Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Introduction Ind. Engg-1
Încărcat de
SujalBhavsarTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Introduction Ind. Engg-1
Încărcat de
SujalBhavsarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
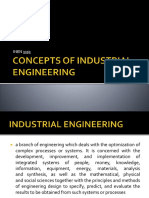
Introduction to Industrial Engineering
Industrial engineering is a branch of engineering that concerns with the development,
improvement, implementation and evaluation of integrated systems of people, money, knowledge,
information, equipment, energy, material and process. It also deals with designing new prototypes to
help save money and make the prototype better. Industrial engineering draws upon the principles
and methods of engineering analysis and synthesis, as well as mathematical, physical and social
sciences together with the principles and methods of engineering analysis and design to specify,
predict and evaluate the results to be obtained from such systems.
Industrial engineers (IEs) apply science, mathematics, and engineering methods to complex
system integration and operations.
Industrial Engineering defined:
Industrial engineering has been defined as the engineering approach applied to all factors,
including human factors involved in the production and distribution of products or services.
The art and science of utilizing and coordinating men, equipment and materials to attain a
desired quantity and quality of output at a specified time and at an optimum cost. This may
include gathering , analyzing and acting upon facts pertaining to building and facilities,
layouts, personnel organization, operating procedures, methods, processes, schedules, time
standards, wage rates, wage payment plans, costs and systems for controlling the quality and
quantity of goals and services (ASME)
American Institute of Industrial Engineers has defined the special field of Industrial
Engineering as: Concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated
systems of people, materials, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge
and skill in the mathematical, physical and social sciences together with the principles and
methods of engineering analysis and design to specify, predict and evaluate the results to be
obtained from such systems.
Functions of Industrial Engineering:
1) Organizational and Management Methods
2) Site Selection and plant Layout
3) Materials Handling Methods
4) Methods Engineering
5) Time Study
6) Production Planning Control
7) Quality Control
8) Cost Control
9) Job Evaluation
10) Wage Incentive
11) Operation Research
Growth of Industrial Engineering
I.E.
Mfg.Engg.
1.
2.
Equipment
specification
Tools, Jigs &
Fixtures Design
Methods
Engineering.
PPC
Inspection &
Quality
Control
Through
Operation Analysis and
Motion Analysis
Achieve
Standardization of methods
1. Work Measurement
2. Determination of Allowance
3. Computation of standard
time
Plant Design
PPC
1. MM
2. Machinery & Man
power
3. Routing
4. Estimating
5. Scheduling
6. Dispatching
7. Expediting
Organizational
Analysis
Wage &
Salary
Admin
Plant Layout
Material
Handling
Budgetary
Control &
Cost Control
Areas of Industrial Engineering:
Some of the important areas are listed below:
1) Method study or Work Simplification: Method study is the process of subjecting work to
systematic, critical scrutiny to make it more effective and/or more efficient. It is one of the
keys to achieving productivity improvement.
2) Time study or Work measurement: It is the application of techniques designed to establish
the time for an average worker to carry out a specified manufacturing task at a defined level
of performance. It is concerned with the length of time it takes to complete a work task
assigned to a specific job.
3) Principles of motion economy
4) Operations research: It is also known as management science: discipline that deals with the
application of advanced analytical methods to help make better decisions
5) Operations management: an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing,
and controlling the process of production and redesigning business operations in the
production of goods or services.
6) Project management: is the process and activity of planning, organizing, motivating, and
controlling resources, procedures and protocols to achieve specific goals in scientific or daily
problems.
7) Incentives: Inducement or supplemental reward that serves as a motivational device
for a desired action or behavior.
8) Inventory Control: inventory control is the processes employed to maximize a company's
use of inventory. The goal is to generate the maximum profit from the least amount of
inventory.
9) Job Evaluation: A job evaluation is a systematic way of determining the value/worth of a
job in relation to other jobs in an organization. It tries to make a systematic comparison
between jobs to assess their relative worth for the purpose of establishing a rational pay
structure.
10) Facility planning: Facility planning is an emerging field with confusing terminology. How
does a master plan differ from a strategic master plan? Is a campus plan part of a master
plan or something else? Every architect, consultant, and builder defines these terms
differently.
11) Material handling: It is the movement, protection, storage and control of materials and
products throughout manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption and disposal.
12) Production Planning & Control: Production planning & Control is the planning of
production and manufacturing modules in a company or industry with proper feedback
system in order to control.
13) Job design, Job Analysis: the specification of contents, methods and relationship of jobs in
order to satisfy technological and organizational requirements as well as the social and
personal requirements of the job holder.
14) Financial engineering: the application of technical methods, especially from mathematical
finance and computational finance, in the practice of finance
15) Management engineering: a specialized form of management that is concerned with the
application of engineering principles to business practice
16) Supply chain management: the management of the flow of goods. It includes the
movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from
point of origin to point of consumption.
17) Process engineering: design, operation, control, and optimization of chemical, physical, and
biological processes.
18) Systems engineering: an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how to design
and manage complex engineering systems over their life cycles.
19) Ergonomics: the practice of designing products, systems or processes to take proper
account of the interaction between them and the people that use them.
20) Safety engineering: an engineering discipline which assures that engineered systems provide
acceptable levels of safety.
21) Cost engineering: practice devoted to the management of project cost, involving such
activities as cost- and control- estimating, which is cost control and cost forecasting,
investment appraisal, and risk analysis.
22) Value engineering: a systematic method to improve the "value" of goods or products and
services by using an examination of function.
23) Quality engineering: a way of preventing mistakes or defects in manufactured products and
avoiding problems when delivering solutions or services to customers.
24) Industrial plant configuration: sizing of necessary infrastructure used in support and
maintenance of a given facility.
25) Facility management: an interdisciplinary field devoted to the coordination of space,
infrastructure, people and organization
26) Engineering design process: formulation of a plan to help an engineer build a product with
a specified performance goal.
27) Logistics: the management of the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of
consumption in order to meet some requirements, of customers or corporations
Role of Industrial Engineer:
Industrial engineers work to eliminate waste of time, money, materials, man-hours, machine time,
energy and other resources that do not generate value.
Various role played by an industrial engineer is depicted in the following figure.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cost Management: A Case for Business Process Re-engineeringDe la EverandCost Management: A Case for Business Process Re-engineeringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Engineering and ManagementDocument4 paginiIndustrial Engineering and Managementjacobjabs0% (1)
- Industrial EngineeringDocument12 paginiIndustrial EngineeringJithesh S.RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial intelligence: AI in the technologies synthesis of creative solutionsDe la EverandArtificial intelligence: AI in the technologies synthesis of creative solutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sejarah PTI-1Document19 paginiSejarah PTI-1Kukuh ArgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEM Material 2022Document68 paginiIEM Material 2022chelluboina satyakiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Engineering Lecture 02Document21 paginiIndustrial Engineering Lecture 02jatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial and ProductionDocument4 paginiIndustrial and ProductionnetsimastudioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concept of Industrial EngineeringDocument17 paginiBasic Concept of Industrial EngineeringSanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject: IE and PM Assignment 1Document66 paginiSubject: IE and PM Assignment 1Rakesh ShÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial and System EngineeringDocument213 paginiIndustrial and System EngineeringAjaikrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Engineering ManagementDocument92 paginiIndustrial Engineering ManagementCharles OndiekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mpmec12 Industral Engineering and ManagementDocument38 paginiMpmec12 Industral Engineering and ManagementNITIN NAUTIYALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial EngineerDocument3 paginiIndustrial EngineerpriyasubhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concepts of Industrial ManagementDocument9 paginiConcepts of Industrial ManagementSandeep Shrivastava50% (2)
- Tools of Industrial EngineeringDocument2 paginiTools of Industrial EngineeringSiddharth GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 3. Ruang Lingkup TIDocument30 paginiPertemuan 3. Ruang Lingkup TIFirly AbdulrahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- OD Unit 5Document16 paginiOD Unit 5dhivyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Engineering Is A Branch ofDocument10 paginiIndustrial Engineering Is A Branch ofashokkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial EngineeringDocument10 paginiIndustrial EngineeringashokkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parshva Classes: Industrial Engineering - IDocument4 paginiParshva Classes: Industrial Engineering - IMehul MunshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Engineering: Dr. Usama Jasim NaeemDocument10 paginiIndustrial Engineering: Dr. Usama Jasim NaeemAli Hassan AHÎncă nu există evaluări
- IndustrialDocument93 paginiIndustrialRahul PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Engineering Course CurricullamDocument2 paginiIndustrial Engineering Course CurricullamVijay Kumar RashimalaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regina Problem DomainDocument62 paginiRegina Problem DomainRmoodiRÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECNG3021 - L01&Tut POS Nov1010Document10 paginiECNG3021 - L01&Tut POS Nov1010Marlon BoucaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 IEDocument26 paginiUnit 1 IEAnkush Singh100% (1)
- Management of Manufacturing SystemsDocument9 paginiManagement of Manufacturing SystemsArvind SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 FD Industrial Engineering & Designing ProductsDocument58 pagini03 FD Industrial Engineering & Designing ProductsTan Tok HoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Part 4Document4 paginiUnit 1 Part 4akash agarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mpe 411-Lecture 1Document45 paginiMpe 411-Lecture 1kandeabigaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Industrial Engineering PJJ-Taufik - D2496Document29 paginiIntroduction To Industrial Engineering PJJ-Taufik - D2496Farain FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 PTI Introduction1Document29 pagini1 PTI Introduction1Creation YourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tarea SistemasDocument5 paginiTarea SistemasDANIELA EUNICE BERNAL ALVAREZÎncă nu există evaluări
- G-2 System Analysis Assignment PDFDocument72 paginiG-2 System Analysis Assignment PDFkefiyalew agegnÎncă nu există evaluări
- G-2 System Analysis Assignment PDFDocument64 paginiG-2 System Analysis Assignment PDFkefiyalew agegnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 323 Chapter 1 Methods, Standards, and Work DesignDocument18 pagini323 Chapter 1 Methods, Standards, and Work DesignCristi EteganÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 PTI Introduction IEDocument28 pagini1 PTI Introduction IEChan WoosungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial EngineeringDocument2 paginiIndustrial EngineeringIrina0% (1)
- iNDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING UINTRODUCTIOMDocument49 paginiiNDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING UINTRODUCTIOMe tutorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management AssignmentDocument40 paginiManagement Assignmentbanchi gashawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Impo.10Document2 paginiNotes Impo.10Anonymous kTVBUxrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 - Introduction To Industrial Eng - r1Document23 pagini01 - Introduction To Industrial Eng - r1Eddy FazwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Industrial Engineering PJJ-Taufik - D2496Document29 paginiIntroduction To Industrial Engineering PJJ-Taufik - D2496Ganggang PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importants of IeDocument2 paginiImportants of IeMd.Habibur RahmamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Requested FileDocument42 paginiRequested Fileedinson rojas ramosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial EnggDocument75 paginiIndustrial EnggAlthaf VAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Management: NHU - 601 Ajay ChaubeyDocument13 paginiIndustrial Management: NHU - 601 Ajay ChaubeyChaubey AjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Facilities Planning CH 1Document28 paginiFacilities Planning CH 1Fakhre Alam100% (2)
- Industrial Engineering Is A Branch of Engineering That Concerns TheDocument1 paginăIndustrial Engineering Is A Branch of Engineering That Concerns TheguadalupeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operations Managment Part-4Document20 paginiOperations Managment Part-4Sai Rock SaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial EngineeringDocument20 paginiIndustrial EngineeringBharath NallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntroIE Assignment1 Chrisshyaren 2015 04Document2 paginiIntroIE Assignment1 Chrisshyaren 2015 04Chris ShyarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bba 303Document218 paginiBba 303ashishkumarsharma123Încă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Engineering: Sanjib Jaypuria SME, KIIT University, BhubaneswarDocument26 paginiIndustrial Engineering: Sanjib Jaypuria SME, KIIT University, Bhubaneswarkunal kumar100% (1)
- Components of Industrial Engineering Class 2Document13 paginiComponents of Industrial Engineering Class 2Vikash KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IE Function ActivitiesDocument6 paginiIE Function ActivitiesraiyanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production Planning & Control-AbridgedDocument21 paginiProduction Planning & Control-AbridgedShanky Jain100% (1)
- Process EngineeringDocument10 paginiProcess Engineeringaida ACHOURÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Layout PDFDocument22 paginiPlant Layout PDFSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Jets/ BansalDocument37 paginiImpact of Jets/ BansalSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch10 Springs/ BhandariDocument28 paginiCh10 Springs/ BhandariSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Threaded Joint - 7bhandariDocument27 paginiThreaded Joint - 7bhandariSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welding Inspection Qualifications PDFDocument117 paginiWelding Inspection Qualifications PDFTakorn WeyheyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Turbines/ BansalDocument61 paginiReaction Turbines/ BansalSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch9 Shafts, Keys, Coupling/ BhandariDocument32 paginiCh9 Shafts, Keys, Coupling/ BhandariSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welded Joints/ BhandariDocument14 paginiWelded Joints/ BhandariSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTE Coating+surface TreatmentDocument6 paginiPTE Coating+surface TreatmentSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Screw/ BhandariDocument18 paginiPower Screw/ BhandariSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Casting Process 1Document14 paginiSpecial Casting Process 1SujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT - SURFACE - FINISH+NDT of WeldingDocument21 paginiPT - SURFACE - FINISH+NDT of WeldingSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Systems/BansalDocument17 paginiFluid Systems/BansalSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepp 1Document8 paginiHepp 1SujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Handling MahajanDocument13 paginiMaterial Handling MahajanSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Welding PDFDocument11 paginiGas Welding PDFMohan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CF PDFDocument45 paginiCF PDFSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reciprocating Pump/ BansalDocument48 paginiReciprocating Pump/ BansalSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Dynamic Force AnalysisDocument22 paginiChapter 2 Dynamic Force AnalysissreeshpsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method Study MahajanDocument32 paginiMethod Study MahajanSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH-18 Hydraulic Machine Turbine /bansalDocument25 paginiCH-18 Hydraulic Machine Turbine /bansalSujalBhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memorial Scoresheet: Jessup Global PartnerDocument1 paginăMemorial Scoresheet: Jessup Global PartnerTakbir AkashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech Sem ReviewDocument63 paginiMech Sem ReviewShraddha BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectivness of Promotional Schemes in Reliance MartDocument22 paginiEffectivness of Promotional Schemes in Reliance MartSavan BhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- RP FoodpandaDocument4 paginiRP FoodpandaDanish HadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outcome Measures January 2019Document39 paginiOutcome Measures January 2019Ashwini KatareÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02Document15 pagini02Sulthan AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- OR2 - Student SolutionsDocument7 paginiOR2 - Student SolutionsSA100% (1)
- GED0113 Module 3 & FA5 DetailsDocument3 paginiGED0113 Module 3 & FA5 DetailsLois LaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- QSP - 09 - Management of Change Rev 0 PDFDocument4 paginiQSP - 09 - Management of Change Rev 0 PDFPhuong HuynhÎncă nu există evaluări
- H. N 418 Manuscript Contents OnlineDocument2 paginiH. N 418 Manuscript Contents OnlineLeogalvez BedanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bid Evaluation PDFDocument3 paginiBid Evaluation PDFCUTto1122Încă nu există evaluări
- Btec HN Computing l4 Pearson Set Release 2023 2024 PDFDocument12 paginiBtec HN Computing l4 Pearson Set Release 2023 2024 PDFMarium BhalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deposit Analysis of Kumari Bank Limited: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Degree ofDocument11 paginiDeposit Analysis of Kumari Bank Limited: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Degree ofAa-ckC-restÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Aiche Sustainability Index: The Factors in DetailDocument4 paginiThe Aiche Sustainability Index: The Factors in DetailAllalannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceo e Climatology PHD ProposalDocument7 paginiCeo e Climatology PHD ProposalskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 Waiting LineDocument17 paginiChapter 11 Waiting LineJega KanagasabaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Background and Key Concepts of Piaget's TheoryDocument37 paginiBackground and Key Concepts of Piaget's Theorybobo_abellsÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Leicester Research Ethics Code of Practice: December 2006 IDocument10 paginiUniversity of Leicester Research Ethics Code of Practice: December 2006 Istxavier5000Încă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness of Backward Design Lesson Planning in Teaching and Learning Physics: A Case StudyDocument9 paginiEffectiveness of Backward Design Lesson Planning in Teaching and Learning Physics: A Case StudyIJELS Research JournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus All Courses 3Document69 paginiSyllabus All Courses 3Andrea Mae QuiniquiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Survey Report On Small CarDocument39 paginiMarket Survey Report On Small CarPrannoy Raj100% (1)
- Systematic Literature Review: Kemampuan Pembuktian MatematisDocument15 paginiSystematic Literature Review: Kemampuan Pembuktian MatematisAdam SIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Planning in Construction ProjectDocument6 paginiQuality Planning in Construction ProjectmaxlehenerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use of PEARL in Assessing TRL AKB LDocument28 paginiUse of PEARL in Assessing TRL AKB LVikas Jawaria100% (1)
- For DissertationDocument13 paginiFor DissertationRegi viniciyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creative Problem SolvingDocument27 paginiCreative Problem Solvingnad_sh31Încă nu există evaluări
- Management in Practice: Assignment 2Document12 paginiManagement in Practice: Assignment 2yeah yeahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Ordinal and ScaleDocument3 paginiDifference Between Ordinal and Scalevg_mrtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of Sociological Research & MethodsDocument4 paginiConcept of Sociological Research & MethodsAun MakenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correlation Between Student'S Vocabulary Mastery and Speaking SkillDocument12 paginiCorrelation Between Student'S Vocabulary Mastery and Speaking SkillMinh ThươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialDe la EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (238)
- PMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersDe la EverandPMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Project Management All-in-One For DummiesDe la EverandProject Management All-in-One For DummiesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (6)
- Agile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe la EverandAgile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (34)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeDe la EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeDe la EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (36)
- 300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionDe la Everand300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)De la EverandManaging Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (47)
- High Velocity Innovation: How to Get Your Best Ideas to Market FasterDe la EverandHigh Velocity Innovation: How to Get Your Best Ideas to Market FasterEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsDe la EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (15)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamDe la EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeDe la EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (99)
- The Third Wave: An Entrepreneur's Vision of the FutureDe la EverandThe Third Wave: An Entrepreneur's Vision of the FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (200)
- Agile Product Management: Product Owner: 27 Tips to Manage Your Product and Work with Scrum TeamsDe la EverandAgile Product Management: Product Owner: 27 Tips to Manage Your Product and Work with Scrum TeamsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (23)
- The Myth of Multitasking: How "Doing It All" Gets Nothing DoneDe la EverandThe Myth of Multitasking: How "Doing It All" Gets Nothing DoneEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- The Strategist: Be the Leader Your Business NeedsDe la EverandThe Strategist: Be the Leader Your Business NeedsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (48)
- PMP Exam Code Cracked: Success Strategies and Quick Questions to Crush the TestDe la EverandPMP Exam Code Cracked: Success Strategies and Quick Questions to Crush the TestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Come Up for Air: How Teams Can Leverage Systems and Tools to Stop Drowning in WorkDe la EverandCome Up for Air: How Teams Can Leverage Systems and Tools to Stop Drowning in WorkEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (7)
- Quiet Leadership: Six Steps to Transforming Performance at WorkDe la EverandQuiet Leadership: Six Steps to Transforming Performance at WorkEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (21)
- Design Thinking for Beginners: Innovation as a Factor for Entrepreneurial SuccessDe la EverandDesign Thinking for Beginners: Innovation as a Factor for Entrepreneurial SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (7)
- Crossing the Chasm, 3rd Edition: Marketing and Selling Disruptive Products to Mainstream CustomersDe la EverandCrossing the Chasm, 3rd Edition: Marketing and Selling Disruptive Products to Mainstream CustomersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (19)