Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Boiler Uptake Fire 3
Încărcat de
krishnaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Boiler Uptake Fire 3
Încărcat de
krishnaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
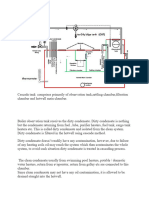
UPTAKE FIRE
Engine exhaust gas contains particulates which consist of partially burnt fuel and/or lubricating oil
and ash. These particulates can form deposits on boiler Tubes. Especially during prolonged low
load operation, which reduces exhaust gas velocity, it may lead to higher soot deposition. It may
be due to
burning poor quality fuel,
poor combustion due to defective injection equipment, or
inefficient fuel treatment.
These deposits on the tubes may get heated and rise above self ignition temperature. Soot
deposits may be ignited by glowing carbon particulates in the exhaust gases. The ignition
temperature of the soot is usually less than 400 C, however if the deposits stick, it could fall
below 200 C.
Soot fires can occur after the engine has shut down, therefore it is important to maintain water
circulation after shut down.
The fire will be indicated by
dark smoke coming out of funnel
large rise in exhaust gas temperature after the boiler.
Action :
If fire does occur the engine should be stopped immediately and the turbocharger air
intake covered to starve the fire of air.
Ensure full water circulation is maintained.
A small fire may burn itself out as the heat will be conducted away by the circulating
water.
If water washing system is fitted, it can be used to extinguish the fire.
Prevention :
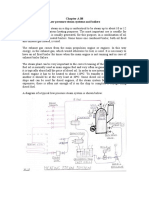
Soot Blowers : Soot blowing should be carried out on regular basis to ensure soot and
ash deposits do not build up on tubes. It should be carried out more frequently when the
engine is operating at low loads or when fuel has high ash content. It should be carried
out after water washing of main engine turbocharger (water side).
Water Washing of Exhaust gas Boiler : The combustion of residual fuel results in
formation of slag. These slag gradually build up on the boiler tubes. Soot blowing keeps
these deposits at low levels, however it does not reach all areas of boiler. These slag
are soluble in water and can be removed by hot water washing.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Safety Valve Setting BoilerDocument2 paginiSafety Valve Setting BoilerkrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of Liquid FuelDocument18 paginiProperties of Liquid FuelTin Aung Kyi100% (2)
- Fractional DistillationDocument5 paginiFractional Distillationwayen8100% (1)
- Physical Study of A Steam Generating UnitDocument13 paginiPhysical Study of A Steam Generating Unitashier dave calulot80% (5)
- Latvia Marine Engineering Test PaperDocument90 paginiLatvia Marine Engineering Test PaperkrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Students Guide To RefineryDocument16 paginiA Students Guide To RefineryManisha RatheeÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Destroy Boiler FullDocument18 paginiHow To Destroy Boiler Fullbanhquangduy90100% (1)
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingDe la EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- Boiler Inspection in FurnaceDocument4 paginiBoiler Inspection in FurnacekrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heater TreatersDocument9 paginiHeater TreatersDeepak Shakya100% (2)
- Presentation On Steam TrapsDocument88 paginiPresentation On Steam TrapsSalman Shafique100% (1)
- Inspections and Survey Procedures in Auxiliary BoilerDocument16 paginiInspections and Survey Procedures in Auxiliary BoilerkrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler:: Heat Exported by Outlet Steam Heat Supplied by The FuelDocument13 paginiBoiler:: Heat Exported by Outlet Steam Heat Supplied by The FuelBrijesh SrivastavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler BurnerDocument30 paginiBoiler BurnerAbdallah MansourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler EfficiencyDocument24 paginiBoiler EfficiencyJovanni OrculloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection On EconomiserDocument2 paginiInspection On Economiserkrishna50% (2)
- Crude Oil RefiningDocument24 paginiCrude Oil RefiningSaranrajPachayappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crankshaft SlippageDocument3 paginiCrankshaft SlippagekrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refinery PDFDocument22 paginiRefinery PDFromulussikalitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boilers OperationDocument50 paginiBoilers Operationtsrinivasan5083100% (1)
- Ic Engine FUELSDocument44 paginiIc Engine FUELSkalaisselvaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Boilers MmsDocument35 pagini1 Boilers MmsTahir MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heater: Hydrate PreventionDocument12 paginiHeater: Hydrate PreventionMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEAM SavingDocument30 paginiSTEAM SavingShariq AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vacuum Distillation in Petroleum RefiningDocument3 paginiVacuum Distillation in Petroleum RefiningUsama Malik100% (1)
- Easy Way To Improve Steam Boiler EfficiencyDocument4 paginiEasy Way To Improve Steam Boiler EfficiencyidigitiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPE-REPORT .Docx (FINAL)Document25 paginiPPE-REPORT .Docx (FINAL)Meer UmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Students Guide To RefiningDocument16 paginiA Students Guide To RefininghuycanphuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil Contamination in Marine BoilerDocument2 paginiOil Contamination in Marine BoilerManish KhakhraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Furnace PDFDocument8 paginiBoiler Furnace PDFசுந்தர மூர்த்தி சேப்பிளையார்Încă nu există evaluări
- F16PG07 (Atmospheric Distillation)Document8 paginiF16PG07 (Atmospheric Distillation)Mahtab SajnaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Firing Steam BoilerDocument22 paginiMethods of Firing Steam BoilerAnonymous mRBbdopMKf100% (2)
- Boiler Feedwater: A. DeaerationDocument11 paginiBoiler Feedwater: A. DeaerationRaja TÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Destroy A Boiler - Part 1Document5 paginiHow To Destroy A Boiler - Part 1mancini10Încă nu există evaluări
- How To Destroy A BoilerDocument22 paginiHow To Destroy A BoilerJoffre BourgeoisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hotwell and Oil in Boiler WaterDocument5 paginiHotwell and Oil in Boiler WaterAbrham DubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why HT Water Temp Should Be Between 75 - 90 Deg. C (Or) Why Preheating of Engine Required?Document14 paginiWhy HT Water Temp Should Be Between 75 - 90 Deg. C (Or) Why Preheating of Engine Required?Ganapathi SankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crude Oil: Specific Objective 3 Student Name: Student Name: ClassDocument3 paginiCrude Oil: Specific Objective 3 Student Name: Student Name: ClassSamanthaKhallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel's and Energy Engineering-5th. LectureDocument30 paginiFuel's and Energy Engineering-5th. Lectureahmed JaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To RefiningDocument29 paginiGuide To Refiningohm keyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Steam Generation & Heat Transfer in BoilerDocument82 pagini04 Steam Generation & Heat Transfer in BoilerEng-Musab Mohammed Alhafiz MahilÎncă nu există evaluări
- EGB FireDocument5 paginiEGB FireAkshay A KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionDocument7 paginiSteam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionDocument7 paginiSteam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERÎncă nu există evaluări
- DunnoDocument3 paginiDunnoMark allenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condensate & UtilisationDocument3 paginiCondensate & Utilisationmohamed faragÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 4 in Situ CombustionDocument33 paginiPart 4 in Situ CombustionFlorian Ananias ByarugabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Scavenge FiresDocument7 pagini01 Scavenge FiresJaimin TandelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel Firing System Power PlantDocument12 paginiFuel Firing System Power PlantRuban Kumar100% (1)
- Types of Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB) Fires and Ways To Prevent ThemDocument4 paginiTypes of Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB) Fires and Ways To Prevent ThemGiorgi KandelakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About Steamers - The Boilers and EnginesDocument7 paginiAll About Steamers - The Boilers and EnginesClyde SteamersÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Coke Oven by Product Plant 07-22-2021Document9 paginiThe Coke Oven by Product Plant 07-22-2021Thiruvengadam SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deaerating Boiler FeedwaterDocument4 paginiDeaerating Boiler Feedwaterritesh sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Cont.Document9 paginiBoiler Cont.adnan mukhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heater Treater: Heat Free Water KnockoutDocument4 paginiHeater Treater: Heat Free Water Knockoutحمامة السلامÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visbreaking, Thermal Cracking, and Coking: ExtractionDocument4 paginiVisbreaking, Thermal Cracking, and Coking: ExtractionChetan CherryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter A 08 L.P. SteamDocument12 paginiChapter A 08 L.P. SteamСергей КороткийÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation and Process: Starting A BoilerDocument3 paginiOperation and Process: Starting A BoilerJoanna MarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anselmo Report No.8Document6 paginiAnselmo Report No.8Vince PatricioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam and Condensate SystemDocument5 paginiSteam and Condensate SystemAayush AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel Oil CombustionDocument35 paginiFuel Oil Combustionchaiya sonwongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impurities in Crude: Separation ProcessesDocument15 paginiImpurities in Crude: Separation ProcessesSandiksha chhabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesDe la EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Early Days Of Motors And Motor-Driving - Steam CarsDe la EverandThe Early Days Of Motors And Motor-Driving - Steam CarsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Family History of Alladi Jagannat (Ebooksread - Com) PDFDocument274 paginiA Family History of Alladi Jagannat (Ebooksread - Com) PDFkrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marine Survey Practice - Surveyor Guide Notes For Bilge Keels SurveyDocument2 paginiMarine Survey Practice - Surveyor Guide Notes For Bilge Keels SurveykrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marine Survey Practice - Notes Relative To Shell and Deck Plate RepairsDocument2 paginiMarine Survey Practice - Notes Relative To Shell and Deck Plate RepairskrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Uptake Fire All NotesDocument2 paginiBoiler Uptake Fire All NoteskrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Plant Interview Questions & AnswersDocument1 paginăPower Plant Interview Questions & AnswerskrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Valve Floating MrthodDocument4 paginiSafety Valve Floating MrthodSanjay ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil Whip and Oil WhirlDocument1 paginăOil Whip and Oil WhirlkrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări