Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Electron motion in a wire
Încărcat de
naziya begumTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Electron motion in a wire
Încărcat de
naziya begumDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
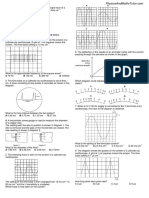
1.
Description of motion:
AB: uniform acceleration OR increases at constant rate
(1)
[Not accelerates constantly]
BC: sudden deceleration OR slows down/stops rapidly
(1)
2
Explanation of cause of motion:
AB: Attraction to positive/power supply/the voltage/energy of
supply/(electric) force from supply OR electric field (in wire)
(1)
BC: collision with ion/atom/electron/nucleus/lattice
(1)
2
Explanation of term drift velocity:
Drift velocity: average mean/net/overall velocity of electron along wire
(1)
[Not speed]
Value shown on graph (allow between 1/3 and 2/3 of maximum velocity)
(1)
[Line or mark on graph axis, label not needed if only one line/mark]
2
Explanation of why wire gets warm:
Collision makes ion/atom vibrate more vigorously
OR in collision energy is transferred to lattice
(1)
1
[7]
2.
t = 2.1s
Represents acceleration of the ball
Force on ball or gravitational field strength
or acceleration is constant or uniform
Relevant equation or correct area
Substitution correct
Displacement /m
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
0.5
1.0
t/s
Displacement scale as shown above
First half of curve correct
Second half correct with reduced height
1.25 m (correct magnitude and direction)
[Look at candidate s displacement origin ]
1
[9]
3.
Gradient
Use a gradient or use of = u + at (1)
10 (either no unit or m s2) (1)
[A bare answer of 9.8 gets no marks; A bare answer of 10 gets 2 marks]
Significance
It is the acceleration (due to gravity) or close to g (1)
Ball at point A
It hit the floor/bounces/(idea of collision with floor) (1)
Calculation of height of window above ground
An area / quote an equation of motion (1)
Put in relevant numbers for large triangle / correct substitution
[ecf from first part, or use of 9.8] (1)
45 m [accept 44 to 46] (1)
3
[7]
4.
(i)
Distance travelled
Attempt to find area under curve/use of suitable equations (1)
Distance = 300 m (1)
(ii)
Averape speed
Use of total distance/20 (1)
Average speed = 15 m s1 [e.c.f. distance above] (1)
[4]
5.
Average deceleration
Select 2 = u2 + 2ax, m 2 = Fx and F = ma OR equations of motion (1)
Correct substitutions of 40 m and 25 m s1 (1)
a = 7.8 m s2 [If a = 7.8 m s2 2/3] (1)
Depth of sand and stopping distance
More sand shorter stopping distance/stops more quickly/slows
down faster Because lorry sinks further/ bigger resisting
force / bigger friction force (1)
1
[4]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
6.
Deceleration of cars
Acceleration = gradient / suitable eqn. of motion. (1)
Correct substitutions [ 0.9 for t is wrong] (1)
6.1 6.3 m s2 [-ve value 1] [no ecf] (1)
Area under velocity-time graph
Distance/displacement (1)
Shaded area
6.9 7.5 (1)
m (1)
[Allow 1 mark for 5.5 6.1 cm2.]
Minimum value of the initial separation
Same as above [ecf] (1)
Area is the extra distance car B travels/how much closer they get
Graph
Both sloping lines continued down to time axis [by eye]
(1)
(1)
Explanation
Area between graphs is larger/B travels faster for longer/B still moving
when A stops (1)
Extra distance B goes is larger/ > 7.2 (1)
Initial separation must be greater (1)
2
1
Max 2
[11]
7.
Maximum velocity
Area = 100 m (1)
Attempt to find area of trapezium by correct method (1)
= 10 m s1 (1)
Sketch graph
Horizontal line parallel to x axis
Some indication that acceleration becomes 0 m s2
The initial acceleration labelled to be max 2 [ initial a = 5 (m s2) (1)
(ecf)]
t = 2 (s) where graph shape changes (1)
4
[7]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 5124 Science (Physics and Chemistry)Document4 pagini5124 Science (Physics and Chemistry)mstudy123456Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers To Oscillations QuestionsDocument27 paginiAnswers To Oscillations QuestionsMimran1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Physics Oscillations AnswersDocument26 paginiUnit 5 Physics Oscillations Answersareyouthere92100% (1)
- PHY10T2KINEMATICSCALULUSDocument51 paginiPHY10T2KINEMATICSCALULUSChristiana Mae Padilla100% (2)
- GCE Physics 2012 Mark SchemeDocument8 paginiGCE Physics 2012 Mark SchemeCka DohaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5124 w11 Ms 2Document5 pagini5124 w11 Ms 2mstudy123456Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit1topic1 Examzone Ms Edexcel As LevelDocument3 paginiUnit1topic1 Examzone Ms Edexcel As LevelKhalid Mohammed0% (1)
- 5124 w09 Ms 2Document4 pagini5124 w09 Ms 2mstudy123456Încă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel A-Level Physics Unit 4 Extra NotesDocument11 paginiEdexcel A-Level Physics Unit 4 Extra NotesKaniz SultanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topper Sample Paper 3 Physics - Xi Q. No Value Points MarksDocument12 paginiTopper Sample Paper 3 Physics - Xi Q. No Value Points MarksShubh GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topper Sample Paper 3 Physics - Xi Q. No Value Points MarksDocument12 paginiTopper Sample Paper 3 Physics - Xi Q. No Value Points MarksAishwarya NaiduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity AnswersDocument13 paginiElectricity Answersnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- EdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsDocument141 paginiEdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsAravinth Pushparaj100% (2)
- A 2 Physics Term 22011 Answer SchemeDocument16 paginiA 2 Physics Term 22011 Answer SchemeannathebitchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark Scheme Practice Mechanics 1110Document26 paginiMark Scheme Practice Mechanics 1110XhanAfaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document4 paginiChapter 5Aadar NÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCE Physics Mark Scheme January 2011Document9 paginiGCE Physics Mark Scheme January 2011shangardeziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Frictional Torque on a Rotating DiscDocument5 paginiMeasuring Frictional Torque on a Rotating DiscSeethaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY 151 Homework Solutions 02ADocument4 paginiPHY 151 Homework Solutions 02AAnderson Del RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Year Physics From 4 2009 - Scheme p1p2Document12 paginiMid Year Physics From 4 2009 - Scheme p1p2Rosmini Abdul RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark Scheme ForcesDocument11 paginiMark Scheme ForcesSteve BishopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 9745/02: Nanyang Junior College JC 2 Preliminary Examination Higher 2Document15 paginiPhysics 9745/02: Nanyang Junior College JC 2 Preliminary Examination Higher 2nasyrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter2 Describing MotionDocument64 paginiChapter2 Describing Motionnii zeliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 16Document20 paginiPhysics 16Kazuto ShibaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AGS AS Physics MC and SA Answers Term 2 2012: Answers / Explanatory Notes Marks AvailableDocument6 paginiAGS AS Physics MC and SA Answers Term 2 2012: Answers / Explanatory Notes Marks AvailableGeneralBrainsÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIPMT 2012 Physics, Biology & Chemistry ExamDocument36 paginiAIPMT 2012 Physics, Biology & Chemistry ExamOnkar JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oscillations Time Period Equations Problems SolutionsDocument8 paginiOscillations Time Period Equations Problems SolutionsMohammad UmairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examples Solutions Answers Section1 01Document5 paginiExamples Solutions Answers Section1 01biligalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics STPM 2005 AnswerDocument23 paginiPhysics STPM 2005 AnswersuhailieliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- NY Regents Physics ExamDocument20 paginiNY Regents Physics ExamAvinash BoodhooÎncă nu există evaluări
- P2 Forces and Motion Higher AnswersDocument8 paginiP2 Forces and Motion Higher AnswersdownendscienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Physics Motion Worksheet AnswersDocument15 paginiGCSE Physics Motion Worksheet AnswersJason LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pagini9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersAbdullah AsgharÎncă nu există evaluări
- RT-3 JMTDocument19 paginiRT-3 JMTDushyant YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 M Schemes 20 OscillationsDocument3 pagini20 M Schemes 20 OscillationsImran Muhammad50% (2)
- January 2010 MS - Unit 1 WJEC Physics A-LevelDocument4 paginiJanuary 2010 MS - Unit 1 WJEC Physics A-Levelfadi baqainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee Advance 2014 Phy I Questions SolutionsDocument9 paginiJee Advance 2014 Phy I Questions SolutionsMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question MVMDocument7 paginiQuestion MVMTusharkanti Sinha RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15P08Q Circular Motion by Inu BansalDocument9 pagini15P08Q Circular Motion by Inu BansalSaurabh LadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Text EditDocument77 paginiDynamic Text EditabikoyeoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AL KHOR INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Physics Worksheet Answer KeyDocument22 paginiAL KHOR INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Physics Worksheet Answer KeyTahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5054 On 2022 P21Document16 pagini5054 On 2022 P21Raahin RahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHM MCQ'sDocument14 paginiSHM MCQ'svishal_kalraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 - OscillationsDocument11 pagini09 - Oscillationsfazeelm24Încă nu există evaluări
- Refraction & Superposition AnswerDocument6 paginiRefraction & Superposition Answergrace_ng_45Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Olympiad 2011 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument5 paginiPhysics Olympiad 2011 Paper 1 SolutionsKarn KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Objectives - Unit 1 OCR Physics A-LevelDocument7 paginiLearning Objectives - Unit 1 OCR Physics A-Leveleugene_970418755Încă nu există evaluări
- Review Test - 2Document16 paginiReview Test - 2vishal110085100% (2)
- Further Mechanics ExamZone AnswersDocument2 paginiFurther Mechanics ExamZone AnswersAmmar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument10 paginiH2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPhO 2010 MSDocument4 paginiBPhO 2010 MSeisnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Council Certificate Level: Mechanical and Structural Engineering C105Document14 paginiEngineering Council Certificate Level: Mechanical and Structural Engineering C105satoni12Încă nu există evaluări
- A Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionDe la EverandA Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Regularly used apparatus Paper 3 physicsDocument1 paginăRegularly used apparatus Paper 3 physicsnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 - 1 - The - MoleDocument17 pagini7 - 1 - The - Molenaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Quantities and Measurement Questions PDFDocument45 paginiPhysical Quantities and Measurement Questions PDFnaziya begum0% (1)
- Physical Quantities and Measurement QuestionsDocument45 paginiPhysical Quantities and Measurement Questionsnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- January 2010 MS - Unit 3 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument7 paginiJanuary 2010 MS - Unit 3 Edexcel Physics A-Levelnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 5 - EM - (B) Current of ElectricityDocument34 paginiCH 5 - EM - (B) Current of ElectricityThapelo SebolaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of MotionDocument8 pagini1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of MotionRakibul Islam RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measur MentsDocument7 paginiMeasur MentsdebbyhooiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagneticwaves 120829053329 Phpapp02Document26 paginiElectromagneticwaves 120829053329 Phpapp02naziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete A Level Physics Definitions PDFDocument5 paginiComplete A Level Physics Definitions PDFnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.4 Electricity PDFDocument23 pagini2.4 Electricity PDFnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Unit-2 Student Book (QuestionDocument15 paginiAs Unit-2 Student Book (QuestionCostas Paschalides100% (2)
- Solving Problems On ProjectilesDocument4 paginiSolving Problems On ProjectilesSyed FahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculations On The Photoelectric Effect PDFDocument3 paginiCalculations On The Photoelectric Effect PDFnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.5.1 Photoelectric EffectDocument9 pagini2.5.1 Photoelectric EffectFaizan SanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity AnswersDocument13 paginiElectricity Answersnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit2topic4 Examzone MsDocument18 paginiUnit2topic4 Examzone Msnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.4 Electricity PDFDocument23 pagini2.4 Electricity PDFnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examzone 3 Waves: 1 of 3 Examzone: Student Book Topic Tests Mark SchemeDocument3 paginiExamzone 3 Waves: 1 of 3 Examzone: Student Book Topic Tests Mark Schemenaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- January 2010 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument18 paginiJanuary 2010 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-Levelnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 4 Electricity AnswersDocument2 paginiTopic 4 Electricity Answersnaziya begumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Further Mechanics ExamZone AnswersDocument2 paginiFurther Mechanics ExamZone AnswersAmmar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pho Sylabus PDFDocument124 paginiPho Sylabus PDFLayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction and 1st LectureDocument26 paginiIntroduction and 1st LectureErica Cabulay SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Theory of Relativity PDFDocument378 paginiGeneral Theory of Relativity PDFSandeep KhareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 18.1 Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument22 paginiScience 9 18.1 Uniformly Accelerated MotionCutszÎncă nu există evaluări
- SampSample Formal Laboratory Report For Physics On The Picket Fence Lab Without The Parachutele Formal Lab ReportDocument5 paginiSampSample Formal Laboratory Report For Physics On The Picket Fence Lab Without The Parachutele Formal Lab ReportKhatri NasrullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pow Sat-3 WepDocument10 paginiPow Sat-3 WepMarcus PoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Force Analysis of Slider Crank MechanismDocument5 paginiDynamic Force Analysis of Slider Crank MechanismKarthik CruiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Documents On Modern Physics) Schwinger Julian - Particles and Sources-Gordon and Breach, Science Publishers (1969) PDFDocument100 pagini(Documents On Modern Physics) Schwinger Julian - Particles and Sources-Gordon and Breach, Science Publishers (1969) PDFLuke Constable100% (1)
- Geometry: 7.5 Glide Reflections and CompositionsDocument24 paginiGeometry: 7.5 Glide Reflections and CompositionsAngus TeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 100 Greatest Lies in Physics by Ray Fleming PDFDocument235 paginiThe 100 Greatest Lies in Physics by Ray Fleming PDFAbir Ghosh100% (2)
- Forces Worksheet ExplainedDocument8 paginiForces Worksheet ExplainedAnasua BasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The New Axiomatics of The Universal Law (Georgi Stankov)Document52 paginiThe New Axiomatics of The Universal Law (Georgi Stankov)Aegil De Vera SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTS CisDocument7 paginiCTS CisKindy NurhakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotation ExerciseDocument21 paginiRotation ExerciseMikaila Denise LoanzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 V1Document47 paginiChapter 2 V1jojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture - Scalar Vector FieldsDocument4 paginiLecture - Scalar Vector FieldsMarlon BoucaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade.10, Chapter.8Document8 paginiGrade.10, Chapter.8Karim AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAKADocument7 paginiCHAKAKennedy Fieldad VagayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument3 pagini8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics: Mit OpencoursewareGeozzzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation CHAPTER6Document30 paginiPresentation CHAPTER6Joschel PiquionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Zone Conversion ChartDocument2 paginiTime Zone Conversion Chartsaric_terrill4785Încă nu există evaluări
- The Infinite Universe of The New CosmologyDocument1 paginăThe Infinite Universe of The New Cosmologytony oneÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Relativity - Tom MarshDocument104 paginiGeneral Relativity - Tom MarshMemo SaucedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline 1614577744333Document1 paginăCourse Outline 1614577744333Mohit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS 2 QuizDocument2 paginiPHYSICS 2 QuizRicci Marcelo ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 13 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument78 paginiLesson 13 Simple Harmonic MotionGLoria, Danica Joy A.Încă nu există evaluări
- GravitationDocument25 paginiGravitationPreeti Jain100% (2)
- Motion and TimeDocument8 paginiMotion and Timesmi_santhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSc Physics Exam on Mechanics at Loyola CollegeDocument2 paginiBSc Physics Exam on Mechanics at Loyola Collegeselvam1981Încă nu există evaluări
- MA1511 Chapter 3Document20 paginiMA1511 Chapter 3Kang Le LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derivation of The Deformed Heisenberg Algebra From Discrete SpacetimeDocument10 paginiDerivation of The Deformed Heisenberg Algebra From Discrete SpacetimePradyumn Kumar SahooÎncă nu există evaluări