Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
b3 Pixl Exchange of Materials Test
Încărcat de
api-342297566Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
b3 Pixl Exchange of Materials Test
Încărcat de
api-342297566Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.
2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
Unit 3: Biology 3
B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances
1: Define the following term: Diffusion
2: Define the following term: Active Transport
3: Define the following term: Osmosis
4: Define the following term: Partially permeable membrane
5: Explain the importance of Active Transport in Plants
6: State the relationship between the rate of respiration and the rate of
active transport
7: State where the energy used in active transport comes from.
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
8: In Active Transport, what does the substrate bind to, in order to get
across the membrane?
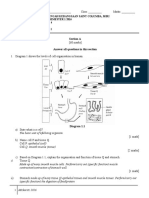
9: Osmosis in Animal Cells: Complete the following flow diagrams using
the words: Shrink, Burst and Shrivel.
If a cell has a more
dilute solution inside
it than outside it,
then the overall
movement of water
is out of the cell.
cell has a more
concentrated solution
inside it than outside
it, then the overall
movement of water is
into the cell
10: Osmosis in Plant Cells: Complete the following flow diagrams using
the words: cytoplasm and membrane push against the cell wall,
membrane and cytoplasm to shrink away from the cell wall, cell beings
to swell, flaccid (limp), Turgid.
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
If a cell has a more
dilute solution inside
it than outside it,
then the overall
movement of water
is out of the cell.
cell has a more
concentrated solution
inside it than outside
it, then the overall
movement of water is
into the cell
11: Draw a diagram in each box to illustrate what a cell would look like
under each condition:
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
12: State how Villi are adapted for the maximum absorption of digested
food molecules
13: State the importance of the villi having villi has a rich blood supply
14: Complete the sentence:
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
Each villus is covered in many microscopic __________. This ___________ the
_____________ available for ____________ even more.
15: State 4 contents of a sports drink:
1:
2:
3:
4:
16: When you exercise what happens to the glucose, water and mineral
ions?
17: What happens to your body if glucose, water and mineral ions are
not replaced following exercise?
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
Unit 3: Biology 3
B3.1.2 Gaseous Exchange
18: State 4 ways in which the effectiveness of an exchange surface can
be increased
19: Complete the table below: use the words in the box below; they will
need to be used more than once.
Contracts, increase, relaxes,
decreases
Intercos
tal
Muscle
Inhale
Exhale
diaphra
gm
Volume
of Chest
Pressure
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
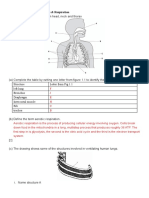
20: Complete the following sentences:
Lungs are located in the ___________ and protected by the ___________.
The abdomen is separated by the ______________.
The digestive organs are located beneath your ____________ in the
abdomen.
21: Explain how the lungs are adapted to make gas exchange more
efficient.
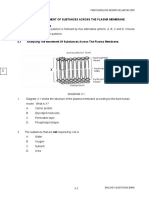
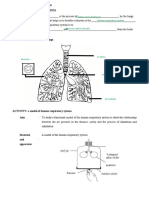
21: Label the diagram below:
h
g
k
f
a
e
d
c
b
22: State 3 ways when a person might struggle to breath
1:
2:
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
3:
23: Explain how Negative Pressure is used for supporting or taking over
breathing, to save lives.
24: Explain how Positive Pressure is used for supporting or taking over
breathing, to save lives.
25: Complete the table below:
Advantages
Negative Pressure
(Developed and
used from the
1920s to treat
polio sufferers)
Positive Pressure
(Used extensively
since the 1950s)
Disadvantage
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
Unit 3: Biology 3
B3.1.3 Exchange Systems in Plants
26: Define the following term: Transpiration
27: Define the following term: Transpiration Stream
28: Explain how transpiration occurs within a plant
29: Do the stomata need to be open or closed to increase the rate of
transpiration?
30: State 5 factors which affect the rate of transpiration.
1:
2:
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
3:
4:
5:
31: State 3 adaptations plants have to prevent water loss.
1:
2:
3:
32: Explain how root hair cells maximise adsorption of water and
mineral ions from the soil.
33: State 3 root hair cells several adaptations
1:
2:
3:
34: Complete the sentence:
Roots absorb water from the soil by __________ and dissolve mineral ions
from the soil by _________________
35: Complete the following sentences:
1. Carbon dioxide enters the leaf cells by _____________ through
_____________.
2. Water and mineral ions are absorbed by ______________ cells
3. Carbon dioxide and ___________ is used during _____________
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
4. Root hair cells ________________ the surface area of the roots and the
____________ shape and _______________ air spaces _____________ the
surface of the leaves.
5. The flattened shape of the leaves increase the surface area for
____________ as the _____________________ is kept short. The internal
air spaces allow _____________________ to come into contact with lots
of cells giving it a large surface area.
6. Osmosis is used to take _______________ from the soil
7. Active transport is used to obtain ____________ from the soil.
8. Leaves are adapted to allow __________________ in only when it is
needed. They are covered with a waxy ______________. Which is a
_________________ and gas proof layer.
9. Plants have _________________ to obtain carbon dioxide from the
atmosphere and to remove oxygen produced in
_________________________.
10.
Plants mainly lose ___________________ from their leaves. Most
of the loss of water vapour takes place through the stomata.
11.
The size of stomata is controlled by ______________________,
which surround them.
12.
Water is lost from the leaves by __________________ when the
stomas are ________________.
36: Explain how the sizes of stomata are controlled.
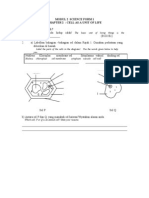
37: Label the diagram below:
[B3.1.1 DISSOLVED SUBSTANCES, B3.1.2
GASEOUS EXCHANGE, B3.1.3 EXCHANGE
SYSTEMS IN PLANTS]
i
b
g
d
c
f
e
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsDe la EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDocument15 paginiBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesDe la EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesÎncă nu există evaluări
- O'level Past Papers of Biology, Physics and ChemistryDocument35 paginiO'level Past Papers of Biology, Physics and ChemistryrAJBS;DF100% (1)
- Biology Quiz 1 Form 5Document3 paginiBiology Quiz 1 Form 5NoniaqAmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionDe la EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Student's Copy Chapter3 BioDocument10 paginiStudent's Copy Chapter3 BioSaidatul Atyah Mohd ApendaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module Chapter 3Document32 paginiModule Chapter 3Miz MiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 2nd 9 Weeks Week 2 2-2 3 Homework 3 Exam 2-3 ReviewDocument3 paginiBiology 2nd 9 Weeks Week 2 2-2 3 Homework 3 Exam 2-3 Reviewapi-262368188Încă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Biology RevisionDocument2 paginiGCSE Biology RevisionsannnnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0610 s11 QP 31Document20 pagini0610 s11 QP 31karan79Încă nu există evaluări
- Modul 2 Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell As A Unit of Life What Is Cell?Document22 paginiModul 2 Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell As A Unit of Life What Is Cell?Nurhuda MitieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Membrane QuestionsDocument7 paginiCell Membrane QuestionsmadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISDocument5 paginiExercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISKristel Bliss RomanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 9 Plants Notes and Work SheetsDocument15 paginiTopic 9 Plants Notes and Work Sheetsbsmith_9837380% (6)
- CHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExerciseDocument8 paginiCHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExerciseLeena HingÎncă nu există evaluări
- S3 Breathing SystemDocument18 paginiS3 Breathing System廖思明Încă nu există evaluări
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument27 paginiMovement of Substances Across The Plasma Membranenurhanim ckÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution ReviewDocument3 paginiEvolution ReviewJenna Vong100% (1)
- REv2 - movementInAndOutOfCells & BiomoleculesDocument13 paginiREv2 - movementInAndOutOfCells & BiomoleculesvimalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecules To and From The Different Parts of The Body. S9LT-la-b-26Document7 paginiMolecules To and From The Different Parts of The Body. S9LT-la-b-26Lara ZuñigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RevisionGrd 10 SA1Document1 paginăRevisionGrd 10 SA1sanjit0907_982377739Încă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Exam EnviedDocument2 paginiMidterm Exam EnviedSu-ho HanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Diffusion & Osmosis - WorksheetDocument3 paginiChapter 3 Diffusion & Osmosis - Worksheetapi-3728508100% (7)
- Earth SubsystemDocument16 paginiEarth SubsystemZei LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Plant Nutrition - WorksheetDocument4 paginiChapter 7 Plant Nutrition - Worksheetapi-372850880% (5)
- Biology Higher ExtendedDocument47 paginiBiology Higher ExtendedAbhinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Systems - CardiovascularDocument78 paginiAnimal Systems - CardiovascularMinecraft 1Încă nu există evaluări
- F3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticeDocument10 paginiF3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticePianna IeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Junior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginDocument4 paginiJunior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginPui Pui LamÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 1 1 Semester Ɩ 1 GRADING Ɩ AY 2020-2021 Answer Sheet CN: NAME (Family Name, Given Name M.I.)Document4 paginiGeneral Biology 1 1 Semester Ɩ 1 GRADING Ɩ AY 2020-2021 Answer Sheet CN: NAME (Family Name, Given Name M.I.)Colline AtanacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Workbook Mid & Final TermDocument81 paginiBiology Workbook Mid & Final TermSayma AkterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure and IonDocument14 paginiCell Structure and IonNur NaNa100% (1)
- Module Chapter 3Document31 paginiModule Chapter 3Azween SabtuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet: Passive Transport Diffusion and OsmosisDocument8 paginiWorksheet: Passive Transport Diffusion and OsmosisJake HagbergÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Respiration - WorksheetDocument4 paginiChapter 10 Respiration - Worksheetapi-3728508100% (4)
- Blood Circulation and Transport ModuleDocument15 paginiBlood Circulation and Transport ModuleSENSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earths Subsystems WorksheetDocument2 paginiEarths Subsystems WorksheetcamachodanahalexandreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- S8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestDocument2 paginiS8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestWilliam Anthony56% (9)
- S8 - End of Unit 1 TestDocument2 paginiS8 - End of Unit 1 Testchicken.nougat123Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Test Cell TransportDocument8 paginiChapter Test Cell Transportandrea dyanne AzoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Fill in The BlanksDocument22 pagini3 Fill in The Blanksapi-342775465Încă nu există evaluări
- Science - Grade 8Document6 paginiScience - Grade 8sajal zeeshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Trilogy Cell BiologyDocument11 paginiBiology Trilogy Cell BiologyShalini MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision For SA1 (Students' Copy)Document7 paginiRevision For SA1 (Students' Copy)SUNDARI SIVASANKARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inhaling and Exhaling Air Breathing Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 paginiInhaling and Exhaling Air Breathing Human Respiratory SystemMSZeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam Leak Part 2Document2 paginiExam Leak Part 2Venz Lei Collyn Atis EsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1468 - Unit 3 - Scaling Up ACCDocument7 pagini1468 - Unit 3 - Scaling Up ACCRajkumar SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Transpiration Transport and Support in Plants 1 PDFDocument10 paginiChapter 10 Transpiration Transport and Support in Plants 1 PDFOlivia LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiration & Gas Exchange Theory QPDocument44 paginiRespiration & Gas Exchange Theory QPVivehaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5a Transport in Plant (P2) Set 1Document4 pagini5a Transport in Plant (P2) Set 1Ahmed HamimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument15 paginiCell Structure and Organisationzulkarnain100% (4)
- Pace Academy: Factors Affecting Gas Exchange, Blood, and Blood VesselsDocument2 paginiPace Academy: Factors Affecting Gas Exchange, Blood, and Blood VesselsKurt ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 10 BiologyDocument15 paginiYear 10 BiologylkipsangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 9-Summative AssessmentDocument2 paginiGrade 9-Summative AssessmentMaryjoy Piosca MolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Unit 1 Repeat Questions PDFDocument12 paginiBiology Unit 1 Repeat Questions PDFFarah100% (1)
- GE-ES Module3Document11 paginiGE-ES Module3EnzuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 Movement of MoleculesDocument8 pagini1.3 Movement of MoleculessimbamundawararaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 5 Feeding RelationshipsDocument22 paginiUNIT 5 Feeding RelationshipsKelly ChamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Questions - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document8 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Questions - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document26 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document17 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Questions - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document9 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Questions - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa p1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document19 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa p1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document27 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa b1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document27 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa b1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Pixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document16 paginiPixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Încă nu există evaluări
- Ground Improvement: by Depth VibratorDocument16 paginiGround Improvement: by Depth VibratornijjjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Septic Systems Handbook - KAPLAN, O. BENJAMINDocument457 paginiSeptic Systems Handbook - KAPLAN, O. BENJAMINvikingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actual Scientific Research - xcі. Part 2 (Web)Document218 paginiActual Scientific Research - xcі. Part 2 (Web)v9g56b7mgjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Hand BookDocument237 paginiConstruction Hand BookNson Lee100% (1)
- Soil Biology and BiochemistryDocument3 paginiSoil Biology and BiochemistryS AbdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pennisetum PurpureumDocument3 paginiPennisetum PurpureumHildan H GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cross 9LVR 0050 5Document17 paginiCross 9LVR 0050 5Chitharanjan VishnukripalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salt MethodsDocument105 paginiSalt MethodsRaj100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions: A. B. D. EDocument11 paginiMultiple Choice Questions: A. B. D. EAmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irrigation System of PakistanDocument127 paginiIrrigation System of PakistanAamir Irshad Chattha100% (2)
- Prathibha Farms and Nursery: Date Palm Cultivation INDIADocument3 paginiPrathibha Farms and Nursery: Date Palm Cultivation INDIAAjay BanahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Assessment of Clay Raw Materials Utilized For Pottery Products in Eastern Tigray, Northern EthiopiaDocument4 paginiQuality Assessment of Clay Raw Materials Utilized For Pottery Products in Eastern Tigray, Northern Ethiopiainternational journal of modern chemistry and applied scienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- TREVI-Jet Grouting Part 1Document50 paginiTREVI-Jet Grouting Part 1chenyi liÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Suicide - Walter and Lao RussellDocument300 paginiAtomic Suicide - Walter and Lao RussellJason Verbelli100% (16)
- Surface Irrigation CE406Document37 paginiSurface Irrigation CE406kundayi shavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Capacity of Bored PilesDocument8 paginiBearing Capacity of Bored PilesRinsunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jagdish Donde OrwDocument24 paginiJagdish Donde OrwJagdish DondeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BOQ Boundary WallDocument3 paginiBOQ Boundary WallAshwani Goel50% (2)
- DFO Land Development GuidelinesDocument129 paginiDFO Land Development GuidelinesnÎncă nu există evaluări
- EP2594645A2Document205 paginiEP2594645A2avalosheÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 PDFDocument48 pagini03 PDFJonathas BritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Info Librel Fe-DPDocument4 paginiTechnical Info Librel Fe-DPRijalul AuthonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weight-Volume Relationships, Plasticity, and Structure of SoilDocument30 paginiWeight-Volume Relationships, Plasticity, and Structure of SoilHanafiahHamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Govpub C13Document216 paginiGovpub C13Mohammed Mohthesham HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- MKSP Detailed Project ReportDocument34 paginiMKSP Detailed Project ReportArun Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xi 0014Document28 paginiXi 0014api-264144691Încă nu există evaluări
- Widening & Strengthening of Kathipudi - Perumallapuram Road From KM 0/000 To 14/000 in E.G.distDocument10 paginiWidening & Strengthening of Kathipudi - Perumallapuram Road From KM 0/000 To 14/000 in E.G.distPhani PitchikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project StudyDocument14 paginiProject StudyDep Ed100% (2)
- Vetting CBTDocument66 paginiVetting CBTSatyabrat GaanÎncă nu există evaluări