Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CH 10 Tests A, B, C
Încărcat de
Mostafa BayoumyTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CH 10 Tests A, B, C
Încărcat de
Mostafa BayoumyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Name
Date
Chapter Test
Class
CHAPTER 10
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
Part A: Multiple Choice
In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers
each question.
1. How many chromosomes are found in human body cells?
A. 11
B. 23
C. 46
D. 92
2. Which describes a gene?
A. chromosome pair
B. chromosome trait
C. DNA segment
D. haploid cell
3. How is an allele described?
A. form of a gene
B. one haploid cell
C. part of a chromosome
D. short segment of DNA
Part B: Matching
Statement
Mitosis
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
For each statement, check the box indicating whether the statement applies to mitosis or
meiosis. Check only one box for each statement.
Meiosis
1. Two sets of cell divisions occur.
2. The DNA of the resulting daughter cells are identical.
3. Gametes are formed.
4. Cell growth and repair is completed.
5. Potential evolutionary changes can occur more frequently.
24
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics CHAPTER 10
Unit 3
Name
Chapter Test
Date
Class
CONTINUED
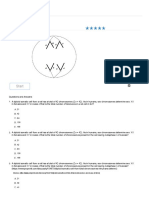
Part C: Interpreting Punnett Squares
Use the Punnett square below to respond to the following statement.
T = tongue rolling
t = unable to roll tongue
TT
Tt
1. Describe the genotypes of the two possible offspring labeled A and B in the Punnett
square above.
A.
B.
Use the Punnett square below to respond to the following statement.
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
R=
r =
Y=
y=
round seeds
wrinkled seeds
yellow seeds
green seeds
RY
RY
Ry
rY
ry
Ry
rY
ry
2. Describe the genotypes of the offspring labeled A, B, and C in the Punnett square above.
A.
Unit 3
B.
C.
CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
25
Name
Date
Chapter Test
Class
CONTINUED
Part D: Short Answer
Write your response to each statement in the space provided.
1. Contrast the genetic makeup of offspring from sexual and asexual reproduction.
2. Contrast the genotype and phenotype of an organism.
Part E: Concept Application
Write your response to each statement in the space provided.
1. A gardener crosses a plant with white flowers and a plant of the same species that
has red flowers. The offspring of these plants have white flowers. Infer how the
observations of the gardener are an example of the terms recessive and dominant.
Include the term F1 generation in your discussion.
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
2. Apply For thousands of years, humans have bred different types of dogs, resulting
in dozens of breeds with a wide diversity of traits. Dogs have 76 chromosomes. Why
are so many different dog traits possible? Use the term genetic recombination in
your answer.
26
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics CHAPTER 10
Unit 3
Name
Date
Chapter Test
Class
CHAPTER 10
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
Part A: Multiple Choice
In the space at the left, write the letter of the number, phrase, or sentence that best completes
each statement or answers each question.
1. Which is a difference between meiosis I and meiosis II?
A. Cytokinesis occurs during meiosis II but not meiosis I.
B. Meiosis I has a prophase stage, but meiosis II does not.
C. Meiosis II results in four haploid cells instead of two diploid cells.
D. Nuclear membranes form during meiosis II but not meiosis I.
2. What is formed as a result of mitosis?
A. four genetically different cells
B. four genetically identical cells
C. two genetically different cells
D. two genetically identical cells
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
3. Which summarizes the genetic research completed by the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel?
A. After years of research, Mendel identified the genes for flower colors.
B. Mendel bred various dog breeds to discover the science of genetics.
C. Mendel hypothesized that the offspring of pea plant traits are inherited.
D. Using Punnett squares, Mendel developed the principles of genetics.
4. An organism with the genotype DD for a trait is
A. heterozygous dominant.
B. heterozygous recessive.
C. homozygous dominant.
D. homozygous recessive.
5. What is the probability that a cross between a heterozygous dominant yellow-seeded pea
plant and a green-seeded pea plant will produce green-seeded offspring?
A. 1:1
B. 1:2
C. 1:4
D. 1:8
Part B: Matching and Completion
Matching Write the letter of the phase of meiosis I on the line next to each statement.
Answers may be used only once or not at all.
1. Chromosome number is reduced from 2n to 1n.
A. anaphase I
2. Two sister chromatids reach opposite poles of the cell.
B. interphase
3. Homologous chromosomes become visible, condense, and form pairs.
C. metaphase I
4. DNA is replicated.
D. prophase I
5. Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the equator.
E. telophase I
F. anaphase II
Unit 3
CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
27
Name
Date
Chapter Test
Class
CONTINUED
Completion Write the correct term in the blank to complete each sentence below.
6. The number of chromosomes in a human body cell equals
7. A segment of DNA is called a(n)
8. An Escherichia coli bacterium daughter cell inherits the exact DNA from its parent cell during the process
of
9. The passing of fur color from a parent leopard to its offspring is an example
of
10. A heterozygous pea plant is also called a(n)
Part C: Interpreting Punnett Squares
Use the Punnett square below to respond to the following statement.
T = tongue rolling
t = unable to roll tongue
1. Predict the genotypes of the four possible gamete combinations labeled AD in the
Punnett square above.
B.
C.
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A.
D.
Use the Punnett square below to respond to the following statement.
R=
r =
Y=
y=
round seeds
wrinkled seeds
yellow seeds
green seeds
RY
RY
Ry
rY
ry
Ry
rY
ry
2. Predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the three
possible gamete combinations labeled A, B, and C in
the Punnett square above.
A.
B.
C.
28
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics CHAPTER 10
Unit 3
Name
Chapter Test
Date
Class
CONTINUED
Part D: Short Answer
Write your response to each statement in the space provided.
1. Describe homologous chromosomes.
2. Explain the process of fertilization. Use the term chromosome in your answer.
3. Contrast dominant and recessive traits.
Part E: Concept Application
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Write your response to each statement in the space provided.
1. Hypothesize An aquarium hobbyist wants to breed guppies with large, fan-shaped,
red tails. The hobbyist has a large number of guppies with assorted tail colors and
shapes in an aquarium. Write a hypothesis that explains how the hobbyist should
proceed to breed a population of guppies with the desired traits.
2. A gardener crosses a snapdragon plant that has white flowers with a snapdragon
plant with red flowers. All the offspring in the F1 generation produce pink flowers.
The gardener crosses two of the plants with pink flowers, and the snapdragon plants
of the F2 generation have red, white, or pink flowers. Infer reasons for the gardeners
observations.
Unit 3
CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
29
Name
Date
Chapter Test
Class
CHAPTER 10
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
Part A: Multiple Choice
In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers
each question.
1. Which is the number of chromosomes in a haploid cell?
A. 1n
B. 2n
C. 3n
D. 4n
2. Which event occurs during meiosis II but not during meiosis I?
A. cytokinesis occurs after the final phase
B. haploid number of chromosomes line equator
C. sister chromotids are pulled to opposite poles
D. spindle apparatus forms inside the cell
3. Which is the ratio of pea plant offspring with green seeds if both parents are hybrids?
A. 1:1
B. 1:2
C. 1:4
D. 1:8
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
4. Which causes genetic recombination?
A. alleles
B. crossing over
C. genes
D. hybrid crosses
5. How is polyploidy defined?
A. extra chromosome sets
B. frequency of crossover
C. independently linked genes
D. random allele assortment
Part B: Matching and Completion
Matching Write the letter of the correct meiosis I phase on the line next to its description.
Answers may be used only once or not at all.
1. Crossover can occur frequently.
A. anaphase I
2. Homologous pairs are at opposite poles.
B. interphase
3. Proteins are synthesized.
C. metaphase I
4. Spindle fibers guide separated homologous
chromosome pairs toward opposite poles.
D. prophase I
5. Homologous pairs line up at the equator.
E. telophase
F. anaphase II
30
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics CHAPTER 10
Unit 3
Name
Chapter Test
Date
Class
CONTINUED
Completion Write the correct term in the blank to complete each sentence below.
6. A DNA segment is called a(n)
7. Genetic variation can occur during meiosis because of the process of
8. Offspring that are genetically identical to their parent are a result of the process
of
9. The possibility for either green or yellow seeds in pea plants is an example of
possible
10. The allele pairs of an individual organism are called its
Part C: Interpreting Punnett Squares
T = tongue rolling
t = unable to roll tongue
Use the Punnett square to the right to respond to the following statement.
1. Describe the genotypes and phenotypes of the two parents that produce the
four possible gamete combinations in the Punnett square.
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Use the Punnett square to the right to respond to the following statement.
2. Discuss the probabilities of all the possible phenotypes of the F1
generation represented by the genetic cross of the Punnett square.
R
r
Y
y
=
=
=
=
TT
Tt
Tt
tt
round seeds
wrinkled seeds
yellow seeds
green seeds
RY
Ry
rY
ry
RY
Ry
Part D: Short Answer
rY
Write your response to each statement in the space provided.
ry
1. Summarize Mendels research on the heredity of plants.
Unit 3
CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
31
Name
Date
Chapter Test
Class
CONTINUED
2. Explain Mendels law of segregation.
3. Describe gene linkage.
Part E: Concept Application
Write your response to each statement in the space provided.
1. The color of rabbit fur can be gray, brown, white, or a mixture of black and white.
A single gene determines the color for rabbit fur. Infer how the phenotype for rabbit
fur is determined.
32
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics CHAPTER 10
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
2. A cross between a homozygous, white-haired horse and a homozygous, black-haired
horse produces offspring that all are the same color, but they are neither black nor
white. Interpret the genotype and phenotype of the F1 generation offspring.
Unit 3
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Study Guide Sexual Reproduction and Genetics English EditableDocument4 paginiStudy Guide Sexual Reproduction and Genetics English Editableapi-342334216Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetics TestDocument26 paginiGenetics TestBaitz5Încă nu există evaluări
- Guided Reading Chapter 16Document5 paginiGuided Reading Chapter 16Tara Gambetta50% (4)
- Biology Chapter 11 TestDocument11 paginiBiology Chapter 11 Testmohamad aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: - Date: - Period: - IB Biology - Meiosis Multiple Choice Practice Questions 1Document5 paginiName: - Date: - Period: - IB Biology - Meiosis Multiple Choice Practice Questions 1Ghazal Fatima100% (2)
- DNA Worksheet #2 PDFDocument2 paginiDNA Worksheet #2 PDFmineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 TestDocument5 paginiUnit 1 Testapi-485795043Încă nu există evaluări
- Chromosome Mitosis Meiosis Review WorksheetDocument4 paginiChromosome Mitosis Meiosis Review Worksheetapi-331662907Încă nu există evaluări
- 11.4 Meiosis: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagini11.4 Meiosis: Multiple ChoiceMING ZHUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 The Biosphere Test ADocument7 paginiChapter 3 The Biosphere Test ATUTORKIMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Division ExerciseDocument3 paginiCell Division ExerciseFauziah Abu BakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEN102 2019 Lecture 1 WO 30326 PDFDocument97 paginiCSEN102 2019 Lecture 1 WO 30326 PDFMostafa BayoumyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheDocument8 paginiPart A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheQueng ElediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2008 Biology: InsightDocument23 pagini2008 Biology: InsightXavier GavinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics AnswerDocument9 paginiGenetics Answer무루파털뭉치Încă nu există evaluări
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocument38 paginiNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 PDFDocument14 paginiChapter 12 PDFJeanPaule Joumaa100% (1)
- 8.3 Section Quiz: Dna ReplicationDocument1 pagină8.3 Section Quiz: Dna Replicationsev :3Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 - 1Document12 paginiChapter 11 - 1JeanPaule JoumaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eoc ReviewDocument33 paginiEoc Reviewapi-237316144Încă nu există evaluări
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyDocument2 paginiRajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyRajeem Outlaw WrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 paginiChapter 10 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction: Multiple Choice Questionsquiet19Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Document6 paginiCell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Tia wkwk100% (1)
- Content Review PacketDocument9 paginiContent Review Packetapi-342334216Încă nu există evaluări
- Kami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - Video - Recap - of - Dna - Replication - by - Amoeba - Sisters - Newheader - v.2Document2 paginiKami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - Video - Recap - of - Dna - Replication - by - Amoeba - Sisters - Newheader - v.2Luuk Van MeursÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeneticsDocument8 paginiGenetics무루파털뭉치Încă nu există evaluări
- Chromosomes and Heredity ReviewDocument8 paginiChromosomes and Heredity ReviewarurusipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chromosomel Structure and MutDocument4 paginiChromosomel Structure and MutAbhishek SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Punnett Square Packet 2012Document13 paginiBiology Punnett Square Packet 2012api-241528754Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Bioa 2015Document10 paginiFinal Bioa 2015api-237801056100% (1)
- 19 Evidence For Evolution-S PDFDocument6 pagini19 Evidence For Evolution-S PDFstlcajun55Încă nu există evaluări
- 16 Genetic Mutations-S PDFDocument7 pagini16 Genetic Mutations-S PDFHelp Me Study TutoringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Chapter 4 TestDocument7 paginiBiology Chapter 4 TestCK. GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chromosome Structure: Chromosomal Changes Occur in Three Basic Categories: Rearrangement, Aneuploidy, and PolyploidyDocument56 paginiChromosome Structure: Chromosomal Changes Occur in Three Basic Categories: Rearrangement, Aneuploidy, and PolyploidyBryce WatsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise On Dynamic EcosystemDocument8 paginiExercise On Dynamic EcosystemNorliyana AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 20Document97 pagini15 20dianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap Biology Mid Term PretestDocument30 paginiAp Biology Mid Term PretestKrisnavimala Krishnan0% (1)
- Cell Organelle MatchingDocument3 paginiCell Organelle MatchingElla LaretaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Exploration: Cell Energy Cycle: Gizmo Warm-UpDocument5 paginiStudent Exploration: Cell Energy Cycle: Gizmo Warm-UpDaniil ByramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretest 10Document5 paginiPretest 10Ghazi DallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Reading StrategyDocument2 paginiSection 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Reading StrategyensentisÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Cell Division QuestionsDocument18 paginiH2 Cell Division QuestionsWesley TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA and RNA WorksheetsDocument6 paginiDNA and RNA WorksheetsA. Nurul Virninda YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pavia National High School Pavia, Iloilo Science and Technology Iii (Biology) Summative TestDocument1 paginăPavia National High School Pavia, Iloilo Science and Technology Iii (Biology) Summative TestLouise Meara SeveroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 - Biochemistry of Life: Chapter 4: Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of LifeDocument44 paginiUnit 2 - Biochemistry of Life: Chapter 4: Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of LifeJeremy CorrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendelian & Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument37 paginiMendelian & Non-Mendelian GeneticsJubair Al-rashid100% (2)
- Cell Transport: Lesson QuizDocument3 paginiCell Transport: Lesson QuizIsabella Hosman RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Chapter 2 - ProProfs QuizDocument9 paginiGenetics Chapter 2 - ProProfs QuizlifecostÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Replication Practice WKSH Blank PDFDocument2 paginiDNA Replication Practice WKSH Blank PDFKim100% (2)
- Viruses: Capsid: The Outer Protein Layer That Surrounds The Genetic Material of A VirusDocument2 paginiViruses: Capsid: The Outer Protein Layer That Surrounds The Genetic Material of A VirusKlutz4LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Chapter 10 Test Answer KeyDocument9 paginiBiology Chapter 10 Test Answer Keymohamad aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketDocument7 paginiUnit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketShannon ErdmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 1 Introduction and Cell SignalingDocument9 paginiProblem Set 1 Introduction and Cell SignalingPreston Adhikari100% (1)
- Plant Structure and Function Post-Lab Sheet Student FormDocument6 paginiPlant Structure and Function Post-Lab Sheet Student Formharrison100% (1)
- CH 15 WorkbookDocument10 paginiCH 15 Workbookapi-237586441100% (1)
- WORKSHEET 14.4 Inheritance of TraitsDocument5 paginiWORKSHEET 14.4 Inheritance of TraitsafzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 12 Additional Questions (Cell Transport)Document31 paginiYear 12 Additional Questions (Cell Transport)dramitrajp9602100% (2)
- 26 Ecological Pyramids-SDocument6 pagini26 Ecological Pyramids-Sapi-290419496100% (1)
- Evolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersDocument10 paginiEvolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersSuhani SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology Principles and Practice 1st Edition Michael M CoxDocument6 paginiTest Bank For Molecular Biology Principles and Practice 1st Edition Michael M CoxglendavictoriabbkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Biology 9Document15 paginiFinal Biology 9marogammaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 11 Reaction EquilbruimDocument24 paginiLecture 11 Reaction EquilbruimMostafa BayoumyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEN202 Practice 1 Solution 31917 PDFDocument8 paginiCSEN202 Practice 1 Solution 31917 PDFMostafa BayoumyÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Do Hydraulic Bridges WorkDocument4 paginiHow Do Hydraulic Bridges WorkMostafa BayoumyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Done By: Mostafa Grade: 10B Bio Teacher: Mr. Kamel: What Is Alzheimer's Disease?Document18 paginiDone By: Mostafa Grade: 10B Bio Teacher: Mr. Kamel: What Is Alzheimer's Disease?Mostafa BayoumyÎncă nu există evaluări
- QQ 02Document17 paginiQQ 02Mostafa BayoumyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contents of A Dead Man QuizDocument2 paginiContents of A Dead Man QuizMostafa BayoumyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teacher's Guide Grade 4: Soil Properties and ExperimentsDocument3 paginiTeacher's Guide Grade 4: Soil Properties and ExperimentsJudelle Marie PedrablancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- June 2001 Acorn Newsletter - Salt Spring Island ConservancyDocument16 paginiJune 2001 Acorn Newsletter - Salt Spring Island ConservancySalt Spring Island ConservancyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018-2027 Marelco PSPPDocument24 pagini2018-2027 Marelco PSPPHans CunananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chicken Soup Cookbook - Chicken RecipesDocument74 paginiChicken Soup Cookbook - Chicken RecipesGary TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Industry IntroductionDocument8 paginiSteel Industry IntroductionAmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Image of War, or Service in The Chin Hills. - NEWLAND, A. G. EDocument3 paginiThe Image of War, or Service in The Chin Hills. - NEWLAND, A. G. ELTTuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- GingerDocument9 paginiGingerthippli100% (1)
- International Code of Nomenclature For Algae, Fungi, and Plants PreambuleDocument1 paginăInternational Code of Nomenclature For Algae, Fungi, and Plants PreambuleSharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uel Sugarcrete Slab Report Oct 2021Document55 paginiUel Sugarcrete Slab Report Oct 2021Jorge Z. Uscanga V.Încă nu există evaluări
- El Día de La Cruz - Los Favoritlos de AhuachapanDocument3 paginiEl Día de La Cruz - Los Favoritlos de AhuachapanCarlos L. HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 3 November 2000Document2 paginiPaper 3 November 2000MSHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irl GekkoDocument51 paginiIrl GekkojcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bozeman Science Ecosystems Guided ViewingDocument2 paginiBozeman Science Ecosystems Guided Viewingapi-236697820Încă nu există evaluări
- Soal Uts Kelas 9 2019Document2 paginiSoal Uts Kelas 9 2019ahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luci Ancora Lunch Menu Sept 2013Document2 paginiLuci Ancora Lunch Menu Sept 2013Luci Ancora & Ristorante LuciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Herbicide Damage Symptoms GuideDocument8 paginiHerbicide Damage Symptoms GuidedickoluckymanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sunday Times Food Weekly Readers' Recipe Collection 2014Document68 paginiSunday Times Food Weekly Readers' Recipe Collection 2014SA Books100% (1)
- (23279834 - HortScience) SEED PELLETING-HISTORY AND MODERN FUNDAMENTALSDocument3 pagini(23279834 - HortScience) SEED PELLETING-HISTORY AND MODERN FUNDAMENTALSTayná Cunha SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.4 PhotoperiodismDocument22 pagini10.4 PhotoperiodismDaksha yashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative TestDocument3 paginiSummative TestJose Rene IlisacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Properties of Tiger Nut Seed PDFDocument3 paginiEngineering Properties of Tiger Nut Seed PDFvodounnouÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification Revision NotesDocument52 paginiCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification Revision NotesHarekrishna DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Endophytes in Plant Health ADocument27 paginiRole of Endophytes in Plant Health AÉtori AguiarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TODAY IN HISTORY: Happy 150th Birthday, Jose RizalDocument3 paginiTODAY IN HISTORY: Happy 150th Birthday, Jose RizalAramis LedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles Tecnico PDFDocument62 paginiIngles Tecnico PDFJUAN PUMACCAHUA ROCCAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure SEDocument8 paginiCell Structure SESandra FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Four New Species of Chaetogastra (Melastomeae, Melastomataceae) From Southern BrazilDocument21 paginiFour New Species of Chaetogastra (Melastomeae, Melastomataceae) From Southern BrazilDiego Alejandro Amaya HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Project DescriptionDocument5 paginiResearch Project DescriptionMeghan BarrettÎncă nu există evaluări
- A B C D A B C D A B: Tabel 1. Jawaban 36 Peserta Tes Terhadap 10 Soal Pilihan Ganda Nomor Soal No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Document31 paginiA B C D A B C D A B: Tabel 1. Jawaban 36 Peserta Tes Terhadap 10 Soal Pilihan Ganda Nomor Soal No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Niniati physicalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forest ProjectDocument11 paginiForest Projectapi-377276621Încă nu există evaluări