnston & Greg W. MarshallDocument1 paginăRead Chapter 4 Minicase: Fondren Publishing, Inc. From The Sales Force Management Textbook by Mark W. Johnston & Greg W. MarshallKJRÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To FractionsDocument18 paginiA Guide To FractionsAnnelyanne RufinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MNLG 4Document2 paginiMNLG 4Kanchana Venkatesh39% (18)
- Item Bank - Science 5 - 2ND QuarterDocument11 paginiItem Bank - Science 5 - 2ND QuarterJasmine AguilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tfa Essay RubricDocument1 paginăTfa Essay Rubricapi-448269753Încă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Conceptual Physics 12th Edition Hewitt Test Bank PDFDocument36 paginiDwnload Full Conceptual Physics 12th Edition Hewitt Test Bank PDFscreamsoaring.pm7hcv100% (13)
- 160 LW Bending Tester v2.0Document4 pagini160 LW Bending Tester v2.0Sá StrapassonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gallery IsKCON Desire Tree PDF MudrasDocument2 paginiGallery IsKCON Desire Tree PDF MudrassanatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of AIDocument27 paginiHistory of AImuzammalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Kompetensi Spiritual Guru Pendidikan Agama Kristen Terhadap Pertumbuhan Iman SiswaDocument13 paginiPengaruh Kompetensi Spiritual Guru Pendidikan Agama Kristen Terhadap Pertumbuhan Iman SiswaK'lala GrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2Document8 paginiPaper 2Antony BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criteria 5 Points 4 Points 3 Points 2 Points 1 Point Total PointsDocument2 paginiCriteria 5 Points 4 Points 3 Points 2 Points 1 Point Total PointsReyno D. Paca-anasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 01 15 12 00 22 PDFDocument26 pagini2016 01 15 12 00 22 PDFABHIJEET SHARMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Employee Loyalty On Customer S PDFDocument37 paginiEffect of Employee Loyalty On Customer S PDFShailendra DasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESC Cardiomyopathy ClassificationDocument7 paginiESC Cardiomyopathy Classificationvalerius83Încă nu există evaluări
- ch09 (POM)Document35 paginich09 (POM)jayvee cahambingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catibayan Reflection AR VRDocument6 paginiCatibayan Reflection AR VRSheina Marie BariÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Magical Number SevenDocument3 paginiThe Magical Number SevenfazlayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument16 paginiErythrocyte Sedimentation Rateapi-3823785100% (2)
- The Students Ovid Selections From The Metamorphoses by Ovid, Margaret Worsham MusgroveDocument425 paginiThe Students Ovid Selections From The Metamorphoses by Ovid, Margaret Worsham MusgroveMiriaam AguirreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic Flour Mills Inc vs. Comm. of Cutoms (39 SCRA 509) Case DigestDocument3 paginiRepublic Flour Mills Inc vs. Comm. of Cutoms (39 SCRA 509) Case DigestCamelle EscaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Catholic Prayer 1Document88 paginiBasic Catholic Prayer 1Josephine PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MInor To ContractsDocument28 paginiMInor To ContractsDakshita DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Portrayal of Gender and A Description of Gender Roles in SelectDocument429 paginiA Portrayal of Gender and A Description of Gender Roles in SelectPtah El100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions 5Document18 paginiMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions 5dee_day_8Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 3 Indigenous People in The PhilippinesDocument6 paginiQuiz 3 Indigenous People in The PhilippinesMa Mae NagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF Certificacion 3dsmaxDocument2 paginiPDF Certificacion 3dsmaxAriel Carrasco AlmanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENG101 Final Term NOTES by VU LearningDocument15 paginiENG101 Final Term NOTES by VU LearningAbdul WahabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 105-0004 - Significant Characteristics For Compliance With Emission RegulationsDocument5 pagini105-0004 - Significant Characteristics For Compliance With Emission RegulationsthisisjineshÎncă nu există evaluări
- BrookfieldDocument8 paginiBrookfieldFariha Naseer Haral - 28336/TCHR/JVAITÎncă nu există evaluări