Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Literature Review On The Effects of Wet Coal On Power Generation
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Literature Review On The Effects of Wet Coal On Power Generation
Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
e-ISSN: 2456-3463
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Science, Vol. 2, No.1, 2017
www.ijies.net
Literature Review on the Effects of Wet Coal on
Power Generation
Ravindra B.Gohane1, Dr.S.V.Deshmukh2
1
Chief Engineering, Khaparkheda Thermal Power Station, MSPGCL, Nagpur, India
2
Principal, S.D. College Of Engineering, Wardha, India..
Abstract: A number of studies had been conducted on
thermal power plants operations & performance
improvement. These studies depended on certain limited
factors like equipment & machinery. The factors such as
coal quality & coal handling & their effects on power
generation hasnt been dealt & considered widely. The
moisture in coal is present naturally and therefore there
is nothing much that can be done on wet coal factor has
been the ideologies of researchers. A change in
approach is need of the hour. Moisture in coal plays a
very significant role in operation & performance of
thermal power plant. It also affects the economics &
environmental impacts of power generation. This leads
us to consider the issue of wet coal as a matter of serious
concern. This paper attempts to review the available
literature& highlight the effects of wet coal on power
generation.
and muddy coal, the coal handling plant system
collapsed frequently.
The efficiencies of power plant is in the range of 30 % to
50 %, this means that there is a loss of 50 to 70 % in
power generation. The losses occur due to various
reasons like incomplete combustion of coal, poor coal
handling, improper working of machinery (turbine,
compressor, fans, combustion chamber, etc.)The
moisture content in coal is one of the main reasons
behind losses. Therefore a lot depends upon the quality
of coal being utilized. Quality of coal affects the
physical, thermal, economical & environmental factors
of a power plant.
COAL WETNESS
It concludes from the coal formation process that coal is
a product of number of natural elements like plant
remains, animal remains, sand, minerals, etc. The carbon
percentage in coal is related to the concentration of these
elements. The amount of these elements determines the
quality of coal. The coal is ranked on its moisture
content, volatile content & carbon content. Excessive
total moisture typically results from excessive rain and
uncontrollably high surface water content in the raw
coal. Coal from the mines, whether open cast or
underground mining, is stored on stockpiles from where
it is reclaimed for power station use. Wet coal poses
more problems for open cast mining operations as it
affects the whole operation of mining, removal of over
burden, coal and transportation of coal to the coal stock
yard operations.
Keywords: Wet Coal, Thermal Power Plant, Moisture in
Coal.
INTRODUCTION
The understanding of the properties and the handling
characteristics of liquids and gases is an essential
requirement for most of the practicing engineers. Over
the years there has been a remarkable amount of
development and literature dealing with the
fundamentals of liquid flow, fluid mechanics, hydraulics
and related topics. But there has been no parallel
development of the Bulk Solids Handling. Bulk
material handling is based on the design of equipment
used for the transportation of materials such as coal
and consists of machinery like conveyors, chutes,
hoppers, stacker and reclaimer, called as coal handling
plant or CHP. While handling the coal in coal handling
plant, lot of problems have been faced. One of the major
problems faced during the rainy season is, wet coal
receipt and its unloading. Due to receipt of wet, sticky
LITERATURE SURVEY
There is no any specific literature available on the
studies related with the effect of excessive wet coal on
electricity & remedial measures for it, but the subject has
been emerged up through some news magazines and
some reports. Some of them are collected and put here.
e-ISSN: 2456-3463
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Science, Vol. 2, No.1, 2017
www.ijies.net
In the report by Govt. of India [12], it is stated that,
Energy losses due to partial unavailability was above
national average in the Western & Eastern Regions
Rod Hatt [18] discusses various reasons of wetness
incoal. The effect of wet coal on heat rate and flow
ability is also discussed. He suggeststhe use of high
molecular weight polypropylene plastic chute liners to
improve the flow ability of coal chutes. But the high
molecular weight polypropylene plastic chute liners
might create the problem when it gets detached from the
chutes/ bunkers by choking the coal path.
mainly due to shortage of coal, coal handling problems,
poor quality/wet coal and other miscellaneous problems
and was minimum in the Southern Region.
M.R.Shelar [13] discussed the challenges before MGCO
under which the wet coal problem is highlighted in the
paragraph of Constraints during the Rainy Season. In
this paragraph, he discussed the issues of wet & sticky
coal received in thermal power stations of MGCO,
inability of LCW to avoid the supply of wet & sticky
coal, constraints of MGCO to unload such wet & sticky
coal and the efforts taking by MGCO to find the
solutions.
In an inspection report of OTATPS [14] the coal quality
related problems are studied& the solutions for
unloading the wet, muddy & sticky coal are suggested
.Results focused only on manual unloading of coal
wagons in case of receipt of wet, muddy & sticky coal.
The author had taken the example of one plant regarding
the wet coal problem. One of the plant struggled for days
with wet coal problems, while the coal yard processed
the coal through hammer mills (coal crushers) as usual.
When these crushers were by-passed, the plant situation
improved considerably. He has not mentioned, how the
crushers were by-passed, but ultimately the problem was
solved after by-passing the crushers. This means that
when the wet coal is received in the plant, the best
solution is to not allow this coal to go through the
crushers in order to run the coal handling plant
smoothly.
Chittatosh Bhattachary, Nilotpl Banerjee, Hari Sadhan
Sarkar, studied the economics of moisture in coal in
power plants. They tabulated the analysis which is
presented in the following table 1. [6]
In the Facts & Figures Sheet From Escom[15], the
effect of excessively wet coal on production of
electricity is discussed. It gives information on why the
coal is wet?& how the power station faces problems in
transportation of this wet coal up to the coal mills by
chocking the transfer chutes, feeders and crusher and
coal mills also. But, no solutions are suggested to handle
this wet coal.
In a report [16], the complaints received from the
consumers, regarding the receipt of excessive wet, sticky
& muddy coal in some rakes are listed. Action taken by
authority in this regard is mentioned in the report
Referred to concerned area for corrective action. But
as per the report it was observed that even after the
instructions to concerned area, the things were repeated
in the succeeding month also. That means authority had
shown their inability to solve the problem of sending
wet, muddy & sticky coal to the power stations during
the rainy season.
Table 1
Cost effects of moisture in coal
Reference coal
Coal rank
Recd HHV
(MJ/kg)
Coal price unit
Coal price / MT
As received coal
moisture (wt %)
Ref case : 2%
decrease in as
fired coal moisture
As fired coal
moisture (wt %)
As fired LHV with
2% less
moisture[wt%(AR)]
in coal (MJ/kg)
Waste heat
recovery savings in
equivalent as
received coal
quantity in MTPD
In airport on Performance Review of Thermal Power
Stations by CEA [17], Coal quality Issues were
discussed. Report on receipt of wet & sticky coal by
some power stations is mentioned in this paragraph. But
no solutions are recommended.
In the report of the Committee Constituted by CEA
[18]the receipt of wet and sticky coal in the form of
slurry during monsoon season is discussed. But again,
solutions to solve this problem were not discussed.
MCL
coal
Noncoking
gr. F
10.878
LCW
coal
Noncoking
gr. D
19.526
ECL
coal
Noncoking
gr.E
20.398
Rs.
(07)
440.00
15.00
Rs.
(07)
1210.00
19.50
Rs.
(07)
1360.00
1.95
13.00
17.50
0.0
10.404
18.889
20.111
139.45
85.79
212.38
e-ISSN: 2456-3463
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Science, Vol. 2, No.1, 2017
www.ijies.net
different technologies for coal drying purposes. It was
observed that although dry coal is desirable, the cost of
drying coal acts as a discouraging factor.
EFFECT OF WET COAL ON POWER PLANT:
The effects of moisture can be classified into three
categories, physical, chemical & cost:
Physical effects [1,2,3,4]
Blocks transfer chutes
Hang ups in bunkers
Hindrance to free flow of coal.
Clogging.
Capacity reduction in tipplers, conveyors,
crushers, bunkers and mills.
Difficult to handle.
Difficulty in grinding, milling and flowing.
coals
Formation of rat-holes.
Difficult to pulverize
More mill power is required.
Incomplete drying of coal.
Increase in coal flow rate.
Increased need for boiler maintenance.
Increase in fan & mill power.
Units may trip
Load hunting.
REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
Chemical effects [5,6,7,8]
The amount of heat energy required to evaporate
the moisture is greater than the boiler design
allows.
Lesser amount of coal fired into the boiler.
Lesser amount of electricity generated.
Decreases the gross calorific value of coal.
Ash content in boiler increases.
Flame temperature is lower.
Decrease in boiler efficiency.
Increase in air, flue gases flow rate.
Increase in co2 & so2 mass emissions.
Cost effects [9,10,11]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14]
Increase in operation cost.
Increase in maintenance costs.
Decrease in coal purchase cost.
The boiler efficiency decreases.
Unit heat rate increases.
Increased cost of generation
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
CONCLUSION
The moisture content of coal plays a predominant role to
differentiate grades of coal. The moisture content of coal
has been the centre of attraction as it affects boiler
efficiency, overall efficiency, working of machinery &
operation & maintenance costs. This paper reviewed the
effect of wet coal on power plant performance &
10
GeeE R.(1940).Moisture in Coal,M.A (Cantab.), FGS,Geological
Survey of India,vol. 6, No. 3, Art-38, Pp. 535-538.
Siddhavrtha M..B.& KumarN. R. (2014).Effect of Surface
Moisture in Coal on Unit Heat Rate and Operating Costs for
Indian Thermal Power Plants, Central Power Research Institute
of India, Electrical India,.
OsmanH., JangamSv., Lease J.D. &MujumdarA. S.
(2011).Drying of Low Rank Coal (LRC) A Review of Recent
Patents & Innovations, Minerals, Metals and Materials
Technology Centre (M3tc) Report, Department of Mechanical
Engineering, Blk-Ea, 06-15, 9, Engineering Drive 1, National
University of Singapore, Singapore, , pp. 1-48.
Cox J. &. NelsonC. R. Coal Weathering Causes Effects &
Implications, Gas Research Institute, 8600 West Bryn Maw
avenue, Illinois, Chicago.
BhattacharyaC., BanerjeeN., SarkarH. S., Feb (2013).Economics
of Removal of Coal Moisture in Thermal Power Generation with
Waste Heat Recovery, International Journal of Emerging
Technology and Advanced Engineering, vol. 3, Issue 3, , Pp. 2228.
Union of Concerned Scientists, How Coal Works,
Http://Www.Ucsusa.Org.
NessM., BullingerC., SarunacN.,. LevyE. K. Coal Drying
Improves Performance and Reduces Emissions. Great River
Energy Underwood, North Dakota and Energy Research Centre
Lehigh University, Bethlehem, Pennsylvania.
HattR.. Sticky When Wet.Moisture Impacts on Coal Handling and
Heat Rate as Published by World Coal. Coal Combustion, Inc.
Versailles, KY.
BhatnagarA., GuptaR., PappuS.,. DuttaG, Mathematical
Modelling for Demurrage Reduction in Coal: Transportation for
an Indian Thermal Power Plant. Capital One Services, Inc,
Richmond, USA, LancorWestminister, Mylapore, Chennai, Indian
Institute of Management, Ahmadabad, Gujarat, India.
SarunacN., Ness M. and BullingerC.. (2014). Improve Plant
Efficiency And ReduceCo2emissions When Firing High-Moisture
Coals, Power Magazine.
The Effect of Excessively Wet Coal on Production of Electricity,
Facts &Figures. (2016). Generation Communication & Primary
Energy, Revision 6, Eskom, www.Eskom.Co.Za,.
Review of Performance of Thermal Power Stations, (2009-10).
taken by Central
Electricity Authority of Govt. of India:
ShelarM.R.. (2011). Paper Published in The Energy Business
(Operation), DirectorMGCO in.
Inspection report of Kota Super Thermal Power Station.(200910).
Facts & Figures sheet from Escom.
Report Showing the Details of Complaints Received By LCW
from the CoalConsumers & Action Taken forredressal.
Report on Performance Review of Thermal Power
Stations.(2006-07). CEA.
Unloading Infrastructure at Thermal Power Stations. Report.
CEA.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Belt Conveyor Pulley Design - Why The FailuresDocument9 paginiBelt Conveyor Pulley Design - Why The FailuresWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPF4801 Assignment T2 - Hopper DesignDocument2 paginiEPF4801 Assignment T2 - Hopper DesignArinaAdilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Series Analysis in RDocument138 paginiTime Series Analysis in RCristiano Christofaro100% (1)
- Role of Various Factors On Coal CombustionDocument51 paginiRole of Various Factors On Coal CombustionAbhijeet DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Slippage SPWP1178ENPR-01Document2 paginiBelt Slippage SPWP1178ENPR-01JrbritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Standards For Thermal Power PlantsDocument29 paginiReference Standards For Thermal Power PlantsSenthil Kumar SubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Pelton Efficiency and CavitationDocument10 paginiOn Pelton Efficiency and CavitationJohn RobinsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pnabx861 PDFDocument145 paginiPnabx861 PDFBindu ChaurasiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research and Innovations For Continuous Miner's Cutting Head, For Efficient Cutting Process of Rock/CoalDocument12 paginiResearch and Innovations For Continuous Miner's Cutting Head, For Efficient Cutting Process of Rock/CoalKarthii Aju100% (1)
- Combined Cycle Gas Turbine Gyanendra Sharma NPTI DelhiDocument148 paginiCombined Cycle Gas Turbine Gyanendra Sharma NPTI DelhiNPTIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chute Design Considerations For Feeding and TransferDocument19 paginiChute Design Considerations For Feeding and TransferovunctezerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Od-Ops-Syst-003 Procedure For Testing and Maintenance To Avoid Excessiveover Speeding of Prime MoversDocument1 paginăOd-Ops-Syst-003 Procedure For Testing and Maintenance To Avoid Excessiveover Speeding of Prime MoversDeepak KansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case History: Power Plant Equipment PreservationDocument2 paginiCase History: Power Plant Equipment PreservationDurga PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- CB Continental CatalogueDocument69 paginiCB Continental CatalogueAina LikuntatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 'Wattsup' 9th Issue Environment Protection Technologies SpecialDocument35 pagini'Wattsup' 9th Issue Environment Protection Technologies SpecialNaveen ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air BechtelDocument34 paginiAir BechtelBhargav ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oin Ops Chem 014 Recommendations of Epri WorkshopDocument15 paginiOin Ops Chem 014 Recommendations of Epri WorkshopraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabric Filter Pulse CleanDocument15 paginiFabric Filter Pulse CleanmjbotelhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal Conveyor Belt Fault DetectionDocument4 paginiCoal Conveyor Belt Fault Detectionc pawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Electro Hydraulic Thruster Brake For Lifting MachineDocument7 paginiDesign and Analysis of Electro Hydraulic Thruster Brake For Lifting MachineIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- U LectureDocument234 paginiU LectureTran DucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obata - Grab Bucket Type Ship UnloaderDocument20 paginiObata - Grab Bucket Type Ship Unloadertrungnq_ktd97Încă nu există evaluări
- Yongseung Yun - Gasification For Practical Applications-InTech (2013) PDFDocument351 paginiYongseung Yun - Gasification For Practical Applications-InTech (2013) PDFDeepak LuintelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation MRT CatalogueDocument28 paginiVentilation MRT Cataloguevikas gahlyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cleaning of Coal - 2008Document17 paginiCleaning of Coal - 2008vineetakaushik83Încă nu există evaluări
- Contributions To The Technology Comparison Between Straight Grate and Grate-KilnDocument15 paginiContributions To The Technology Comparison Between Straight Grate and Grate-KilnAjay Singh100% (1)
- Emission Regulations Part - 2 PDFDocument24 paginiEmission Regulations Part - 2 PDFAkul SenapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFD Analysis of A 210 MW Tangential Fired BoilerDocument6 paginiCFD Analysis of A 210 MW Tangential Fired BoilerInnovative Research PublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Desalination Cost EstimationsDocument17 paginiHistory of Desalination Cost EstimationsGiovanniStirelliÎncă nu există evaluări
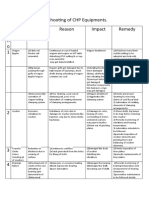
- Troubleshooting in CHPDocument2 paginiTroubleshooting in CHPMilind RahatgaonkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dispatch Protocol Issue No. 13.1: WESM Market ManualDocument115 paginiDispatch Protocol Issue No. 13.1: WESM Market ManualMarc ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Thermal Power Plant Steam BoilerDocument13 paginiCalculation of Thermal Power Plant Steam BoilerNenad JerinicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Coal Flame in Tangentially Fired BoilerDocument4 paginiReading Coal Flame in Tangentially Fired Boilerbhaskar1rkumar4092Încă nu există evaluări
- Data SAF2205 04Document8 paginiData SAF2205 04il_yoo_1Încă nu există evaluări
- RCA en Fajas - 2 PDFDocument6 paginiRCA en Fajas - 2 PDFVíctor Fernández Narváez100% (1)
- TSPL GST Petition - AnnexuresDocument407 paginiTSPL GST Petition - AnnexuresVIVEK anandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatic PrecipitatorsDocument71 paginiElectrostatic PrecipitatorsPratick DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview With GMRDocument8 paginiInterview With GMRAnupamaa SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bauxite ComparisonDocument12 paginiBauxite Comparisondr_drk4503Încă nu există evaluări
- Energy Saving Belt ConveyorDocument11 paginiEnergy Saving Belt ConveyorVINCENZOVECCHIO100% (1)
- ElectricActuatorBasics CEPMagazine JustinLedger PDFDocument6 paginiElectricActuatorBasics CEPMagazine JustinLedger PDFElvis Alberto Rodriguez BravoÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Blueprint" Your Pulverizer For Improved Performance: by Richard F. (Dick) Storm, PE, Storm Technologies IncDocument4 pagini"Blueprint" Your Pulverizer For Improved Performance: by Richard F. (Dick) Storm, PE, Storm Technologies IncvnchromeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.bulk Materials Handling by Belt Conveyors at New Denmark CollieryDocument10 pagini10.bulk Materials Handling by Belt Conveyors at New Denmark CollieryjsaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal Beneficiation TechnologyDocument5 paginiCoal Beneficiation TechnologyChandan Das100% (1)
- Type of Failure in Conveyor SystemDocument13 paginiType of Failure in Conveyor Systemzainonayra100% (2)
- Air Venting Heat Loss and SummaryDocument9 paginiAir Venting Heat Loss and Summarysandeep kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel Cell Technology in PakistanDocument12 paginiFuel Cell Technology in PakistanMuhammad Ali Abro50% (2)
- T4S5O4 Paper PDFDocument17 paginiT4S5O4 Paper PDFtrung2iÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Tube CoatingsDocument61 paginiBoiler Tube CoatingsRahul DeshmukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barro Alto Presentation February.2012Document60 paginiBarro Alto Presentation February.2012FelipecmtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Thoughts On Chute Design PhilosophyDocument3 paginiSome Thoughts On Chute Design PhilosophyneilradcliffeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combustion Analysis Basics: Tune-Up Procedure-Using An Electronic Combustion AnalyzerDocument19 paginiCombustion Analysis Basics: Tune-Up Procedure-Using An Electronic Combustion AnalyzerTin Aung KyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal Quality Impacts-FinalJan - 2010 PDFDocument15 paginiCoal Quality Impacts-FinalJan - 2010 PDFaruninchinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure Analysis of Belt Conveyor SystemsDocument17 paginiFailure Analysis of Belt Conveyor SystemsGogyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Kamyr Digester ControlDocument12 paginiAdvanced Kamyr Digester ControlFernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studies On The Operation of Loop-Seal in Circulating Fluidized Bed BoilersDocument9 paginiStudies On The Operation of Loop-Seal in Circulating Fluidized Bed BoilersUsman NaseemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal MillDocument6 paginiCoal MillAnonymous NxpnI6jCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Health MonitoringDe la EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PF 09 04 ccc147Document2 paginiPF 09 04 ccc147ukalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal Flow Improves Coke Process-IMPDocument11 paginiCoal Flow Improves Coke Process-IMPsamdanismsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flyash ManagementDocument13 paginiFlyash ManagementShahinshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Analysis and Design of Multi-Storied RC Building Using STAAD Pro and ETABSDocument4 paginiSeismic Analysis and Design of Multi-Storied RC Building Using STAAD Pro and ETABSInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Fabrication of Three Wheeler Drive Forklift For Industrial WarehousesDocument3 paginiDesign and Fabrication of Three Wheeler Drive Forklift For Industrial WarehousesInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static Seismic Analysis of RCC Building As Per Is 18932002 by Using STAAD-Pro SoftwareDocument7 paginiStatic Seismic Analysis of RCC Building As Per Is 18932002 by Using STAAD-Pro SoftwareInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Science100% (1)
- Study of Supraharmonics and Its Reduction by Using Novel ControllerDocument4 paginiStudy of Supraharmonics and Its Reduction by Using Novel ControllerInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligent Transportation System-Recent Trends in Transportation System A ReviewDocument6 paginiIntelligent Transportation System-Recent Trends in Transportation System A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Design of (G+100) Storied Building by Using SoftwareDocument3 paginiAnalysis and Design of (G+100) Storied Building by Using SoftwareInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Seismic Analysis of RCC Building As Per Is 18932002 by Using STAAD-Pro SoftwareDocument7 paginiDynamic Seismic Analysis of RCC Building As Per Is 18932002 by Using STAAD-Pro SoftwareInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey On Automatic Solar Tracking SystemDocument3 paginiSurvey On Automatic Solar Tracking SystemInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Satisfaction Analysis in Four Wheeler Service CentreDocument4 paginiCustomer Satisfaction Analysis in Four Wheeler Service CentreInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Aided Analysis of Vibration in Machine Tool and Design of Damping SystemDocument4 paginiComputer Aided Analysis of Vibration in Machine Tool and Design of Damping SystemInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Multi-Stage GeneratorDocument4 paginiDesign and Analysis of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Multi-Stage GeneratorInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Go-Kart ChassisDocument6 paginiDesign and Analysis of Go-Kart ChassisInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Ration Card System Using RFIDDocument3 paginiSmart Ration Card System Using RFIDInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentiment Analysis of Product ReviewDocument6 paginiSentiment Analysis of Product ReviewInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navigo: Harshal Kamble, Mayuri Waghmare, Rajeshree Sonwane, Sonal Shende, Sonali Tiwari. Prof.N.R.HatwarDocument3 paginiNavigo: Harshal Kamble, Mayuri Waghmare, Rajeshree Sonwane, Sonal Shende, Sonali Tiwari. Prof.N.R.HatwarInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Analysis of Hardenability of Steel Using Jominy End Quench TestDocument3 paginiComparative Analysis of Hardenability of Steel Using Jominy End Quench TestInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development and Fabrication of Waste Paper Recycling MachineDocument2 paginiDevelopment and Fabrication of Waste Paper Recycling MachineInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Diaphragm Flexibility On The Seismic Response of RCC Framed Building Considering Diaphragm DiscontinuityDocument9 paginiEffect of Diaphragm Flexibility On The Seismic Response of RCC Framed Building Considering Diaphragm DiscontinuityInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Science100% (1)
- Detecting Malicious Data Using FidgetDocument5 paginiDetecting Malicious Data Using FidgetInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Savonius Vertical Axis Wind TurbineDocument7 paginiDesign and Analysis of Savonius Vertical Axis Wind TurbineInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation in Burr Removal TechniquesDocument4 paginiAutomation in Burr Removal TechniquesInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scene 3Document22 paginiScene 3Christopher ThorntonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling Hazard Management - Part 1Document6 paginiDrilling Hazard Management - Part 1Yamamoto_KZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Science 9 3rdDocument4 paginiLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Science 9 3rdMelanie Tagudin TrinidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iess 104Document16 paginiIess 104ashish kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conditional Sentences Type 1Document28 paginiConditional Sentences Type 1saimaabedi100% (1)
- V07a Mooring 1206Document48 paginiV07a Mooring 1206Htin Lin Aung100% (1)
- Analisa Harga Satuan 2007 Dan 2002Document5 paginiAnalisa Harga Satuan 2007 Dan 2002Yayatto KungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospekt Rainstar - EnglischDocument18 paginiProspekt Rainstar - EnglischCharles FequiereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spesifikasi Detail & Jual Total Station Topcon GTS-102N (081297551995)Document2 paginiSpesifikasi Detail & Jual Total Station Topcon GTS-102N (081297551995)Rina Wahyuni100% (1)
- 5 Precipitation 1Document72 pagini5 Precipitation 1Muhammad Haris Khattak100% (1)
- Blood Mage - Class D&DDocument1 paginăBlood Mage - Class D&DKronusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Process Systems Analysis and Control 3rd Edition Coughanowr Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 paginiDwnload Full Process Systems Analysis and Control 3rd Edition Coughanowr Solutions Manual PDFmarcuspaulhcsr6100% (8)
- Air Cooled Chiller Product Data CatalogDocument16 paginiAir Cooled Chiller Product Data Catalograza514Încă nu există evaluări
- 4300Document9 pagini4300justyna6216Încă nu există evaluări
- Yellowstone TextDocument1 paginăYellowstone TextEstefania Aranda JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tornado ReportDocument5 paginiTornado ReportDASE GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- VRC Power Line Ice Management De-Icing System Smart Grid (English)Document26 paginiVRC Power Line Ice Management De-Icing System Smart Grid (English)PolarStar100% (1)
- ESSC - Flood Disaster Risk Assessment For Riverside Zones - October 2014 - ReducedDocument53 paginiESSC - Flood Disaster Risk Assessment For Riverside Zones - October 2014 - ReducedEnp Titus VelezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthquake Seismology PracticalsDocument27 paginiEarthquake Seismology PracticalsbchnumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cause and Effect ExamplesDocument2 paginiCause and Effect ExamplesZaki Azman100% (1)
- Practicetest A Noun ClausesDocument3 paginiPracticetest A Noun Clausesmarisa destiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job Safety Analysis: Location Date New Revised Jsa No. Task Supervisor Analysis by Approved byDocument2 paginiJob Safety Analysis: Location Date New Revised Jsa No. Task Supervisor Analysis by Approved byDavid GlawsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predicting Weather Forecaste Uncertainty With Machine LearningDocument17 paginiPredicting Weather Forecaste Uncertainty With Machine LearningJUAN LOPEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- RTN 380 V100R008 Quick Installation GuideDocument32 paginiRTN 380 V100R008 Quick Installation GuideTilin TolonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geology of Sarawak - 1856Document6 paginiGeology of Sarawak - 1856Martin LavertyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1CENEO1 - Cameroon Coffee Supply Chain Risk AssessmentDocument34 pagini1CENEO1 - Cameroon Coffee Supply Chain Risk AssessmentRomir ChatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter5 Modal AuxiliariesDocument24 paginiChapter5 Modal AuxiliariesDNIndriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Heat Transfer Question BankDocument12 paginiAnna University Heat Transfer Question BankGoutham R80% (5)