Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Extra Parts of Plant Cells
Încărcat de
Anonymous doCtd0IJDN0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
4 vizualizări1 paginăTitlu original
Part.docx
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
4 vizualizări1 paginăExtra Parts of Plant Cells
Încărcat de
Anonymous doCtd0IJDNDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
Part
Function
Nucleus
Contains genetic material, which controls the activities of the cell
Cytoplasm
Most chemical processes take place here, controlled by enzymes
Cell membrane
Controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell
Mitochondria
Most energy is released by respiration here
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis happens here
Plant cells also have extra parts:
Extra parts of plant cells
Part
Function
Cell wall
Strengthens the cell
Chloroplasts
Contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
Permanent vacuole
Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid
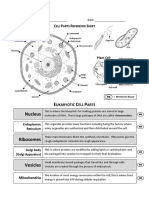
Parts of Plant Cell
Back to Top
Plants cell constitute of membrane bound nucleus and many cellular structures. These organelles carry
out functions that are necessary for the proper functioning and survival of the cell. The cell organelles of
the plant are enclosed by a cell wall and cell membrane. The constituents of the cell are suspended in the
cytoplasm or cytosol.
The parts of the plant cell are as follows:
Cell wall is the outermost rigid covering of the plant cell. It is a salient feature of plant cell.
Cell membrane or the plasma membrane is the outer lining of the cell inside the cell wall.
Cytosol or cytoplasm is the gel-like matrix inside the cell membrane which constitutes all other cell
organelles.
Nucleus is the control center of the cell. It is a membrane bound structure which contains the hereditary
material of the cell - the DNA
Chloroplast is a plastid with green pigment chlorophyll. It traps light energy and converts it to chemical
energy by the process of photosynthesis.
Mitochondria carries out cellular respiration and provides energy to the cells.
Vacuoles are the temporary storage center of the cell.
Golgi body is the unit where proteins are sorted and packed.
Ribosomes are structures that assemble proteins.
Endoplasmic reticulum are membrane covered organelles that transport materials.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Animal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 paginiAnimal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisNicole CatolicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 paginiOrganelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisLuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- текстDocument2 paginiтекстSamina KamilovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles: What You Need To KnowDocument15 paginiCell Organelles: What You Need To KnowRaj GobalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NucleusDocument10 paginiNucleusjhariesargente05Încă nu există evaluări
- Ch#4Document5 paginiCh#4surprisinglysarahytÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 paginiCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459Încă nu există evaluări
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 paginiCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 paginiKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Cells and Its FunctionDocument6 paginiParts of Cells and Its FunctionMary CartonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Cell StructureDocument3 paginiAnimal Cell StructurejwoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CELLSDocument6 paginiCELLSFenny May SebonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal CellDocument7 paginiAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 paginiAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Cytoplasm in A CellDocument5 paginiThe Role of Cytoplasm in A CellRishikesh BhintadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CellsDocument26 paginiCellsNairita LetipoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab #2Document8 paginiLab #2Regina RazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 paginiAnimal and Plant CellElmer Tunggolh, Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesDocument10 paginiHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesS PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 paginiParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Cell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Document5 paginiCell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."shankaram shankaram100% (1)
- Bio NotesDocument43 paginiBio NotesKyi ThitsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells NotesDocument3 paginiCells NotesmisosoupÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 paginiThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organelles - Presentation With GraphicsDocument34 paginiOrganelles - Presentation With GraphicsFrederick LoganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in Science BDocument5 paginiReviewer in Science BAshliah Aira MarohomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cell StructureDocument3 paginiPlant Cell Structurengozi duffrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CellDocument4 paginiCellPrincess MillanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocument22 paginiCell Organelles and Their FunctionsJoseph Al Bayonas100% (2)
- Vocab For First UnitDocument6 paginiVocab For First UnitCharmaine LIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell WallDocument4 paginiCell WallSamia KhandkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles DefinitionDocument40 paginiCell Organelles Definitionmuhammad aslam0% (1)
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 paginiTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Plant CellDocument4 paginiPlant CellKenneth FungoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 paginiActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- Animal and Plant CellDocument41 paginiAnimal and Plant CellSabrina LavegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 paginiAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Lecture No.1 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Topic:-Plant CellDocument11 paginiOnline Lecture No.1 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Topic:-Plant CellwatashiwayakinikuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cell PROJECTDocument6 paginiPlant Cell PROJECTYoussef AmrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cells PDFDocument7 paginiPlant Cells PDFMarcus Ben AlgerreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagram of Plant CellDocument4 paginiDiagram of Plant CellekongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Cell StructureDocument2 paginiAnimal Cell StructureShaik HamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Cell Parts Reference SheetDocument2 pagini2 Cell Parts Reference Sheetapi-3268559130% (1)
- Cell OrganellesDocument28 paginiCell OrganellesPrecy Ann ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elsc Easy Learn Singh Classes: Cell OrganelleDocument13 paginiElsc Easy Learn Singh Classes: Cell OrganelleNandini SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Document20 paginiPlant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Marifer DapatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5-4Document84 paginiGroup 5-4googlegirl18Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Cells: 1. Unicellular: Organisms Made Up of Only One Cell Are Known As UnicellularDocument6 paginiUnit 5 Cells: 1. Unicellular: Organisms Made Up of Only One Cell Are Known As Unicellularpraneeth satishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 1Document5 paginiBiology 1Zeynep AkıÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDocument7 paginiLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Cell and Plant CellDocument7 paginiAnimal Cell and Plant CellNancy judith Vallejo ToroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Plant Cell 21Document2 paginiNotes Plant Cell 21Samantha JerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pagini1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cell 2Document12 paginiPlant Cell 2Icy MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Note Grade 8 Chapter: CellsDocument7 paginiBiology Note Grade 8 Chapter: CellsAfrida AnnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells and OrganellesDocument3 paginiCells and OrganellesAnnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 paginiPlant Cell - LayoutMahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts and Function of Plant CellDocument3 paginiParts and Function of Plant CellAmy A. OgnayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 paginiCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDe la EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- TR - Housekeeping NC IIDocument69 paginiTR - Housekeeping NC IIAnonymous bMyvbkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnimalsDocument2 paginiAnimalsAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test PaperDocument4 paginiTest PaperAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- SuicojakeDocument1 paginăSuicojakeAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Royce S. Torres, Ph. D: Elton Venz J. EsponillaDocument2 paginiDr. Royce S. Torres, Ph. D: Elton Venz J. EsponillaAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Road Gravelling Operational Expenses (Partial) Four Road ProjectsDocument1 paginăRoad Gravelling Operational Expenses (Partial) Four Road ProjectsAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1'717Document20 pagini1'717Anonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- AssignmentDocument7 paginiAssignmentAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristics & Types of Business LetterDocument13 paginiCharacteristics & Types of Business LetterAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00Document7 pagini00Anonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project 2Document2 paginiProject 2Anonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- MendelDocument2 paginiMendelAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respectfully Yours,: Abdul Khalid Daco (Student)Document1 paginăRespectfully Yours,: Abdul Khalid Daco (Student)Anonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument2 paginiCurriculum DevelopmentAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document3 paginiChapter 2Anonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter II AaaaaaDocument9 paginiChapter II AaaaaaAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuya J and Loloys FestfoodDocument2 paginiKuya J and Loloys FestfoodAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Law of DominanceDocument1 paginăThe Law of DominanceAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- BobDocument1 paginăBobAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- References ResearchDocument1 paginăReferences ResearchAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristic S and Types of Business LetterDocument4 paginiCharacteristic S and Types of Business LetterAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELEMENTDocument1 paginăELEMENTAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hybrids: Mendel's GeneticsDocument5 paginiHybrids: Mendel's GeneticsAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROJECTDocument2 paginiPROJECTAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerpoint MACATAMPODocument36 paginiPowerpoint MACATAMPOAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- MACAPAARDocument2 paginiMACAPAARAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- POLAYAGANDocument2 paginiPOLAYAGANAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări
- MANSORDocument3 paginiMANSORAnonymous doCtd0IJDNÎncă nu există evaluări